Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (13): 2108-2113.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2054
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immunomodulatory characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells mediated by inflammatory factors
Wang Jie1, 2, Yu Limei1, 2, 3
- 1Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Science and Technology Innovation Talent Team of Bone Marrow and Amniotic Stem Cell Foundation and Clinical Research in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 3Center of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Engineering of Zunyi, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2019-09-09Revised:2019-09-12Accepted:2019-10-24Online:2020-05-08Published:2020-03-10 -
Contact:Yu Limei, MD, Master’s supervisor, Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Science and Technology Innovation Talent Team of Bone Marrow and Amniotic Stem Cell Foundation and Clinical Research in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; Center of Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Engineering of Zunyi, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Jie, Master candidate, Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Major Science and Technology Project of Guizhou Province, No. [2011]6002
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Jie, Yu Limei. Immunomodulatory characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells mediated by inflammatory factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2108-2113.
share this article
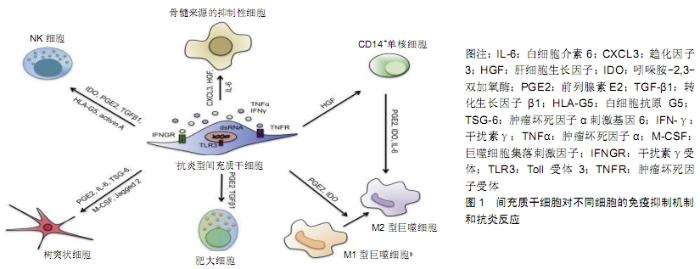
2.1 炎症因子对间充质干细胞免疫调节可塑性的影响 间充质干细胞可以从各种成体组织中分离,例如骨髓、脐带、脂肪、外周血、肝脏和牙根[10-11]。多种来源间充质干细胞均显示出较低的免疫原性和突出的免疫调节能力,不仅能在外周免疫耐受、移植耐受、自身免疫、肿瘤逃避中发挥作用,还能在母-胎耐受中进行调节[12],原因在于间充质干细胞低表达人类白细胞抗原和主要组织相容性复合体,不表达或低表达CD80、CD86及CD40L等免疫共刺激分子。间充质干细胞能分泌一氧化氮、吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶、前列腺素E2、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素10等,均对树突状细胞、自然杀伤细胞、巨噬细胞、B细胞以及 CD4+和CD8+ T细胞有免疫调控作用[13-14]。间充质干细胞本身对多种免疫细胞具有调控作用[15],见图1。这一效应需要一定水平炎症因子预先刺激,如干扰素γ或至少一种其他细胞因子,特别是肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1α或白细胞介素1β[16-17]。炎性细胞因子刺激的间充质干细胞能上调诱导型一氧化氮合酶和环加氧酶2表达,增强一氧化氮和前列腺素E2调节免疫反应[18]。 "
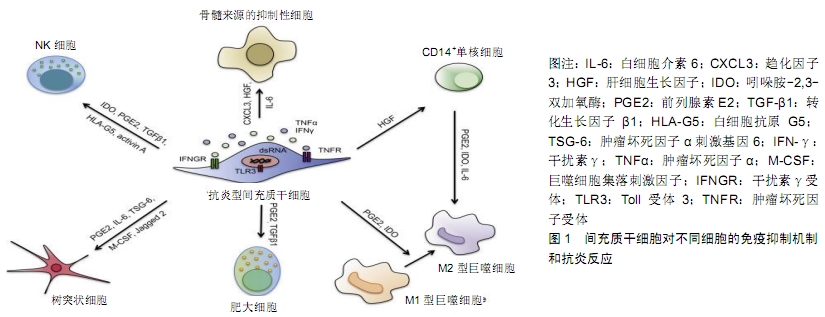

