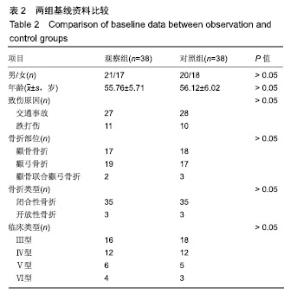
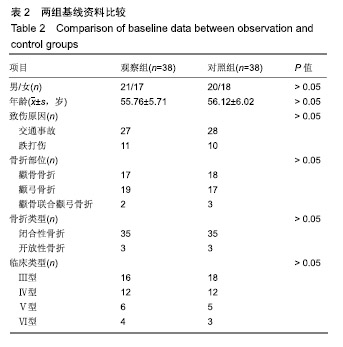
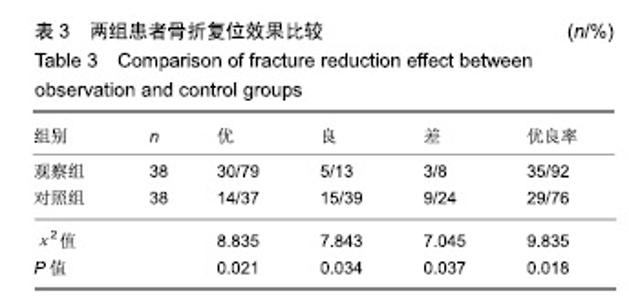
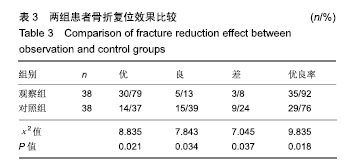
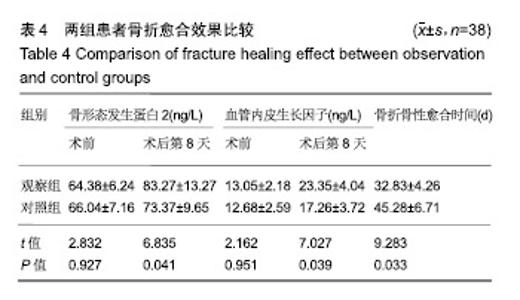
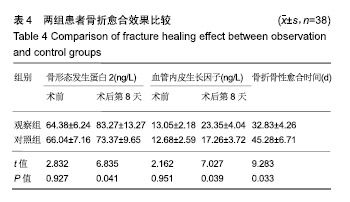
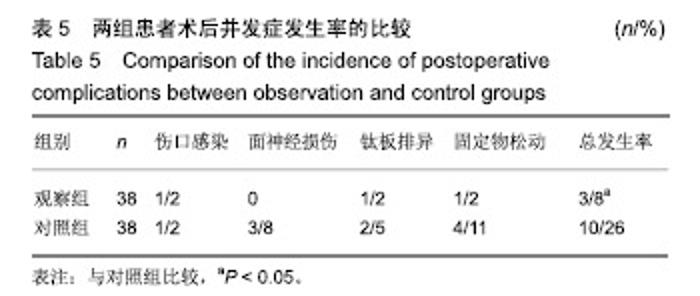
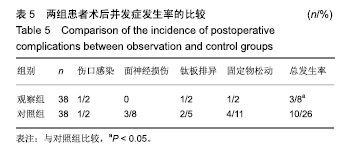
| [1]白建中,王永祥,王静成,等. 3D打印辅助手术与传统手术治疗Pilon骨折疗效比较的荟萃分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018, 26(22):2073-2077.[2]张擎柱,万乾,张义,等.3D打印技术辅助改良后内侧倒L入路切开复位内固定术治疗复杂胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2018,32(11):1091-1093.[3]阳宏奇,雷青,蔡立宏,等.3D打印导板辅助空心螺钉内固定治疗不稳定性骨盆骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(2):145-151.[4]何藻鹏,李卫,刘金伟,等.3D打印技术在SandersⅢ型跟骨骨折内固定手术设计中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2017,19(9):791-796.[5]郑锋,余正希,陈宣煌,等.基于数字化设计和3D打印胫骨近端骨折内固定的关键技术[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(26): 3837-3842.[6]李振威,蒋玮,桂斌捷,等.3D打印钢板在儿童骨折内固定手术中的应用研究[J].生物医学工程与临床,2018,22(5):546-550.[7]王向前,张计超,李军,等. 3D打印技术辅助跗骨窦入路钢板内固定治疗Sanders Ⅱ、Ⅲ型跟骨骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2018,33(8):881-883.[8]柳鑫,曾参军,卢键森,等.3D打印计算机虚拟辅助技术在髋臼骨折术前规划中的应用[J].南方医科大学学报, 2017,37(3): 378-382.[9]许思亮,古汉南,何玥,等.3D打印技术在桡骨远端骨折复位内固定手术中的应用[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志, 2018,10(3): 133-139.[10]赵景新,马雅昌,朱雅文,等.3D打印用于青少年Salter-Harris Ⅱ型桡骨远端骨折辅助治疗的临床效果分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2018,36(3):346-348,351.[11]肖维维,陈媛丽,宗春琳,等.应用外科导航技术经皮微小切口拆除颧骨颧弓骨折术后内固定钛板[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2018,12(1):31-36.