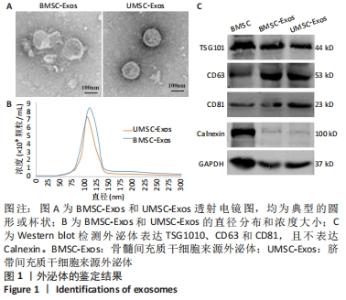
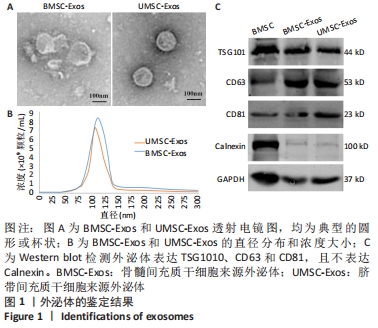
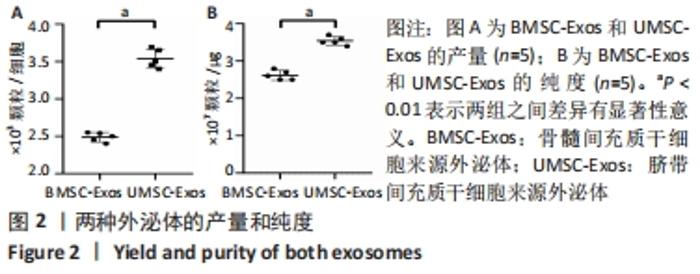
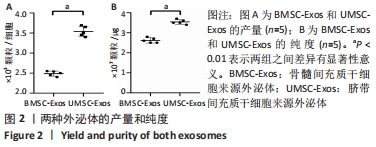
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (25): 3980-3985.doi: 10.12307/2022.402
Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparison of effects of exosomes secreted by different mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis
Wang Xianfeng, Ou Xin, Deng Biyong
- Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-13Accepted:2021-03-12Online:2022-09-08Published:2022-01-25 -
Contact:Deng Biyong, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Xianfeng, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Guizhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guiyang 550000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Plan Project of Guizhou Province, No. [2017]1093 (to DBY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Xianfeng, Ou Xin, Deng Biyong. Comparison of effects of exosomes secreted by different mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3980-3985.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
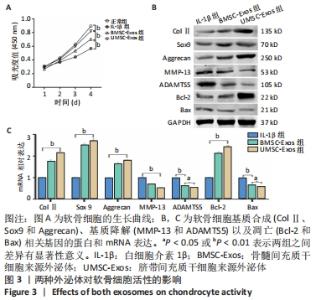
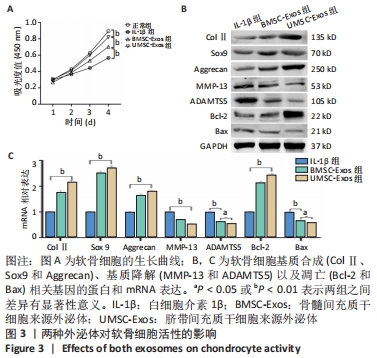
2.3 外泌体对软骨细胞活性的影响 通过白细胞介素1β预处理模拟骨关节炎环境,发现软骨细胞的增殖活性明显下降(P < 0.01);在加入外泌体共培养后,软骨细胞的增殖活性得到恢复,UMSC-Exos组的恢复作用强于BMSC-Exos组(P < 0.01),见图3A。采用Western blot实验检测了与软骨细胞基质合成(ColⅡ、Sox9和Aggrecan)、基质降解(MMP-13和ADAMTS5)以及凋亡(Bcl-2和Bax)相关基因的蛋白表达,发现软骨细胞与外泌体共培养后其基质合成增加、分解降低并且凋亡活性被抑制,且UMSC-Exos组生物活性强于BMSC-Exos组,见图3B;实时荧光定量PCR结果进一步证实了Western blot的结果,见图3C。"
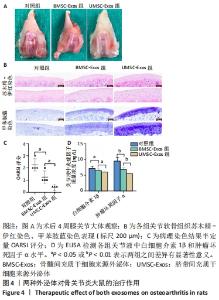
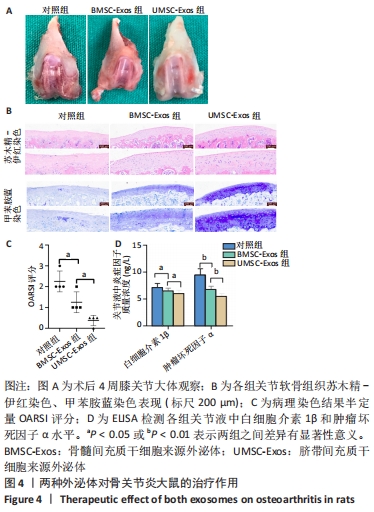
2.4 外泌体对骨关节炎大鼠的治疗作用 12只SD大鼠均进入结果分析。如图4A所示,大体观察可见对照组关节软骨表面粗糙、色泽变暗,软骨细胞纤维化,软骨下骨质暴露,出现严重的骨关节炎表现;BMSC-Exos组骨关节炎症状较对照组有所改善,部分关节面出现骨关节炎特征表现;UMSC-Exos组大体观最接近正常软骨,大部分关节表面未见明显破坏,仅有小部分软骨菲薄。 如图4B所示,苏木精-伊红染色可见对照组软骨细胞排列紊乱,成簇分布,潮线漂移中断;而外泌体组软骨细胞排列整齐,细胞分布均匀,潮线光滑平整,但BMSC-Exos组的软骨表面偶见不规则裂隙且细胞数小于UMSC-Exos组。甲苯胺蓝染色可见对照组染色呈阴性,表明软骨细胞结构改变伴随软骨特异性蛋白多糖的大量丢失;而外泌体组染色呈阳性, UMSC-Exos组的染色强度大于BMSC-Exos组。用OARSI评分将上述病理染色结果作半定量分析,发现UMSC-Exos组的骨关节炎表现最轻,见图4C。采用ELISA检测关节液中的炎症因子水平,发现外泌体组白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α水平降低,且UMSC-Exos组的下降趋势最强(P < 0.05),见图4D。"
| [1] PORTAL-NÚÑEZ S, ESBRIT P, ALCARAZ MJ, et al. Oxidative stress, autophagy, epigenetic changes and regulation by miRNAs as potential therapeutic targets in osteoarthritis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;108:1-10. [2] HUNTER DJ. Imaging insights on the epidemiology and pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009;35(3):447-463. [3] SHAMOON M, HOCHBERG MC. Treatment of osteoarthritis with acetaminophen: efficacy, safety, and comparison with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2000;2(6):454-458. [4] Platas J, Guillén MI, Pérez Del Caz MD, et al. Paracrine effects of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in inflammatory stress-induced senescence features of osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Aging (Albany NY). 2016;8(8):1703-1717. [5] KIM YG, CHOI J, KIM K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for Effective Cartilage Tissue Repair and Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Biotechnol J. 2020;15(12):e2000082. [6] COSENZA S, TOUPET K, MAUMUS M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics. 2018;8(5):1399-1410. [7] CASADO JG, BLÁZQUEZ R, VELA FJ, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Immunomodulatory Evaluation in an Antigen-Induced Synovitis Porcine Model. Front Vet Sci. 2017;4:39. [8] WU X, LI SH, LOU LM, et al. The effect of the microgravity rotating culture system on the chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Biotechnol. 