Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (30): 4889-4895.doi: 10.12307/2022.771
Previous Articles Next Articles
Epimedium in regulating bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and preventing osteoporosis related signaling pathways
Huang Wei1, Dong Panfeng1, Huang Yourong1, Xia Tian2
- 1Department of Orthopedics and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2021-11-04Accepted:2021-12-01Online:2022-10-28Published:2022-03-29 -
Contact:Xia Tian, Doctoral candidate, Associate professor, College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Huang Wei, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760796, 81960803; Natural Science Foundation for the Youth of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2020GXNSFBA159053; Young Teachers' Basic Ability Improvement Project of Guangxi Universities, No. 2019KY0352; Wei Guikang National Medical Master Team Capacity Building, No. {2018} 1; National Famous and Old Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance Studio Construction Project in 2016, No. {2016} 11
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Wei, Dong Panfeng, Huang Yourong, Xia Tian. Epimedium in regulating bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and preventing osteoporosis related signaling pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4889-4895.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
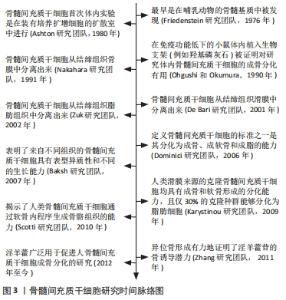
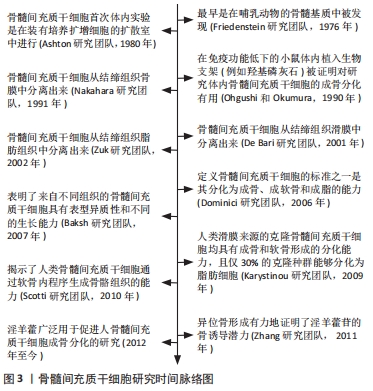
2.1 淫羊藿-骨质疏松症 淫羊藿又被称为仙灵脾、铁打杵,古籍最早发现于《神农本草经》,其具有强筋骨、补命门、祛风湿、壮肾阳等独特功效,临床常用于治疗男子阳痿遗精、小便不禁以及女子不孕等症[8]。作为中国历史悠久的中药淫羊藿,早已在古人的历史长河中临床运用了千年,李时珍在《本草纲目》提到:“其可强腰膝,补精气,强心力”[9]。现代研究表明,淫羊藿主要包括淫羊藿苷、宝藿苷Ⅰ、宝藿苷Ⅱ、淫羊藿次苷Ⅰ、淫羊藿次苷Ⅱ、去甲淫藿素、淫羊藿素、鞣质、挥发油、蜡醇等及其他生物活性成分[10],其中研究最为广泛的是淫羊藿苷,同时现代药理学表明其具有降压(引起周围血管舒张)、降血糖、改善心脑血管、利尿、镇咳祛痰、抗衰老、抗肿瘤以及抗骨质疏松等作用[11]。 近年来随着骨质疏松患者不断增加,研究最多的则是淫羊藿用于防治骨质疏松[12]。淫羊藿提取物淫羊藿总黄酮与其他黄酮单体成分具有增加骨密度、诱导骨形成、保持骨代谢平衡等作用[13]。研究表明,淫羊藿总黄酮不仅能够刺激成骨细胞分化,而且可以加快成骨细胞的成熟速度[14],此外还能抑制破骨细胞分化,通过加快成骨的速度来有效防治骨质疏松的发生,从而发挥抗骨质疏松的作用。姜涛等[15]在大鼠实验中发现,淫羊藿苷能够促进成骨细胞的分化,同时也能提高大鼠动物骨组织模型中ATG13及FIP200等不同蛋白的表达水平,从而起到治疗骨质疏松的作用。QIAN等[16]的结果表明,淫羊藿苷能够通过p53等信号通路调控PEDF,NPAT和HSP7等蛋白的表达,进一步诱导成骨细胞的分化。SUN等[17]研究表明,淫羊藿苷能够通过雌激素受体上调成骨细胞OPG/RANKL的表达,来促使成骨细胞的分化,进而防治或延缓骨质疏松发病。除以上研究之外,还有大量的细胞、动物实验已证明淫羊藿及其提取物可以促进成骨细胞的增殖分化,增强骨细胞成熟的速度,进而有效防治骨质疏松的发生。此外还有研究发现,中药淫羊藿还与骨髓间充质干细胞有着密切联系,其可通过调控骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖来促进成骨分化,进而起到治疗骨质疏松的作用。 2.2 骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化防治骨质疏松 骨髓间充质干细胞最早是在哺乳动物的骨髓基质中被发现,是一种来源于中胚层的成体干细胞,它在外界的诱导下具有分化为骨细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞、成肌细胞和神经细胞等各种细胞的能力,同时也能够定向分化为成骨细胞并在骨代谢平衡维持中起着重要的调控作用[18],若骨髓间充质干细胞分化失衡则会引发骨质疏松的发生。正常情况下,骨髓间充质干细胞需要经历从骨前体细胞、成骨细胞等不同分化最终演变为骨细胞的过程,然而随着年龄的增长,女性体内雌激素的减少,导致破骨细胞分化因子增加、骨代谢失衡以及骨髓间充质干细胞分化降低,进一步引起骨钙结合能力减弱,破骨细胞调控骨吸收作用增强,进而造成骨质丢失速度大大加快,最终加重骨质疏松症发生的风 险[19]。骨髓间充质干细胞研究的时间脉络图,见图3。"