[12]徐冰冰,李雅南,来庆国,等.3D打印术前设计和内镜辅助在颧骨颧弓骨折复位固定术中的应用[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2018, 16(1):44-47.[13]克热木•阿巴司,凌彬,买买提吐逊•吐尔地,等.改良耳颞-结膜-口内联合切口治疗眼眶-上颌-颧骨、颧弓复合体骨折[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(5):464-469.[14]Kalfarentzos EF,Deligianni D,Mitros G,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of plating techniques for fixing mandibular angle fractures: the introduction of a new 3D plate approach.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;13(3):139-144.[15]吴海斌,张昊天.中医骨折分期治疗对骨折愈合bFGF、TGF-β、VEGF、BMP-2基因表达影响的实验研究[J].哈尔滨医药,2016, 36(3):290-291.[16]曾中华,余黎,龚玲玲,等.骨折愈合过程中BMP-2和VEGF的表达[J].武汉大学学报(医学版),2005,26(4):467-469.[17]熊为,丁金玉,张劲松,等.血府逐瘀汤对股骨颈骨折患者TGF-β、VEGF及BMP-2表达的影响[J].现代生物医学进展, 2016,16(5): 901-903. [18]郭瑞,洪凯峰,郭栋,等.3D打印技术在胫骨骨折畸形愈合矫形手术中的应用[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(1):50-52,57.[19]马腾,魏代好,秦悦,等.常规影像学结合3D打印技术在复杂胫骨平台骨折治疗中的应用[J].宁夏医科大学学报, 2017,39(12): 1452-1454.[20]刘正武,覃向明,陈凤强,等.内窥镜辅助下3D打印技术治疗颧骨颧弓骨折的临床效果[J].广西医学,2019,41(2):255-257.[21]申智敏,段宜强,叶川,等.3D打印导航模块及联合数字化设计在髋臼骨折中的应用研究[J].重庆医学,2019,48(2):301-304,309.[22]张擎柱,张义,付世杰,等.采用3D打印技术辅助手术治疗复杂髋臼骨折效果分析[J].临床误诊误治,2018,31(12):37-40.[23]杨伟兵,张勇智,杨登峰,等.3D打印技术辅助髂骨翼重建髋臼后壁联合内固定治疗髋臼后壁粉碎性骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(12):1270-1271.[24]赵殿才,聂玉洁,欧阳舢,等.3D打印复合型种植导板在游离端牙缺失种植修复中的临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(14):2179-2184.[25]郇科,苏菲,王飞,等.3D打印技术在骶骨骨折治疗中的临床应用[J].中国医药导报,2018,15(24):67-70,83. |