Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (11): 1715-1721.doi: 10.12307/2023.116
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of thioredoxin-interacting protein-mediated inflammatory response and apoptosis in myocardial infarction
Wang Xuejiao, Shi Wenjuan, Zhang Yan, Xing Dehai, Li Dongxue, Jiao Xiangying
- Key Laboratory of Cellular Physiology (Shanxi Medical University), Ministry of Education, Department of Physiology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2022-02-25Accepted:2022-05-09Online:2023-04-18Published:2022-09-27 -
Contact:Jiao Xiangying, MD, Professor, Key Laboratory of Cellular Physiology (Shanxi Medical University), Ministry of Education, Department of Physiology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Wang Xuejiao, Master, Key Laboratory of Cellular Physiology (Shanxi Medical University), Ministry of Education, Department of Physiology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Shanxi Province Applied Basic Research Program, No. 201901D111192 (to JXY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xuejiao, Shi Wenjuan, Zhang Yan, Xing Dehai, Li Dongxue, Jiao Xiangying. Role of thioredoxin-interacting protein-mediated inflammatory response and apoptosis in myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1715-1721.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
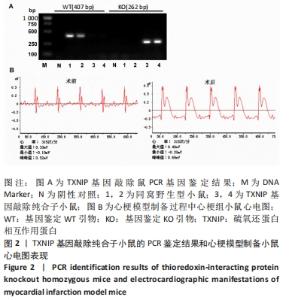
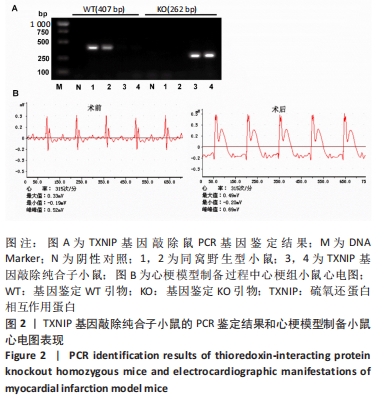
2.1 实验动物数量分析 纳入TXNIP基因敲除纯合子小鼠和同窝野生C57BL/6J小鼠各30只,2种小鼠分别随机分为伪手术组心梗组,每组15只。全部进入结果分析,无脱失。 2.2 TXNIP基因敲除纯合子小鼠模型的筛选和心梗模型建立 TXNIP基因敲除杂合小鼠交配繁殖,子代小鼠于3周剪取鼠尾常规PCR鉴定基因型,如图2A所示,同窝野生C57BL/6J小鼠(图2A中1号和2号)只在407 bp处可看到明显条带,TXNIP基因敲除纯合子小鼠(图2A中3号和4号)只在262 bp处可见明显条带。 对纳入梗死组的8周龄小鼠建立心梗模型,进行冠状动脉左前降支结扎,结扎后可见心脏左室前壁变白,心脏搏动减弱,心电图结果显示心梗术后ST段显著抬高,见图2B,提示心梗模型成功建立。 "
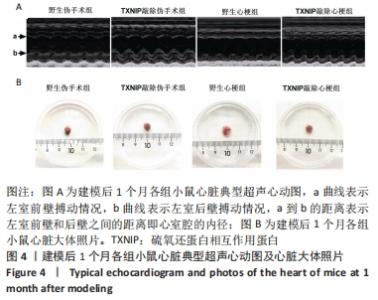
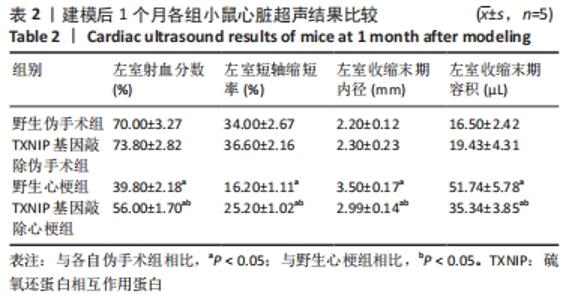
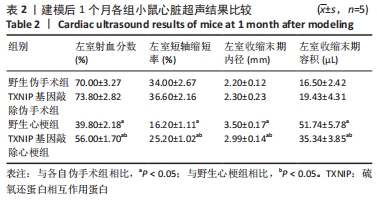
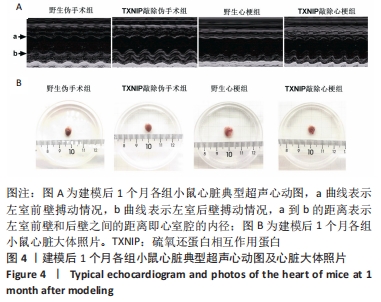
2.4 TXNIP基因敲除可改善心梗术后左心室功能障碍 术后1个月,使用小动物超声仪检测各组小鼠心脏左室功能,见图4及表2。结果可见,野生伪手术组与TXNIP基因敲除伪手术组相比,各超声指标均无显著差异(P > 0.05),心脏超声图显示两组心脏左室前壁和后壁搏动情况接近,心脏大体照片也无明显差异。与各自伪手术组相比,野生心梗组和TXNIP基因敲除心梗组的左室射血分数和左室短轴缩短率显著降低,左心室收缩末期内径和左心室收缩末期容积显著升高(P < 0.05);心脏大体照片可见到明显的梗死区域。与野生心梗组相比,TXNIP基因敲除心梗组左室射血分数和左室短轴缩短显著升高,左心室收缩末期内径和左心室收缩末期容积明显降低(P < 0.05),同时超声心动图可见野生心梗组小鼠左室前壁搏动明显减弱甚至接近直线,而TXNIP基因敲除心梗组小鼠左室前壁搏动情况较好。心脏大体照片显示,野生心梗组心梗面积大于TXNIP基因敲除心梗组心肌的梗死面积。以上结果提示TXNIP基因敲除可减轻心梗术后造成的左室功能障碍。"
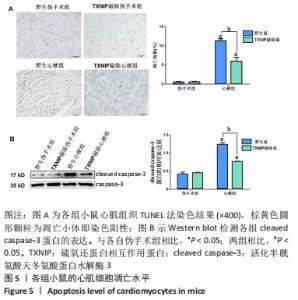
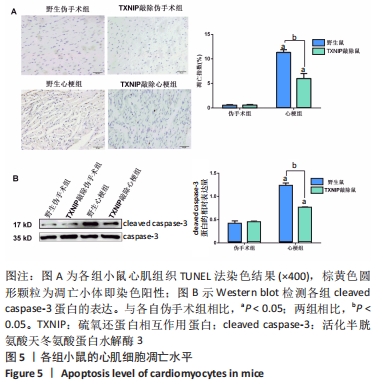
2.5 TXNIP基因敲除可以改善心梗后心肌细胞凋亡 心梗手术4 d后,使用TUNEL法测定了心肌组织细胞凋亡情况,结果见图5A。野生伪手术组和TXNIP基因敲除伪手术组仅可见苏木精蓝染的细胞核,视野中几乎看不到呈棕黄色的凋亡阳性染色细胞核;野生心梗组和TXNIP基因敲除心梗组视野中可见到较多的棕黄色颗粒,但TXNIP基因敲除心梗组阳性细胞的数量较野生心梗组显著减少,心肌细胞凋亡指数明显降低(P < 0.05)。Western blot检测凋亡相关蛋白cleaved caspase-3的表达,结果发现,与各自伪手术组相比,野生心梗组和TXNIP基因敲除心梗组cleaved caspase-3蛋白表达均明显增加(P < 0.05);而与野生心梗组相比,TXNIP基因敲除心梗组cleaved caspase-3蛋白表达明显减少(P < 0.05),见图5B。以上结果提示,心梗可引起显著的心肌细胞凋亡,而TXNIP基因敲除可减轻心梗后心肌细胞凋亡的发生。"
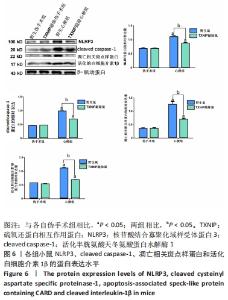
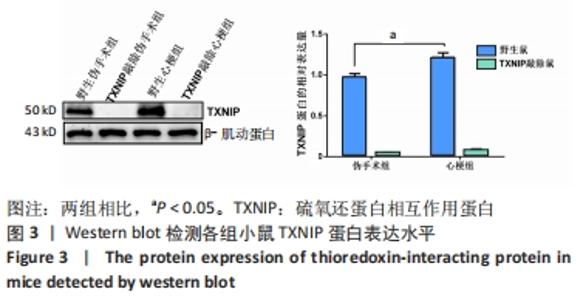
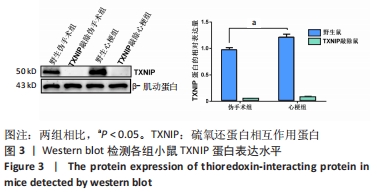
