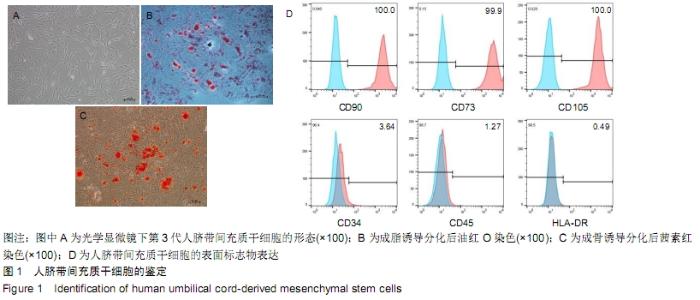
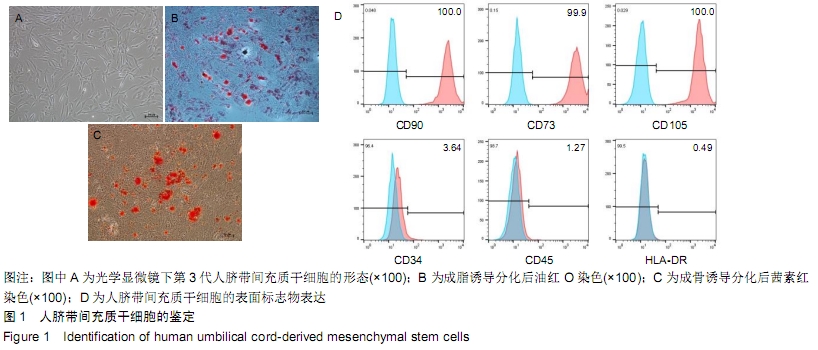
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (13): 2020-2027.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2050
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interferon-gamma combined with lipopolysaccharide polarizes human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells to a MSC2 phenotype
Huang Tian1, 2, Huang Xin2, Lai
Peilong2, Geng Suxia2, Chen Xiaomei2, Wang Yulian2,
Guo Liyan2, Zeng Gaochun2, Han Fengzhen3, Li Xiaohong4,
Du Xin1, 2, Weng Jianyu1, 2
- 1School of Medicine, South China University of Technology; 2Department of Hematology, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences; 3Department of Obstetrics, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences; 4Medical Research Center of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences
-
Received:2019-08-05Revised:2019-08-08Accepted:2019-10-14Online:2020-05-08Published:2020-03-08 -
Contact:Weng Jianyu, MD, Chief physician, School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Hematology, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Tian, Master candidate, School of Medicine, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Hematology, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81671585 and 81370665
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Tian, Huang Xin, Lai Peilong, Geng Suxia, Chen Xiaomei, Wang Yulian, Guo Liyan, Zeng Gaochun, Han Fengzhen, Li Xiaohong, Du Xin, Weng Jianyu. Interferon-gamma combined with lipopolysaccharide polarizes human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells to a MSC2 phenotype[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2020-2027.
share this article
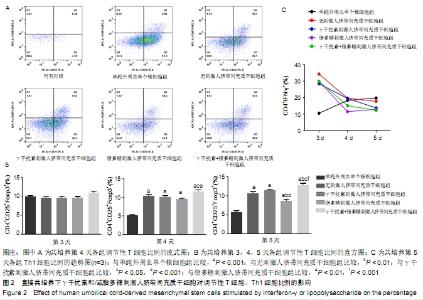
2.2 人脐带间充质干细胞对调节性T细胞、Th1细胞的影响 2.2.1 直接共培养 (1)γ干扰素、脂多糖刺激人脐带间充质干细胞对调节性T细胞比例的影响:共培养第3天,刺激组与无刺激组间的调节性T细胞比例未见明显变化(P > 0.05)。共培养第4天和第5天,与单纯外周血单个核细胞组相比,刺激与无刺激人脐带间充质干细胞各组均发现调节性T细胞比例明显增加(P < 0.05)。共培养第4天时,与γ干扰素刺激组(10.11±0.7)%、脂多糖刺激组(9.55±0.4)%相比,γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激组的调节性T细胞比例增加,为(11.6± 0.8)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);共培养第5天时,γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激组的调节性T细胞比例亦增加,为(12.8±0.8)%,与γ干扰素刺激组(11.5±0.7)%、脂多糖刺激组(8.7±0.8)%和无刺激组(10.7±1.2)%比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。连续观察结果显示:γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激组共培养第5天的调节性T细胞比例未见明显高于第4天(P > 0.05)。 直接共培养条件下,人脐带间充质干细胞需要与外周血单个核细胞直接接触相互作用至少4 d的时间,调节性T细胞比例才发生显著性的差异,γ干扰素和脂多糖联合刺激提高调节性T细胞比例的作用最佳,见图2A、B。 "
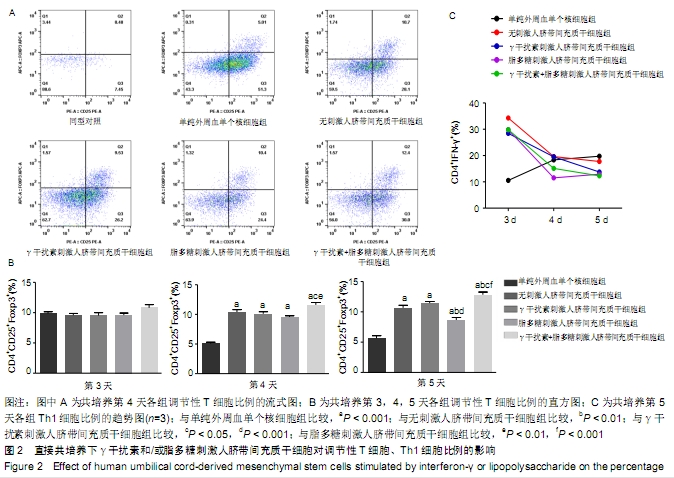
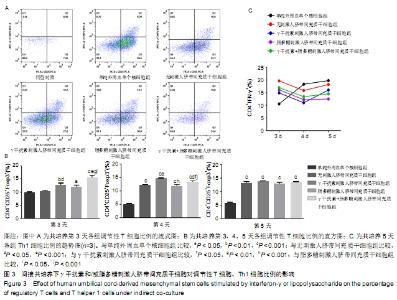
(2)γ干扰素、脂多糖刺激人脐带间充质干细胞对Th1细胞比例的影响:共培养第3天,与单纯外周血单个核细胞组相比,刺激与无刺激人脐带间充质干细胞各组的Th1细胞比例均明显升高(P < 0.05)。共培养第4天,与单纯外周血单个核细胞组及无刺激人脐带间充质干细胞组相比,经γ干扰素、脂多糖或γ干扰素+脂多糖刺激人脐带间充质干细胞组Th1细胞比例均出现下降趋势(P > 0.05)。共培养第5天,与单纯外周血单个核细胞组相比,刺激人脐带间充质干细胞各组Th1细胞比例均明显下降,单纯外周血单个核细胞组为(19.8±3.4)%、γ干扰素刺激组为(13.7±1.1)%、脂多糖刺激组为(13±4)%、γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激组为(12.3±4.0)%,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。结果表明:随着培养时间延长,单纯外周血单个核细胞组的Th1细胞比例逐步上升,人脐带间充质干细胞共培养各组的Th1细胞比例逐步下降;在共培养第5天时,刺激人脐带间充质干细胞各组抑制Th1分化的作用优于无刺激人脐带间充质干细胞组,见图2C。γ干扰素和/或脂多糖刺激后可以降低Th1细胞比例,同时也表明其发挥免疫调节作用需要四五天的时间。 2.2.2 间接共培养 (1)γ干扰素、脂多糖刺激人脐带间充质干细胞对调节性T细胞比例的影响:共培养第3天,γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激组调节性T细胞比例为(15.9±1.6)%,明显高于单纯外周血单个核细胞组(9.7±0.5)%、γ干扰素刺激组(12.6± 1.2)%、脂多糖刺激组(11.8±1.3)%和无刺激组 (10.4± 0.8)%,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激组和γ干扰素刺激组优于无刺激组(P < 0.05),见图3A、B。共培养第4天和第5天,与单纯外周血单个核细胞组相比,刺激与无刺激的人脐带间充质干细胞各组调节性T细胞比例均明显增加(P < 0.05)。结果表明:间接共培养下,刺激后的人脐带间充质干细胞在早期(第3天)即可促进调节性T细胞比例增加,同时γ干扰素单独或联合脂多糖刺激人脐带间充质干细胞均可显著增强调节性T细胞比例。 "