由于免疫炎症性疾病中炎症状态常常发生变化,因此炎症微环境中不同亚群免疫细胞的数量和功能、免疫调控分子和炎症因子的功能和水平等因素,均能影响间充质干细胞的免疫调节特性。间充质干细胞拥有促炎和抑炎2种能力,微环境中的炎症水平决定了间充质干细胞的免疫调节趋势。微环境中细胞因子或分子介质可以诱导间充质干细胞从静息状态极化成促炎型MSC1或抑炎型MSC2。当微环境中的炎症水平较低时,间充质干细胞可以促进免疫反应;当炎症水平较高时,间充质干细胞则可以大幅抑制免疫反应。高浓度的一氧化氮或者色氨酸分解产物吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶能够发挥间充质干细胞的免疫抑制能力;当一氧化氮或者色氨酸水平较低时,间充质干细胞发挥免疫促进能力[19]。炎性因子刺激间充质干细胞分泌大量的免疫抑制因子、趋化因子,并表达黏附分子,其中趋化因子大量分泌将导致免疫细胞趋向间充质干细胞,也可分泌大量抗炎因子,增加或减少miRNA的生成而影响炎症反应与免疫功能。在这种微环境下间充质干细胞在局部分泌的免疫抑制因子发挥效应将产生强有力的免疫抑制效果[20]。在没有T细胞激活信号的情况下,将间充质干细胞和T细胞共培养,间充质干细胞并不能抑制T细胞的增殖,将间充质干细胞暴露于干扰素γ、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1环境时,间充质干细胞则完全抑制T细胞杂交瘤和T细胞母细胞的增殖[21]。T细胞激活时释放的干扰素γ协同肿瘤坏死因子α或白细胞介素1对间充质干细胞的免疫抑制功能有决定性的作用[5]。 2.2 炎症因子预处理间充质干细胞的免疫调控特性变化 2.2.1 干扰素γ预处理的间充质干细胞 间充质干细胞具有免疫调节特性,可通过分泌吲哚胺-2,3-双加氧酶和前列腺素E2来发挥免疫调节作用,同时又能在炎性因子如干扰素γ的预刺激下增强间充质干细胞的免疫调节功能[22]。干扰素γ预处理的骨髓间充质干细胞与淋巴细胞共培养,能明显抑制CD8+ T淋巴细胞的增殖,随着干扰素γ浓度的增加,抑制能力逐渐增强,且加入干扰素γ抑制剂后,依剂量依赖的方式逆转其对CD8+T淋巴细胞的增殖作用[23]。用干扰素γ预处理的脂肪间充质干细胞低表达MHC-Ⅰ,高表达MHC-Ⅱ,细胞培养上清液中白细胞介素10水平明显增加,转化生长因子β水平明显降低,且Jagged-2分子表达增加,而Delta-1不表达,干扰素γ预处理脂肪间充质干细胞可能通过Notch信号通路中Jagged-2配体来增强免疫抑制活性[24]。 促炎因子能够影响间充质干细胞的MHC-Ⅱ分子表达水平,低浓度干扰素γ能刺激间充质干细胞 MHC-Ⅱ表达上调,高浓度的干扰素γ则抑制MHC-Ⅱ表达,同时上调程序性死亡配体1。间充质干细胞中程序性死亡配体1表达的下调会减弱间充质干细胞的免疫抑制作用[25]。因此,存在一个干扰素γ水平决定的反馈环路,即影响间充质干细胞的MHC-Ⅱ和程序性死亡配体1表达,也导致免疫反应的增强或减弱[26]。当间充质干细胞暴露在损伤因素下如细菌感染时,低浓度干扰素γ促进间充质干细胞 MHC-Ⅱ分子表达上调,促进细菌抗原的呈递,导致T细胞活化并分泌干扰素γ;高浓度干扰素γ抑制间充质干细胞 MHC-Ⅱ分子表达,关闭间充质干细胞抗原提呈作用并上调程序性死亡配体1表达,抑制T细胞活化。然而利用RNA干扰技术沉默大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的干扰素γ基因表达,与大鼠脾淋巴细胞共培养之后,脾淋巴细胞活力明显降低,肿瘤坏死因子α水平增加,而白细胞介素10水平明显降低[27]。利用炎症因子干扰素γ、肿瘤坏死因子α或miRNA干扰技术适当对间充质干细胞进行预处理,可能是提高间充质干细胞治疗免疫相关疾病可行方法之一。 2.2.2 转化生长因子β预处理的间充质干细胞 转化生长因子β1作为免疫系统家族的重要调控分子,不但参与了免疫反应的调控,还能在调节受损组织细胞增殖和神经系统分化等方面起重要作用。排斥反应和移植物抗宿主病是许多器官和细胞移植后的常见并发症,间充质干细胞预防排斥反应也越来越多地受到关注。间充质干细胞可通过自分泌的方式产生大量的转化生长因子β1,直接调节免疫功能[28]。与未修饰的人羊膜间充质干细胞相比,转化生长因子β1基因修饰的人羊膜间充质干细胞分泌更多的转化生长因子β1和白细胞介素22,并能明显减轻小鼠移植异种外周神经的排斥反应[13]。研究表明,转化生长因子β1预处理骨髓间充质干细胞表达黏附分子CD51、CD29、CD61含量明显增加[29],通过整合素激酶FAK介导的Smad通路来增强细胞迁移和黏附能力,提高大鼠背部创面治疗效果。与未干预的脐带间充质干细胞相比,转化生长因子β1预处理的脐带间充质干细胞表型和成骨成脂肪分化能力未发生变化,增殖能力明显增强,且在受损肺部存活较长时间,明显减轻脂多糖诱导的肺损伤[30]。携带转化生长因子β1基因慢病毒转染骨髓间充质干细胞治疗缺血性再灌注损伤小鼠,转染的骨髓间充质干细胞明显集中于损伤的肾组织,且转化生长因子β1和CXCR4表达量明显增加,表明转化生长因子β1和CXCR4能促进间充质干细胞的归巢[31]。研究表明,转化生长因子β1干预骨髓间充质干细胞明显增加半乳糖苷酶和线粒体活性氧表达,减少超氧化物歧化酶的产生,加快间充质干细胞衰老进程[32]。 2.2.3 白细胞介素17预处理的间充质干细胞 白细胞介素17主要由Th17细胞产生,是免疫反应中的关键炎性细胞因子。白细胞介素17家族尤其是白细胞介素17A在自身免疫性疾病、过敏性疾病和宿主防御感染中的作用得到了广泛的研究[33-35]。白细胞介素17信号由白细胞介素17RA和白细胞介素17RC组成的异聚体受体复合物介导[36]。变态反应性脑脊髓膜炎是以特异性致敏性的CD4+T细胞介导的自身免疫性疾病,抗白细胞介素17治疗能延缓脑脊髓膜炎的发生,逆转其进展[37]。与未处理的脐带间充质干细胞相比,白细胞介素17B预处理脐带间充质干细胞的增殖能力和迁移能力明显增强,且干性基因的表达增加[38]。白细胞介素17A预处理的骨髓间充质干细胞向抗炎型MSC2方向分化,明显高表达Toll样受体3和Toll样受体4,且增殖能力增强[39]。背部移植异体皮肤的小鼠注射白细胞介素17预处理的骨髓间充质干细胞,在移植部位发现骨髓间充质干细胞数量增多,且小鼠脾脏Treg细胞比例明显增加,血清白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β增多,干扰素γ显著降低,表明白细胞介素17干预的骨髓间充质干细胞增强了归巢能力,提高了免疫抑制功能[40]。白细胞介素17干预的骨髓间充质干细胞与未干预的骨髓间充质干细胞一样,低表达MHC-Ⅰ,不表达MHC-Ⅱ,成骨、成脂肪和成软骨分化能力没有差异,白细胞介素17预处理的间充质干细胞与T淋巴细胞共培养,有利于诱导CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞,且共培养上清液中检测到较高浓度的前列腺素E2[41]。