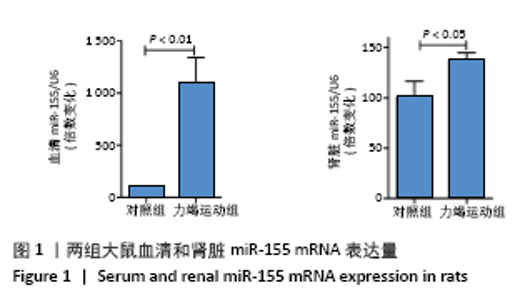
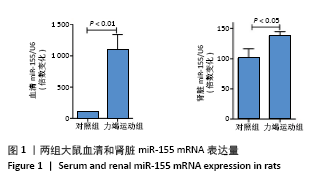
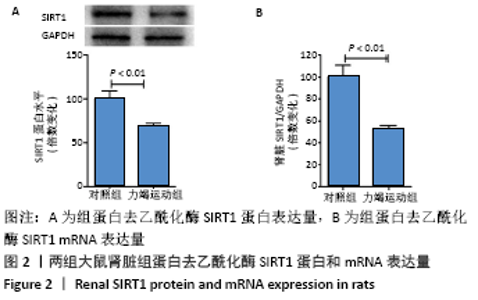
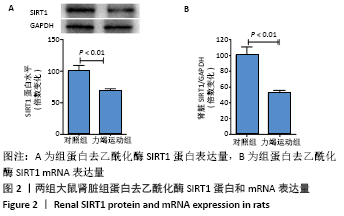
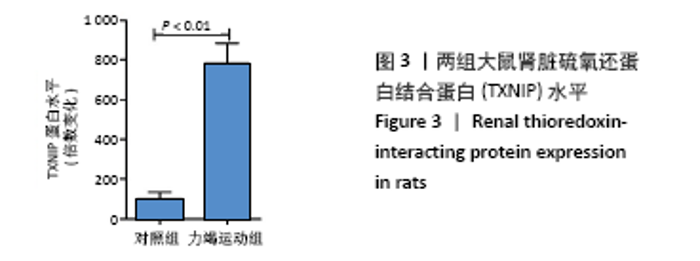
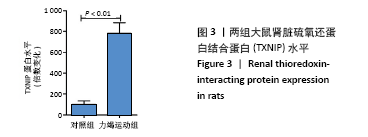
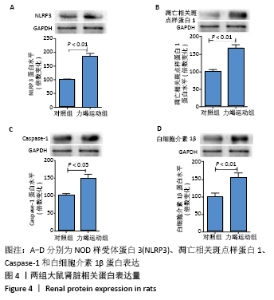
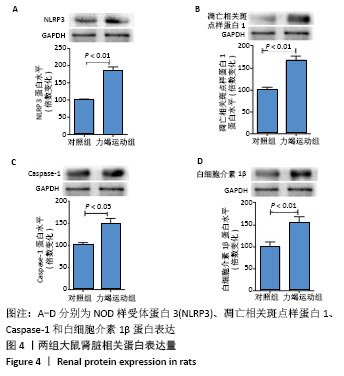
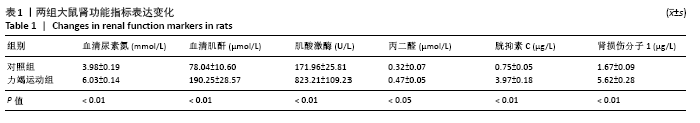
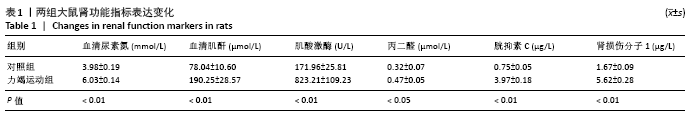
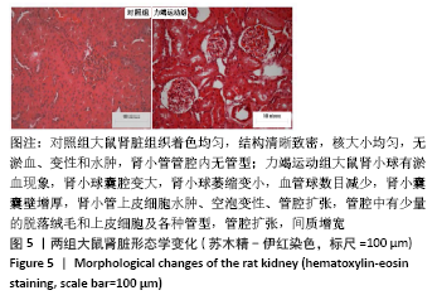
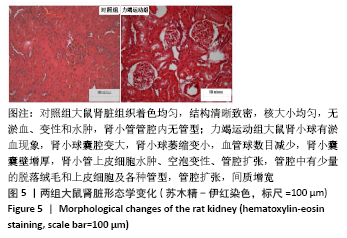
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 190-196.doi: 10.12307/2022.032
Previous Articles Next Articles
A single bout of exhaustive exercise induces renal NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome expression in rats
Geng Yuanwen1, Lin Qinqin1, Li Ruoming1, Tang Shaokai1, Wang Baihui1, Tian Zhenjun2
- 1School of Physical Education, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao 066004, Hebei Province, China; 2School of Physical Education, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi′an 710062, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-18Revised:2021-01-20Accepted:2021-03-16Online:2022-01-18Published:2021-10-27 -
Contact:Lin Qinqin, PhD, Associate professor, School of Physical Education, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao 066004, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Geng Yuanwen, Master, Lecturer, School of Physical Education, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao 066004, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31300978 (to LQQ); the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, No. C2019203537 (to LQQ); Scientific and Technological Project of Colleges and Universities in Hebei Province, No. QN2019068 (to LQQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Geng Yuanwen, Lin Qinqin, Li Ruoming, Tang Shaokai, Wang Baihui, Tian Zhenjun. A single bout of exhaustive exercise induces renal NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome expression in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 190-196.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 陈丽娜,周刚,吴乐,等.力竭运动对大鼠肾脏的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2016,22(7):789-792. [2] 林喜秀,邱继旺,罗自强,等.急性力竭运动模型大鼠鱼腥草素干预后的肾滤过屏障变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(36): 5793-5798. [3] RAO Z, ZHENG L, HUANG H, et al. α-Klotho Expression in Mouse Tissues Following Acute Exhaustive Exercise. Front Physiol. 2019;10:1498. [4] TSCHOPP J, MARTINON F, BURNS K. NALPs: a novel protein family involved in inflammation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(2):95-104. [5] KIM HJ, LEE DW, Ravichandran K, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome knockout mice are protected against ischemic but not cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013;346(3):465-472. [6] SCHRODER K, ZHOU R, TSCHOPP J. The NLRP3 inflammasome: a sensor for metabolic danger? Science. 2010;327(5963):296-300. [7] BAI M, CHEN Y, ZHAO M, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to aldosterone-induced podocyte injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017;312(4):F556-F564. [8] LI H, MIAO W, MA J, et al. Acute Exercise-Induced Mitochondrial Stress Triggers an Inflammatory Response in the Myocardium via NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation with Mitophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016:1987149. [9] 林琴琴,耿元文,田振军.白藜芦醇对一次性力竭运动大鼠心肌NLRP3炎性小体表达的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2018,41(6): 57-62. [10] 焦春利,徐鹏,曹雪滨.运动预适应调控力竭运动大鼠NLRP3炎性体信号通路保护心肌的机制研究[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2016, 28(7):618-623. [11] MAHESH G, BISWAS R. MicroRNA-155: A Master Regulator of Inflammation. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019;39(6):321-330. [12] ZHENG C, ZHANG J, CHEN X, et al. MicroRNA-155 Mediates Obesity-Induced Renal Inflammation and Dysfunction. Inflammation. 