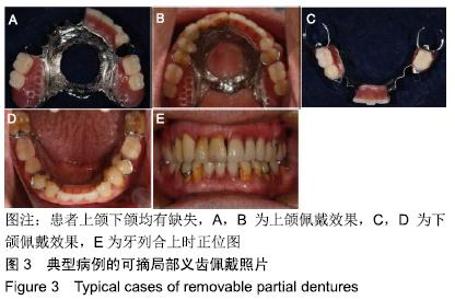
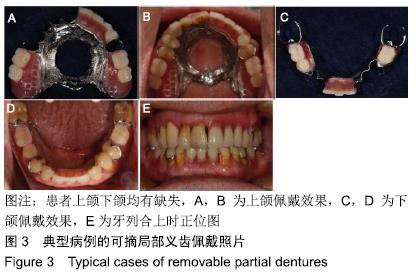
[1] ZIERDEN K, KURZROCK L, WÖSTMANN B, et al.Nonprecious Alloy vs Precious Alloy Telescopic Crown-Retained Removable Partial Dentures: Survival and Maintenance Needs.Int J Prosthodont. 2018;31(5):459-464.
[2] DISHA V, ČELEBIĆ A, RENER-SITAR K, et al. Mini Dental Implant-Retained Removable Partial Dentures: Treatment Effect Size and 6-Months Follow-up.Acta Stomatol Croat.2018;52(3):184-192.
[3] 谢煜庭,乔志萍.不同材料支架式可摘局部义齿修复牙列缺损:义齿就位率与生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(16):2593-2597.
[4] CHEN X, ZHANG Y, ZHOU J, et al. Effect of different surface treatments and retainer designs on the retention of posterior Pd-Ag porcelain-fused-to-metal resin-bonded fixed partial dentures.Exp Ther Med.2018;15(2):2006-2014.
[5] 叶红强,李欣欣,周永胜.一体化可摘局部义齿的数字化设计与制作及其适合性评价[C].第十五次全国口腔医学计算机应用学术研讨会,中国广西南宁, 2017.
[6] 袁琳,刘聪,桑雪,等.3种不同固位结构义齿修复游离端缺失咀嚼效率比较分析[J].中国实验诊断学,2017,21(1):83-85.
[7] CHEN J, AHMAD R, SUENAGA H, et al.Shape Optimization for Additive Manufacturing of Removable Partial Dentures--A New Paradigm for Prosthetic CAD/CAM.PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0132552.
[8] 胡丹丹,吴琳.可摘局部义齿临床应用和研究现状[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2018,11(8): 498-503.
[9] ARAFA KAO.Assessment of the fit of removable partial denture fabricated by computer-aided designing/computer aided manufacturing technology.Saudi Med J. 2018;39(1):17-22.
[10] 林鸿雷,王月燕,卢阳.不同材料支架式可摘局部义齿修复牙列缺损的生物相容性分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(8):1171-1176.
[11] 程蕙娟,吴丹,孙健.三维打印技术制作上颌全口义齿基托蜡型的初步研究[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2014,23(1):23-26.
[12] 何传鑫.基于3D打印技术的上颌赝复体数字化设计与制造研究[D].杭州:浙江工业大学,2017.
[13] BILGIN MS, BAYTAROĞLU EN, ERDEM A, et al.A review of computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacture techniques for removable denture fabrication.Eur J Dent. 2016;10(2):286-291.
[14] 王勇,吕培军,吴琳,等.可摘局部义齿支架三维CAD方法的初步研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2007,23(3):321-324.
[15] 诸森阳,蔡玉惠,戴宁,等.可摘局部义齿铸造支架铸型CAD/CAM技术的临床初步应用研究[J].口腔医学,2009,29(3):126-129.
[16] 黄丽娟,景双林,聂蓉蓉,等.3D打印技术制作可摘局部义齿支架的临床应用[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2016,36(10):1259-1262.
[17] 田芝娟,苏俭生.CAD/CAM口腔修复技术的研究现状[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2008,6(3):179-182.
[18] HAN W, LI Y, ZHANG Y, et al.Design and fabrication of complete dentures using CAD/CAM technology.Medicine. 2017;96(1):e5435.
[19] JANEVA NM, KOVACEVSKA G, ELENCEVSKI S, et al. Advantages of CAD/CAM versus Conventional Complete Dentures - A Review.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018;6(8):1498-1502.
[20] STEINMASSL O, OFFERMANNS V, STÖCKL W, et al.In Vitro Analysis of the Fracture Resistance of CAD/CAM Denture Base Resins. Materials. 2018;11(3):401.
[21] 陈虎,赵甜,王勇,等.基于初印模三维扫描的无牙颌上颌个性化托盘计算机辅助设计及三维打印[J].北京大学学报(医学版), 2016,48(5):900-904.
[22] 牛茂,许在俊,李月.基于三维打印技术制作可摘局部义齿支架树脂熔模的适合性研究[J].重庆医学,2015,44(9):1235-1238.
[23] HASSAN B, GREVEN M, WISMEIJER D.Integrating 3D facial scanning in a digital workflow to CAD/CAM design and fabricate complete dentures for immediate total mouth rehabilitation. J Adv Prosthodont. 2017;9(5):381-386.
[24] 刘靖,刘杰.3D打印技术制备可摘局部义齿基托与带模铸造制备可摘局部义齿基托性能的比较研究[C].中华口腔医学会口腔修复学专业委员会第十次全国口腔修复学术大会,中国浙江杭州, 2016.
[25] JEONG KW, KIM SH.Influence of surface treatments and repair materials on the shear bond strength of CAD/CAM provisional restorations.J Adv Prosthodont. 2019;11(2):95-104.
[26] 张倩,吴文孟,宁宝麟,等.3D打印钴铬合金应用于可摘局部义齿支架制作的机械性能评价[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2016,3(1):87-89.
[27] 王璐.垫式可摘局部义齿在牙列缺损合并重度磨损患者咬合功能恢复的影响[J].实用临床医药杂志,2019,23(8):54-56,60.
[28] 鲍艳娜.不同材料支架式可摘局部义齿修复后不良反应比较[J].现代仪器与医疗,2018,24(3):120-124.
[29] 丁虹,张红,孟翔峰.精细印模技术用于可摘局部义齿修复的临床评价[J].口腔疾病防治,2018,26(12):779-784.
[30] 张楠,刘庆,刘娜,常文晓,康洁,窦海瑞.数字化印模对可摘局部义齿临床适合性的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(1):67-70.
[31] 胡杉杉,王剑.3D打印技术在口腔修复学实验教学中的应用初探[J].北京口腔医学,2019,27(3):171-172.
[32] VIRARD F, VENET L, RICHERT R, et al. Manufacturing of an immediate removable partial denture with an intraoral scanner and CAD-CAM technology: a case report.BMC Oral Health. 2018;18(1): 120.
[33] 姜鸣,俞明,徐睿.老年患者重度磨耗伴牙列缺损垫式可摘义齿进行咬合重建的疗效分析[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2018,16(4):220-224.
[34] 白莹.纯钛支架义齿与钴铬合金支架义齿的咀嚼效率与修复效果比较[J].医疗装备,2016,29(22):68.
[35] 李景成,李传厚,王松,等.不同修复方式修复游离端缺失的效果及价值对比[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志,2019,6(16):34,42.
|