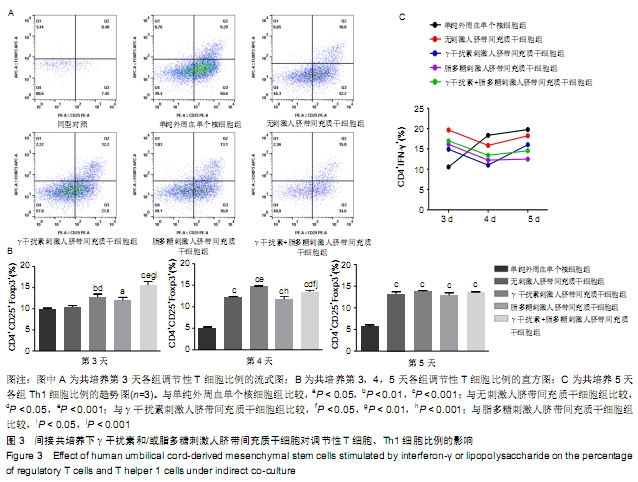

(2)γ干扰素、脂多糖刺激人脐带间充质干细胞对Th1细胞比例的影响:随着培养的时间延长,单纯外周血单个核细胞组的Th1细胞比例逐步上升。共培养第4天,与外周血单个核细胞组相比,刺激与无刺激的人脐带间充质干细胞各组Th1细胞比例均开始下降,但持续时间较短;共培养第5天,仅脂多糖刺激组的Th1细胞比例仍明显下降 (P < 0.05),其余各组均有回升趋势,见图3C。结果表明:在间接共培养体系下,人脐带间充质干细胞各组对Th1细胞的作用持续时间较短。 2.3 间接共培养体系下人脐带间充质干细胞Toll样受体2,3,4 mRNA的表达 间接共培养第3天,γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激人脐带间充质干细胞显著上调调节性T细胞比例,检测该状态下人脐带间充质干细胞Toll样受体2,3,4 mRNA的表达。与无刺激组比较,γ干扰素刺激组和γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激组的Toll样受体3 mRNA表达水平明显增加(P < 0.05);刺激各组之间相比,γ干扰素联合脂多糖刺激组Toll样受体3 mRNA的表达增加最显著,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图4;100 μg/L 脂多糖联合γ干扰素有协同促进Toll样受体3表达的作用。刺激各组与无刺激组比较,Toll样受体2,4 mRNA的表达无明显差异。 "

| [1] WUCHTER P, BIEBACK K, SCHREZENMEIER H, et al. Standardization of Good Manufacturing Practice-compliant production of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stromal cells for immunotherapeutic applications. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(2):128-139. [2] TESSIER L, BIENZLE D, WILLIAMS LB, et al. Phenotypic and immunomodulatory properties of equine cord blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. PLoS One. 2015; 10(4):e0122954. [3] XU AL, RODRIGUEZ LA 2ND, WALKER KP 3RD, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reconditioned in Their Own Serum Exhibit Augmented Therapeutic Properties in the Setting of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(10):1092-1106. [4] WENG JY, DU X, GENG SX, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell as salvage treatment for refractory chronic GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010;45(12):1732-1740. [5] WANG Y, CHEN X, CAO W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016. [6] TOMCHUCK SL, ZWEZDARYK KJ, COFFELT SB, et al. Toll-like receptors on human mesenchymal stem cells drive their migration and immunomodulating responses. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):99-107. [7] WATERMAN RS, TOMCHUCK SL, HENKLE SL, et al. A new mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) paradigm: polarization into a pro-inflammatory MSC1 or an Immunosuppressive MSC2 phenotype. PLoS One. 2010;5(4):e10088. [8] ROMIEU-MOUREZ R, FRANÇOIS M, BOIVIN MN, et al. Bouchentouf M,Cytokine modulation of TLR expression and activation in mesenchymal stromal cells leads to a proinflammatory phenotype. J Immunol. 2009;182(12): 7963-7973. [9] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [10] CRAIN SK, ROBINSON SR, THANE KE, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress CD4 Expressing T Cells Through Transforming Growth Factor Beta and Adenosine Signaling in a Canine Model. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(3):212-226. [11] SHI Y, WANG Y, LI Q, et al. Immunoregulatory mechanisms of mesenchymal stem and stromal cells in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14(8):493-507. [12] KHOSRAVI M, BIDMESHKIPOUR A, MORAVEJ A, et al. Induction of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells by mesenchymal stem cells is associated with RUNX complex factors. Immunol Res. 2018;66(1):207-218. [13] 陈柄全,彭漪,肖轶,等.