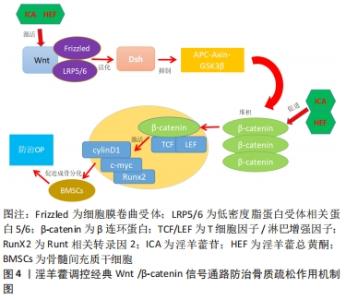
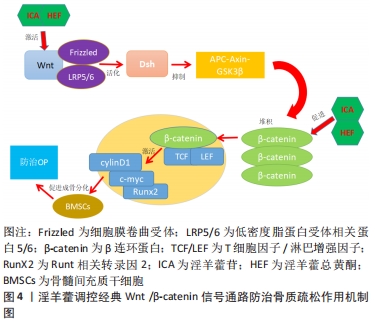
最近的研究发现,淫羊藿能够促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞增殖和分化,进而有效地防治骨质疏松[20]。XU等[21]的研究发现,淫羊藿苷通过miR-23a介导的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活,进而上调碱性磷酸酶(Alkaline phosphatase,ALP)活性及骨唾液酸蛋白Ⅱ(Bone sialoprotein,BSP-II)和Runt相关转录因子2(Runt-related transcription factor 2,RunX2)的表达,最终诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨分化。JIAO等[22]的研究表明,淫羊藿可能通过MAPK信号通路来促进成骨和软骨分化,从而诱导肌动蛋白应激纤维的形成,进一步促进骨髓间充质干细胞在体内和体外的迁移。李智奎等[23]在淫羊藿苷对SD大鼠的实验中发现,淫羊藿苷可通过诱导激活经典Wnt信号通路来提高Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶和骨桥蛋白(osteopontin,OPN)等成骨分化相关基因的表达,从而促使大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。综上所述,传统中药淫羊藿可能通过影响Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶和骨桥蛋白等相关因子的变化、激活相关信号通路等方面来促使骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,起到治疗骨质疏松的作用,然而目前骨质疏松的发病机制还不明确。因此,下文将对相关信号通路进行阐述,归纳近年来中药淫羊藿调控骨髓间充质干细胞防治骨质疏松的分子机制,为补肾中药淫羊藿的临床应用提供依据。 2.3 淫羊藿调控相关信号通路影响骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化 2.3.1 淫羊藿调控经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路 经典Wnt/β-catenin信号是一种高度保守的通路,是目前研究最为广泛的一条经典信号通路。近年来,经典Wnt/β-catenin信号异常激活在骨性疾病中的作用越来越突出,特别是在骨质疏松症[24]。在经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中,Wnt蛋白首先与细胞膜表面的卷曲蛋白受体(Frizzled)以及低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5/6(low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein5/6,LRP5/6)互相结合形成复合体,促进Wnt信号通路的激活并将信号传导至细胞内,接下来活化后的Dsh 抑制APC-Axin-GSK3β复合体,使细胞内β-catenin大量堆积,然后伴随着游离的β-catenin转入至胞核内,接下来与T细胞因子/淋巴增强因子结合形成复合体,以达到激活下游靶基因c-myc、cylinD1等转录因子,发挥促进骨细胞的发育并防止细胞凋亡的调控作用[25]。除了经典信号通路之外,还有部分Wnt蛋白可通过其他非经典途径激活,例如Wnt/Ca2+途径、Wnt/平面细胞极性途径及Wnt/蛋白激酶A途径等。经典Wnt/β-catenin信号是调控骨形成和骨吸收重要的通路,随着人们对淫羊藿的不断深入研究发现[26],淫羊藿可以通过激活经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中 β-catenin蛋白的表达来诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,达到防治骨质疏松的目的,见图4。"
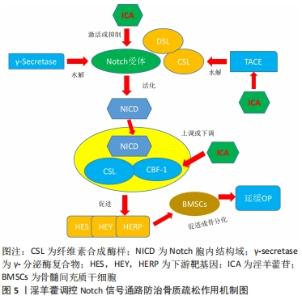
GAO等[27]的研究发现,淫羊藿苷通过激活wnt/β-catenin信号通路来促进β-catenin、c-myc的上调,进而诱导骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、成骨分化,从而提高骨髓间充质干细胞在骨质疏松中的治疗作用。ZHANG等[28]实验表明,淫羊藿总黄酮可能通过刺激Wnt/β-catenin信号通路来提高β-catenin和CyclinD1 mRNA的表达,从而发挥促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用,这可能是防治骨质疏松的潜在选择。XU等[29]实验发现,淫羊藿总黄酮能够使Wnt/β-catenin信号通路活化,从而增加碱性磷酸酶和早期成骨细胞分化因子如Runt相关转录因2、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和骨钙素的表达水平,同时降低脂质体增殖物激活受体γ2 (peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors-γ,PPARγ-2)和CCAAT增强子结合蛋白α(C/EBPα)的表达水平,进一步调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化与成脂分化的平衡,可能是其治疗绝经后骨质疏松的重要途径之一。总之,淫羊藿促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化主要是通过对 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的调控,主要与 β-catenin蛋白、c-myc及CyclinD1因子等有关。 