白细胞介素17A预处理间充质干细胞治疗急性肾缺血再灌注损伤小鼠,可显著降低小鼠血清白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α和干扰素γ水平,明显提高血清白细胞介素10水平和脾、肾Treg细胞百分比,此外血清环氧合酶2和前列腺素E2水平升高较明显,提示白细胞介素17预处理间充质干细胞可能通过环氧合酶2/前列腺素E2途径增加Treg细胞百分比而增强间充质干细胞对T细胞的免疫抑制功能[42]。 2.2.4 白细胞介素35预处理的间充质干细胞 白细胞介素35是一种免疫调控细胞因子,属于白细胞介素12家族。不同于白细胞介素12其他家族成员,白细胞介素35由Treg细胞[43]、调节性B细胞等产生[44]。白细胞介素35是免疫抑制因子,其可以抑制效应T细胞增殖,同时诱导幼稚T细胞向CD4+CD25+Treg细胞转化[43]。大量研究证明白细胞介素35可以抑制Th17细胞的分化和功能。因此,白细胞介素35在平衡Th17细胞和Treg细胞两者之间发挥关键作用。最近的研究表明白细胞介素35促使人类B细胞朝Breg细胞方向分化,Breg细胞也产生白细胞介素35和白细胞介素10[44]。脐带间充质干细胞不产生白细胞介素35,慢病毒载体携带白细胞介素35基因转染脐带间充质干细胞明显产生白细胞介素35,与小鼠脾淋巴细胞共培养能明显抑制CD4+T细胞增殖,增加CD4+CD25+Treg细胞百分比[45]。白细胞介素35基因转染的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞与大鼠T淋巴细胞共培养,明显降低CD8+T细胞的比例,提高CD4+CD25+Treg细胞水平,转染的间充质干细胞与加入脂多糖的树突状细胞共培养,上清液白细胞介素12水平明显下降,抑制了脂多糖所诱导的树突状细胞的成熟[46]。与未转染白细胞介素35的脂肪间充质干细胞移植组相比,白细胞介素35基因慢病毒载体转染脂肪间充质干细胞移植小鼠血清白细胞介素35水平明显增加,转染组和未转染组小鼠脾淋巴细胞共培养,上清液白细胞介素35和白细胞介素10水平明显增加,白细胞介素17A水平明显降低,且CD4+ CD25+Treg比例显著升高,CD4+T细胞比例降低[47],说明转染白细胞介素35的脂肪间充质干细胞通过下调Th17细胞而上调CD4+CD25+Treg细胞,促进抗炎细胞因子白细胞介素10的表达,抑制CD4+T细胞的增殖和功能。与单纯脂肪间充质干细胞治疗组相比,白细胞介素35基因修饰脂肪间充质干细胞治疗组肝组织检测到白细胞介素35修饰的脂肪间充质干细胞,还可通过JAK1-STAT1/STAT4信号通路降低肝组织干扰素γ的分泌量[48],表明白细胞介素35修饰后的脂肪间充质干细胞具有更强大的免疫调节功能,可能在器官移植耐受领域有广泛的应用前景。 2.2.5 前列腺素E2预处理的间充质干细胞 前列腺素E2是细胞膜磷脂的代谢产物花生四烯酸在环氧合酶以及前列腺素E2合酶作用下产生的终产物之一,在体内发挥重要的生理功能,特别是对免疫系统具有调节作用,与免疫耐受、自身免疫病、移植以及肿瘤免疫的关系密切[49]。前列腺素E2通过G蛋白偶联受体作用于靶细胞。与前列腺素E2结合发挥作用的4个受体转导信号是不同的,最主要的是受体是EP2和EP4。受体信号激活G蛋白偶联受体,刺激腺苷酸环化酶活性以提高细胞内cAMP浓度发挥作用[50]。前列腺素E2抑制Th1相关细胞因子的分泌,提高Th2型细胞因子的产生,能够调节Th免疫细胞反应[51]。 前列腺素E2也是间充质干细胞免疫调节活性的关键递质,在间充质干细胞抑制T细胞增殖、分化和功能,影响树突状细胞分化与成熟及抗原呈递,以及多种炎症因子产生方面都具有重要作用[52]。脂肪间充质干细胞释放的前列腺素E2,可通过上调Treg细胞比例、降低促炎因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、干扰素γ、白细胞介素6水平,提高抗炎因子白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10水平来减轻葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎症状[53]。间充质干细胞产生前列腺素E2发挥免疫抑制功能,主要是抑制T细胞增殖,而不是诱导T细胞凋亡,前列腺素E2在间充质干细胞保护T细胞凋亡过程中还发挥一定的作用,间充质干细胞抗T细胞凋亡的机制可能涉及下调Fas或者其配体FasL的表达来实现的[54-55]。前列腺素E2预处理骨髓间充质干细胞后,血管内皮生长因子明显增加,且迁移的骨髓间充质干细胞明显增多[56]。携带EP2基因慢病毒载体转染骨髓间充质干细胞治疗小鼠急性肺损伤,骨髓间充质干细胞归巢到损伤的肺组织,肺组织中白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α水平降低,白细胞介素10水平明显升高,改善了肺部炎症[57],FAK及其下游的ERK1/2是介导迁移的关键信号分子[58]。间充质干细胞在肿瘤部位的归巢表明间充质干细胞通过增加炎症浸润、抑制血管生成、抑制Wnt信号传导和AKT信号传导以及诱导细胞周期停滞和凋亡来抑制肿瘤生长。间充质干细胞的归巢表现出向病灶迁移特性,利用这一特性可将间充质干细胞作为肿瘤治疗靶向传递载体的潜在工具。 "