人脐血间充质干细胞对小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞M2亚型的转化作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(25): 3987-3992. [14] PENG Y, CHEN X, LIU Q, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells infusions improve refractory chronic graft versus host disease through an increase of CD5+ regulatory B cells producing interleukin 10. Leukemia. 2015;29(3):636-646. [15] SAKAGUCHI S, YAMAGUCHI T, NOMURA T, et al. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133(5): 775-787. [16] WING K, SAKAGUCHI S. Regulatory T cells exert checks and balances on self tolerance and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(1):7-13. [17] LIN X, CHEN M, LIU Y, et al. Advances in distinguishing natural from induced Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(2):116-123. [18] CHAMBERS CA, KANG J, WU Y, et al. The lymphoproliferative defect in CTLA-4-deficient mice is ameliorated by an inhibitory NK cell receptor. Blood. 2002;99(12):4509-4516. [19] COPSEL S, WOLF D, KOMANDURI KV, et al. The promise of CD4+FoxP3+ regulatory T-cell manipulation in vivo: applications for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2019;104(7):1309-1321. [20] TAYLOR PA, NOELLE RJ, BLAZAR BR. CD4(+)CD25(+) immune regulatory cells are required for induction of tolerance to alloantigen via costimulatory blockade. J Exp Med. 2001;193(11):1311-1318. [21] BERES AJ, DROBYSKI WR. The role of regulatory T cells in the biology of graft versus host disease. Front Immunol. 2013;4:163. [22] ELIAS S, RUDENSKY AY. Therapeutic use of regulatory T cells for graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2019; 187(1):25-38. [23] BRUNSTEIN CG, MILLER JS, MCKENNA DH, et al. Umbilical cord blood-derived T regulatory cells to prevent GVHD: kinetics, toxicity profile, and clinical effect. Blood. 2016;127(8): 1044-1051. [24] BLAZAR BR, MACDONALD KPA, HILL GR. Immune regulatory cell infusion for graft-versus-host disease prevention and therapy. Blood. 2018;131(24):2651-2660. [25] CHAN JL, TANG KC, PATEL AP, et al. Antigen-presenting property of mesenchymal stem cells occurs during a narrow window at low levels of interferon-gamma. Blood. 2006; 107(12):4817-4824. [26] WATERMAN RS, HENKLE SL, BETANCOURT AM. Mesenchymal stem cell 1 (MSC1)-based therapy attenuates tumor growth whereas MSC2-treatment promotes tumor growth and metastasis. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45590. [27] OPITZ CA, LITZENBURGER UM, LUTZ C, et al. Toll-like receptor engagement enhances the immunosuppressive properties of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by inducing indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-1 via interferon-beta and protein kinase R. Stem Cells. 2009;27(4): 909-919. [28] REN G, ZHANG L, ZHAO X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(2):141-150. [29] BOLAND L, BURAND AJ, BROWN AJ, et al. IFN-γ and TNF-α Pre-licensing Protects Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from the Pro-inflammatory Effects of Palmitate. Mol Ther. 2018;26(3): 860-873. [30] VEGA-LETTER AM, KURTE M, FERNÁNDEZ-O'RYAN C, et al. Differential TLR activation of murine mesenchymal stem cells generates distinct immunomodulatory effects in EAE. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):150. [31] KRAMPERA M, GLENNIE S, DYSON J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729. [32] GLENNIE S, SOEIRO I, DYSON PJ, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells. Blood. 