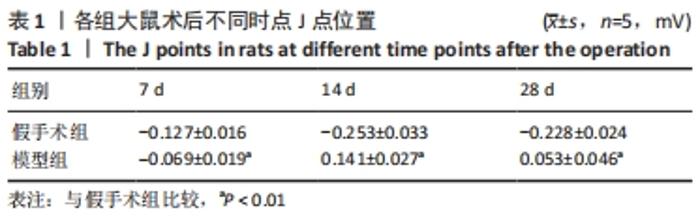
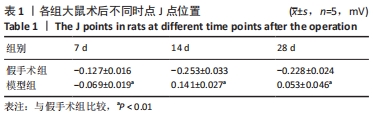
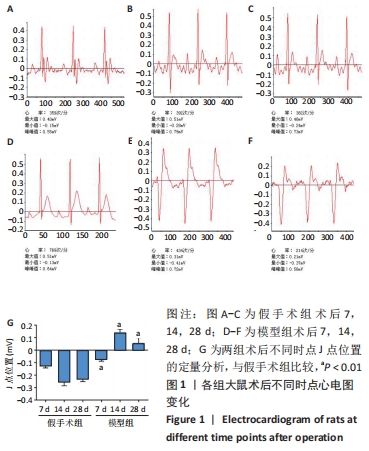
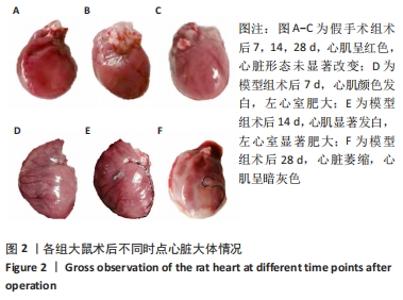
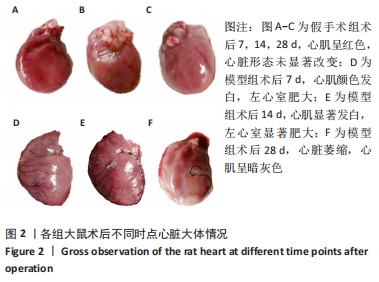
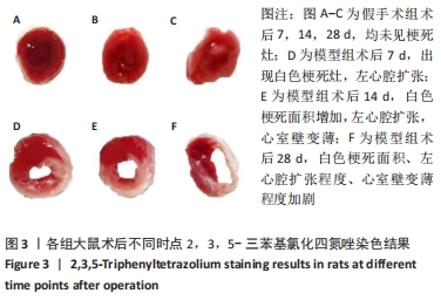
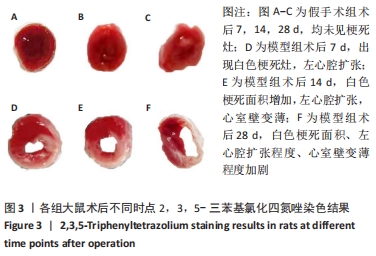
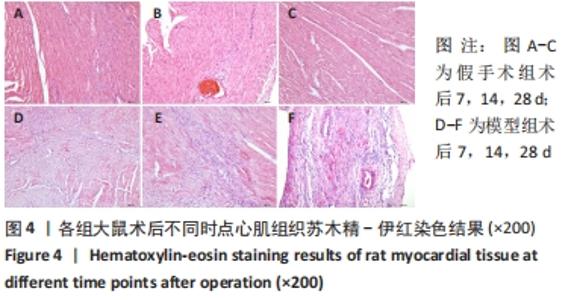
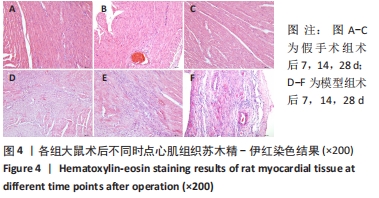
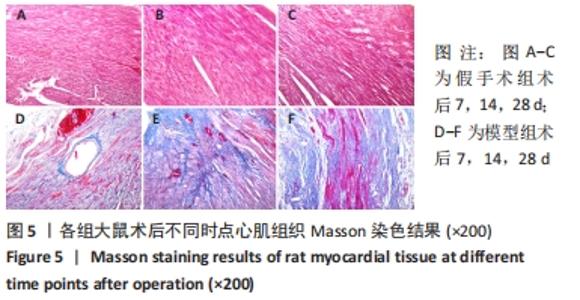
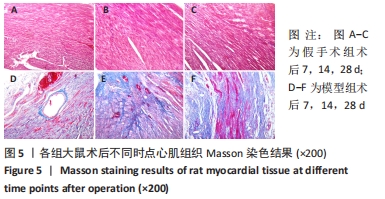
[1] 李宏亮, 薛智慧, 龙抗胜, 等. 线栓法制备MCAO模型大鼠的经验体会[J]. 中国中医急症,2014,23(12):2216-2219.
