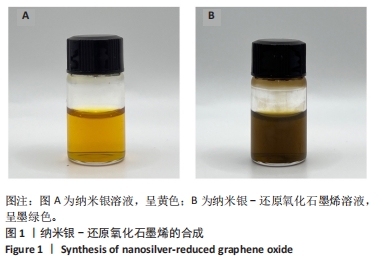
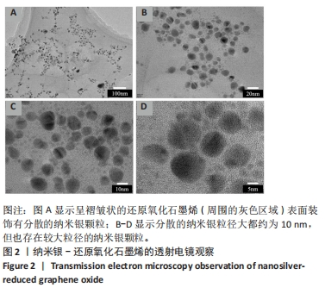
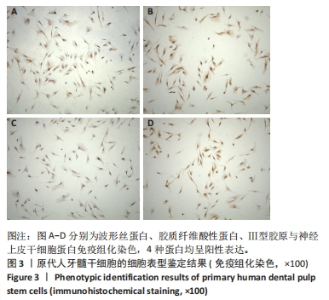
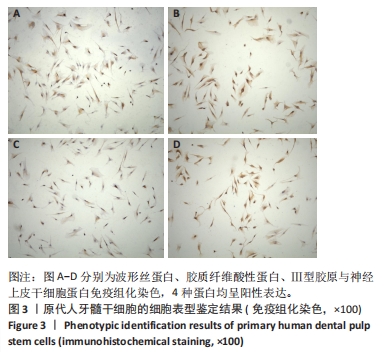
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (34): 7333-7343.doi: 10.12307/2025.886
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation and antibacterial evaluation of nanosilver-reduced graphene oxide/polydopamine/methacrylated gelatin@Gap19 hydrogel
Li Ruotong1, 2, 3, Wu Yuening1, 2, 3, Deng Yunyi2, 3, 4, Chen Shichao2, 3, 4, Lan Xiaorong2, 3, 4, Li Shiting1, 2, 3, Li Guangwen2, 3, 4
- 1Department of Endodontics, 4Department of Implantology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 3Institute of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-09-18Accepted:2024-10-11Online:2025-12-08Published:2025-01-17 -
Contact:Li Guangwen, Doctoral candidate, Attending physician, Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Institute of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Department of Implantology, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China Li Shiting, MD, Associate professor, Department of Endodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Institute of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Ruotong, MS, Department of Endodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Luzhou Key Laboratory of Oral & Maxillofacial Reconstruction and Regeneration, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Institute of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Sichuan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (General Project), No. 2024NSFSC0680 (to LGW); Key Research and Development Project of Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 22YFS0634 (to LXR); Key Research and Development Plan of Luzhou Science and Technology Bureau (surface), No. 2022-SYF-33 (to LGW); Key Natural Science Project of Southwest Medical University, No. 2022ZD015 (to LGW); Hospital Level Key Project of Stomatology Hospital Affiliated to Southwest Medical University, No. 2022Z01 (to LGW); Science and Technology Project of Health Commission of Sichuan Province, No. 24QNMP018 (to LGW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Ruotong, Wu Yuening, Deng Yunyi, Chen Shichao, Lan Xiaorong, Li Shiting, Li Guangwen. Preparation and antibacterial evaluation of nanosilver-reduced graphene oxide/polydopamine/methacrylated gelatin@Gap19 hydrogel[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7333-7343.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
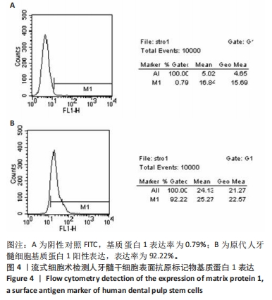
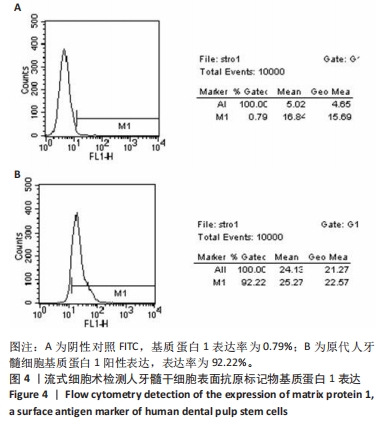
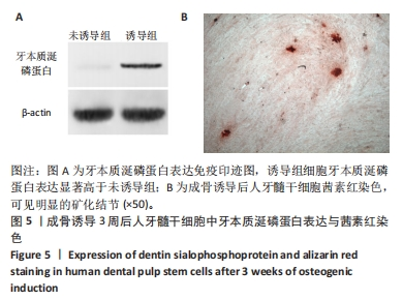
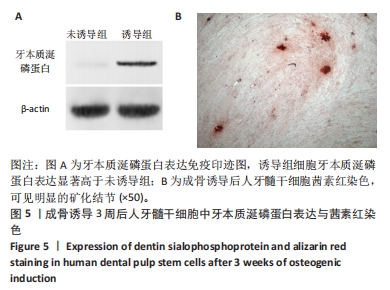
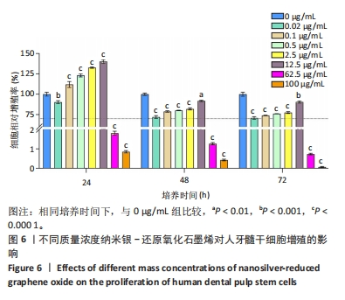
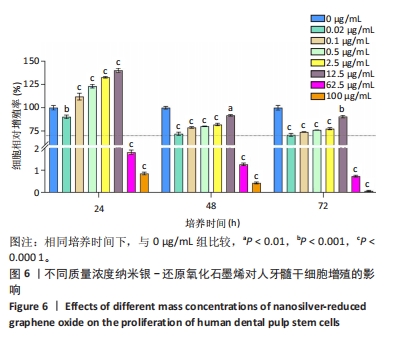