2005;105(7):2821-2827. [33] DEL FATTORE A, LUCIANO R, PASCUCCI L, et al. Immunoregulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on T Lymphocytes. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(12):2615-2627. [34] PIANTA S, BONASSI SIGNORONI P, MURADORE I, et al. Amniotic membrane mesenchymal cells-derived factors skew T cell polarization toward Treg and downregulate Th1 and Th17 cells subsets. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2015;11(3):394-407. [35] KAY AG, LONG G, TYLER G, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Reduces Disease Severity and Immune Responses in Inflammatory Arthritis. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):18019. [36] POLCHERT D, SOBINSKY J, DOUGLAS G, et al. IFN-gamma activation of mesenchymal stem cells for treatment and prevention of graft versus host disease. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(6):1745-1755. [37] DUIJVESTEIN M, WILDENBERG ME, WELLING MM, et al. Pretreatment with interferon-γ enhances the therapeutic activity of mesenchymal stromal cells in animal models of colitis. Stem Cells. 2011;29(10):1549-1558. [38] CASSANO JM, SCHNABEL LV, GOODALE MB, et al. The immunomodulatory function of equine MSCs is enhanced by priming through an inflammatory microenvironment or TLR3 ligand. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2018;195:33-39. [39] MEISEL R, ZIBERT A, LARYEA M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells inhibit allogeneic T-cell responses by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated tryptophan degradation. Blood. 2004;103(12):4619-4621. [40] GHANNAM S, BOUFFI C, DJOUAD F, et al. Immunosuppression by mesenchymal stem cells: mechanisms and clinical applications. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(1):2. [41] KRAMPERA M, COSMI L, ANGELI R, et al. Role for interferon-gamma in the immunomodulatory activity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2006; 24(2):386-398. [42] LAI RC, YEO RW, LIM SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88. [43] LIA G, BRUNELLO L, BRUNO S, et al. Extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers of acute graft-vs-host disease. Leukemia. 2018;32(3):765-773. [44] WANG L, GU Z, ZHAO X, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released from Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Prevent Life-Threatening Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease in a Mouse Model of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(24):1874-1883. [45] KORDELAS L, REBMANN V, LUDWIG AK, et al. MSC-derived exosomes: a novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia. 2014;28(4):970-973. [46] BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, CAMUSSI G. The secretome of mesenchymal stromal cells: Role of extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation. Immunol Lett. 2015;168(2):154-158. [47] LAI P, WENG J, GUO L, et al. Novel insights into MSC-EVs therapy for immune diseases. Biomark Res. 2019;7:6. [48] LAI P, CHEN X, GUO L, et al. A potent immunomodulatory role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stromal cells in preventing cGVHD. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1):135. |
