[1] LOBBEZOO F, AHLBERG J, GLAROS AG, et al. Bruxism defined and graded: an international consensus. J Oral Rehabil. 2013;40(1):2-4.
[2] MALULY M, ANDERSEN ML, DAL-FABBRO C, et al. Polysomnographic study of the prevalence of sleep bruxism in a population sample. J Dent Res. 2013; 92 (7 Suppl): 97S.
[3] DE MEYER MD, DE BOEVER JA. The role of bruxism in the appearance of temporomandibular joint disorders. Rev Belge Med Dent. 1997;52(4):124.
[4] VANDERAS AP, MANETAS KJ. Relationship between malocclusion and bruxism in children and adolescents: a review. Pediatr Dent. 1995;17(1): 7-12.
[5] CLARK GT, ADLER RC. A critical evaluation of occlusal therapy: occlusal adjustment procedures. J Am Dent Assoc.1985;110(5):743-750.
[6] SHETTY S, PITTI V, SATISH BABU CL, et al. Bruxism: a literature review. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2010;10(3):141-148.
[7] KUHN M, TüRP JC. Risk factors for bruxism. Swiss Dent. 2018; 128(2): 118.
[8] NUKAZAWA S, YOSHIMI H, SATO S. Autonomic nervous activities associated with bruxism events during sleep. Cranio. 2018;36(2):106-112.
[9] FAN X, QU F, WANG JJ, et al. Decreased GABA Levels in the Brainstem in Patients with Possible Sleep Bruxism: A Pilot Study. J Oral Rehabil. 2017; 44(12):934-940.
[10] RAICHLE ME. The brain’s default mode network. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2015;38: 433-447.
[11] RAICHLE ME, MACLEOD AM, SNYDER AZ, et al. A default mode of brain function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(2):676-682.
[12] MAREK T, FAFROWICZ M, GOLONKA K, et al. Diurnal patterns of activity of the orienting and executive attention neuronal networks in subjects performing a Stroop-like task: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Chronobiol Int. 2010;27(5):945-958.
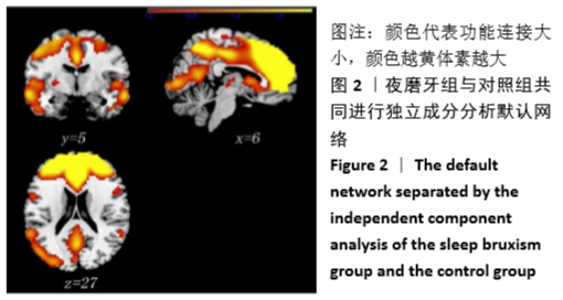
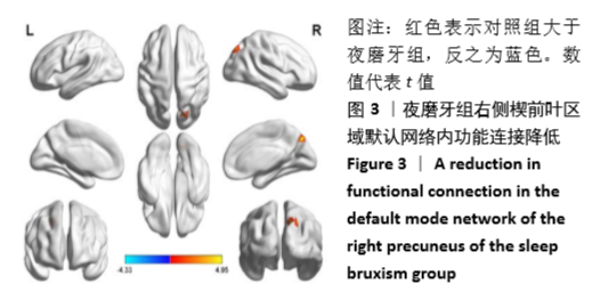
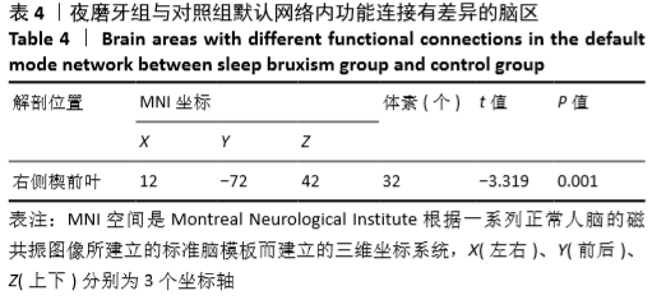
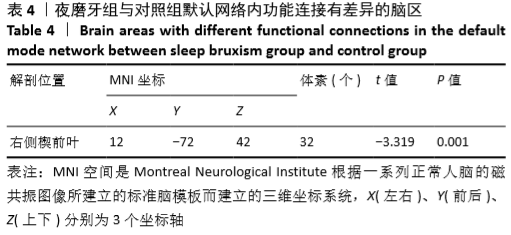
[13] 张艳波,郑金瓯.脑默认网络的神经机制及临床应用研究进展[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2017,36(9): 206-211.
[14] DUCHNA HW. Sleep-related breathing disorders--a second edition of the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-2) of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM). Pneumologie. 2006; 60(9): 568-575.
[15] LAVIGNE GJ, KATO T, KOLTA A, et al. Neurobiological mechanisms involved in sleep bruxism. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003; 14(1): 30.
[16] KARA MI, YANıK S, KESKINRUZGAR A, et al. Oxidative imbalance and anxiety in patients with sleep bruxism. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012; 114(5): 604-609.
[17] AZEVEDO MR, SENA R, De FREITAS AM, et al. Neuro-behavioral pattern of sleep bruxism in wakefulness. Res Biomed Eng. 2018; 34(1): 1-8.
[18] YILMAZ S. To see bruxism: a functional MRI study. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2015; 44(7):20150019.
[19] LAVIGNE GJ, HUYNH N, KATO T, et al. Genesis of sleep bruxism: motor and autonomic-cardiac interactions. Arch Oral Biol. 2007;52(4):381-384.
[20] KERVANCIOGLU BB, TEISMANN IK, RAIN M, et al. Sensorimotor cortical activation in patients with sleep bruxism. J Sleep Res. 2012; 21(5): 507-514.
[21] VAN DEN HEUVEL MP, HULSHOFF POL HE. Exploring the brain network: a review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010; 20(8):519-534.
[22] GAO W, CHEN S, BISWAL B, et al. Temporal dynamics of spontaneous default-mode network activity mediate the association between reappraisal and depression. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2018;13(12):1235-1247.
[23] VICENTINI JE, WEILER M, ALMEIDA SRM, et al. Depression and anxiety symptoms are associated to disruption of default mode network in subacute ischemic stroke. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017;11(6):1571-1580.
[24] CHEN WH, CHEN J, LIN X, et al. Dissociable effects of sleep deprivation on functional connectivity in the dorsal and ventral default mode networks. Sleep Med. 2018;50:137-144.
[25] LUNSFORD-AVERY JR, DAMME KSF, ENGELHARD MM, et al. Sleep/Wake Regularity Associated with Default Mode Network Structure among Healthy Adolescents and Young Adults. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):509.
[26] CABEZA R, NYBERG L. Imaging cognition II: An empirical review of 275 PET and fMRI studies. J Cogn Neurosci. 2000;12(1):1-47.
[27] MAQUET P, DEGUELDRE C, DELFIORE G, et al. Functional neuroanatomy of human slow wave sleep. J Neurosci. 1997; 17(8): 2807-2812.
[28] MAQUET P, PéTERS JM, AERTS J, et al. Functional neuroanatomy of human rapid-eye-movement sleep and dreaming. Nature. 1996; 383(6596): 163-166.
[29] RAINVILLE P, HOFBAUER RK, PAUS T, et al. Cerebral mechanisms of hypnotic induction and suggestion. J Cogn Neurosci. 1999;11(1):110-125.
[30] ZHANG L, HUANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Enhanced high-frequency precuneus-cortical effective connectivity is associated with decreased sensory gating following total sleep deprivation. Neuroimage. 2019;197:255-263. |