Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (2): 197-204.doi: 10.12307/2022.033
Previous Articles Next Articles
Pharmacological mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
Li Anan1, Jiang Tao2, Zhan Min3, Cai Yuning2, Song Min1, Li Congcong1, Lin Wenzheng2, Zhang Jiayuan1, Liu Wengang2
- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China; 3Nanfang Hospital of Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-11-13Revised:2020-11-17Accepted:2021-01-07Online:2022-01-18Published:2021-10-27 -
Contact:Liu Wengang, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Guangdong Second Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Anan, Master candidate, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Research Project of Guangdong Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 20191021; Guangdong Medical Science and Technology Research Fund, No. A2020071
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Anan, Jiang Tao, Zhan Min, Cai Yuning, Song Min, Li Congcong, Lin Wenzheng, Zhang Jiayuan, Liu Wengang. Pharmacological mechanism of Shenling Baizhu San in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 197-204.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
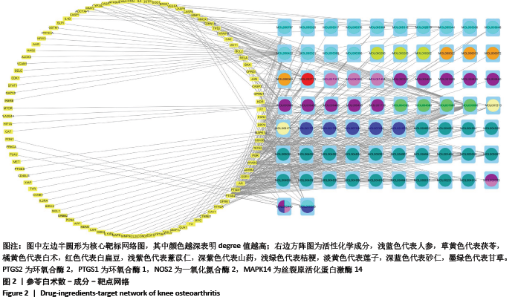
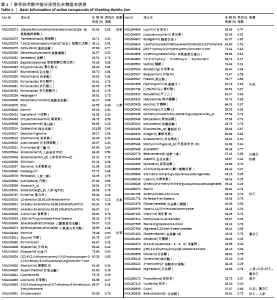
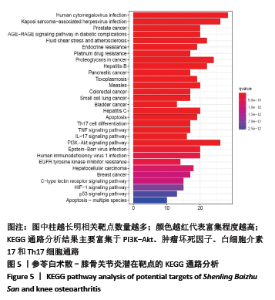
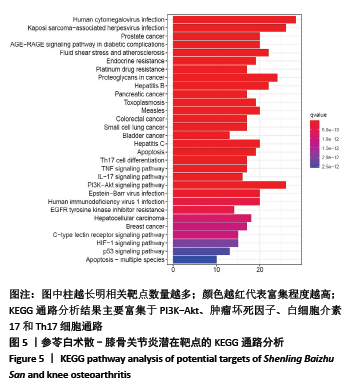
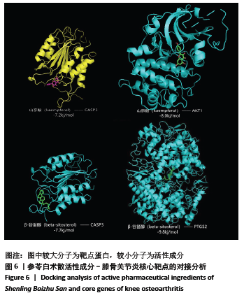
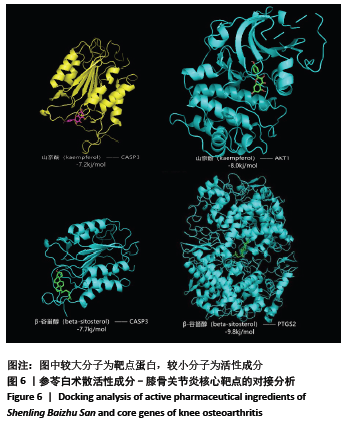
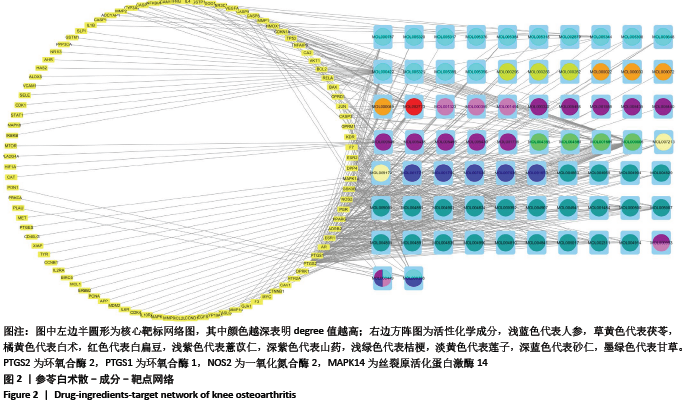
2.3.2 构建成分-靶点网络图 运用Cytoscape 3.7.1软件中Network Analyze插件构建复方化学成分-靶点作用网络,见图2。网络共有167个节点,440条边。左边代表核心靶标,其中颜色越深表明degree值越高。右边代表活性化学成分,不同颜色代表来自不同药物。右边颜色从上至下,浅蓝色代表人参,草黄色代表茯苓,橘黄色代表白术,红色代表白扁豆,浅紫色代表薏苡仁,深紫色代表山药,浅绿色代表桔梗,淡黄色代表莲子,深蓝色代表砂仁,墨绿色代表甘草。每条边代表化合物与靶点的关系。从图2可知,一个化学成分常与多个交集基因靶点对应,且一个交集基因与靶点也同时对应多个化学成分,化学成分又从属于不同的中药,这说明参苓白术散治疗膝骨关节炎是通过多成分、多靶点、多通路起效的,其中木犀草素(luteolin)、山奈酚(kaempferol)和β-谷甾醇(beta-sitosterol)含有较高Degree值,为主要活性成分。"

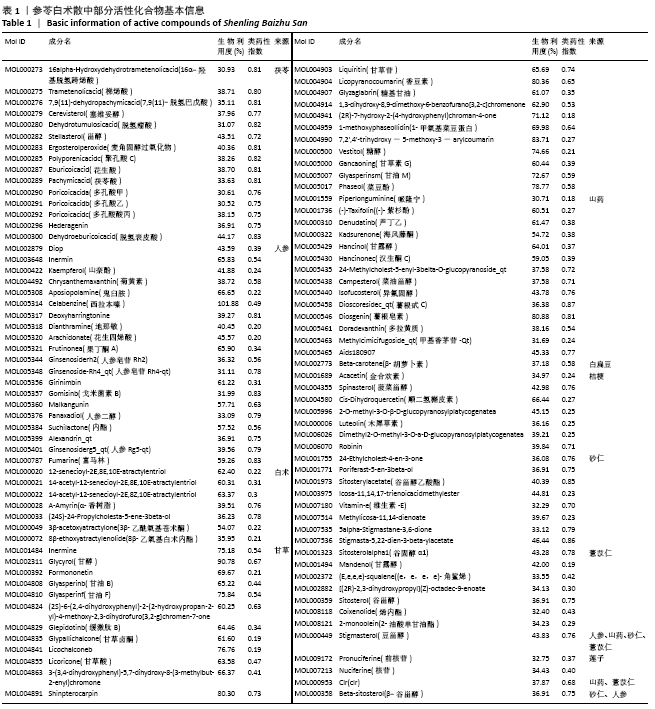
2.4 交集基因PPI网络构建与分析 应用STRING数据库对交集基因初步构建蛋白作用网络,见图3。网络图包括97个节点,3 058条边。节点代表蛋白,边代表蛋白与蛋白之间的作用关系。网络连接程度越高说明蛋白间关系越密切。为进一步筛选核心蛋白,将STRING数据库获得的interaction.tsv文件导入到Cytoscape中的,通过CytoHubba插件对网络进行分析,筛选条件按MCC排列,颜色越深、越靠近中心表明RANK更前,关键性越高。其中 PTGS2,CASP3,AKT1,MAPK1,MAPK8,TP53,BCL2L1,EGFR,VEGFA,JUN在网络中连接程度较高,说明这些靶蛋白是网络中的关键靶点。"

| [1] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387. [2] HüGLE T, GEURTS J. What drives osteoarthritis?-synovial versus subchondral bone pathology. Rheumatology. 2017; 56(9):1461-1471. [3] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715. [4] MA Q, OUYANG Y, MENG F, et al. A review of pharmacological and clinical studies on the application of Shenling Baizhu San in treatment of ulcerative colitis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019;244:112105. [5] 高玲玲,单颖.参苓白术散对感染鼠伤寒沙门菌小鼠的免疫调节作用[J].现代预防医学,2019,46(8):1450-1455. [6] 周波,戴飞跃.参苓白术散对胃癌IV期患者外周血CD4+CD25+ Tregs的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2015,35(5):50-52. [7] LV WJ, LIU C, LI YF, et al. Systems Pharmacology and Microbiome Dissection of Shen Ling Bai Zhu San Reveal Multiscale Treatment Strategy for IBD. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:8194804. [8] 潘玉甄.参苓白术散加减联合非布司他治疗非急性期痛风性关节炎脾虚湿阻证的临床观察[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2020. [9] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13. [10] XUE R, FANG Z, ZHANG M, et al. TCMID: Traditional Chinese Medicine integrative database for herb molecular mechanism analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(Database issue):D1089-D1895. [11] 曾令烽,杨伟毅,梁桂洪,等.岭南中医湿证与慢性病防治创新模式探讨[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(6):2345-2349. [12] FEI J, LIANG B, JIANG C, et al. Luteolin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in rat chondrocytes and attenuates osteoarthritis progression in a rat model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1586-1592. [13] LEE SA, PARK BR, MOON SM, et al. Chondroprotective effect of cynaroside in IL-1β-Induced primary rat chondrocytes and organ explants via NF-κB and MAPK signaling inhibition. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:9358080. [14] XUE J, YE J, XIA Z, et al. Effect of luteolin on apoptosis, MAPK and JNK signaling pathways in guinea pig chondrocyte with osteoarthritis. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2019;65(6):91-95. [15] LI Y, ZHENG D, SHEN D, et al. Protective effects of two safflower derived compounds, kaempferol and hydroxysafflor yellow a, on hyperglycaemic stress-induced podocyte apoptosis via modulating of macrophage M1/M2 polarization. J Immunol Res. 2020;2020:2462039. [16] XIE J, HUANG Z, YU X, et al. Clinical implications of macrophage dysfunction in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:36-44. [17] LEE WS, LEE EG, SUNG MS, et al. Kaempferol inhibits IL-1β-stimulated, RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis via downregulation of MAPKs, c-Fos, and NFATc1. Inflammation. 2014;37(4):1221-1230. [18] XIAO HB, LU XY, LIU ZK, et al. Kaempferol inhibits the production of ROS to modulate OPN-αvβ3 integrin pathway in HUVECs. J Physiol Biochem. 2016;72(2):303-313. [19] BABU S, JAYARAMAN S. An update on β-sitosterol: a potential herbal nutraceutical for diabetic management. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110702. [20] KURUMBAIL RG, KIEFER JR, MARNETT LJ. Cyclooxygenase enzymes: catalysis and inhibition. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11(6):752-760. [21] SHARMA V, BHATIA P, ALAM O, et al. Recent advancement in the discovery and development of COX-2 inhibitors: insight into biological activities and SAR studies (2008-2019). Bioorg Chem. 2019;89:103007. [22] PULJAK L, MARIN A, VRDOLJAK D, et al. Celecoxib for osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;5(5):Cd009865. [23] THORNBERRY NA, LAZEBNIK Y. Caspases: enemies within. Science. 1998;281(5381):1312-1316. [24] ZHAROVA TA, KOGAN EA, MAKAROV VI, et al. Correlation of synovial caspase-3 concentration and the photodynamic effectiveness in osteoarthritis treatment. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020;30: 101669. [25] YASSIN AM, ABUBAKR HO, ABDELGALIL AI, et al. COL2A1 and Caspase-3 as promising biomarkers for osteoarthritis prognosis in an equus asinus model. Biomolecules. 2020;10(3):354. [26] ABDULLAH A, RAVANAN P. Kaempferol mitigates endoplasmic reticulum stress induced cell death by targeting caspase 3/7. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):2189. [27] ZHAO X, WANG T, CAI B, et al. MicroRNA-495 enhances chondrocyte apoptosis, senescence and promotes the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting AKT1. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(4):2232-2244. [28] DONG YH, WANG P, YANG YG, et al. PRMT5 inhibition attenuates cartilage degradation by reducing MAPK and NF-kappaB signaling. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):201. [29] CHU X, YU T, HUANG X, et al. Tomatidine suppresses inflammation in primary articular chondrocytes and attenuates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritic rats. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(13):12799-12811. [30] QIN L, BEIER F. EGFR signaling: friend or foe for cartilage? JBMR Plus. 2019;3(2):e10177. [31] BOLDUC JA, COLLINS JA, LOESER RF. Reactive oxygen species, aging and articular cartilage homeostasis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;132:73-82. [32] KOIKE M. NOJIRI H, OZAWAY, et al. Mechanical overloading causes mitochondrial superoxide and SOD2 imbalance in chondrocytes resulting in cartilage degeneration. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11722. [33] HUANG ZY, STABLER T, PEI FX, et al. Both systemic and local lipopolysaccharide (LPS) burden are associated with knee OA severity and inflammation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(10):1769-1775. [34] JIN J, YU X, HU Z, et al. Isofraxidin targets the TLR4/MD-2 axis to prevent osteoarthritis development. Food Funct. 2018;9(11):5641-5652. [35] ZHONG JT, YU J, WANG HJ, et al. Effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress on the autophagy, apoptosis, and chemotherapy resistance of human breast cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Tumour Biol. 2017;39(5):1010428317697562. [36] DIBBLE CC, CANTLEY LC. Regulation of mTORC1 by PI3K signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25(9):545-555. [37] ROSA SC, RUFINO AT, JUDAS F, et al. Expression and function of the insulin receptor in normal and osteoarthritic human chondrocytes: modulation of anabolic gene expression, glucose transport and GLUT-1 content by insulin. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(6):719-727. [38] CHOI MC, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-κB signaling pathways in osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734. [39] CHISARI E, YAGHMOUR KM, KHAN WS. The effects of TNF-alpha inhibition on cartilage: a systematic review of preclinical studies. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(5):708-718. [40] WEHLING N, PALMER GD, PILAPIL C, et al. Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit chondrogenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells through NF-kappaB-dependent pathways. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(3):801-812. [41] OSSENDORFF R, GRAD S, STODDART MJ, et al. Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation in Osteoarthritic Surroundings: TNFα and Its Inhibition by Adalimumab in a Knee-Specific Bioreactor. Am J Sports Med. 2018; 46(2):431-440. [42] 冯方,刘英,彭毅,等.膝骨关节炎患者关节滑液中IL-17水平与疾病严重程度的相关性[J].西部医学,2020,32(6):845-848. [43] 王迷娜,刘璐,赵洛鹏,等.膝骨关节炎炎性因子及信号通路的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(4):388-392. |
| [1] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [2] | Xiang Xinjian, Liu Fang, Wu Liangliang, Jia Daping, Tao Yue, Zhao Zhengnan, Zhao Yu. High-dose vitamin C promotes the survival of autologous fat transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1242-1246. |
| [3] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [4] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [5] | Zhang Yujie, Yang Jiandong, Cai Jun, Zhu Shoulei, Tian Yuan. Mechanism by which allicin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1080-1084. |
| [6] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [7] | Deng Shuang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Zhang Jianchao, Yuan Lingyan . Effects of exercise preconditioning on myocardial protection and apoptosis in a mouse model of myocardial remodeling due to early stress overload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 717-723. |
| [8] | Zhao Yuwei, Gao Yuting, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin . Mechanism of Ermiao San in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 742-748. |
| [9] | Li Jiajun, Xia Tian, Liu Jiamin, Chen Feng, Chen Haote, Zhuo Yinghong, Wu Weifeng. Molecular mechanism by which icariin regulates osteogenic signaling pathways in the treatment of steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 780-785. |
| [10] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [11] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [12] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| [13] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Li Huanan, Chen Feng, Chai Yuan, Gan Bin, Li Song, Chen Dingpeng. Potential molecular mechanism of Guizhi Shaoyao Zhimu Decoction in the treatment of gouty arthritis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 245-252. |
| [14] | Na Risong, Sun Liang, Zhao Zhenqun, Liang Rong, Wang Xin. Molecular mechanism by which miR-26b regulates fatty acid-binding protein 4-mediated adipocyte differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 260-265. |
| [15] | Cao Wei, Mao Furong, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. N-6 methyladenosine RNA methylation regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 266-270. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||