| [1] | Yuan Baohong, Zhao Weishan, Wang Ruotian, Guan Aoran, Wang Yu, Li Ruhong. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from pigs inhibit inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide and improve islet cell dysfunction in pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 1969-1975. |
| [2] | Zhang Sheng, Bai Jijia, Xu Yanping, Wang Xiaohong. Constructing and assessing a rat model of sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1249-1253. |
| [3] | Li Zhenxiang, Jiang Xiaokui, Shen Fangfang, Li Shaoshan. Immuoregulatory effects of colorectal cancer cell-derived exosomes on CD8+ T cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5002-5006. |
| [4] | He Qiang, Qian Weiqing, Yao Nianwei, Zhou Mengling, Liu Yixin, Yin Hong. Protection of inflammatory osteoblasts in neonatal rats using catalpol from the root of Rehmannia glutinosa [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4626-4631. |
| [5] |
Wang Zhen, Li Xiaolan, Liu Jianguo.
Insights into immunoregulatory properties of dental-derived mesenchymal stem cells in oral diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4060-4067. |
| [6] | Liu Ying, Gao Jie, Wu Buling. Biological characteristics of dental pulp stem cells induced by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2028-2033. |
| [7] | Wang Jie, Yu Limei. Immunomodulatory characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells mediated by inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2108-2113. |
| [8] | Xu Huijun, Shi Dongmei, Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Effect of sex combing protein 1 on proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts in inflammatory microenvironment#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 130-135. |
| [9] | Liu Dayong, Zhou Weiwei, Xiao Rui, Wang Meirui, Zhao Mengming, Jia Zhi. Lipopolysaccharides affect osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells derived from ob/ob mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 703-709. |
| [10] | Feng Fang, Dong Chenming, Chen Yu, Qi Yan. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating septic rats with acute respiratory distress syndrome and the underlying mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 741-748. |
| [11] | Gao Hua1, 2, Li Yanxia1, Wang Dan1, Yang Xinling1 . Protective effects and the mechanism of lipoic acid on cell model of Parkinson’s disease induced by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 447-452. |
| [12] | Feng Ruxue, Cai Rengang, Xie Dandan. Lipopolysaccharide can influence and regulate proliferation and migration of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(29): 4688-4693. |
| [13] |
Li Xianghe, Luo Wei, Hu Junxian, Yang Jing, Han Xinyun, Dong Shiwu, Yang Xianteng, Li Senlei, Yan Zhihui, Nie Yingjie, Tian Xiaobin, Sun Li.
Chrysin inhibits mouse osteoclastogenesis induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(25): 3978-3986.
|
| [14] | Yu Sujiao, Tan Hui. Astragaloside IV suppresses the expression of inflammatory cytokines in chondrocytes via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(11): 1652-1656. |
| [15] | Zhang Ni, Chen Lan-ying, Li Xue-liang, Guan Zi-yi, Fang Cong, Zhou Meng-jing, Luo Ying-ying, Liu Rong-hua. Viability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in inflammation-induced ischemia-reperfusion environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5259-5267. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||