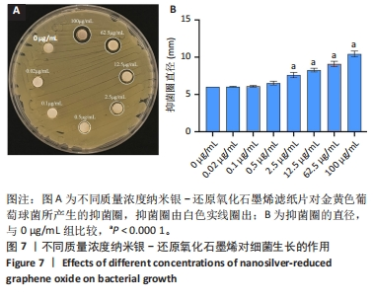
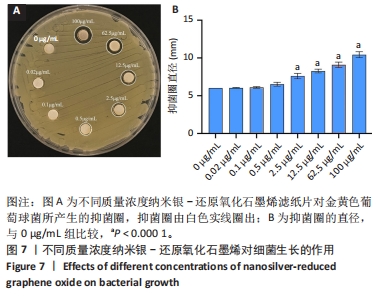
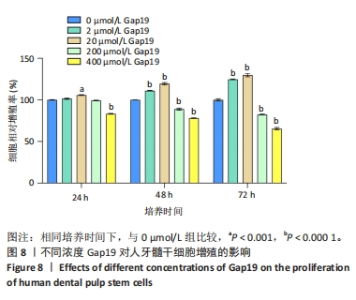
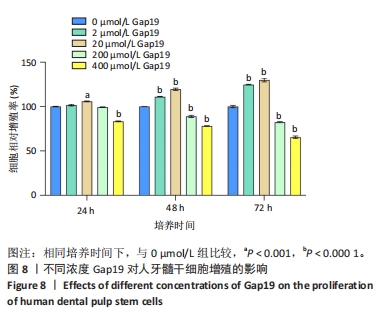
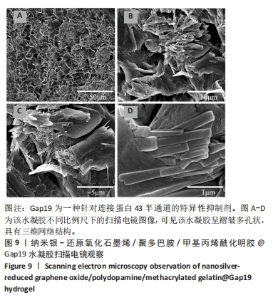
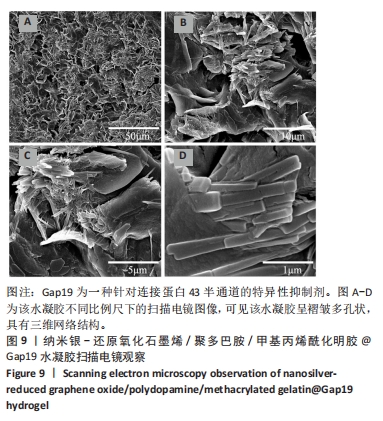
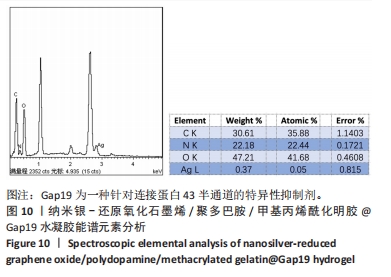
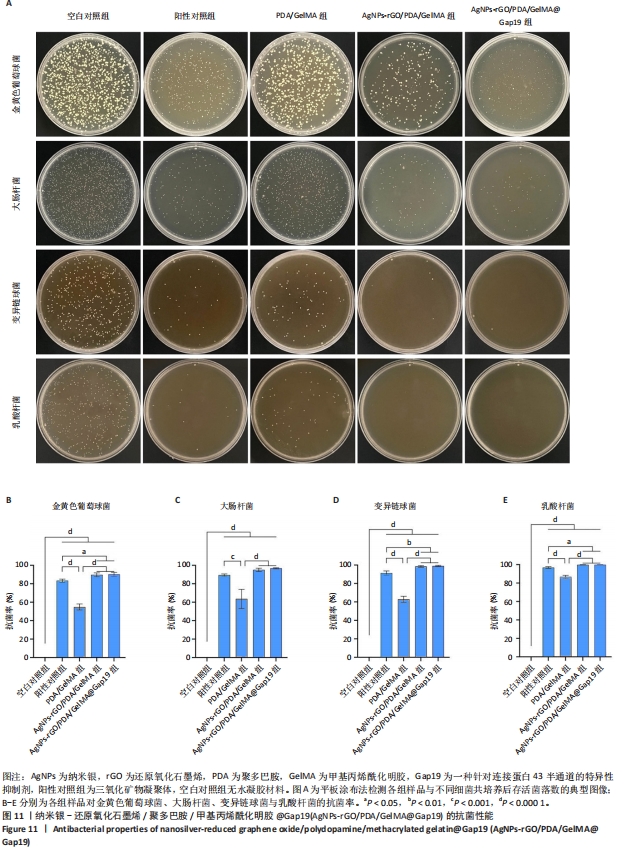
2.7 AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA@Gap19水凝胶的抗菌性能评价 赋予盖髓材料的抗菌性是预防盖髓术后细菌感染的关键。为了研究AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA@Gap19水凝胶的抗菌效果,进行了菌落形成单位实验,结果显示,对于金黄色葡萄球菌(或大肠杆菌、变异链球菌、乳酸杆菌),与空白对照组相比,AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA组和AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA@Gap19组细菌菌落数量最少,其次为阳性对照组,见图11A,表明AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA@Gap19水凝胶具备一定的广谱抗菌作用。 抗菌率计算结果显示,AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA组和AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA@Gap19组对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌率分别为89.74%,90.14%,对大肠杆菌的抗菌率分别为95.11%,96.79%,对变异链球菌的抗菌率分别为98.55%,99.05%,对乳酸杆菌的抗菌率分别为99.78%,99.85%,均明显高于空白对照组和PDA/GelMA组(P < 0.000 1),AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA组和AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA@Gap19组之间抗菌率比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);阳性对照组也对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、变异链球菌和乳酸杆菌表现出抗菌性,抗菌率分别为83.41%,89.42%,91.31%和96.82%,对金黄色葡萄球菌、变异链球菌及乳酸杆菌的抗菌率均低于AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA组和AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA@Gap19组(P < 0.05,P < 0.01),见图11B-E,说明AgNPs-rGO/PDA/GelMA@Gap19水凝胶具备良好的抗菌性能。"
| [1] RUSU D, STRATUL SI, CALNICEANU H, et al. A qualitative and semiquantitative SEM study of the morphology of the biofilm on root surfaces of human teeth with endodontic-periodontal lesions. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(6):201. [2] LARSEN T, FIEHN NE. Dental biofilm infections-an update. APMIS. 2017; 125(4):376-384. [3] RICUCCI D, LOGHIN S, NIU LN, et al. Changes in the radicular pulp-dentine complex in healthy intact teeth and in response to deep caries or restorations: A histological and histobacteriological study. J Dent. 2018;73:76-90. [4] BRYNIARSKA-KUBIAK N, BASTA-KAIM A, KUBIAK A. Mechanobiology of Dental Pulp Cells. Cells. 2024;13(5):375. [5] CĂLIN C, SAJIN M, MOLDOVAN VT, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of non-collagenous extracellular matrix molecules involved in tertiary dentinogenesis following direct pulp capping: a systematic review. Ann Anat. 2021;235:151674. [6] DONNELLY A, FOSCHI F, MCCABE P, et al. Pulpotomy for treatment of complicated crown fractures in permanent teeth: A systematic review. Int Endod J. 2022;55(4):290-311. [7] CUSHLEY S, DUNCAN HF, LUNDY FT, et al. Outcomes reporting in systematic reviews on