Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (25): 4060-4067.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2100
Previous Articles Next Articles
Insights into immunoregulatory properties of dental-derived mesenchymal stem cells in oral diseases
Wang Zhen1, Li Xiaolan1, Liu Jianguo1, 2
1School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China; 2Guizhou Province Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research and Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2019-11-22Revised:2019-11-29Accepted:2020-02-12Online:2020-09-08Published:2020-08-26 -
Contact:Liu Jianguo, MD, Professor, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China; Guizhou Province Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research and Key Laboratory of Oral Disease Research, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Zhen, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563099, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Key Discipline Construction Project of Guizhou Provincial High Institutions of Higher Education, No. ZDXK[2017]5 ; Provincial and Municipal Science and Technology Cooperation Special Fund (Subsidy Plan), No. (2014)41)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zhen, Li Xiaolan, Liu Jianguo.
Insights into immunoregulatory properties of dental-derived mesenchymal stem cells in oral diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4060-4067.
share this article
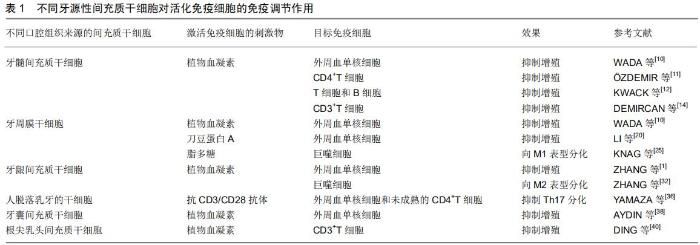
2 结果 Results 2.1 牙源性间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用 通常采用间充质干细胞和不同的免疫细胞亚群共培养的细胞模型进行体外间充质干细胞免疫调节能力的研究。大多数研究采用牙源性间充质干细胞与外周血单核细胞共同培养,然后通过分析免疫细胞亚群的特异性标记物来判断其功能特征的改变。外周血单核细胞由70%-90%的淋巴细胞(T细胞、B细胞和NK细胞)、10%-20%的单核细胞和1%-2%的树突状细胞组成。这些共培养模型容易控制,便于研究间充质干细胞免疫调节作用的机制,但是这样的共培养模型不能模仿细胞在体内环境中的相互作用,也不能评估间充质干细胞对不同亚群外周血单核细胞的直接影响。因此,将牙源性间充质干细胞与分离后的单一免疫细胞亚群进行共培养,成为当前研究的一大趋势。在这种共培养模式中,免疫细胞被不同的刺激物激活,如刀豆蛋白A、植物血凝素、抗CD3/CD28抗体、脂多糖等,虽然这些人为刺激激活的免疫细胞也不能完全代表体内的情况,但是这种方法能够更好地研究激活免疫细胞对牙源性间充质干细胞免疫调节能力的影响。间充质干细胞至少需要符合以下最低标准:第一,在标准细胞培养条件下,它们能够黏附于塑料培养板;第二,它们表达间充质干细胞的表面标记物CD29、CD73、CD90和CD105,而不表达造血干细胞的表面标记物CD11b、CD14、CD34、CD45和HLA-DR;第三,它们在体外一定条件下能够分化为成骨细胞、脂肪细胞和软骨细胞[8]。牙源性间充质干细胞可以从几种不同的口腔组织中提取分离,它们之间在组织学上存在差异,但这些牙源性间充质干细胞与身体其他组织来源的间充质干细胞一样,都具有调节不同免疫细胞亚群活性的能力。 