| [1] JAVAN MR, KHOSROJERDI A, MOAZZENI SM. New Insights Into Implementation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cancer Therapy: Prospects for Anti-angiogenesis Treatment. Front Oncol. 2019;9:840. [2] LI N, HUA J. Interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and the immune system. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(13):2345-2360. [3] 蒋珊珊,王峰,余丽梅. 间充质干细胞免疫调节特性及在器官移植中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1):103-109. [4] LIN T, PAJARINEN J, KOHNO Y, et al. Trained murine mesenchymal stem cells have anti-inflammatory effect on macrophages, but defective regulation on T-cell proliferation. FASEB J. 2019;33(3): 4203-4211. [5] WANG Y, CHEN X, CAO W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016. [6] SZABÓ E, FAJKA-BOJA R, KRISTON-PÁL É, et al. Licensing by Inflammatory Cytokines Abolishes Heterogeneity of Immunosuppressive Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Population. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(18):2171-2180. [7] KALAMEGAM G, SAIT KHW, ANFINAN N, et al. Cytokines secreted by human Wharton's jelly stem cells inhibit the proliferation of ovarian cancer (OVCAR3) cells in vitro. Oncol Lett. 2019;17(5):4521-4531. [8] SOHNI A, VERFAILLIE CM. Mesenchymal stem cells migration homing and tracking. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:130763. [9] LEE HY, HONG IS. Double-edged sword of mesenchymal stem cells: Cancer-promoting versus therapeutic potential. Cancer Sci. 2017; 108(10):1939-1946. [10] HASS R, KASPER C, BÖHM S, et al. Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC): A comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell Commun Signal. 2011;9:12. [11] ELAHI KC, KLEIN G, AVCI-ADALI M, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Different Sources Diverge in Their Expression of Cell Surface Proteins and Display Distinct Differentiation Patterns. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:5646384. [12] KRISTJÁNSSON B, HONSAWEK S. Mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. World J Orthop. 2017;8(9): 674-680. [13] SATO K, OZAKI K, OH I, et al. Nitric oxide plays a critical role in suppression of T-cell proliferation by mesenchymal stem cells. Blood. 2007;109(1):228-234. [14] RHEE KJ, LEE JI, EOM YW. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Mediated Effects of Tumor Support or Suppression. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(12): 30015-30033. [15] LE BLANC K, DAVIES LC. Mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune response. Immunol Lett. 2015;168(2):140-146. [16] MUNN DH. Blocking IDO activity to enhance anti-tumor immunity. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012;4:734-745. [17] MEISEL R, ZIBERT A, LARYEA M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells inhibit allogeneic T-cell responses by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase- mediated tryptophan degradation. Blood. 