2.3.2 淫羊藿调控Notch信号通路的 Notch是一条广泛存在于脊柱与非脊柱动物组织细胞的信号通路,并具有高度保守性,通过介导细胞间信号在细胞增殖、分化和凋亡的过程中发挥至关重要的调控作用[30]。在真核哺乳动物中有Notch4,Notch3,Notch2,Notch 1等4种受体和Jagged1,Jagged2,DLL1,DLL3,DLL4等5种配体;另外Notch信号通路主要是以Notch受体及其配体(CSL与DSL蛋白)、Notch的调节蛋白和其他调节分子等为主。由于该信号通路的激活不需要胞内第二信使的参与,因此当Notch受体的胞外部分与配体相互结合后,经TACE、γ-分泌酶水解的作用下,引起Notch受体胞内区域(NICD)活化,并将信号传至细胞核内与CSL/CBF-1蛋白互相结合,从而与转录因子特异性结合后,最终促进HES(hairy/enhancer of split)家族、HEY(hairy/enhancer of split with YRPW motif familymembers)家族、HERP家族等相关基因的表达[31-32]。研究显示Notch信号通路在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中发挥着至关重要的作用[33],见图5。"
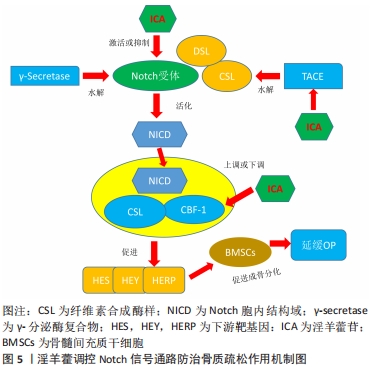
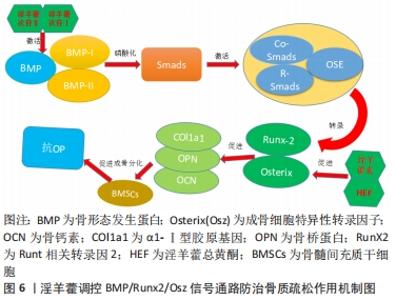
BIAN等[34]采用皮质酮和去卵巢术诱导大鼠骨质疏松实验发现,淫羊藿苷通过调节Delta(DLL1)和TACE(ADAM 17)表达,激活Notch信号通路,进一步促进去卵巢模型大鼠骨钙素、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、矮小相关转录因子2的分泌增加,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,从而在骨质疏松中发挥着重要的调控作用。邓宇等[35]的实验表明,淫羊藿苷能够通过上调HES、Runt相关转录因2 mRNA表达以及增加Jagged-1,Notch1,CBF-1等蛋白表达,来进一步激活Notch信号通路,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,进而改善骨质疏松的发生。徐娅等[36]的研究显示,淫羊藿苷能够通过阻断Notch信号通路,从而降低通路中关键蛋白Notch1、CBF1的表达,促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化,发挥延缓骨质疏松作用。综上所述,淫羊藿能够通过Notch信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化来发挥抗骨质疏松的作用,其主要与Notch通路具有活化或抑制的双重作用有关,通过激活或抑制来调控Jagged-1、Notch1及CBF-1等相关因子,促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化,从而发挥抗骨质疏松的作用。尽管目前已有细胞及动物实验来表明淫羊藿与骨质疏松的通路机制有着密切的联系,但仍需进一步深入探讨信号通路中不同蛋白因子的相互作用机制,才有望更加明确其信号通路的作用机制,为临床应用打下坚实的基础。 2.3.3 淫羊藿调控骨形态发生蛋白/Runx2/Osz信号通路 骨形态发生蛋白/Runx2/Osz信号是一条参与调控成骨细胞分化的重要通路,并且在骨代谢、形成及修复过程中发挥着关键作用。骨形态发生蛋白是转化生长因子β超家族成员,并且是骨生长的启动因子,具有促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成软骨、成骨、成牙本质等细胞分化的能力[37];Runt相关转录因2能够促进成骨细胞向成熟成骨细胞的转变,是成骨细胞中的关键转录、调节因子[38];而成骨细胞特异性转录因子(Osterix,Osx)信号可调控成骨细胞功能蛋白的表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨转化,是Runt相关转录因2的下游关键性转录因子[39]。在骨形态发生蛋白/Runx2/Osz信号通路中,首先骨形态发生蛋白可与细胞膜表面的异二聚体受体(骨形态发生蛋白Ⅰ,Ⅱ)结合,进而磷酸化使Smads蛋白激活,接下来将Co-Smads、R-Smads蛋白与细胞核内OSE序列(成骨细胞特异性顺式作用元件)相结合,从而诱导Runt相关转录因2及其下游Osx的转录,进一步达到促进骨桥蛋白、Ⅰ型胶原基因和骨桥素等多种成骨细胞标志物的转录和表达,促进膜内和软骨内骨化成骨,从而起到抗骨质疏松的作用[40-41],见图6。"
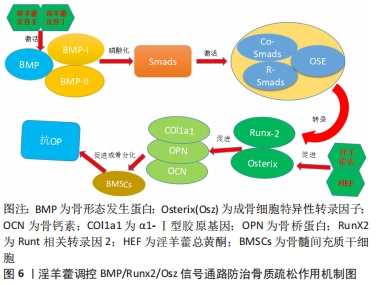
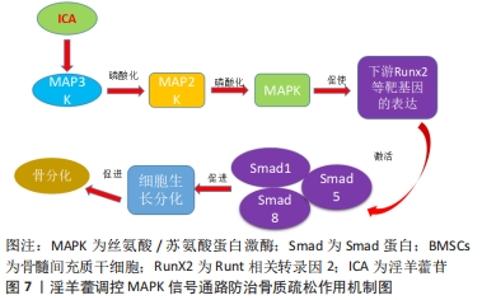
訾慧等[42]在其实验中发现,淫羊藿素可能通过促进骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白9蛋白,进而激活骨形态发生蛋白/Smads/Runx2/Osx信号通路,进一步提高对骨形态发生蛋白/Runx2/Osx信号通路下游相关基因成骨细胞特异性转录因子、Runt相关转录因2的调控,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨转化。LIANG等[43]在淫羊藿总黄酮的实验发现,与对照组相比,20 mg/L淫羊藿总黄酮通过激活骨形态发生蛋白2/Runx 2/Osx信号通路,促使Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素、骨桥蛋白表达增加来增加碱性磷酸酶活性和钙结节密度,进而促进骨髓间充质干细胞定向成骨分化,加快骨形成,有效延缓骨质疏松的进一步发展。研究报道,淫羊藿次苷Ⅰ能通过激活骨形态发生蛋白/Runx2/Osx信号通路,促进骨髓间充质干细胞定向成骨转化[44],同时淫羊藿次苷Ⅰ代谢产物:淫羊藿次苷Ⅱ也能够促进对骨形态发生蛋白/Runx2/Osx信号通路下游基因的调控,从而进一步促进骨髓间充质干细胞定向成骨分化,这说明淫羊藿提取物淫羊藿次苷Ⅰ、Ⅱ均能通过 骨形态发生蛋白2/RunX2/Osx信号通路促使骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。