2.1.1 牙髓干细胞的免疫调节作用 2002年,GRONTHOS等[9]第一次从牙髓中分离出间充质干细胞,并且符合关于间充质干细胞的所有标准。随后许多团队对牙髓干细胞与天然免疫系统和适应性免疫系统(T细胞、自然杀伤细胞、巨噬细胞以及补体系统)的相互作用进行了广泛的研究,并且取得了一定的进展。牙髓干细胞在免疫调节方面的作用主要体现在3个方面:①抑制免疫细胞的增殖。WADA等[10]研究中牙髓干细胞以细胞间非接触的方式抑制由植物血凝素激活的外周血单核细胞的增殖,并且使用干扰素γ预处理后的培养基对外周血单核细胞增殖也有抑制作用。在一项牙髓干细胞对植物血凝素激活的CD4+T细胞影响的实验中,干扰素γ启动的牙髓干细胞抑制T细胞增殖,降低白细胞介素17的产生,刺激调节性T细胞分化[11]。但也有另外的学者认为干扰素γ增强了牙髓干细胞对T细胞和B细胞的抑制作用,对调节性T细胞分化无影响[12]。因此,针对干扰素γ调节的牙髓干细胞对调节性T细胞分化的影响还存在争议。②诱导T细胞凋亡。体内T细胞凋亡被认为是抗炎反应的一种表现[13],牙髓干细胞与植物血凝素激活的CD3+T细胞共培养,能够抑制T细胞增殖、诱导T细胞凋亡及刺激调节性T细胞形成[14]。③牙髓干细胞可以影响体内巨噬细胞极化和激活补体系统。将牙髓干细胞移植到单侧后肢骨骼肌中会触发M2巨噬细胞极化并抑制坐骨神经炎症[15]。从健康和发炎牙髓组织中分离出的牙髓干细胞都能通过吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶依赖性机制抑制脂多糖触发的巨噬细胞分泌肿瘤坏死因子α[16]。此外,经脂磷壁酸处理过的牙髓干细胞几乎可以表达激活补体系统所需的所有因子。补体系统可能通过由牙髓干细胞表达的C3a和C5a补体系统受体来影响牙髓干细胞的增殖和动员[17]。 2.1.2 牙周膜干细胞的免疫调节作用 SEO等[18] 2004年首次从牙周膜中分离出牙周膜干细胞,并对其细胞生物学表征进行了分析。迄今为止,这些细胞已显示出对T细胞、B细胞、树突状细胞、巨噬细胞和嗜中性粒细胞的体外和体内免疫调节作用。首先,在对免疫细胞增殖的抑制方面,牙周膜干细胞与牙髓干细胞相似,可通过旁分泌机制抑制外周血单核细胞的增殖[10]。干扰素γ预处理的牙周膜干细胞与由植物血凝素激活的外周血单核细胞共同培养能够抑制T细胞增殖,刺激调节性T细胞分化并减少T细胞产生白细胞介素17[19]。从发炎牙周膜组织中分离出的牙周膜干细胞可以抑制T细胞分化为Th1和干扰素γ分泌,而从健康组织中分离出的牙周膜干细胞并没有这种作用。牙周膜干细胞还可以间接通过可溶性介质和直接细胞间接触抑制刀豆蛋白A激活的外周血单核细胞的增殖[20]。牙周膜干细胞具有抑制植物血凝素激活的外周血单核细胞的增殖能力和白细胞介素2和干扰素γ的分泌能力[21]。研究表明,牙周膜干细胞的STRO1+CD146+亚群通过抑制树突状细胞中非经典的主要组织相容性复合物样糖蛋白CD1b的表达来抑制T细胞增殖[22]。在人牙周膜干细胞移植到小型猪牙周炎模型的研究中,牙周膜干细胞主要通过程序性细胞死亡配体1介导的细胞间接触机制,对B细胞的增殖、分化和趋化性产生负调控,并通过白细胞介素6依赖性机制抑制B细胞凋亡[23]。然而,牙周膜干细胞对巨噬细胞的作用在文献中尚有争议。有文献报道,牙周膜干细胞可抑制鼠单核细胞/巨噬细胞RAW264.7细胞系中肿瘤坏死因子α的表达[24]。相反,另一项报道称未发现脂多糖预处理的牙周膜干细胞对人单核细胞/巨噬细胞THP-1细胞系极化产生影响,但可促进巨噬细胞向炎性M1表型分化[25]。此外,牙周膜干细胞可以诱导免疫细胞的抗炎反应。牙周膜干细胞与牙周膜细胞具有许多相同的特性。牙周膜成纤维细胞会增加巨噬细胞对牙龈卟啉单胞菌的吞噬作用[26]。牙龈卟啉单胞菌可通过细胞间接触和刺激牙周膜细胞分泌白细胞介素6和白细胞介素10来下调THP-1巨噬细胞产生肿瘤坏死因子α[27]。牙周膜干细胞也通过依赖于白细胞介素6的机制减少嗜中性粒细胞凋亡从而增强机体的抗菌能力[28]。除了对不同免疫细胞亚群的影响外,牙周膜干细胞还可以影响免疫细胞在组织中募集。脂多糖刺激的牙周膜干细胞降低了外周血单核细胞中CD29的表达,并抑制了外周血单核细胞的跨内皮迁移[29]。由中性粒细胞分化的白血病HL-60细胞具有产生活性氧的能力,当HL-60细胞与健康牙周膜干细胞共培养时,活性氧的产生被抑制;而与被牙龈卟啉单胞菌处理过的牙周膜干细胞共培养时,该能力又被激活了[30]。 2.1.3 牙龈间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用 牙龈是附着在牙槽骨上的一种特殊的口腔组织,被认为对口腔黏膜免疫具有重要意义。牙龈间充质干细胞被认为是以细胞为基础的治疗和再生的最佳干细胞来源[31]。ZHANG 等[1]于2009年首次分离出牙龈间充质干细胞并研究了其免疫调节特性,牙龈间充质干细胞被证明可以抑制由植物血凝素诱导的外周血单核细胞增殖。牙龈间充质干细胞不仅可以抑制小鼠CD4+T细胞增殖和向Th1/Th2/Th17分化,还可以促进外周血单核细胞衍生的巨噬细胞向M2表型极化[32]。利用THP-1巨噬细胞进行的一项研究表明,牙龈间充质干细胞抑制了M1巨噬细胞的活化,并促进了它们向M2表型的极化[33]。