2.6 TXNIP基因敲除抑制NLRP3、cleaved caspase-1、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白和活化白细胞介素1β的蛋白表达 心梗手术4 d后,取各组小鼠的心脏组织,使用Western blot方法检测NLRP3、cleaved caspase-1、凋亡相关斑点样蛋白和活化白细胞介素1β的蛋白表达水平,见图6。与野生伪手术组相比,TXNIP基因敲除伪手术组4种蛋白的表达均无明显变化(P > 0.05);与各自伪手术组相比,野生心梗组和TXNIP基因敲除心梗组4种蛋白的表达均显著升高(P < 0.05);与野生心梗组相比,TXNIP基因敲除心梗组4种蛋白的表达均降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。以上结果提示,TXNIP基因敲除可抑制NLRP3、cleaved caspase-1和凋亡相关斑点样蛋白的蛋白表达,并减少下游活化白细胞介素1β的蛋白表达,从而减轻心梗后小鼠心脏组织的炎症反应。"

| [1] NUNEZ-GIL IJ, RIHA H, RAMAKRISHNA H. Review of the 2017 European Society of Cardiology’s Guidelines for the Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction in Patients Presenting with ST-Segment Elevation and Focused Update on Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Coronary Artery Disease Developed in Collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2019;33(8):2334-2343. [2] IBANEZ B, JAMES S, AGEWALL S, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2018;39(2):119-177. [3] SHARMA V, DASH SK, GOVARTHANAN K, et al. Recent Advances in Cardiac Tissue Engineering for the Management of Myocardium Infarction. Cells. 2021;10(10):2538. [4] WU X, IROEGBU CD, PENG J, et al. Cell Death and Exosomes Regulation After Myocardial Infarction and Ischemia-Reperfusion. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:673677. [5] YOUNIS NS, MOHAMED ME. Anethole’s effects against myocardial infarction: The role of TLR4/NFkappaB and Nrf2/HO1 pathways. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;360:109947. [6] LIANG B, ZHANG XX, LI R, et al. Guanxin V alleviates acute myocardial infarction by restraining oxidative stress damage, apoptosis, and fibrosis through the TGF-β1 signalling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2022; 100:154077. [7] LIU W, FENG Y, WANG X, et al. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells-derived exosomes enhance cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):8850-8865. [8] HU J, YU Y. The Function of Thioredoxin-Binding Protein-2 (TBP-2) in Different Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;5:4582130. [9] QAYYUM N, HASEEB M, KIM MS, et al. Role of Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein in Diseases and Its Therapeutic Outlook. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(5):2754. [10] ALHAWITI NM, AL MAHRI S, AZIZ MA, et al. TXNIP in Metabolic Regulation: Physiological Role and Therapeutic Outlook. Curr Drug Targets. 2017;18(9):1095-1103. [11] DOMINGUES A, JOLIBOIS J, MARQUET DE ROUGE P, et al. The Emerging Role of TXNIP in Ischemic and Cardiovascular Diseases; A Novel Marker and Therapeutic Target. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1693. [12] NAKAYAMA Y, MUKAI N, WANG BF, et al. Txnip C247S mutation protects the heart against acute myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021; 155:36-49. [13] ZHANG KZ, SHEN XY, WANG M, et al. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Promotes Cardiac Injury After Myocardial Infarction Via Inducing Cardiomyocyte Pyroptosis Through an Interaction With NLRP3. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(22):e022011. [14] HOFBAUER D, MOUGIAKAKOS D, BROGGINI L, et al. beta2-microglobulin triggers NLRP3 inflammasome activation in tumor-associated macrophages to promote multiple myeloma progression. Immunity. 2021;54(8):1772-1787. e9. [15] SHEN S, WANG Z, SUN H, et al. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Ventricular Remodeling. Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e934255. [16] MENG Z, SONG MY, LI CF, et al. shRNA interference of NLRP3 inflammasome alleviate ischemia reperfusion-induced myocardial damage through autophagy activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;494(3-4):728-735. [17] PICH K, RESPEKTA N, DAWID M, et al. New insights into cell apoptosis and proliferation: the potential role of vaspin. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021;72(6).doi: 10.26402/jpp.2021.6.02. [18] CHEN Z, WU J, LI S, et al. Inhibition of Myocardial Cell Apoptosis Is Important Mechanism for Ginsenoside in the Limitation of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:806216. [19] YIN H, WANG K, DAS A, et al. The REDD1/TXNIP Complex Accelerates Oxidative Stress-Induced Apoptosis of Nucleus Pulposus Cells through the Mitochondrial Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021: 7397516. [20] CHEN N, SONG S, YANG Z, et al. ChREBP deficiency alleviates apoptosis by inhibiting TXNIP/oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2021;35(12):108050. [21] PAN M, ZHANG F, QU K, et al. TXNIP: A Double-Edged Sword in Disease and Therapeutic Outlook. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:7805115. [22] SAYED RKA, FERNANDEZ-ORTIZ M, RAHIM I, et al. The Impact of Melatonin Supplementation and NLRP3 Inflammasome Deletion on Age-Accompanied Cardiac Damage. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(8): 1269. [23] CHEN Y, ZENG M, ZHANG Y, et al. Nlrp3 Deficiency Alleviates Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiomyopathy by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:6679100. [24] FU Y, SHEN J, LI Y, et al. Inhibition of the PERK/TXNIP/NLRP3 Axis by Baicalin Reduces NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis in Macrophages Infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:1805147. [25] LI L, ISMAEL S, NASOOHI S, et al. Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Associated NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Human Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;68(1):255-265. [26] CHIU LY, HUANG DY, LIN WW. PARP-1 regulates inflammasome activity by poly-ADP-ribosylation of NLRP3 and interaction with TXNIP in primary macrophages. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(2):108. [27] MOHAMED IN, LI L, ISMAEL S, et al. Thioredoxin interacting protein, a key molecular switch between oxidative stress and sterile inflammation in cellular response. World J Diabetes. 2021;12(12):1979-1999. [28] VAN HOUT GP, BOSCH L, ELLENBROEK GH, et al. The selective NLRP3-inflammasome inhibitor MCC950 reduces infarct size and preserves cardiac function in a pig model of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(11):828-836. [29] SHI J, GAO W, SHAO F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(4):245-254. [30] GAO L, QIN JX, SHI JQ, et al. Fine particulate matter exposure aggravates ischemic injury via NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022;28(7):1045-1058.. [31] ABBATE A, TOLDO S, MARCHETTI C, et al. Interleukin-1 and the Inflammasome as Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2020;126(9):1260-1280. [32] QUAN XZ, YE JH, YANG XZ, et al. HOXA9-induced chemerin signals through CMKLR1/AMPK/TXNIP/NLRP3 pathway to induce pyroptosis of trophoblasts and aggravate preeclampsia. Exp Cell Resh. 2021;408(2): 112802. |
