Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (25): 3947-3954.doi: 10.12307/2024.182
Previous Articles Next Articles
Detection of immune-related cytokines of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis mice by antibody chip and analysis of key differential genes
Yang Shanshan1, 2, Ouyang Renjun1, 2, Tian Jia1, 2, Linghu Min1, 2, Wang Zhen1, 2, Yang Xiaohong1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Basic Pharmacology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-05-13Accepted:2023-07-11Online:2024-09-08Published:2023-11-23 -
Contact:Yang Xiaohong, MD, Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Yang Shanshan, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China; Key Laboratory of Basic Pharmacology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 8206030955 (YXH); Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project, No. ZK[2023]540 (to YXH); Zunyi Science and Technology Plan Project, No. HZ(2022)424 (to YXH); Postgraduate Scientific Research Fund of Zunyi Medical University, No. ZYK203 (to WZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Shanshan, Ouyang Renjun, Tian Jia, Linghu Min, Wang Zhen, Yang Xiaohong. Detection of immune-related cytokines of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis mice by antibody chip and analysis of key differential genes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 3947-3954.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
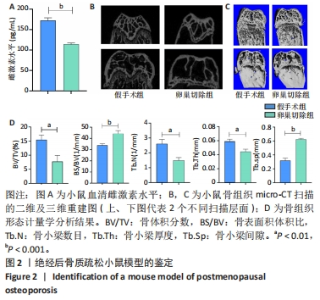
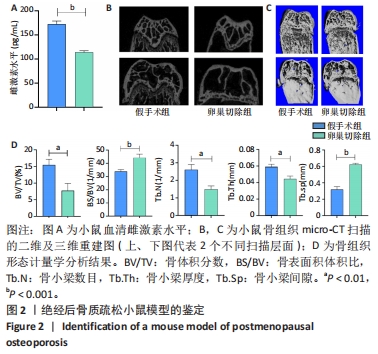
2.1 POP小鼠模型的鉴定结果 建模术后12周,使用ELISA试剂盒检测假手术组与卵巢切除组血清雌二醇水平,见图2A,卵巢切除组小鼠血清雌二醇水平低于假手术组,差异有显著性意义(t=13.368,P < 0.001)。Micro CT扫描假手术组与卵巢切除组小鼠的股骨并进行形态学分析,见图2B-D,结果显示与假手术组相比,卵巢切除组骨小梁数目(Tb.N,t=5.188,P=0.003)、骨小梁厚度(Tb.Th,t=5.124,P=0.003)与骨体积分数(BV/TV,t=4.677,P=0.005)均显著低于假手术组,而卵巢切除组骨表面积体积比(BS/BV,t=5.650,P=0.002)及骨小梁间隙(Tb.Sp,t=12.779,P < 0.001)均显著高于假手术组,表明卵巢切除组小鼠存在明显的骨质疏松样改变。"
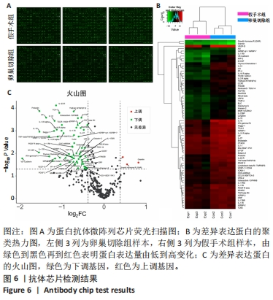
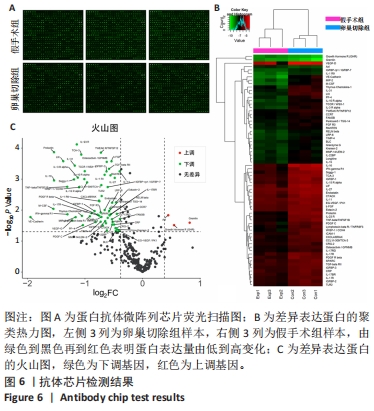
2.3 抗体芯片检测结果 通过细胞因子抗体芯片检测假手术组和卵巢切除组中存在差异表达的蛋白,荧光检测后获得荧光扫描图,见图6A。以卵巢切除组的蛋白表达量与假手术组的蛋白表达量的比值作为差异倍数。其中上调组需满足FC≥1.3且 P值< 0.05;下调组需满足FC≤0.7且P值< 0.05。差异蛋白聚类热力图与火山图揭示两组样本中存在明显差异表达且具有统计学意义的蛋白,见图6B,C。结果显示,与假手术组相比,卵巢切除组中表达上调的蛋白有3个,分别是Gremlin,GHR,Ax1;下调的有VE-Cadherin,M-CSF,Prolactin,IL-16,CXCL5,TNF-beta/TNFSF1B,IFN-gamma R1,VEGF-D,Soggy-1等65个蛋白。"
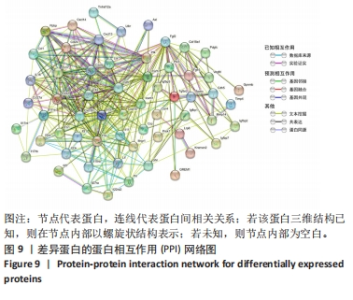
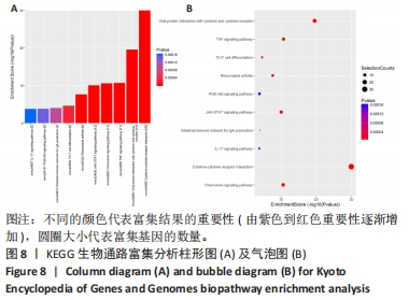
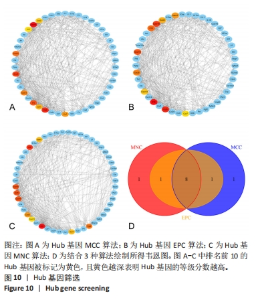
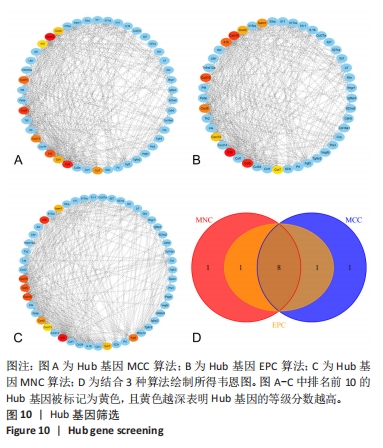
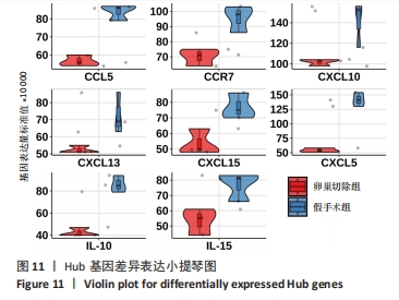
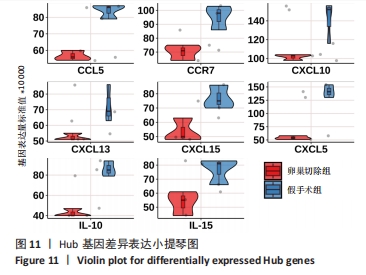
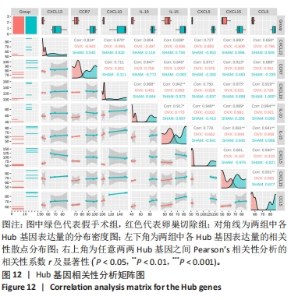
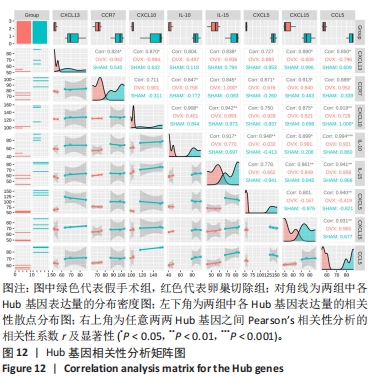
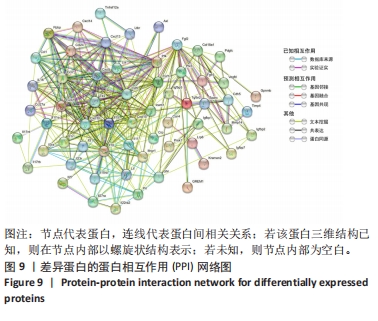
2.6 PPI分析和Hub基因筛选 芯片检测样本中308种蛋白,结果显示68种蛋白存在差异,通过 String 数据库分析存在差异表达的 mRNAs 间的相互作用,构建PPI网络,见图9。结果显示,网络包含49个节点和239条边,网络中平均节点度为9.67,集聚系数为 0.614,PPI 富集 P值为< 1.0×10-16。将String 数据分析结果导入Cytoscape软件进一步分析,通过cytoHubba(版本0.1)进行Hub基因筛选,运用MCC、MNC和EPC算法分别获得了排名前10的基因作为Hub基因,见图10A-C(图中Hub基因标记为黄色),颜色越深代表ranked score排名越靠前。将3种算法所得Hub基因绘制韦恩图,见图10D,取交集或并集增加Hub基因可信度,最终得到8个共同的Hub基因,分别为CXCL10、CCL5、CXCL5、IL-10、CXCL15、CXCL13、CCR7和IL-15。对以上8个Hub基因绘制差异表达小提琴图,见图11,图中可见在卵巢切除组中以上8个基因较假手术组均显著下调;再对以上8个基因的表达水平绘制相关性矩阵,见图12,图中可见不同的Hub基因之间存在较强的正相关关系,说明各基因的表达水平的上升及下降趋势一致,这与图10所示各基因均为下调基因的结果相一致。"