2013;54(2):331-336. [9] MURPHY C, WITHROW J, HUNTER M, et al. Emerging role of extracellular vesicles in musculoskeletal diseases. Mol Aspects Med. 2018;60:123-128. [10] BURKE J, KOLHE R, HUNTER M, et al. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Potential Alternative Therapeutic Agent in Orthopaedics. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:5802529. [11] HARRELL CR, JOVICIC N, DJONOV V, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles as New Remedies in the Therapy of Inflammatory Diseases. Cells. 2019;8(12):1605. [12] VIZOSO FJ, EIRO N, COSTA L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Homeostasis and Systemic Diseases: Hypothesis, Evidences, and Therapeutic Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3738. [13] YAGHOUBI Y, MOVASSAGHPOUR A, ZAMANI M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells derived-exosomes in diseases treatment. Life Sci. 2019;233:116733. [14] LIU X, YANG Y, LI Y, et al. Integration of stem cell-derived exosomes with in situ hydrogel glue as a promising tissue patch for articular cartilage regeneration. Nanoscale. 2017;9(13):4430-4438. [15] MAO G, HU S, ZHANG Z, et al. Exosomal miR-95-5p regulates chondrogenesis and cartilage degradation via histone deacetylase 2/8. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(11):5354-5366. [16] PATEL DB, SANTORO M, BORN LJ, et al. Towards rationally designed biomanufacturing of therapeutic extracellular vesicles: impact of the bioproduction microenvironment. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(8):2051-2059. [17] PRITZKER KP, GAY S, JIMENEZ SA, et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(1):13-29. [18] NAM Y, RIM YA, LEE J, et al. Current Therapeutic Strategies for Stem Cell-Based Cartilage Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:8490489. [19] TOH WS, LAI RC, HUI JHP, et al. MSC exosome as a cell-free MSC therapy for cartilage regeneration: Implications for osteoarthritis treatment. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;67:56-64. [20] SUN L, XU R, SUN X, et al. Safety evaluation of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell. Cytotherapy. 2016; 18(3):413-422. [21] MIANEHSAZ E, MIRZAEI HR, MAHJOUBIN-TEHRAN M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: a new therapeutic approach to osteoarthritis? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):340. [22] ZHANG R, MA J, HAN J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell related therapies for cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(10): 6275-6289. [23] TAO SC, YUAN T, ZHANG YL, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics. 2017;7(1):180-195. [24] WANG Y, YU D, LIU Z, et al. Exosomes from embryonic mesenchymal stem cells alleviate osteoarthritis through balancing synthesis and degradation of cartilage extracellular matrix. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017; 8(1):189. [25] ZHANG B, YIN Y, LAI RC, et al. Immunotherapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles. Front Immunol. 