2019; 42(3):994-1003. [13] WU H, HUANG T, YING L, et al. MiR-155 is Involved in Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Direct Targeting of FoxO3a and Regulating Renal Tubular Cell Pyroptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(6):1692-1705. [14] WU X, CHANG SC, JIN J, et al. NLRP3 in flammasome mediates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced renal injury implication of the microRNA-155/FOXO3a signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(12): 9404-9415. [15] KONG L, WU H, ZHOU W, et al. Sirtuin 1: A Target for Kidney Diseases. Mol Med. 2015;21:87-97. [16] LIN QQ, GENG YW, JIANG ZW, et al. SIRT1 regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced CD40 expression in renal medullary collecting duct cells by suppressing the TLR4-NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2017;170: 100-107. [17] YANG SY, LIN SL, CHEN YM, et al. Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-kappaB by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 33705. [18] LI Y, YANG X, HE Y, et al. Negative regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome by SIRT1 in vascular endothelial cell. Immunobiology. 2017;222(3):552-561. [19] JIANG L, ZHANG L, KANG K, et al. Resveratrol ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury via NLRP3 inflammasome modulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84: 130-138. [20] WANG Y, ZHENG ZJ, JIA YJ, et al. Role of p53/miR-155-5p/sirt1 loop in renal tubular injury of diabetic kidney disease J Transl Med. 2018;16(1): 146. [21] 谢文杰,周刚,谢金美,等.一次性力竭运动模型大鼠心肌氧化损伤的作用途径[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):247-252. [22] ICHIMURA T, HUNG CC, YANG SA, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1: a tissue and urinary biomarker for nephrotoxicant-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004;286(3): F552-563. [23] HERGET-ROSENTHAL S, MARGGRAF G, HUSING J, et al. Early detection of acute renal failure by serum cystatin C. Kidney Int. 2004;66(3): 1115-1122. [24] WEN Y, LIU YR, TANG TT, et al. mROS-TXNIP axis activates NLRP3 inflammasome to mediate renal injury during ischemic AKI. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018;98:43-53. [25] FERNANDEZ-SANJURJO M, DE GONZALO-CALVO D, FERNANDEZ-GARCIA B, et al. Circulating microRNA as Emerging Biomarkers of Exercise. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2018;46(3):160-171. [26] POLAKOVICOVA M, MUSIL P, LACZO E, et al. Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Exercise Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10): 1553. [27] XU T, LIU Q, YAO J, et al. Circulating microRNAs in response to exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(2):e149-154. [28] BAGGISH AL, HALE A, WEINER RB, et al. Dynamic regulation of circulating microRNA during acute exhaustive exercise and sustained aerobic exercise training. J Physiol. 2011;589(Pt 16):3983-3994. [29] XU T, ZHOU Q, CHE L, et al. Circulating miR-21, miR-378, and miR-940 increase in response to an acute exhaustive exercise in chronic heart failure patients. Oncotarget. 2016;7(11):12414-12425. [30] PASTUSZAK-LEWANDOSKA D, DOMAŃSKA-SENDEROWSKA D, KISZAŁKIEWICZ J, et al. Expression levels of selected cytokines and microRNAs in response to vitamin D supplementation in ultra-marathon runners. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(2):219-228. [31] OGURA S, SHIMOSAWA T. Oxidative stress and organ damages. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2014;16(8):452. [32] SAIKUMAR J, HOFFMANN D, KIM TM, et al. Expression, circulation, and excretion profile of microRNA-21, -155, and -18a following acute kidney injury. Toxicol Sci. 2012;129(2):256-267. [33] LIN X, YOU Y, WANG J, et al. MicroRNA-155 deficiency promotes nephrin acetylation and attenuates renal damage in hyperglycemia-induced nephropathy. Inflammation. 2015;38(2):546-554. [34] KLIMCZAK D, KUCH M, PILECKI T, et al. Plasma microRNA-155-5p is increased among patients with chronic kidney disease and nocturnal hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2017;11(12):831-841. [35] BELTRAMI C, SIMPSON K, JESKY M, et al. Association of Elevated Urinary miR-126, miR-155, and miR-29b with Diabetic Kidney Disease. Am J Pathol. 2018;188(9):1982-1992. [36] 李方,曹建民,王传军,等.