牙龈间充质干细胞还被证明通过前列腺素E2依赖机制抑制人肥大细胞株HMC-1释放炎性细胞因子,同时通过该机制抑制单核细胞来源树突状细胞的成熟和分化。牙龈成纤维细胞是从牙龈组织中分离出来的,在免疫调节能力上与牙龈间充质干细胞有许多共同的特性[34]。牙龈成纤维细胞对刀豆蛋白A诱导的外周血单核细胞增殖有抑制作用,这种作用在效果上与牙髓干细胞和牙周膜干细胞的作用相似[10]。 2.1.4 人脱落乳牙干细胞的免疫调节作用 2003年,MIURA等[35]首先从人脱落的乳牙中分离出间充质干细胞,并称其为人脱落的乳牙干细胞。这些细胞是从乳牙牙髓中获得的,与从恒牙分离的牙髓干细胞相比,它们具有更高的增殖率,更短的细胞增殖倍增时间和更强的骨诱导能力。一项使用抗CD3/CD28抗体激活的外周血单核细胞和未成熟的CD4+T细胞共培养实验表明,人脱落的乳牙干细胞具有比骨髓间充质干细胞更强的抑制Th17分化的作用效果[36]。此外,人脱落的乳牙干细胞能够使树突状细胞分泌的炎性细胞因子白细胞介素2、肿瘤坏死因子α和干扰素γ降低,以及抗炎性细胞因子白细胞介素10升高,增强树突状细胞诱导调节性T细胞的能力。人脱落的乳牙干细胞还能促进小鼠骨髓巨噬细胞向M2表型的极化[37]。 2.1.5 牙囊干细胞和根尖乳头干细胞的免疫调节作用 牙囊间充质干细胞和根尖乳头间充质干细胞分别于2005年和2006年从牙胚周围的外胚层组织和人根尖乳头组织中分离出来。只有少量的研究涉及这些牙间充质干细胞的免疫调节能力。在用Toll样受体3或Toll样受体4激动剂激活后,牙囊间充质干细胞通过吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶和转化生长因子β途径抑制由植物血凝素刺激的外周血单核细胞增殖[38]。感染牙周病原体(中间普氏菌或福赛斯坦纳菌)的牙囊间充质干细胞可降低中性粒细胞的趋化性和吞噬活性[39]。根尖乳头间充质干细胞与植物血凝素刺激的猪外周血单核细胞共培养可抑制CD3+ T细胞增殖[40]。 不同牙源性间充质干细胞对活化免疫细胞的免疫调节作用,见表1。 "
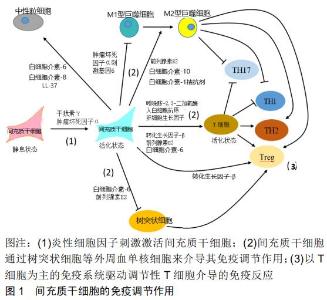
2.2 活化的免疫细胞对牙源性间充质干细胞免疫调节特性的调控 牙源性间充质干细胞的免疫调节特性是由周围的微环境决定的,未激活间充质干细胞的免疫调节能力通常较低。与其他来源间充质干细胞相似,炎症细胞因子可以激活牙源性间充质干细胞的免疫调节活性,活化的免疫细胞可以产生大量的炎性细胞因子,通过激活间充质干细胞显著增强间充质干细胞的免疫调节能力[41]。根据炎症水平,间充质干细胞可能采用免疫抑制表型或免疫刺激表型,再反向调节免疫细胞的活化,见图1[5]。 将牙源性间充质干细胞与刀豆蛋白A激活的外周血单核细胞直接共培养可抑制外周血单核细胞增殖,但与未被激活的外周血单核细胞共培养则没有表现出这种抑制作用[10]。干扰素γ可以增强牙髓干细胞抑制B细胞分泌免疫球蛋白的能力,而加入抗干扰素γ抗体后则可以抑制该能力[12]。在没有任何刺激因素的情况下牙龈成纤维细胞与外周血单核细胞共培养,牙龈成纤维细胞诱导了几种淋巴细胞的存活和增殖,但没有表现出免疫抑制作用[42]。这进一步说明活化的免疫细胞在诱导牙源性间充质干细胞免疫调节中起着重要的作用,两者之间存在着紧密的相互调节关系。 活化的免疫细胞诱导牙源性间充质干细胞中各种免疫调节蛋白表达上调。牙周膜干细胞、牙髓干细胞和牙龈成纤维细胞在与刀豆蛋白A激活的外周血单核细胞共培养时,可以明显上调吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶、环氧合酶2、肿瘤坏死因子Α-刺激基因6、白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β1和肝细胞生长因子的表达[20]。经多种刺激物如佛波醇乙酸甲酯/离子霉素、脂多糖、顺铂A和抗CD3/CD28抗体刺激后的外周血单核细胞条件培养基,也可上调牙周膜干细胞中吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶和环氧合酶2的表达[42]。与植物血凝素激活的CD3+ T细胞共培养后,牙髓干细胞中肝细胞生长因子、人白细胞抗原G5、白细胞介素6和转化生长因子β的表达上调[14]。植物血凝素活化的外周血单核细胞可以促进牙髓干细胞产生前列腺素E2、转化生长因子β和白细胞介素10[43]。与活化的B细胞共培养后,牙周膜干细胞中程序性细胞死亡配体1和程序性细胞死亡配体2的表达上调[44]。活化的肥大细胞通过肿瘤坏死因子α依赖性机制上调牙龈间充质干细胞中环氧合酶2表达和前列腺素E2的产生[45]。 炎性细胞因子可以上调牙源性间充质干细胞中各种免疫调节因子的表达[46]。在牙周膜干细胞和牙龈成纤维细胞中,干扰素γ诱导的吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶基因表达水平显著高于白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α,并且干扰素γ还显著提高了吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶的活 性[10,47]。干扰素γ诱导牙周膜干细胞中人白细胞抗原G5表达上调[44]。