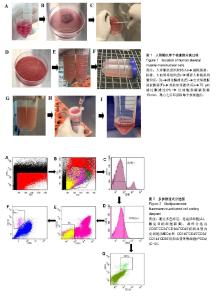
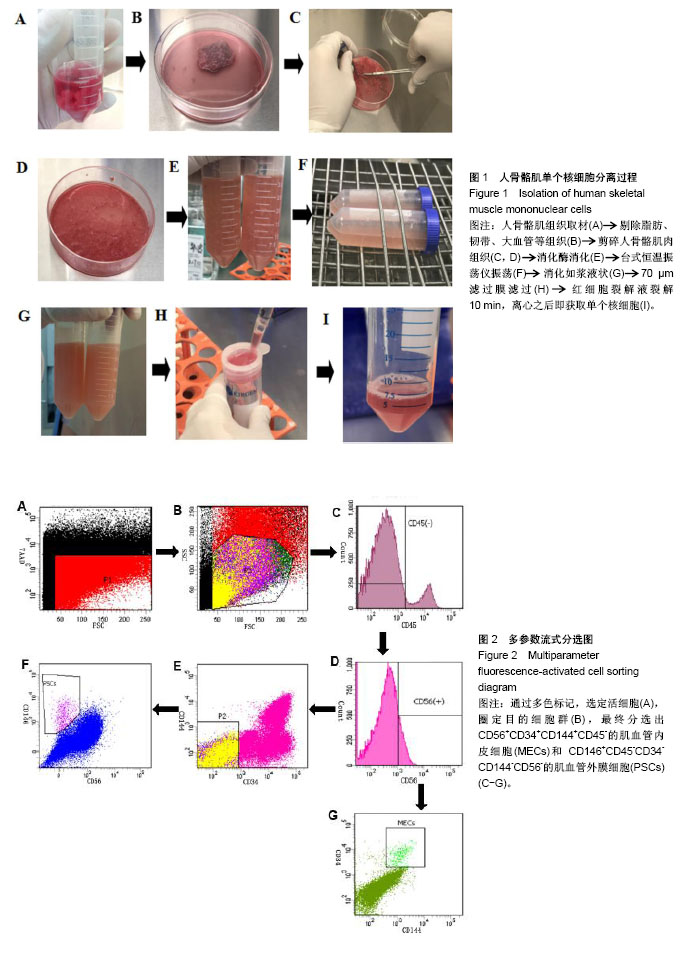
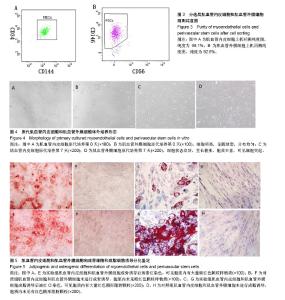
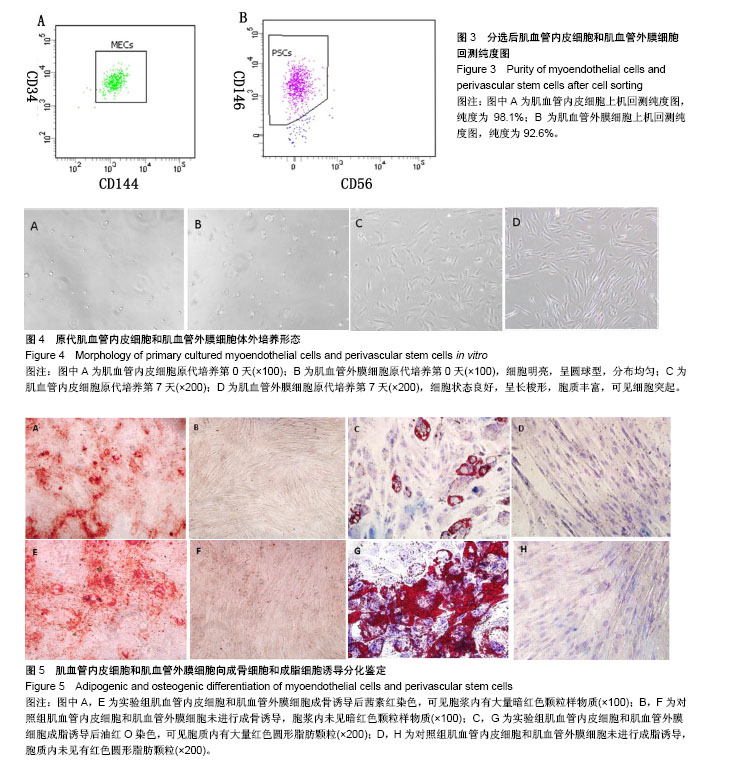
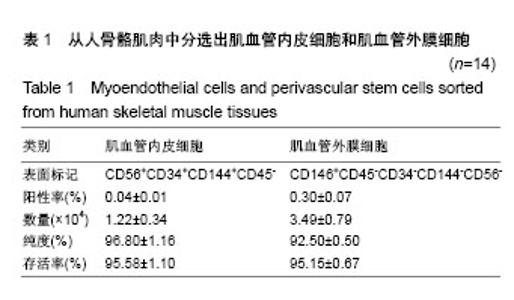
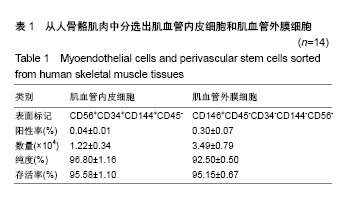
| [1] 田晨. 流式细胞术在小鼠造血干细胞分析分选中的应用[J]. 国际输血及血液学杂志, 2012, 35(4):370-372.[2] Corselli M, Crisan M, Murray IR, et al. Identification of perivascular mesenchymal stromal/stem cells by flow cytometry.Cytometry A. 2013;83(8):714-720.[3] 中国免疫学会血液免疫分会临床流式细胞术学组. 多参数流式细胞术检测急性白血病及浆细胞肿瘤微小残留病中国专家共识(2017年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2017,38(12):1001-1011.[4] Crisan M, Deasy B, Gavina M, et al. Purification and long-term culture of multipotent progenitor cells affiliated with the walls of human blood vessels: myoendothelial cells and pericytes.Methods Cell Biol. 2008;86:295-309.[5] 杨伯齐,高凤娟,吴继红. 应用流式细胞分选技术高效纯化大鼠视网膜神经节细胞及其鉴定[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2016, 16(4):234-238.[6] Crisan M, Huard J, Zheng B, et al. Purification and culture of human blood vessel-associated progenitor cells.Curr Protoc Stem Cell Biol. 2008;Chapter 2:Unit 2B.2.1-2B.2.13.[7] 郝晓娟,郝海英,朱敏杰,等. 内皮样细胞与脐静脉内皮细胞的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(1):83-88.[8] 李豫皖,朱喜忠,金瑛,等.体外定向诱导人羊膜间充质干细胞向骨、软骨及脂肪细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(1):122-127.[9] Chen WC, Saparov A, Corselli M, et al. Isolation of blood-vessel-derived multipotent precursors from human skeletal muscle.J Vis Exp. 2014;(90):e51195.[10] 朱文俊,谭媛元,梁敏. 人CD146+牙周膜干细胞的分选及其干细胞特性的鉴定[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2013,11(2):74-78.[11] Carr LK, Steele D, Steele S, et al. 1-year follow-up of autologous muscle-derived stem cell injection pilot study to treat stress urinary incontinence.Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2008;19(6):881-883.[12] Cerletti M, Jurga S, Witczak CA, et al. Highly efficient, functional engraftment of skeletal muscle stem cells in dystrophic muscles.Cell. 2008;134(1):37-47.[13] Collins CA, Zammit PS, Ruiz AP, et al. A population of myogenic stem cells that survives skeletal muscle aging.Stem Cells. 2007;25(4):885-894.