[2] 刘宇, 杨娟, 韦婷, 等. 改良冠脉结扎法大鼠心肌缺血模型的制备[J]. 中药药理与临床,2015,1(6):202-205.
[3] 张世田, 庞路路, 唐汉庆, 等. 大鼠心肌缺血模型制备方法的比较及改进浅析[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2017,27(7):98-101.
[4] YEH RW, SIDNEY S, CHANDRA M, et al. Population trends in the incidence and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2155-2165.
[5] 徐叔云, 卞如濂, 陈修. 药理实验方法学[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2002:1052-1053.
[6] KAJSTURA J, LIU Y, BALDINI A, et al. Coronary artery constriction in rats: necrotic and apoptotic myocyte death. Am J Cardiol. 1998;82(5):30-41.
[7] 高金环, 张红, 杨洪军, 等. 冠状动脉结扎模型大鼠制作的经验体会[J]. 中国中医急症,2018,27(12):2242-2244.
[8] SWIRSKI FK, NAHRENDORF M, ETZRODT M, et al. Identification of splenic reservoir monocytes and their deployment to inflammatory sites. Science. 2009;325:612-616.
[9] VAN LINTHOUT S, MITEVA K, TSCHOPE C. Crosstalk between fibroblasts and inflammatory cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2014;102:258-269.
[10] FERTIN M, LEMESLE G, TURKIEH A, et al. Serum MMP-8: a novel indicator of left ventricular remodeling and cardiac outcome in patients after acute myocardial infarction. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e71280.
[11] PFEFFER MA, BRAUNWALD E. Ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction. Experimental observations and clinical implications. Circulation. 1990; 81: 1161-1172.
[12] SUTTON MG, SHARPE N. Left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction: pathophysiology and therapy. Circulation. 2000;101:2981-2988.
[13] VAN ZUYLEN VL, DEN HAAN MC, GEUTSKENS SB, et al. Post-myocardial infarct inflammation and the potential role of cell therapy. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2015;29(1):29-73.
[14] TAKAHASHI T, ANZAI T, KANEKO H, et al. Increased C-reactive protein expression exacerbates left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling after myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;299(6): H1795-H1804.
[15] TANG Y, FUNG E, XU A, et al. C-reactive protein and ageing. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017;44 Suppl 1:9-14.
[16] KLEINBONGARD P, SCHULZ R, HEUSCH G. TNFalpha in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion, remodeling and heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2011;16(1):49-69.
[17] YANG CM, LEE IT, LIN CC, et al. c-Src-dependent MAPKs/AP-1 activation is involved in TNF-alpha-induced matix metalloproteinase-9 expression in rat heart-derived H9c2 cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85(8):1115-1123.
[18] TAKIMOTO E, KASS DA. Role of oxidative stress in cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling. Hypertension. 2007;49:241-248.
[19] TSUTSUI H, KINUGAWA S, MATSUSHIMA S. Oxidative stress and heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;30(6):H2181-2190.
|