2014;5:518. [26] ZHANG B, YIN Y, LAI RC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells secrete immunologically active exosomes. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(11):1233-1244. [27] ZHANG S, CHUAH SJ, LAI RC, et al. MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials. 2018;156:16-27. [28] CHEN P, ZHENG L, WANG Y, et al. Desktop-stereolithography 3D printing of a radially oriented extracellular matrix/mesenchymal stem cell exosome bioink for osteochondral defect regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(9):2439-2459. [29] MAO G, ZHANG Z, HU S, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-92a-3p-overexpressing human mesenchymal stem cells enhance chondrogenesis and suppress cartilage degradation via targeting WNT5A. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):247. [30] WON LEE G, THANGAVELU M, JOUNG CHOI M, et al. Exosome mediated transfer of miRNA-140 promotes enhanced chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cells for enhanced cartilage repair and regeneration. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(7):3642-3652. [31] WU J, KUANG L, CHEN C, et al. miR-100-5p-abundant exosomes derived from infrapatellar fat pad MSCs protect articular cartilage and ameliorate gait abnormalities via inhibition of mTOR in osteoarthritis. Biomaterials. 2019;206:87-100. [32] LIU Y, ZOU R, WANG Z, et al. Exosomal KLF3-AS1 from hMSCs promoted cartilage repair and chondrocyte proliferation in osteoarthritis. Biochem J. 2018;475(22):3629-3638. [33] LIU Y, LIN L, ZOU R, et al. MSC-derived exosomes promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of chondrocytes via lncRNA-KLF3-AS1/miR-206/GIT1 axis in osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle. 2018;17(21-22):2411-2422. [34] YAN L, LIU G, WU X. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in mechanical environment show improved osteochondral activity via upregulation of LncRNA H19. J Orthop Translat. 2020;26:111-120. [35] YAN L, LIU G, WU X. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 improves osteochondral activity through miR-29b-3p/FoxO3 axis. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e255. [36] HARASZTI RA, MILLER R, STOPPATO M, et al. Exosomes Produced from 3D Cultures of MSCs by Tangential Flow Filtration Show Higher Yield and Improved Activity. Mol Ther. 2018;26(12):2838-2847. |
| [1] | Tan Xinfang, Guo Yanxing, Qin Xiaofei, Zhang Binqing, Zhao Dongliang, Pan Kunkun, Li Yuzhuo, Chen Haoyu. Effect of uniaxial fatigue exercise on patellofemoral cartilage injury in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [3] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [4] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [5] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [6] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [7] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [8] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [9] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [10] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [11] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [12] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [13] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [14] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [15] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||