总之,淫羊藿诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化主要是通过对骨形态发生蛋白/Runx2/Osx通路的调控,主要通过激活骨形态发生蛋白、Runt相关转录因2、成骨细胞特异性转录因子等上、下靶基因来促进骨钙素、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨桥蛋白等成骨基因的表达,进而促使骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。目前,对骨形态发生蛋白/Smads/Runx2/Osx信号通路在骨质疏松中作用机制认识尚浅,与其他不同信号通路之间的相互作用还有待深入研究,因此在今后研究中应深入探索 骨形态发生蛋白/Smads/Runx2/Osx信号通路在骨质疏松中的作用机制,为骨质疏松的治疗提供新的思路。 2.3.4 淫羊藿调控MAPK信号通路 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinases,MAPKs)是一条广泛存在于真核细胞体内的信号通路,并且是细胞表面传导至细胞核内的重要载体。其主要是由细胞外信号调节激酶1/2(extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2,ERK1/2)、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)和p38MAPK3种激酶所构成,其中ERK信号是最为经典的一条通路,主要调节细胞起始增殖和分化,并在成骨细胞中发挥重要的作用[45];而p38MAPK通路目前主要有p38α/β/γ/δ种亚族,调控p38MAPK可促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[46];另外JNK信号通路对成骨细胞的活性起着关键作用[47]。在受到外界刺激时,MAPKs信号也是通过三级酶促级联反应激活转录因子,MAPKK激酶(MAP3K)首先被激活,进而将MAPK激酶(MAP2K)磷酸化,接下来被磷酸化的MAP2K使得 MAPK磷酸化激活,继而促进Runt相关转录因2等成骨转录因子的表达,并同时激活 Smad1/5/8蛋白,然后将细胞外信号因子传至细胞内,从而促使细胞的分化,最终起到促进骨分化的作用[48-49]。据报道,MAPK信号通路在淫羊藿苷的刺激下将促使骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[50],从而起到改善骨质疏松的作用,见图7。"
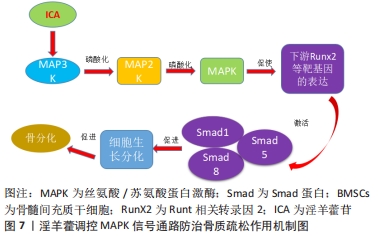

QIN等[51]的实验结果表明,淫羊藿苷通过激活ERK和p38MAPK信号通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖,进而导致其下游转录因子ELK1和c-Myc的上调,为治疗骨质疏松提供了新的临床思路。WU等[52]的研究发现,淫羊藿苷可通过激活MAPK通路,磷酸化细胞外信号调节激酶、p38激酶和c-Jun氨基末端激酶,进而明显增强碱性磷酸酶活性、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨钙素和骨桥蛋白基因表达,发挥调控骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化的作用,最终达到治疗骨质疏松的目的。MAO等[53]的实验表明,淫羊藿提取物淫羊藿苷可通过抑制MAPK信号通路中ERK的表达和激活p38的表达,进而促进间充质干细胞C3H10T1/2向成骨细胞的分化,以达到改善骨质疏松的作用。总之,淫羊藿介导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化与通过对MAPK通路的调节是密不可分的,主要与ERK,p38MAPK,ELK1,c-Myc,JNK调控因子等有关。 2.3.5 淫羊藿调控OPG/RANK/RANKL信号通路 骨保护素(osteoprotegerin,OPG)是OPG/RANK/RANKL信号通路的上游因子,它可以通过与破骨细胞膜表面的RANK相竞争,进而阻断RANK与RANKL结合,进一步阻止信号传导过程,从而抑制骨吸收[54]。 OPG,RANK和RANKL共同构成了OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路,并在骨重建中发挥着至关重要的作用[55-56]。OPG/RANK/RANKL信号通路可能与以下几条通路有着密切的联系[57-58]:①核转录因子κB信号通路:首先RANK与转化生长因子受体相关因子6相结合,进一步激活核转录因子κB诱导激酶,接下来让核转录因子κB复合物从细胞浆进入细胞核内,促进核内c-Fox表达增加,并与活化的T细胞核因子结合,从而促进骨钙素成熟分化;②AKT信号通路:最初RANK与转化生长因子受体相关因子6结合,促使磷脂酰肌醇活化,进一步诱导激活核转录因子κB信号通路,从而加速破骨细胞的分化;③JNK信号通路:是MAPK的主要通路之一,RANK开始与转化生长因子受体相关因子6相结合,激活ERK和JNK,进一步刺激JNK信号通路激活,并促进c-Jun/Fos激活蛋白1活化,然后使c-Jun磷酸化,同时提高了c-Fox表达,促进破骨前体细胞的分化;④钙调磷酸酶/活化T细胞核因子(CN/NFATc1)通路:其通路被活化后,促进破骨细胞相关基因的表达。因此,若能充分了解OPG-RANK-RANKL信号通路,今后将对防治骨质疏松具有重要作用。 骨髓间充质干细胞和成骨细胞可以分泌骨保护素,保持RANKL/OPG稳定,进而使得成骨细胞促进骨形成与破骨细胞调控骨吸收保持在稳态水平,从而维持骨代谢的平衡。吴峻等[59]的动物实验表明,淫羊藿苷能通过上调骨组织骨保护素mRNA表达并下调RANKL及RANK mRNA表达,增加去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨密度和骨矿含量,改善碱性磷酸酶及钙水平,从而抑制骨细胞及成骨细胞凋亡,以达到维持骨形成与骨吸收的稳定。吴祖锋等[60]研究发现,淫羊藿苷可明显上调大鼠骨保护素的蛋白水平,同时并下调RANKL/RANK的表达,从而进一步抑制破骨细胞的分化,达到治疗骨质疏松症的目的。马小妮等[61]实验发现,淫羊藿苷可以通过提高骨保护素及OPG/RANKL的比值,降低破骨细胞的活性,进而抑制骨吸收,起到防治抗骨质疏松的作用。综上所述,淫羊藿主要通过影响骨保护素、RANK及RANKL等相关因子,促进骨形成与骨吸收保持在稳态水平,因此在今后研究中应深入研究OPG-RANK-RANKL信号通路在骨质疏松中的作用,为骨质疏松的治疗提供新的思路。"