| [1] | Yue Feifei, Song Yu, Wang Xiaobei, Wang Lin. Application and effect of extracellular vesicles in cardiac repair after myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1610-1617. |
| [2] | Yin Tingting, Du Dayong, Jiang Zhixin, Liu Yang, Liu Qilin, Li Yuntian. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factors improve myocardial fibrosis in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 730-735. |
| [3] | You Yihui, Song Chunhui, Chen Xi, Yao Xiaohong, Ke Junyu, Du Qun, Song Ning, Li Yanwu. Characteristic changes of intestinal mucosal morphology and transcriptomics in silent information regulator 6 gene knockout mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5119-5125. |
| [4] | Wang Xiangyu, Zhu Ruizhi, Zhao Zhiping, Zhang Yuda, Zhang Yongtao, Wang Changyao. Construction of bromodomain-containing protein 4 gene knockout mice by CRISPR/Cas9 combined with Cre-loxP technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(32): 5179-5184. |
| [5] | Li Yan, Zhang Yan, Zhang Ningkun, Chen Yu. Effect and mechanism of conditioned medium from hypoxia preconditioned human Wharton’s Jelly derived mesenchymal stem cells on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5008-5013. |
| [6] | Sun Ying, Xiang Guangda, Xu Xiaoli. Effects of myeloid-derived growth factor on ventricular remodeling in aging mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(31): 5020-5025. |
| [7] | Jiang Jie, Zhao Baixiao, Chen Libin, Wen Li, Zhang Shanshan, Ma Jie, Zhao Hua. Effect of moxibustion pretreatment on autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome expression in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3615-3619. |
| [8] | Yang Qian, Zhang Yiou, Jia Lili, Xie Jun, Feng Mali, Li Tingkai. Establishment and disease progression in a rat myocardial infarction model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(23): 3733-3737. |
| [9] | Geng Yuanwen, Lin Qinqin, Li Ruoming, Tang Shaokai, Wang Baihui, Tian Zhenjun. A single bout of exhaustive exercise induces renal NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome expression in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 190-196. |
| [10] | Ding Yan, Xiang Guangda, Meng Biying, Xu Xiaoli, Chen Yuefu. Establishment and identification of a myeloid-derived growth factor deficiency model in apolipoprotein E knockout mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2196-2201. |
| [11] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [12] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| [13] | Zhou Quan, Zhang Yanan, Bai Yiguang, Zhang Qiong, Nong Haibin, Liu Mingfu, Zeng Gaofeng, Zong Shaohui. Effect of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 regulating osteoclasts on bone mineral density in osteoporotic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(29): 4680-4684. |
| [14] | Zhang Lishu, Liu Anqi, He Xiaoning, Jin Yan, Li Bei, Jin Fang. Alpl gene affects the therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on ulcerative colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3970-3975. |
| [15] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||