| [1] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691. [2] YU F, XIA W. The epidemiology of osteoporosis, associated fragility fractures, and management gap in China. Arch Osteoporos. 2019;14(1):32. [3] BREUIL V, TICCHIONI M, TESTA J, et al. Immune changes in post-menopausal osteoporosis: the Immunos study. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(5):805-814. [4] FANG H, ZHANG H, WANG Z, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis and could predict the risk of osteoporotic fracture. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020;34(1):e23016. [5] WANG L, ZHAO Y, LIU Y, et al. IFN-γ and TNF-α synergistically induce mesenchymal stem cell impairment and tumorigenesis via NFκB signaling. Stem Cells. 2013; 31(7):1383-1395. [6] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21. [7] ZHANG W, DANG K, HUAI Y, et al. Osteoimmunology: The Regulatory Roles of T Lymphocytes in Osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:465. [8] YU M, PAL S, PATERSON CW, et al. Ovariectomy induces bone loss via microbial-dependent trafficking of intestinal TNF+ T cells and Th17 cells. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(4):e143137. [9] WANG Z, GERSTEIN M, SNYDER M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(1):57-63. [10] 周子墨,陈佳慧,陈森相,等.基于生物信息学分析老年骨质疏松差异表达基因及m6A相关蛋白的研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2022,51(11):975-979,986. [11] KIM PG, NIROULA A, SHKOLNIK V, et al. Dnmt3a-mutated clonal hematopoiesis promotes osteoporosis. J Exp Med. 2021;218(12):e20211872. [12] QIAN GF, YUAN LS, CHEN M, et al. PPWD1 is associated with the occurrence of postmenopausal osteoporosis as determined by weighted gene co‑expression network analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3202-3214. [13] CAMACHO PM, PETAK SM, BINKLEY N, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists/american college of endocrinology clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis- 2020 update executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2020;26(5):564-570. [14] XIAO PL, CUI AY, HSU CJ, et al. Global, regional prevalence, and risk factors of osteoporosis according to the World Health Organization diagnostic criteria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(10):2137-2153. [15] KHOSLA S, MONROE DG. Regulation of Bone Metabolism by Sex Steroids. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(1):a031211. [16] LEE JW, HOSHINO A, INOUE K, et al. The HIV co-receptor CCR5 regulates osteoclast function. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):2226. [17] SAITO H, GASSER A, BOLAMPERTI S, et al. TG-interacting factor 1 (Tgif1)-deficiency attenuates bone remodeling and blunts the anabolic response to parathyroid hormone. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1354. [18] CHEN K, QIU P, YUAN Y, et al. Pseurotin A Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomized-Induced Bone Loss by Suppressing Reactive Oxygen Species. Theranostics. 2019;9(6):1634-1650. [19] LI J, AYOUB A, XIU Y, et al. TGFβ-induced degradation of TRAF3 in mesenchymal progenitor cells causes age-related osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2795. [20] WALSH MC, TAKEGAHARA N, KIM H, et al. Updating osteoimmunology: regulation of bone cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14(3):146-156. [21] WALSH MC, KIM N, KADONO Y, et al. Osteoimmunology: interplay between the immune system and bone metabolism. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:33-63. [22] TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(4):292-304. [23] JONES DC, WEIN MN, OUKKA M, et al. Regulation of adult bone mass by the zinc finger adapter protein Schnurri-3. Science. 2006;312(5777):1223-1227. [24] CENCI S, WEITZMANN MN, ROGGIA C, et al. Estrogen deficiency induces bone loss by enhancing T-cell production of TNF-alpha. J Clin Invest. 2000;106(10):1229-1237. [25] TEITELBAUM SL. Postmenopausal osteoporosis, T cells, and immune dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(48):16711-16712. [26] LEE SK, KADONO Y, OKADA F, et al. T lymphocyte-deficient mice lose trabecular bone mass with ovariectomy. J Bone Miner Res. 2006;21(11):1704-1712. [27] LEE EY, LEE ZH, SONG YW. CXCL10 and autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8(5):379-383. [28] LEE EY, LEE ZH, SONG YW. The interaction between CXCL10 and cytokines in chronic inflammatory arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12(5):554-557. [29] LARANJEIRA P, PEDROSA M, DUARTE C, et al. Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Regulate the Proinflammatory Response of Monocytes and Myeloid Dendritic Cells from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(2):404. [30] FENG SY, LEI J, LI YX, et al. Increased joint loading induces subchondral bone loss of the temporomandibular joint via the RANTES-CCRs-Akt2 axis. JCI Insight. 2022;7(21):e158874. [31] CHEN Y, WANG H, YANG Q, et al. Single-cell RNA landscape of the osteoimmunology microenvironment in periodontitis. Theranostics. 2022;12(3): 1074-1096. [32] CHEN X, WAN Z, YANG L, et al. Exosomes derived from reparative M2-like macrophages prevent bone loss in murine periodontitis models via IL-10 mRNA. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):110. [33] WU X, MA Y, CHEN H, et al. Lysophosphatidic acid induces interleukin-6 and CXCL15 secretion from MLO-Y4 cells through activation of the LPA1 receptor and PKCθ signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;74:105664. [34] LE MERCIER A, BONNAVION R, YU W, et al. GPR182 is an endothelium-specific atypical chemokine receptor that maintains hematopoietic stem cell homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(17):e2021596118. [35] KOH JM, OH B, HA MH, et al. Association of IL-15 polymorphisms with bone mineral density in postmenopausal Korean women. Calcif Tissue Int. 2009;85(5): 369-378. |