| [1] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutics for osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7623. [2] SOTORNIK I. Osteoporóza-epidemiologie a patogeneze [Osteoporosis-epidemiology and pathogenesis]. Vnitr Lek. 2016;62 Suppl 6:84-87. [3] LIU W, YANG LH, KONG XC, et al. Meta-analysis of osteoporosis: fracture risks, medication and treatment. Minerva Med. 2015;106(4):203-214. [4] COTTS KG, CIFU AS. Treatment of Osteoporosis. JAMA. 2018;319(10):1040-1041. [5] 赵金龙,曾令烽,梁桂洪,等.基于信号通路的中药有效成分治疗骨质疏松机制研究进展[J].中草药,2020,51(23):6084-6094. [6] 项国梁,陈跃平,卓映宏.淫羊藿苷调控骨髓间充质干细胞相关分化机制及应用研究进展[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2020,40(8):1019-1024. [7] XIAO YP, ZENG J, JIAO LN, et al. Review for treatment effect and signaling pathway regulation of kidney-tonifying traditional Chinese medicine on osteoporosis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2018;43(1):21-30. [8] 华臻,杨俊锋,潘娅岚,等.补肾中药促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(9):3222-3226. [9] 李建国,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.中药淫羊藿治疗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(3):389-393. [10] ZHAI YK, GUO X, PAN YL, et al. A systematic review of the efficacy and pharmacological profile of Herba Epimedii in osteoporosis therapy. Pharmazie. 2013;68(9):713-722. [11] 曾华婷,郭健,陈彦.淫羊藿素药理作用及其新型给药系统的研究进展[J].中草药,2020,51(20):5372-5380. [12] WANG L, LI Y, GUO Y, et al. Herba epimedii: an ancient chinese herbal medicine in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(3): 328-349. [13] 陈克明.淫羊藿总黄酮的抗骨质疏松作用机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2017, 32(12):5485-5489. [14] 王洁,王萧枫.淫羊藿总黄酮的抗骨质疏松作用及其对调控成骨细胞分化及骨形成关键信号通路的影响[J].中医正骨,2017,29(1):45-48. [15] 姜涛,凌翠敏,陈庆真,等.淫羊藿苷通过提高自噬促进成骨细胞分化防治骨质疏松[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(17):2643-2649. [16] QIAN W, SU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Secretome analysis of rat osteoblasts during icariin treatment induced osteogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(5):6515-6525. [17] SUN LJ, LI C, WEN XH, et al. Icariin stimulates hFOB 1.19 osteoblast proliferation and differentiation via OPG/RANKL mediated by the estrogen receptor. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(1):168-175. [18] WANG C, MENG H, WANG X, et al. Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoblasts and adipocytes and its role in treatment of osteoporosis. Med Sci Monit. 