几种炎性细胞因子(包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、干扰素γ)对程序性细胞死亡配体1在牙周膜干细胞中的表达均有促进作用,其中肿瘤坏死因子α的作用明显大于其他细胞因子。此外,同时应用其他细胞因子可增强肿瘤坏死因子α对程序性细胞死亡配体1表达的影响[48-49]。有些免疫调节因子例如肝细胞生长因子和转化生长因子β在人牙周膜干细胞、牙髓干细胞和牙龈成纤维细胞中的表达不受干扰素γ的影响[10,44]。研究发现,只有同时应用白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素17A和干扰素γ才能上调牙周膜干细胞中转化生长因子β的表达,单独使用某一个细胞因子对转化生长因子β的影响不明显[50]。因此,可以假设某些炎性细胞因子仅激活特定的免疫调节特性。在这种假设下,用不同的细胞因子可能激活牙源性间充质干细胞中的特定免疫调节功能。 总之,活化免疫细胞与牙源性间充质干细胞之间通过炎性细胞因子互相调节,只有在活化的免疫细胞存在时,牙源性间充质干细胞抑制外周血单核细胞增殖的免疫调节能力才会产生。活化的免疫细胞可以刺激牙源性间充质干细胞中各种相应的免疫调节蛋白的上调,从而对间充质干细胞的免疫调节能力产生调控。如果能够明确每一种炎性细胞因子的具体免疫调节功能,将会显著提高间充质干细胞在疾病中的应用范围。 2.3 口腔致病菌对牙源性间充质干细胞免疫调节特性的调控 口腔是各种微生物的栖息地,宿主微生物的动态平衡是维持口腔健康的关键因素[51]。口腔疾病通常与这种动态平衡的破坏和细菌侵入口腔组织有关。龋病是在以细菌为主的多种因素作用下,牙体硬组织发生慢性进行性破坏的一种疾病,通常伴随革兰阳性菌及革兰阴性菌混合感染[52]。脂多糖作为这些细菌的主要毒力因子,沿着牙本质小管走行,入侵牙髓组织后可有效地激活免疫系统,诱导细胞释放炎症因子及抗炎因子,诱发宿主的炎症反应[53]。牙周炎症发生时,其主要致病菌牙龈卟啉单胞菌细胞外膜上的脂多糖会对牙周膜细胞产生很强的毒性和抗原性,在牙周病的发生发展过程中起重要作用[54]。牙周膜干细胞受脂多糖作用后可以合成并分泌前列腺素E2、白细胞介素1等多种细胞因子[55]。 在口腔疾病的炎症过程中,牙源性间充质干细胞移动至发炎区域被认为是促成炎症反应进程的重要因素,Toll样受体家族成员在不同牙源性间充质干细胞中都有表达,与牙源性间充质干细胞的免疫调节特性关系密 切[56]。口腔致病菌所表达的多种产物都可作为Toll样受体家族的激动剂被识别。如Toll样受体2可以识别细菌表面的三酰基脂肽(Pam3CSK4),Toll样受体4可以识别革兰阴性菌表面的脂多糖,Toll样受体5可以识别细菌表面的菌毛蛋白等[57]。脂多糖作为激动剂在间充质干细胞的体外细胞实验中得到了广泛研究,用牙龈卟啉单胞菌衍生的脂多糖可以增强牙龈成纤维细胞抑制外周血单核细胞增殖的能力,虽然它的增强作用比干扰素γ小的多,但当牙龈卟啉单胞菌衍生的脂多糖与干扰素γ共同使用时,可增强干扰素γ诱导的牙龈成纤维细胞的免疫抑制能力[58]。 Toll样受体激动剂和细菌代谢产物可能会刺激牙源性间充质干细胞中各种免疫调节蛋白的表达。以吲哚 胺-2,3-二加氧酶的表达为例,大肠杆菌(E. coli)衍生的脂多糖可刺激牙周膜干细胞产生犬尿氨酸,从而提高吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶的表达水平和活性[59]。但是不同类别的Toll样受体激动剂对吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶表达的影响也存在不同。Toll样受体2激动剂Pam3CSK4可以增加吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶的基因表达,对蛋白表达没有任何影响。Toll样受体4激动剂脂多糖诱导的吲哚 胺-2,3-二加氧酶在基因水平和蛋白质水平上都有明显的表达增加[47]。细菌脂多糖、Toll样受体3激动剂和Toll样受体5激动剂都可以诱导牙龈细胞中具有更高的吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶mRNA表达水平,其中Toll样受体3激动剂的诱导效果显著高于其他Toll样受体激动剂[60]。不同组织来源的牙源性间充质干细胞在Toll样受体激动剂对吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶表达的影响上也存在差异。例如,在脂多糖诱导时牙囊间充质干细胞中吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶表达不受影响,而牙髓干细胞中吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶表达受到抑制[61]。在牙龈成纤维细胞中,牙龈卟啉单胞菌产生的脂多糖诱导吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶的基因表达显著增加,但对吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶活性没有影响[44]。 