| [1] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [2] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [3] | Dai Yuexing, Zheng Liqin, Wu Minhui, Li Zhihong, Li Shaobin, Zheng Desheng, Lin Ziling. Effect of vessel number on computational fluid dynamics in vascular networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [4] | Zhang Min, Peng Jing, Zhang Qiang, Chen Dewang. Mechanical properties of L3/4 laminar decompression and intervertebral fusion in elderly osteoporosis patients analyzed by finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 847-851. |
| [5] | Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [6] | Kaiyisaier•Abudukelimu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Li Lei, Yang Xiaokai, Zhang Yukun, Liu Shuai. Effect of lumbar CT values in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women patients with lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 945-949. |
| [7] | Wang Liping, Lian Tianxing, Hu Yongrong, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Liu Hao, Qu Bo. HU value of chest CT vertebral body in the opportunistic screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 950-954. |
| [8] | Yu Zhaoyu, Tan Lixin, Sun Kai, Lu Yao, Li Yong. Meta-analysis of cement-augmented pedicle screw for thoracolumbar degenerative diseases with osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 813-820. |
| [9] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [10] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [11] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Maimaitimin·Abulimiti, Tuerhongjiang·Abudurexiti. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of terlipatide and bisphosphate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 639-645. |
| [12] | Lin Feng, Cheng Ling, Gao Yong, Zhou Jianye, Shang Qingqing. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel-encapsulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote cardiac function in myocardial infarction rats (III) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 355-359. |
| [13] | Bi Yujie, Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Zhou Ziqiong, Zhao Jing, Zhu Houjun, Zhong Qiuhui, Yang Yuxin. Strategy and significance of Chinese medicine combined with medical hydrogel for disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(3): 419-425. |
| [14] | Yang Qipei, Chen Feng, Cui Wei, Zhang Chi, Wu Ruiqi, Song Zhenheng, Meng Xin. Signaling pathways related to kaempferol active monomers in the treatment of osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4242-4249. |
| [15] | Yang Qihang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Leng Siyi, Song Yongjing, Liu Hui, Du Guangyou. Intestinal flora and osteoporosis and exercise intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4250-4256. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||