2004;103(12):4619-4621. [18] LING W, ZHANG J, YUAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use IDO to regulate immunity in tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(5):1576-1587. [19] 朱雅姝,赵春华.间充质干细胞的免疫调节能力——临床治疗的希望[J].中国科学(C辑:生命科学),2009,39(8):727-735. [20] CHAI HH, CHEN MB, CHEN GZ, et al. Inhibitory effect of TGF-β gene modified human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells on rejection after xenotransplantation of peripheral nerves. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(8):3198-3205. [21] REN G, ZHANG L, ZHAO X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(2):141-150. [22] 韩秋青,师帅南,王玉亮.脂肪来源间充质干细胞与免疫调节因子间作用的研究进展[J].天津医药,2018,46(1):109-112. [23] HONG J, HUECKELHOVEN A, WANG L, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase mediates inhibition of virus-specific CD8(+) T cell proliferation by human mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(5):621-629. [24] XISHAN Z, BIN Z, HAIYUE Z, et al. Jagged-2 enhances immunomodulatory activity in adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:14284. [25] 何骁,黄宏,徐祥.间充质干细胞在炎症调节中的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2015,37(8): 1173-1179. [26] SHENG H, WANG Y, JIN Y, et al. A critical role of IFNgamma in priming MSC-mediated suppression of T cell proliferation through up-regulation of B7-H1. Cell Res. 2008;18(8):846-857. [27] 兰绍阳,谭梅傲,陶双友,等.沉默IFN-γR表达对大鼠BMMSCs免疫调节能力的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(3): 559-564. [28] XU C, YU P, HAN X, et al. TGF-β promotes immune responses in the presence of mesenchymal stem cells. J Immunol. 2014;192(1):103-109. [29] GHOSH D, MCGRAIL DJ, DAWSON MR. TGF-β1 Pretreatment Improves the Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Wound Bed. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017;5:28. [30] LI D, LIU Q, QI L, et al. Low levels of TGF-β1 enhance human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell fibronectin production and extend survival time in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(2):1681-1692. [31] SI X, LIU X, LI J, et al. Transforming growth factor-β1 promotes homing of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10):12368-12378. [32] WU J, NIU J, LI X, et al. TGF-β1 induces senescence of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via increase of mitochondrial ROS production. BMC Dev Biol. 2014;14:21. [33] LÓPEZ P, RODRÍGUEZ-CARRIO J, CAMINAL-MONTERO L, et al. A pathogenic IFNα, BLyS and IL-17 axis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20651. [34] LORÈ NI, CIGANA C, RIVA C, et al. IL-17A impairs host tolerance during airway chronic infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25937. [35] TIAN J, RUI K, TANG X, et al. IL-17 down-regulates the immunosuppressive capacity of olfactory ecto-mesenchymal stem cells in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(28): 42953-42962. [36] TOY D, KUGLER D, WOLFSON M, et al. Cutting edge: interleukin 17 signals through a heteromeric receptor complex. J Immunol. 