vital pulp treatment: A scoping review for the development of a core outcome set. Int Endod J. 2022;55(9):891-909. [8] DASTPAK M, GHODDUSI J, JAFARIAN AH, et al. Association between Clinical Symptoms and Histological Features of Molars with Acute Pulpitis. Iran Endod J. 2023;18(2):91-95. [9] BARBOSA VM, PITONDO-SILVA A, OLIVEIRA-SILVA M, et al. Antibacterial Activity of a New Ready-To-Use Calcium Silicate-Based Sealer. Braz Dent J. 2020;31(6):611-616. [10] RUIZ-LINARES M, DE OLIVEIRA FAGUNDES J, SOLANA C, et al. Current status on antimicrobial activity of a tricalcium silicate cement. J Oral Sci. 2022;64(2):113-117. [11] PAULA A, LARANJO M, MARTO CM, et al. Biodentine™ Boosts, WhiteProRoot®MTA Increases and Life® Suppresses Odontoblast Activity. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(7):1184. [12] HOLIEL AA, MAHMOUD EM, ABDEL-FATTAH WM, et al. Histological evaluation of the regenerative potential of a novel treated dentin matrix hydrogel in direct pulp capping. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(4): 2101-2112. [13] HUANG L, CHEN X, YANG X, et al. GelMA-based hydrogel biomaterial scaffold: A versatile platform for regenerative endodontics. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2024;112(5):e35412. [14] XIN T, GU Y, CHENG R, et al. Inorganic Strengthened Hydrogel Membrane as Regenerative Periosteum. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(47):41168-41180. [15] PARANDHAMAN T, CHOUDHARY P, RAMALINGAM B, et al. Antibacterial and Antibiofouling Activities of Antimicrobial Peptide-Functionalized Graphene-Silver Nanocomposites for the Inhibition and Disruption of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(12):5899-5917. [16] KIEW SF, KIEW LV, LEE HB, et al. Assessing biocompatibility of graphene oxide-based nanocarriers: A review. J Control Release. 2016;226:217-228. [17] ZHOU Y, YANG Y, LIU R, et al. Research Progress of Polydopamine Hydrogel in the Prevention and Treatment of Oral Diseases. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:2623-2645. [18] XU H, GU S, RIQUELME MA, et al. Connexin 43 channels are essential for normal bone structure and osteocyte viability. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(3):436-448. [19] BONACQUISTI EE, NGUYEN J. Connexin 43 (Cx43) in cancer: Implications for therapeutic approaches via gap junctions. Cancer Lett. 2019;442:439-444. [20] NASER AL DEEN N, ABOUHAIDAR M, TALHOUK R. Connexin43 as a Tumor Suppressor: Proposed Connexin43 mRNA-circularRNAs-microRNAs Axis Towards Prevention and Early Detection in Breast Cancer. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019;6:192. [21] YIN J, XU J, CHENG R, et al. Role of connexin 43 in odontoblastic differentiation and structural maintenance in pulp damage repair. Int J Oral Sci. 2021;13(1):1. [22] DELVAEYE T, VANDENABEELE P, BULTYNCK G, et al. Therapeutic Targeting of Connexin Channels: New Views and Challenges. Trends Mol Med. 2018;24(12):1036-1053. [23] LONG P, XIONG L, DING C, et al. Connexin43 reduces LPS-induced inflammation in hDPCs through TLR4-NF-κB pathway via hemichannels. Oral Dis. 2024;30(5):3239-3249. [24] 张安妮,丁灿灿,黄丽苹,等.抑制连接蛋白43介导半通道活性促进脂多糖诱导的人牙髓细胞成牙本质分化[J].上海口腔医学, 2024,33(1):22-29. [25] MOHAMMED EEA, BEHEREI HH, EL-ZAWAHRY M, et al. Osteogenic enhancement of modular ceramic nanocomposites impregnated with human dental pulp stem cells: an approach for bone repair and regenerative medicine. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022;20(1):123. [26] ZHANG CY, CHENG YL, TONG XW, et al. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Self-Adhesive Dual-Cured Resin Cement Polymerized Beneath Three Different Cusp Inclinations of Zirconia. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019: 7404038. [27] 何文喜,余擎.牙髓炎的活髓保存及再生治疗新进展:从基础到临床[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2022,57(1):16-22. [28] KURIAN AG, SINGH RK, PATEL KD, et al. Multifunctional GelMA platforms with nanomaterials for advanced tissue therapeutics. Bioact Mater. 2021;8:267-295. [29] WANG Y, LI H, FENG Y, et al. Dual micelles-loaded gelatin nanofibers and their application in lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontal disease. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:963-976. [30] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271. [31] PEPELANOVA I, KRUPPA K, SCHEPER T, et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels with Defined Degree of Functionalization as a Versatile Toolkit for 3D Cell Culture and Extrusion Bioprinting. Bioengineering (Basel). 2018;5(3):55. [32] SHIRAHAMA H, LEE BH, TAN LP, et al. Precise Tuning of Facile One-Pot Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Synthesis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31036. [33] FERNANDEZ CC, SOKOLONSKI AR, FONSECA MS, et al. Applications of Silver Nanoparticles in Dentistry: Advances and Technological Innovation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2485. [34] TĂRĂBOANȚĂ I, BURLEC AF, STOLERIU S, et al. Influence of the Loading with Newly Green Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Equisetum sylvaticum on the Antibacterial Activity and Surface Hardness of a Composite Resin. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(8):402. [35] LUCERI A, FRANCESE R, LEMBO D, et al. Silver Nanoparticles: Review of Antiviral Properties, Mechanism of Action and Applications. Microorganisms. 