[14] Dellavalle A, Sampaolesi M, Tonlorenzi R, et al. Pericytes of human skeletal muscle are myogenic precursors distinct from satellite cells.Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(3):255-267.[15] Drowley L, Okada M, Payne TR, et al. Sex of muscle stem cells does not influence potency for cardiac cell therapy.Cell Transplant. 2009;18(10):1137-1146.[16] Jankowski RJ, Deasy BM, Huard J.Muscle-derived stem cells.Gene Ther. 2002;9(10):642-647.[17] Oshima H, Payne TR, Urish KL, et al. Differential myocardial infarct repair with muscle stem cells compared to myoblasts. Mol Ther. 2005;12(6):1130-1141.[18] Torrente Y, Belicchi M, Marchesi C, et al. Autologous transplantation of muscle-derived CD133+ stem cells in Duchenne muscle patients.Cell Transplant. 2007;16(6): 563-577.[19] Goodell MA.Introduction: Focus on hematology. CD34(+) or CD34(-): does it really matter. Blood. 1999;94(8):2545-2547.[20] Crisan M, Yap S, Casteilla L, et al. A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs.Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(3):301-313.[21] James AW, Zara JN, Corselli M, et al. An abundant perivascular source of stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(9):673-684.[22] James AW, Zara JN, Zhang X, et al. Perivascular stem cells: a prospectively purified mesenchymal stem cell population for bone tissue engineering.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(6): 510-519.[23] Farrington-Rock C, Crofts NJ, Doherty MJ, et al. Chondrogenic and adipogenic potential of microvascular pericytes.Circulation. 2004;110(15):2226-2232.[24] Chen CW, Montelatici E, Crisan M, et al. Perivascular multi-lineage progenitor cells in human organs: regenerative units, cytokine sources or both. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(5-6):429-434.[25] Zheng B, Cao B, Crisan M, et al. Prospective identification of myogenic endothelial cells in human skeletal muscle.Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(9):1025-1034.[26] Zheng B, Chen CW, Li G, et al. Isolation of myogenic stem cells from cultures of cryopreserved human skeletal muscle. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(6):1087-1093.