2006; 177(1):36-39. [37] PARK H, LI Z, YANG XO, et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(11):1133-1141. [38] BIE Q, ZHANG B, SUN C, et al. IL-17B activated mesenchymal stem cells enhance proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8(12):18914-18923. [39] HE T, HUANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. Interleukin-17A-promoted MSC2 polarization related with new bone formation of ankylosing spondylitis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(57):96993-97008. [40] MA T, WANG X, JIAO Y, et al. Interleukin 17 (IL-17)-Induced Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prolong the Survival of Allogeneic Skin Grafts. Ann Transplant. 2018;23:615-621. [41] SIVANATHAN KN, ROJAS-CANALES DM, HOPE CM, et al. Interleukin- 17A-Induced Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Are Superior Modulators of Immunological Function. Stem Cells. 2015;33(9):2850-2863. [42] BAI M, ZHANG L, FU B, et al. IL-17A improves the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in ischemic-reperfusion renal injury by increasing Treg percentages by the COX-2/PGE2 pathway. Kidney Int. 2018;93(4):814-825. [43] COLLISON LW, CHATURVEDI V, HENDERSON AL, et al. IL-35-mediated induction of a potent regulatory T cell population. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(12):1093-1101. [44] SHEN P, ROCH T, LAMPROPOULOU V, et al. IL-35-producing B cells are critical regulators of immunity during autoimmune and infectious diseases. Nature. 2014;507(7492):366-370. [45] AMARI A, EBTEKAR M, MOAZZENI SM, et al. In Vitro Generation of IL-35-expressing Human Wharton's Jelly-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Lentiviral Vector. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015; 14(4):416-426. [46] 张志强. IL-35修饰的间充质干细胞免疫调节性能初探[D]. 天津:天津医科大学, 2015. [47] GUO H, ZHAO N, GAO H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Overexpressing Interleukin-35 Propagate Immunosuppressive Effects in Mice. Scand J Immunol. 2017;86(5):389-395. [48] WANG W, GUO H, LI H, et al. Interleukin-35 Gene-Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Concanavalin A-Induced Fulminant Hepatitis by Decreasing the Interferon Gamma Level. Hum Gene Ther. 2018;29(2):234-241. [49] HARRIS SG, PADILLA J, KOUMAS L, et al. Prostaglandins as modulators of immunity. Trends Immunol. 