2023;11(3):629. [36] WANG J, ZHENG W, CHEN L, et al. Enhancement of Schwann Cells Function Using Graphene-Oxide-Modified Nanofiber Scaffolds for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(5):2444-2456. [37] ZHIHUI K, MIN D. Application of Graphene Oxide-Based Hydrogels in Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022;8(7):2849-2857. [38] BAN G, HOU Y, SHEN Z, et al. Potential Biomedical Limitations of Graphene Nanomaterials. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:1695-1708. [39] LI XP, QU KY, ZHOU B, et al. Electrical stimulation of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes using conductive polydopamine-reduced graphene oxide-hybrid hydrogels for constructing cardiac microtissues. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;205:111844. [40] ZHOU K, YU P, SHI X, et al. Hierarchically Porous Hydroxyapatite Hybrid Scaffold Incorporated with Reduced Graphene Oxide for Rapid Bone Ingrowth and Repair. ACS Nano. 2019;13(8):9595-9606. [41] CHEN J, FAN L, YANG C, et al. Facile synthesis of Ag nanoparticles-loaded chitosan antibacterial nanocomposite and its application in polypropylene. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;161:1286-1295. [42] LI Y, ZHANG Y, DONG Y, et al. Ablation of Gap Junction Protein Improves the Efficiency of Nanozyme-Mediated Catalytic/Starvation/Mild-Temperature Photothermal Therapy. Adv Mater. 2023;35(22): e2210464. [43] 薛俊杰,李婧瑜,张莉,等.缝隙连接蛋白43在骨关节炎软骨及细胞中表达及shRNA慢病毒载体的构建[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(23):3627-3635. [44] 赵丹,魏碧玉,高明龙.星形胶质细胞缝隙连接蛋白43在痛觉敏化中作用机制研究进展[J].武警医学,2020,31(4):357-360. [45] TARZEMANY R, JIANG G, JIANG JX, et al. Connexin 43 Hemichannels Regulate the Expression of Wound Healing-Associated Genes in Human Gingival Fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14157. [46] LI S, HE H, ZHANG G, et al. Connexin43-containing gap junctions potentiate extracellular Ca²⁺-induced odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via Erk1/2. Exp Cell Res. 2015;338(1):1-9. [47] LIU H, YANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Melanin-Like Nanomaterials for Advanced Biomedical Applications: A Versatile Platform with Extraordinary Promise. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(7):1903129. [48] SARFRAZ S, MÄNTYNEN PH, LAURILA M, et al. Comparison of Titanium and PEEK Medical Plastic Implant Materials for Their Bacterial Biofilm Formation Properties. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(18):3862. [49] HELIAWATI L, LESTARI S, HASANAH U, et al. Phytochemical Profile of Antibacterial Agents from Red Betel Leaf (Piper crocatum Ruiz and Pav) against Bacteria in Dental Caries. Molecules. 2022;27(9):2861. [50] SAKARYALı UYAR D, ÜSKÜDAR GÜÇLÜ A, ÇELIK E, et al. Evaluation of probiotics’ efficiency on cariogenic bacteria: randomized controlled clinical study. BMC Oral Health. 2024;24(1):886. |