最初,人们认为脂多糖作为Toll样受体4激动剂激活间充质干细胞会产生一种促炎表现,能够刺激免疫反应;用Toll样受体3激动剂激活的间充质干细胞可能产生抗炎表现,抑制免疫反应。然而,最近的一项研究却得出了不同的结论,在Toll样受体3和Toll样受体4激活后,间充质干细胞诱导调节性T细胞分化的能力得到了增强,对T细胞活化的抑制能力则减弱了,两者都表现出了明显的免疫促进作用[60]。另外,相同的Toll样受体激动剂针对不同来源间充质干细胞也可能表现出不一样的作用,例如Toll样受体4激动剂增强了牙囊间充质干细胞对外周血单核细胞增殖的抑制作用,却减弱了牙髓干细胞对外周血单核细胞增殖的抑制特性[61]。Toll样受体激动剂与牙源性间充质干细胞免疫调节方面的具体作用机制还有待进一步探索。 2.4 牙源性间充质干细胞介导的免疫调节在口腔疾病中的潜在作用 细菌来源的Toll样受体激动剂可以影响牙源性间充质干细胞中免疫调节因子的表达,在厌氧条件下牙周病原体(牙龈卟啉单胞菌和核梭形杆菌)可以诱导牙囊间充质干细胞产生白细胞介素10,上调牙周膜干细胞中程序性细胞死亡配体1的表达[49]。因此,受炎症程度和微环境的影响,牙源性间充质干细胞的促炎和抗炎特性在口腔疾病的发展进程中可能发挥着非常重要的作用。尽管牙源性间充质干细胞的免疫调节能力已得到广泛认可,但它在各种口腔疾病的中的确切作用机制仍然停留在假设阶段。炎症环境可能对间充质干细胞的免疫调节特性产生重大影响,这一点在从发炎组织和健康组织中分离出的各种间充质干细胞表现中已经得到了充分体现。从发炎组织中分离出的牙周膜干细胞比从健康组织中分离出的牙周膜干细胞具有更高的增殖和迁移能力,发炎组织中分离的牙周膜干细胞和外周血单核细胞共培养后白细胞介素2、肿瘤坏死因子α和干扰素γ水平更高,牙周膜干细胞促进调节性T细胞诱导和抑制Th17分化的能力在炎性条件下受到抑制[21]。提取自牙髓炎患牙中的牙髓干细胞不能抑制外周血单核细胞增殖,但是通过加入干扰素γ后可以恢复抑制增殖的能力[62]。在调节巨噬细胞功能的能力上,两者没有差别[15]。在小鼠牙周炎模型中,牙周组织和牙周膜干细胞中程序性细胞死亡配体1的表达量与涂抹牙龈卟啉单胞菌所引起的牙周疾病的严重程度呈负相关[49]。在发炎的人类牙髓组织中,巨噬细胞和间充质干细胞中吲哚胺-2,3-二加氧酶的表达量显著增加[15]。经肿瘤坏死因子Α-刺激基因6激活的间充质干细胞局部或者全身应用到患有实验性牙周炎大鼠中,可降低炎性细胞因子白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达水平,并能减少破骨细胞形成,显著改善大鼠牙槽骨吸收[63]。 通过这些实验结果,可以得出这样的假设:牙源性间充质干细胞可以影响牙髓炎、牙龈炎和牙周炎等口腔疾病的发展,还可以改善疾病的治疗效果。如果能够更进一步明确每一种炎性细胞因子在间充质干细胞免疫调节特性中的具体功能,以及口腔微生物如何通过Toll样受体途径影响牙源性间充质干细胞的免疫调节能力。在未来的口腔疾病治疗中,不同组织的疾病可以使用相应组织来源的活化干细胞,通过调控免疫特性来达到治疗疾病的目的。例如,牙周疾病可以使用具有特定调节作用的炎性细胞因子活化牙周膜干细胞,调控疾病进程,这为口腔疾病的治疗手段提供了一个新的思路。 "
|
[1] ZHANG Q, SHI S, LIU Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human gingiva are capable of immunomodulatory functions and ameliorate inflammation-related tissue destruction in experimental colitis. J Immunol. 2009;183(12):7787-7798.
[2] YANG R, YU T, ZHOU Y. Interplay between craniofacial stem cells and immune stimulus. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):147.
[3] MA OK, CHAN KH. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells: Interplay between mesenchymal stem cells and regulatory lymphocytes. World J Stem Cells. 2016;8(9):268-278.
[4] MUNN DH, MELLOR AL. Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase and metabolic control of immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2013;34(3):137-143.
[5] FONTAINE MJ, SHIH H, SCHÄFER R, et al. Unraveling the Mesenchymal Stromal Cells' Paracrine Immunomodulatory Effects. Transfus Med Rev. 2016;30(1):37-43.