2016;22:226-233. [19] HIKITA A, YANA I, WAKEYAMA H, et al. Negative regulation of osteoclastogenesis by ectodomain shedding of receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(48):36846-36855. [20] YANG A, YU C, LU Q, et al. Mechanism of action of icariin in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:5747298. [21] XU Y, JIANG Y, JIA B, et al. Icariin stimulates osteogenesis and suppresses adipogenesis of human bone mesenchymal stem cells via miR-23a-mediated activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2021;85: 153485. [22] JIAO F, TANG W, HUANG H, et al. Icariin promotes the migration of BMSCs in vitro and in vivo via the MAPK signaling pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018: 2562105. [23] 李智奎,孔俊博,赵王林.淫羊藿苷调控Wnt/β-catenin信号通路干预大鼠MSCs成脂成骨双向分化实验研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(24):2985-2990. [24] MAEDA K, KOBAYASHI Y, KOIDE M, et al. The regulation of bone metabolism and disorders by wnt signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5525. [25] 吴铭,张岩.调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路及相关因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(1):116-122. [26] JING H, SU X, GAO B, et al. Epigenetic inhibition of Wnt pathway suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs during osteoporosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018; 9(2):176. [27] GAO J, XIANG S, WEI X, et al. Icariin promotes the osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through regulating sclerostin and activating the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6666836. [28] ZHANG JF, LI G, CHAN CY, et al. Flavonoids of Herba Epimedii regulate osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through BMP and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010;314(1):70-74. [29] XU YX, WU CL, WU Y, et al. Epimedium-derived flavonoids modulate the balance between osteogenic differentiation and adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells of ovariectomized rats via Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway activation. Chin J Integr Med. 2012;18(12):909-917. [30] PENTON AL, LEONARD LD, SPINNER NB. Notch signaling in human development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012;23(4):450-457. [31] Xu Y, Li L, Tang Y, et al. Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation by suppressing Notch signaling. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;865:172794. [32] MAJIDINIA M, SADEGHPOUR A, YOUSEFI B. The roles of signaling pathways in bone repair and regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(4):2937-2948. [33] FAN JZ, YANG L, MENG GL, et al. Estrogen improves the proliferation and differentiation of hBMSCs derived from postmenopausal osteoporosis through notch signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;392(1-2):85-93. [34] BIAN Q, HUANG JH, LIU SF, et al. Different molecular targets of Icariin on bMSCs in CORT and OVX -rats. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012;4:1224-1236. [35] 邓宇,陈廖斌.淫羊藿苷通过激活Notch信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].中医学报,2017,32(12):2393-2398, 2403. [36] 徐娅,王攀攀,许青青.淫羊藿苷在促大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化过程中对Notch信号通路Notch1、CBF1蛋白表达的影响[A].中国中西医结合学会虚证与老年医学专业委员会、暨南大学.第十三次全国中西医结合虚证与老年医学学术研讨会论文集[C].中国中西医结合学会虚证与老年医学专业委员会、暨南大学:中国中西医结合学会,2013:9. [37] KIM HK, LEE JS, KIM JH, et al. Bone-forming peptide-2 derived from BMP-7 enhances osteoblast differentiation from multipotent bone marrow stromal cells and bone formation. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(5):e328. [38] GOMATHI K, AKSHAYA N, SRINAATH N, et al. Regulation of Runx2 by post-translational modifications in osteoblast differentiation. Life Sci. 2020;245: 117389. [39] LONG F, ORNITZ DM. Development of the endochondral skeleton. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(1):a008334. [40] MA HP, MA XN, GE BF, et al. Icariin attenuates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in osteoblasts and preserves their osteogenic differentiation potential in vitro. Cell Prolif. 2014;47(6):527-539. [41] 梁广胜,陈伟才,殷嫦嫦,等.淫羊藿总黄酮对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程BMP-2/RunX2/Osx通路的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2016, 36(5):614-618. [42] 訾慧,郑洪新,蒋宁.淫羊藿素通过BMP/Runx2/Osx信号通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(7):212-215, 270. [43] LIANG GS, CHEN WC, YIN CC, et al. Effect of total ravonoids of herba epimedium on BMP-2/RunX2/Osx signaling pathway during osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2016;36(5):614-618. [44] 訾慧,范颖,蒋宁.淫羊藿次苷Ⅰ及淫羊藿次苷Ⅱ通过BMP/Runx2/Osx信号通路促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(5):690-695. [45] LIU Y, WANG X, CHANG H, et al. Mongolian Medicine echinops prevented postmenopausal osteoporosis and induced ER/AKT/ERK pathway in BMSCs. Biosci Trends. 2018;12(3):275-281. [46] ZHANG X, LI H, LIN C, et al. Synergetic topography and chemistry cues guiding osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells through ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(2):418-430. [47] ZHAO P, XIAO L, PENG J, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve osteoporosis through promoting osteoblast proliferation via MAPK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(12):3962-3970. [48] 张玲莉,雷乐,吴伟.MAPK信号通路在骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化中的作用[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2021,14(1):75-81. [49] 周陈晨,吴祖平,邹淑娟.