2002;23(3):144-150. [50] BREYER RM, BAGDASSARIAN CK, MYERS SA, et al. Prostanoid receptors: subtypes and signaling. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:661-690. [51] WOOLARD MD, WILSON JE, HENSLEY LL, et al. Francisella tularensis-infected macrophages release prostaglandin E2 that blocks T cell proliferation and promotes a Th2-like response. J Immunol. 2007;178(4):2065-2074. [52] ROZENBERG A, REZK A, BOIVIN MN, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Impact Th17 and Th1 Responses Through a Prostaglandin E2 and Myeloid-Dependent Mechanism. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016; 5(11):1506-1514. [53] AN JH, SONG WJ, LI Q, et al. Prostaglandin E2 secreted from feline adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate DSS-induced colitis by increasing regulatory T cells in mice. BMC Vet Res. 2018;14(1):354. [54] ZHUANG Y, ZHAO F, LIANG J, et al. Activation of COX-2/mPGES-1/ PGE2 Cascade via NLRP3 Inflammasome Contributes to Albumin-Induced Proximal Tubule Cell Injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2):797-807. [55] LUZ-CRAWFORD P, JORGENSEN C, DJOUAD F. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Direct the Immunological Fate of Macrophages. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017;62:61-72. [56] 曾宽,张露,邓保平,等. 前列腺素E1干预大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的旁分泌和迁移[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(17):2656-2660. [57] HAN J, LU X, ZOU L, et al. E-Prostanoid 2 Receptor Overexpression Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cell Attenuated Lung Injury. Hum Gene Ther. 2016;27(8):621-630. [58] 韩继斌. PGE2/EP2介导间充质干细胞向急性肺损伤小鼠肺组织归巢的效应和机制研究[D].南京:东南大学,2016. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [5] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [6] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [7] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [8] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [9] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [10] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [11] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [12] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [13] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [14] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [15] | Nie Huijuan, Huang Zhichun. The role of Hedgehog signaling pathway in transforming growth factor beta1-induced myofibroblast transdifferentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 754-760. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||