[6] KALINSKI P. Regulation of immune responses by prostaglandin E2. J Immunol. 2012;188(1):21-28.
[7] NEMETH K,KEANE-MYERS A, BROWN JM, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells use TGF-beta to suppress allergic responses in a mouse model of ragweed-induced asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107(12):5652-5657.
[8] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006; 8(4):315-317.
[9] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[10] WADA N, MENICANIN D, SHI S, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of human periodontal ligament stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219(3): 667-676.
[11] ÖZDEMIR AT, ÖZGÜL ÖZDEMIR RB, KIRMAZ C, et al. The paracrine immunomodulatory interactions between the human dental pulp derived mesenchymal stem cells and CD4 T cell subsets. Cell Immunol. 2016;310:108-115.
[12] KWACK KH, LEE JM, PARK SH, et al. Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Suppress Alloantigen-induced Immunity by Stimulating T Cells to Release Transforming Growth Factor Beta. J Endod. 2017;43(1): 100-108.
[13] ZHAO Y, WANG L, JIN Y, et al. Fas ligand regulates the immunomodulatory properties of dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2012;91(10):948-954.
[14] DEMIRCAN PC, SARIBOYACI AE, UNAL ZS, et al. Immunoregulatory effects of human dental pulp-derived stem cells on T cells: comparison of transwell co-culture and mixed lymphocyte reaction systems. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(10):1205-1220.
[15] OMI M, HATA M, NAKAMURA N, et al. Transplantation of dental pulp stem cells suppressed inflammation in sciatic nerves by promoting macrophage polarization towards anti-inflammation phenotypes and ameliorated diabetic polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Investig. 2016;7(4): 485-496.
[16] LEE S, ZHANG QZ, KARABUCAK B, et al. DPSCs from Inflamed Pulp Modulate Macrophage Function via the TNF-α/IDO Axis. J Dent Res. 2016;95(11):1274-1281.
[17] RUFAS P, JEANNEAU C, ROMBOUTS C, et al. Complement C3a Mobilizes Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Specifically Guides Pulp Fibroblast Recruitment. J Endod. 2016;42(9):1377-1384.
