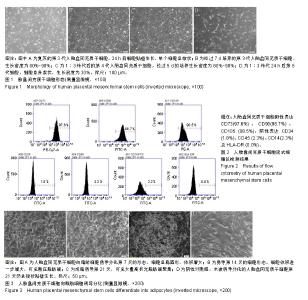
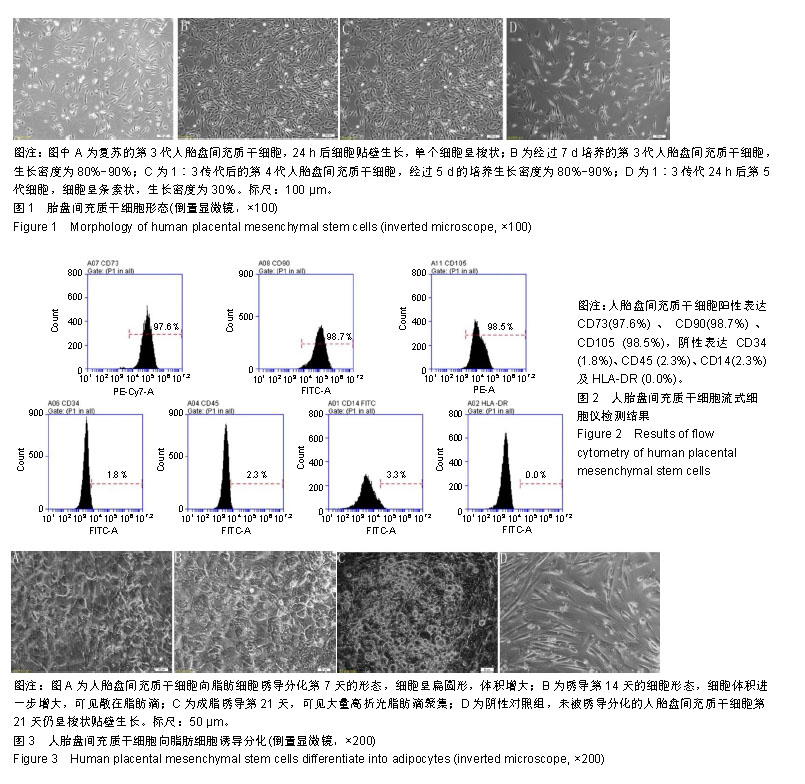
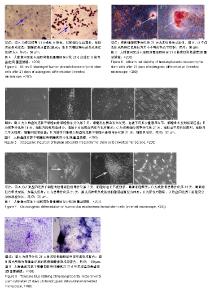
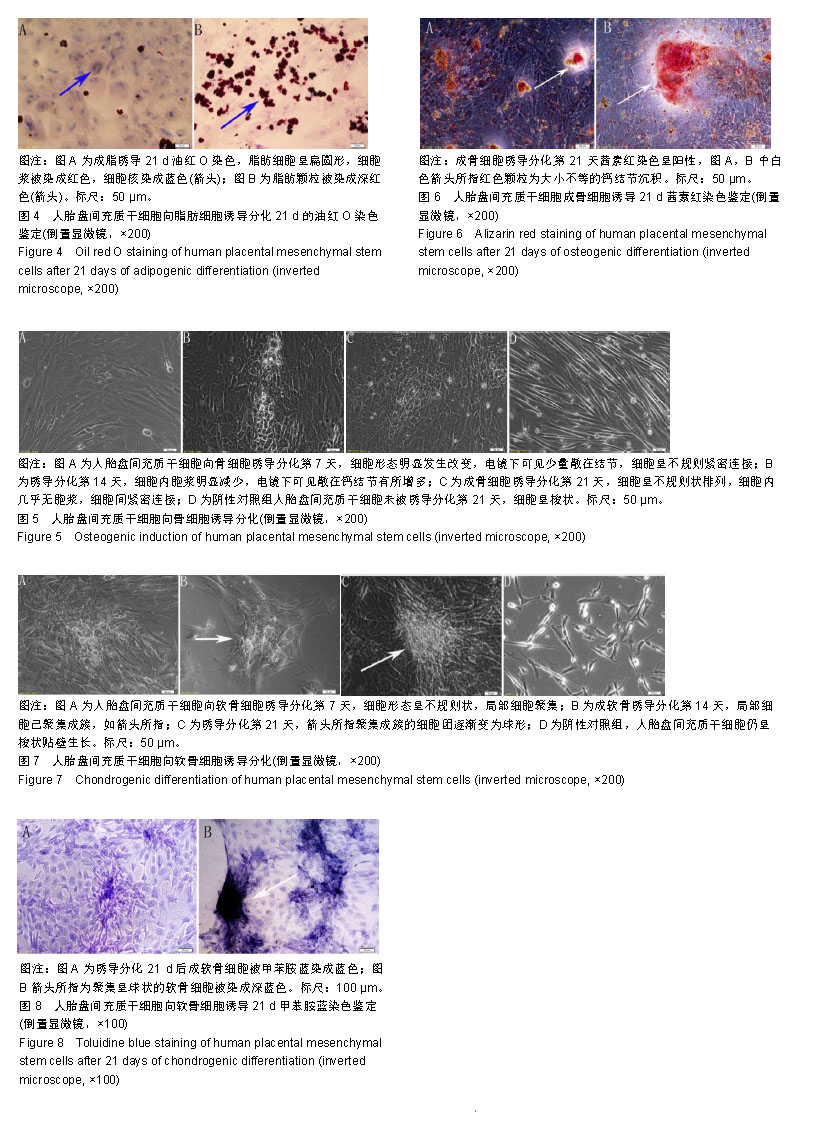
| [1]Pelekanos RA, Sardesai VS, Futrega K, et al.Isolation and Expansion of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells Derived from Human Placenta Tissue.J Vis Exp. 2016;(112). doi: 10.3791/54204.[2]Pham H, Tonai R, Wu M, et al.CD73, CD90, CD105 and Cadherin-11 RT-PCR Screening for Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Cryopreserved Human Cord Tissue.Int J Stem Cells. 2018;11(1):26-38.[3]Huang YC, Yang ZM, Chen XH, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human placental decidua basalis and resistance to hypoxia and serum deprivation. Stem Cell Rev. 2009;5(3):247-255. [4]Barlow S, Brooke G, Chatterjee K, et al. Comparison of human placenta- and bone marrow-derived multipotent mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(6):1095-1107.[5]Antoniadou E, David AL. Placental stem cells. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2016;31:13-29.[6]Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy.2006;8(4):315-317.[7]Sousa BR, Parreira RC, Fonseca EA, et al. Human adult stem cells from diverse origins: An overview from multiparametric immunophenotyping to clinical applications. Cytometry A. 2014;85(1):43-77.[8]Kobolak J, Dinnyes A, Memic A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: Identification, phenotypic characterization, biological properties and potential for regenerative medicine through biomaterial micro-engineering of their niche.Methods. 2016;99:62-68.[9]Bharti D, Shivakumar SB, Park JK, et al. Comparative analysis of human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells derived from different parts of the same umbilical cord. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;372(1):51-65. [10]朱永朝,马海滨,刘婷,等.干扰素-γ对人胎盘胎儿来源间充质干细胞免疫调节功能的影响[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2012, 28(10):1058-1061. [11]Xu M, Liu G, Jia Y, et al.Transplantation of human placenta mesenchymal stem cells reduces the level of inflammatory factors in lung tissues of mice with acute lung injury.Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;34(2):105-109. [12]Horn P, Bork S, Wagner W. Standardized Isolation of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells with Red Blood Cell Lysis. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;698:23-35.[13]Tuan RS, Boland G, Tuli R. Adult mesenchymal stem cells and cell-based tissue engineering. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003; 5(1):32-45.[14]Jo CH, Lim HJ, Yoon KS. Characterization of Tendon-Specific Markers in Various Human Tissues, Tenocytes and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019; 16(2):151-159.[15]Wang Q, Yang Q, Wang Z, et al. Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from fetal-bone marrow, adipose tissue, and Warton''s jelly as sources of cell immunomodulatory therapy. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016;12(1):85-96.[16]Le Blanc K, Gtherstrm C, Ringdn O, et al. Fetal mesenchymal stem-cell engraftment in bone after in utero transplantation in a patient with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. Transplantation. 2005;79(11):1607-1614.[17]Murabayashi D, Mochizuki M, Tamaki Y, et al. Practical methods for handling human periodontal ligament stem cells in serum-free and serum-containing culture conditions under hypoxia: implications for regenerative medicine. Human Cell.2017;30(3):169-180.[18]Gentile P, Scioli MG, Bielli A, et al. Stem cells from human hair follicles: first mechanical isolation for immediate autologous clinical use in androgenetic alopecia and hair loss[J]. Stem Cell Investigation, 2017,4(7):58-58.[19]Khosravi M, Azarpira N, Shamdani S, et al. Differentiation of umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells to hepatocyte cells by transfection of miR-106a, miR-574-3p, and miR-451. Gene. 2018;667:1-9.[20]Lu Y, Wang Z, Chen L, et al. The in vitro differentiation of GDNF gene-engineered amniotic fluid-derived stem cells into renal tubular epithelial-like cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27(9): 590-599.[21]Brooke G, Rossetti T, Pelekanos R, et al. Manufacturing of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells for clinical trials.Br J Haematol. 2009;144(4):571-579. [22]Tran TC, Kimura K, Nagano M, et al. Identification of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells involved in re-endothelialization. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226(1):224-235.