[27] Grimaldi A, Banfi S, Gerosa L, et al. Identification, isolation and expansion of myoendothelial cells involved in leech muscle regeneration.PLoS One. 2009;4(10):e7652.[28] 徐峰,刘舒云,彭江,等. 血管周围干细胞在大鼠脂肪组织中的含量及其体外扩增后比例的变化[J]. 中国医药生物技术, 2015, 10(2):97-101. [29] Pate DW, Southerland SS, Grande DA, et al. Isolation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cell from rabbit muscle. Surgical Forum. 1993; XLIV:587-589.[30] Young HE, Ceballos EM, Smith JC, et al. Pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells reside within avian connective tissue matrices.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1993;29A(9):723-736.[31] Young HE, Ceballos EM, Smith JC, et al. Isolation of embryonic chick myosatellite and pluripotent stem cells. Journal of Tissue Culture Methods. 1992; 14(2):85-92.[32] Williams JT, Southerland SS, Souza J, et al. Cells isolated from adult human skeletal muscle capable of differentiating into multiple mesodermal phenotypes.Am Surg. 1999;65(1): 22-26.[33] Gussoni E, Soneoka Y, Strickland CD,Dystrophin expression in the mdx mouse restored by stem cell transplantation. Nature.1999;401(6751):390-394.[34] Hwang JH, Yuk SH, Lee JH,Isolation of muscle derived stem cells from rat and its smooth muscle differentiation [corrected]. Mol Cells. 2004;17(1):57-61.[35] Alessandri G, Pagano S, Bez A, et al. Isolation and culture of human muscle-derived stem cells able to differentiate into myogenic and neurogenic cell lineages.Lancet. 2004;364 (9448):1872-1883.[36] Gharaibeh B, Lu A, Tebbets J, et al. Isolation of a slowly adhering cell fraction containing stem cells from murine skeletal muscle by the preplate technique.Nat Protoc. 2008; 3(9):1501-1509.[37] Leavitt T, Hu MS, Longaker MT.Isolation of Live Fibroblasts by Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting.Methods Mol Biol. 2017; 1627:205-212.[38] Esteves CL, Sheldrake TA, Mesquita SP, et al. Isolation and characterization of equine native MSC populations.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):80.[39] 宋赫楠,张宇,丁亚辉,等. 单个人造血干细胞体外培养体系用于小分子化合物筛选[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2016, 24(3): 845-851.[40] 江欣星.与OP9细胞共培养诱导人ES细胞向造血分化体系的研究[D]. 郑州:郑州大学, 2016. |