[18] SEO BM, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):149-155.
[19] LIU D, XU J, LIU O, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from inflamed periodontal ligaments exhibit impaired immunomodulation. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(12):1174-1182.
[20] LI C, WANG X, TAN J, et al. The immunomodulatory properties of periodontal ligament stem cells isolated from inflamed periodontal granulation. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014;199(4):256-265.
[21] TANG HN, XIA Y, YU Y, et al. Stem cells derived from "inflamed" and healthy periodontal ligament tissues and their sheet functionalities: a patient-matched comparison. J Clin Periodontol. 2016;43(1):72-84.
[22] SHIN C, KIM M, HAN JA, et al. Human periodontal ligament stem cells suppress T-cell proliferation via down-regulation of non-classical major histocompatibility complex-like glycoprotein CD1b on dendritic cells. J Periodontal Res. 2017;52(1):135-146.
[23] LIU O, XU J, DING G, et al. Periodontal ligament stem cells regulate B lymphocyte function via programmed cell death protein 1. Stem Cells. 2013;31(7):1371-1382.
[24] NAGATA M, IWASAKI K, AKAZAWA K, et al. Conditioned Medium from Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Enhances Periodontal Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(9-10):367-377.
[25] KANG H, LEE MJ, PARK SJ, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Preconditioned Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Induce M1 Polarization of Macrophages through Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(12): E3843.
[26] SILVÉRIO KG, RODRIGUES TL, COLETTA RD, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell properties of periodontal ligament cells from deciduous and permanent teeth. J Periodontol. 2010;81(8):1207-1215.
[27] TZACH-NAHMAN R, NASHEF R, FLEISSIG O, et al. Oral fibroblasts modulate the macrophage response to bacterial challenge. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):11516.
[28] WANG Q, DING G, XU X. Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Regulate Apoptosis of Neutrophils. Open Med (Wars). 2017;12:19-23.
[29] KUKOLJ T, TRIVANOVIĆ D, DJORDJEVIĆ IO, et al. Lipopolysaccharide can modify differentiation and immunomodulatory potential of periodontal ligament stem cells via ERK1,2 signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(1):447-462.
[30] MISAWA MYO, SILVÉRIO RUIZ KG, NOCITI FH Jr, et al. Periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate neutrophil responses via paracrine mechanisms. J Periodontol. 2019;90(7): 747-755.
[31] GRAWISH ME. Gingival-derived mesenchymal stem cells: An endless resource for regenerative dentistry. World J Stem Cells. 2018;10(9): 116-118.
[32] ZHANG QZ, SU WR, SHI SH, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells elicit polarization of m2 macrophages and enhance cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells. 2010;28(10): 1856-1868.
[33] ZHANG X, HUANG F, LI W, et al. Human Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulate Monocytes/Macrophages and Alleviate Atherosclerosis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:878.
[34] DU L, YANG P, GE S. Isolation and characterization of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells using limiting dilution method. J Dent Sci. 2016;11(3):304-314.
[35] MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, ZHAO M, et al. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003; 100(10):5807-5812.
[36] YAMAZA T, KENTARO A, CHEN C, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(1):5.
[37] GAO X, SHEN Z, GUAN M, et al. Immunomodulatory Role of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth on Periodontal Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(17-18):1341-1353.
[38] AYDIN S, ŞAHIN F. Stem Cells Derived from Dental Tissues. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1144:123-132.
[39] HIEKE C, KRIEBEL K, ENGELMANN R, et al. Human dental stem cells suppress PMN activity after infection with the periodontopathogens Prevotella intermedia and Tannerella forsythia. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39096.
[40] DING G, LIU Y, AN Y, et al. Suppression of T cell proliferation by root apical papilla stem cells in vitro. Cells Tissues Organs. 2010;191(5): 357-364.
[41] KRAMPERA M. Mesenchymal stromal cell 'licensing': a multistep process. Leukemia. 2011;25(9):1408-1414.
[42] MOONEN CGJ, ALDERS ST, BONTKES HJ, et al. Survival, Retention, and Selective Proliferation of Lymphocytes Is Mediated by Gingival Fibroblasts. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1725.
[43] HOSSEIN-KHANNAZER N, HASHEMI SM, NAMAKI S, et al. Study of the immunomodulatory effects of osteogenic differentiated human dental pulp stem cells. Life Sci. 2019;216:111-118.
[44] KIM JH, JO CH, KIM HR, et al. Comparison of Immunological Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Periodontal Ligament, Umbilical Cord, and Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells Int. 2018; 2018:8429042.
