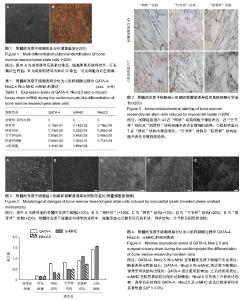
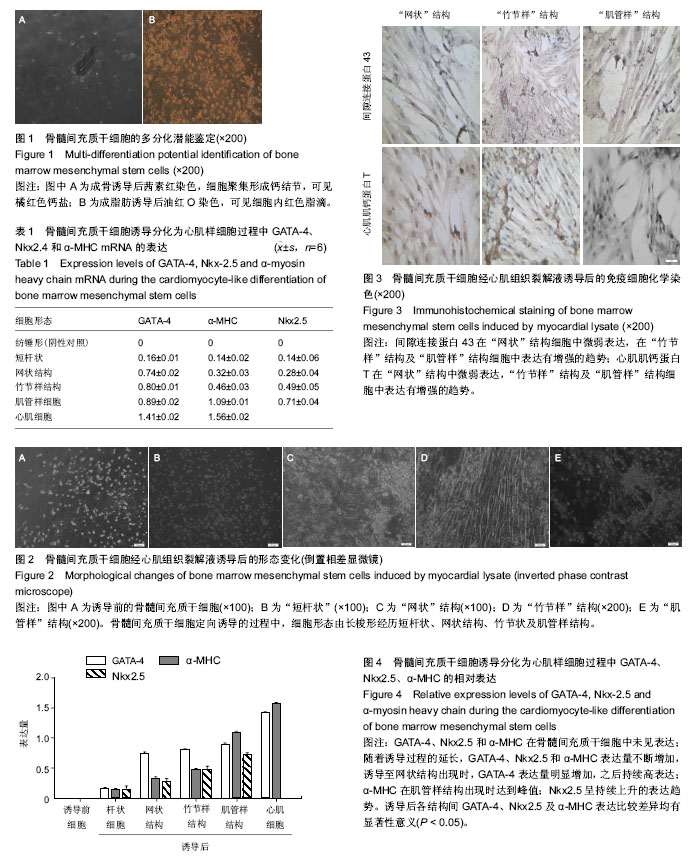
| [1] Makino S,Fukuda K,Miyoshi S,et al.Cardiomyocytes can be generated from marrow stromal cells in vitro.J Clin Invest. 1999;103(5):697-705.[2] 段明军,魏琴,张春,等.诱导多能干细胞向心肌细胞定向分化调控的研究进展[J].生物医学工程研究,2013,23(3):195-200.[3] Badylak SF,Weiss DJ,Caplan A,et al.Engineered whole organs and complex tissues. Lancet. 2012; 379(9819):943-952.[4] Gao Q,Guo M,Jiang X,et al.A cocktail method for promoting cardiomyocyte differentiation from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells Int. 2014; 2014(291): 162024-162024.[5] Yang X,Pabon L,Murry CE.Engineering adolescence: maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.Circ Res.2014;114(3):511-523.[6] .哈艳平,王振良,雷洪,等.过表达Notch1胞内域对c-Kit^+骨髓间充质干细胞分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(6):785-792.[7] Badylak SF, Weiss DJ, Caplan A et al. Engineered whole organs and complex tissues. Lancet. 2012;379(9819): 943-952.[8] Jin ES, Min JM, Jeon SR, et al. Analysis of molecular expression in adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: prospects for use in the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Korean Neurosurg Soc.2013;(4):207-212.[9] 魏欣,陈连凤,刘博江,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为具有起搏功能的心肌细胞[J].基础医学与临床,2008,28(10): 1060-1065.[10] 李琴,赵文婧,寇雅丽,等.心肌组织裂解液诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(10):1726-1730.[11] Wu JY,Liao C,Xu ZP,et al.A modified method to isolate and identify the adult mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow.Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2006;14(3): 557-560.[12] Gottipamula S,Ashwin KM,Muttigi MS,et al.Isolation, expansion and characterization of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in serum-free conditions.Cell Tissue Res.2014;356(1):123-135.[13] Dominici M,Le Blanc K,Mueller I,et al.Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy.2006;8(4):315-317.[14] 唐文洁,李玛琳,邱垂源,等.FGF-2对人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和向成骨细胞分化的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2005,27(6): 673-678.[15] Rickard DJ,Wang FL,Rodriguez-Rojas AM,et al.Intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone (PTH) as well as a non-peptide small molecule agonist of the PTH1 receptor inhibits adipocyte differentiation in human bone marrow stromal cells.Bone.2007;39(6):1361-1372.[16] 赵文婧,李琴,吴卓,等.心肌组织裂解液诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌组织样结构的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(10): 1729-1732.[17] 李平,皇甫春荣,汤春辉,等.在5-杂氮胞苷诱导下人脐带间充质干细胞生物活性特性及向心肌样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(14):2117-2122.[18] Fukuda K.Development of regenerative cardiomyocytes from mesenchymal stem cells for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Artif Organs.2001;25(3):187-193.[19] Friedenstein AJ,Gorskaja JF,Kulagina NN.Fibroblast precursors in normal and irradiated mouse hematopoietic organs.Exp Hematol.1976;4(5):267-274.[20] Fukuhara S,Tomita S,Yamashiro S,et al.Direct cell-cell interaction of cardiomyocytes is key for bone marrow stromal cells to go into cardiac lineage in vitro.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;125(6):1470-1480.[21] 袁岩,陈连凤,张抒扬,等.心肌细胞裂解液对骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌细胞分化诱导作用的研究[J].中华心血管病杂志,2005, 33(2):170-173.[22] 张蕾,陈沅,田杰,等.心肌细胞介导骨髓间充质干细胞的心肌样分化[J].第三军医大学学报, 2005,27(16):1681-1684.[23] 郭志坤.现代心脏组织学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2007.[24] 吴秀山.信号调控与心脏发育[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2006.[25] Grépin C,Nemer G,Nemer M.Enhanced cardiogenesis in embryonic stem cells overexpressing the GATA-4 transcription factor.Development.1997;124(12):2387-2395.[26] Hu DL,Chen FK,Liu YQ,et al.GATA-4 promotes the differentiation of P19 cells into cardiacmyocytes.Int J Mol Med.2010;26(3):365-372.[27] Olson E.Gene regulatory networks in the evolution and development of theheart. Science.2006;313(5795): 1922-1927.[28] Cleaver OB,Patterson KD,Krieg PA.Overexpression of the tinman-related genes XNkx-2.5 and XNkx-2.3 in Xenopus embryos results in myocardial hyperplasia. Development. 1996;122(11):3549-3556. |