信号通路调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2020,51(6):777-782. [50] YAO X, JING X, GUO J, et al. Icariin protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against iron overload induced dysfunction through mitochondrial fusion and fission, PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:163. [51] QIN S, ZHOU W, LIU S, et al. Icariin stimulates the proliferation of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells via ERK and p38 MAPK signaling. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(5):7125-7133. [52] WU Y, XIA L, ZHOU Y, et al. Icariin induces osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells in a MAPK-dependent manner. Cell Prolif. 2015;48(3): 375-384. [53] MAO XY, BIAN Q, SHEN ZY, et al. Analysis of the osteogenetic effects exerted on mesenchymal stem cell strain C3H10T1/2 by icariin via MAPK signaling pathway in vitro. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012;10(11):1272-1278. [54] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):19-26. [55] Ono T, Nakashima T. Recent advances in osteoclast biology. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149(4):325-341. [56] HE XF, ZHANG L, ZHANGg CH, et al. Berberine alleviates oxidative stress in rats with osteoporosis through receptor activator of NF-kB/receptor activator of NF-kB ligand/osteoprotegerin (RANK/RANKL/OPG) pathway. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2017;17(4):295-301. [57] ZHANG S, WANG X, LI G, et al. Osteoclast regulation of osteoblasts via RANK RANKL reverse signal transduction in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):3994-4000. [58] LIU W, ZHANG X. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin system in bone and other tissues (review). Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(5):3212-3218. [59] 吴峻.淫羊藿苷对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨细胞凋亡及骨组织OPG、RANKL mRNA表达影响[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(2):19-22. [60] 吴祖锋,袁垒,吴风晴,等.淫羊藿苷对骨质疏松症模型大鼠OPG/RANKL/RANK轴系统影响的实验研究[J].甘肃中医药大学学报,2016,33(3):4-7. [61] 马小妮,葛宝丰,陈克明,等.淫羊藿苷通过OPG/RANKL信号途径调节骨吸收的机理研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(1):1-5. |
| [1] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [2] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [5] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [6] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [7] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [8] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [9] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [10] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [11] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [12] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [13] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [14] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [15] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||