[23]Semenov OV, Koestenbauer S, Riegel M, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from human placenta: critical parameters for isolation and maintenance of stemness after isolation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202(2):193.e1-193.e13. [24]Katsiani E, Garas A, Skentou C, et al. Chorionic villi derived mesenchymal like stem cells and expression of embryonic stem cells markers during long-term culturing.Cell Tissue Bank. 2016;17(3):517-529.[25]易桥,卢燕勤,黄宏宇,等.间充质干细胞在免疫调节过程中的作用与应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(41):6216-6224.[26]Li Y, Li Y, Li H, et al. Placenta derived mesenchymal stem cells improve airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in asthmatic rats by modulating the Th17/Treg balance. Molecular Medicine Reports. 2017;16(6):8137-8145.[27]González PL, Carvajal C, Cuenca J, et al. Chorion Mesenchymal Stem Cells Show Superior Differentiation, Immunosuppressive, and Angiogenic Potentials in Comparison With Haploidentical Maternal Placental Cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(10):1109-1121.[28]Zhang Y, Zhang W, Wang H, et al.miR-21 Contributes to Human Amniotic Membrane-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Human Amniotic Membrane-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Induced Immunoregulation.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2018;22(12):665-673..[29]施剑明,邬亚华,耿书国,等.间充质干细胞增殖、衰老及分化: Wnt信号通路经典与非经典的调控作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(41):6719-6724.[30]章毅,许惠利,王锋,等. 不同代次人胎盘间充质干细胞的生物活性比较研究[J].中国医药生物技术, 2016, 11(5):400-406.[31]白金萍,李秀英,李雪,等.胎盘间充质干细胞传代后的增殖能力[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(10:1591-1596.[32]Liu Y, Goldberg AJ, Dennis JE, et al.One-step derivation of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-like cells from human pluripotent stem cells on a fibrillar collagen coating.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33225. [33]Chen YS, Pelekanos RA, Ellis RL, et al. Small Molecule Mesengenic Induction of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells to Generate Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med.2012;1(2):83-95.[34]Ziadlou R, Shahhoseini M, Safari F, et al.Comparative analysis of neural differentiation potential in human mesenchymal stem cells derived from chorion and adult bone marrow.Cell Tissue Res. 2015;362(2):367-377. |