| [1] | Chen Haojie, Wang Dai, Shen Shan. Immune inflammatory microenvironment mechanisms in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2054-2062. |
| [2] | Yang Qiongqiong, Liu Wei. Comparison of performance and clinical effects of zirconia and titanium implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2063-2071. |
| [3] | Liu Yang, Liu Donghui , Xu Lei, Zhan Xu, Sun Haobo, Kang Kai. Role and trend of stimuli-responsive injectable hydrogels in precise myocardial infarction therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [4] | Wang Zheng, Cheng Ji, Yu Jinlong, Liu Wenhong, Wang Zhaohong, Zhou Luxing. Progress and future perspectives on the application of hydrogel materials in stroke therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [5] | Guo Yuchao, Ni Qianwei, Yin Chen, Jigeer·Saiyilihan, Gao Zhan . Quaternized chitosan hemostatic materials: synthesis, mechanism, and application [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [6] | Liu Hongjie, Mu Qiuju, Shen Yuxue, Liang Fei, Zhu Lili. Metal organic framework/carboxymethyl chitosan-oxidized sodium alginate/platelet-rich plasma hydrogel promotes healing of diabetic infected wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [7] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [8] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [9] | Wang Yu, Fan Minjie, Zheng Pengfei. Application of multistimuli-responsive hydrogels in bone damage repair: special responsiveness and diverse functions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| [10] | Li Ruiqiang, Yin Chen, Ma Yan. Effect of carbamide peroxide and hydrogen peroxide bleaching agents on laser-induced fluorescence in dentin Raman spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 296-302. |
| [11] | Zhao Chunhong, He Li. Comparison of effects of three machined nitinol instruments on preparing curved root canals using different methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 303-309. |
| [12] | Cheng Yanan, Yu Jiazhi, Liu Yinchang, Wu Jie, Yu Tong, Wang Lu, Li Xiaoguang. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of molar distalization with clear aligners with different thicknesses and edges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 310-318. |
| [13] | Huang Xinxu, Zhang Xin, Wang Jian. Living microecological hydrogels promote skin wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 489-498. |
| [14] | Bai Xiangyu, Huo Feng, Hao Yan, Wang Zecheng, Guo Xiaoyu. Platelet-derived growth factor BB-loaded chitosan/reduced graphene oxide scaffold for repairing alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 329-337. |
| [15] | Liu Xiaohong, Zhao Tian, Mu Yunping, Feng Wenjin, Lyu Cunsheng, Zhang Zhiyong, Zhao Zijian, Li Fanghong. Acellular dermal matrix hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||