[45] SU WR, ZHANG QZ, SHI SH, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate contact hypersensitivity via prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanisms. Stem Cells. 2011;29(11): 1849-1860.
[46] 岳艳,屈艺,母得志.间充质干细胞源性外泌体在脑损伤治疗中的研究进展[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2017,19(12):1285-1290.
[47] ANDRUKHOV O, HONG JS, ANDRUKHOVA O, et al. Response of human periodontal ligament stem cells to IFN-γ and TLR-agonists. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12856.
[48] ISSARANGGUN NA AYUTHAYA B, SATRAVAHA P, PAVASANT P. Interleukin-12 modulates the immunomodulatory properties of human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 2017;52(3):546-555.
[49] ZHANG J, WANG CM, ZHANG P, et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligand 1 on periodontal tissue cells as a possible protective feedback mechanism against periodontal tissue destruction. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):2423-2430.
[50] KONERMANN A, BEYER M, DESCHNER J, et al. Human periodontal ligament cells facilitate leukocyte recruitment and are influenced in their immunomodulatory function by Th17 cytokine release. Cell Immunol. 2012;272(2):137-143.
[51] OLSEN I, LAMBRIS JD, HAJISHENGALLIS G. Porphyromonas gingivalis disturbs host-commensal homeostasis by changing complement function. J Oral Microbiol. 2017;9(1):1340085.
[52] 刘畅,王家凤,张志民.Toll样受体的免疫调节在口腔疾病中的研究进展[J].口腔生物医学, 2018,9(1):45-48.
[53] LIU Y, GAO Y, ZHAN X, et al. TLR4 activation by lipopolysaccharide and Streptococcus mutans induces differential regulation of proliferation and migration in human dental pulp stem cells. J Endod. 2014;40(9):1375-1381.
[54] 曹采方.牙周病学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2013.
[55] 范芹,管晓燕,李小娜,等.茶多酚对脂多糖介导下人牙周膜成纤维细胞COX-2表达的影响[J].广东医学,2016,37(17):2566-2568.
[56] MEKHEMAR MK, ADAM-KLAGES S, KABELITZ D, et al. TLR-induced immunomodulatory cytokine expression by human gingival stem/progenitor cells. Cell Immunol. 2018;326:60-67.
[57] COCHET F, PERI F. The Role of Carbohydrates in the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Signalling. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11): E2318.
[58] MAHANONDA R, SA-ARD-IAM N, MONTREEKACHON P, et al. IL-8 and IDO expression by human gingival fibroblasts via TLRs. J Immunol. 2007;178(2):1151-1157.
[59] MOON JS, CHEONG NR, YANG SY, et al. Lipopolysaccharide- induced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression in the periodontal ligament. J Periodontal Res. 2013;48(6):733-739.
[60] RASHEDI I, GÓMEZ-ARISTIZÁBAL A, WANG XH, et al. TLR3 or TLR4 Activation Enhances Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Mediated Treg Induction via Notch Signaling. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):265-275.
[61] TOMIC S, DJOKIC J, VASILIJIC S, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp and dental follicle are susceptible to activation by toll-like receptor agonists. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(4):695-708.
[62] SONODA S, YAMAZA H, MA L, et al. Interferon-gamma improves impaired dentinogenic and immunosuppressive functions of irreversible pulpitis-derived human dental pulp stem cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19286.
[63] YANG H, APRECIO RM, ZHOU X, et al. Therapeutic effect of TSG-6 engineered iPSC-derived MSCs on experimental periodontitis in rats: a pilot study. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100285.
[64] MESTAS J, HUGHES CC. Of mice and not men: differences between mouse and human immunology. J Immunol. 2004;172(5):2731-2738. |
| [1] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [2] | Cheng Yanan, Wu Yucong, Mao Qiuhua, Chen Ling, Lu Liying, Xu Pu. Restoration effect and stability of resin infiltration combined with bioactive glass on demineralized tooth enamel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3522-3526. |
| [3] | Jing Huimin, Yu Wenjuan, Wang Sijia, Chen Cong, Li Yifan, Wang Yonglan, Li Xin, Zhang Juan, Liang Meng. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of the brain’s default mode network in patients with sleep bruxism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 685-689. |
| [4] |
Li Junqing, Wu Jiayuan.
Effect of mechanical stimulation on dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4054-4059. |
| [5] | Wu Dalei, Zhou Shouheng, Yan Jianwei, Li Bo, Xu Nuo, Shi Chun, Gao Yang. Alcohol extract of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. promotes bone healing in rats with periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3685-3689. |
| [6] | Xu Nuo, Cao Zhen, Li Xiaojie, Shi Chun. MicroRNA-21 regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoclasts in periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1225-1230. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||