白藜芦醇通过调节SIRT1/NF-κB通路减轻力竭训练致大鼠肾的炎症反应[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2019,35(7):773-779. [37] HUANG X, SHI Y, CHEN H, et al. Isoliquiritigenin prevents hyperglycemia-induced renal injuries by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress via SIRT1-dependent mechanism. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(12):1040. [38] CHOU X, DING F, ZHANG X, et al. Sirtuin-1 ameliorates cadmium-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis through XBP-1s deacetylation in human renal tubular epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol. 2019;93(4):965-986. [39] CHEN L, LAN Z. Polydatin attenuates potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation by inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Food Funct. 2017;8(5):1785-1792. [40] PARK JE, LEE H, KIM SY, et al. Lespedeza bicolor Extract Ameliorated Renal Inflammation by Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Associated Hyperinflammation in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(2):148. [41] WU M, LI R, HOU Y, et al. Thioredoxin-interacting protein deficiency ameliorates kidney inflammation and fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction. Lab Invest. 2018;98(9):1211-1224. [42] KUMAR A, MITTAL R. Mapping Txnip: Key connexions in progression of diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol Rep. 2018;70(3):614-622. [43] WU Y, HE F, LI Y, et al. Effects of Shizhifang on NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Renal Tubular Injury in Hyperuricemic Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:7674240. [44] WANG M, ZHAO J, ZHANG N, et al. Astilbin improves potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and kidney injury through regulating oxidative stress and inflammation response in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;83:975-988. [45] XU L, LIN X, GUAN M, et al. Verapamil Attenuated Prediabetic Neuropathy in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice through Inhibiting TXNIP-Mediated Apoptosis and Inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019; 2019:1896041. [46] CHOI SE, KEMPER JK. Regulation of SIRT1 by microRNAs. Mol Cells. 2013;36(5):385-392. [47] LU S, DONG L, JING X, et al. Abnormal lncRNA CCAT1/microRNA-155/SIRT1 axis promoted inflammatory response and apoptosis of tubular epithelial cells in LPS caused acute kidney injury. Mitochondrion. 2020;53:76-90. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Zhang Haobo, Zhao Yunan, Yang Xuejun. Role and therapeutic implications of pyroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1445-1451. |
| [3] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [4] | Li Huo, Wang Peng, Gao Jianming, Jiang Haoran, Lu Xiaobo, Peng Jiang. Relationship between revascularization and internal microstructure changes in osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1323-1328. |
| [5] | Bao Xianguo, Gao Zengxin, Wu Zhanpo, Chen Youmin, Cheng Qinghua, Lu Haitao, Guo Changzheng, Xu Shuai. Correlation between lumbar posterior muscle and local kyphosis in patients with degenerative thoracolumbar kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1418-1423. |
| [6] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [7] | Gu Zhengqiu, Xu Fei, Wei Jia, Zou Yongdi, Wang Xiaolu, Li Yongming. Exploratory study on talk test as a measure of intensity in blood flow restriction training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1154-1159. |
| [8] | Kong Yamin, Yan Juntao, Ma Bingxiang, Li Huawei. Massage vibration intervenes with MyoD expression and proliferation and differentiation of muscle satellite cells in rats with sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1160-1166. |
| [9] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [10] | Li Zhiyi, He Pengcheng, Bian Tianyue, Xiao Yuxia, Gao Lu, Liu Huasheng. Bibliometric and visualized analysis of ferroptosis mechanism research [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1202-1209. |
| [11] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [12] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [13] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [14] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [15] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||