Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (22): 3570-3576.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1283
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory role of Sox9 in metabolism of articular cartilage extracellular matrix
- Department of Orthopedics, Jinling Hospital of Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2019-02-27 -
Contact:Zhang Lei, MD, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Jinling Hospital of Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Fang Peng, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Jinling Hospital of Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China for the Youth of China, No. 81702170 (to ZL); the Natural Science Foundation of China for the Youth of Jiangsu Province, No. BK20170624 (to ZL); the National Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China, No. 2017T00826 (to ZL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Peng, Zhao Jianning, Zhang Lei. Regulatory role of Sox9 in metabolism of articular cartilage extracellular matrix[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(22): 3570-3576.
share this article
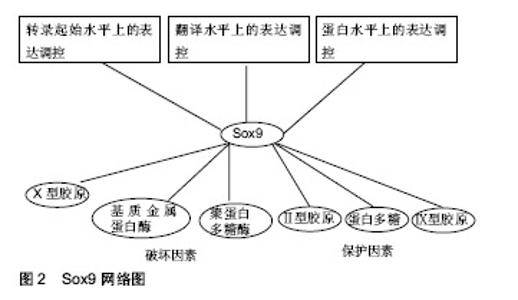
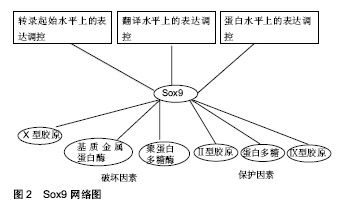
2.1 Sox9的基因、氨基酸序列及结构 人类的Sox9基因位于染色体17q上,cDNA全长约为2.2 kb,编码509个氨基酸,其中104-182位的79个氨基酸构成HMG盒。Sox9基因启动子包含着几个关键的顺式元件,这些元件包括低氧诱导因子1α、核因子κB成员rela、Notch信号介质RBPj以及 cAMP反应元件结合蛋白crb和锌指转录因子sp1[1]。Sox9蛋白的N端含有一个能与DNA结合的HMG盒,HMG盒内包括DNA结合区和蛋白结合区。DNA结合区可以与靶基因的特异核酸序列结合,调节转录。蛋白结合区是与Sox9协同作用的辅因子蛋白的结合位点。另外在HMG盒末端存在NLS(ntlcleaf localization signal)基序。转录因子必须由细胞质转至细胞核才能发挥调控功能,这个转运过程由转运蛋白家族的Importins完成。Importin-β能识别并结合Sox9的NLS,将Sox9由胞质运至胞核,NLS突变会致使Sox9不能进行正确的核定位[2]。Sox9蛋白的C端是含有一段富含脯氨酸、谷氨酰胺和丝氨酸的转录激活区域。 2.2 Sox9在正常关节软骨与骨关节炎关节软骨的表达 冀全博[3]通过对骨关节炎关节软骨进行病理染色分期,然后测定Sox9与骨关节炎病理染色分期的关系,结果显示,与正常关节软骨相比Sox9 mRNA在骨关节炎早期表达上调,在骨关节炎进展期表达抑制。肖瑜[4]也发现退变软骨组织随着Outerbridge分级逐渐加重,Sox9的蛋白表达明显逐渐下降的趋势。有学者曾在小鼠膝关节腔内注射Sox9转染骨髓间充质干细胞来研究Sox9在软骨修复作用,结果提示Sox9转染小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞对小鼠膝关节炎病变软骨修复有促进作用[5]。由此可见Sox9在关节软骨损伤修复过程中扮演着重要的角色,因此如何在骨关节炎晚期提高Sox9的表达有望成为治疗骨关节炎的一个重要的方向。 2.3 Sox9在关节软骨细胞外基质代谢的作用 2.3.1 正常关节软骨细胞外基质组成成分及功能 正常关节软骨是一种具有很强耐受力且结构单一的组织,其功能主要由细胞外基质提供。在关节软骨中软骨细胞以较低的细胞浓度(104 cells/mm3)嵌入基质中,只占组织体积的1%。在其分化状态下,软骨细胞一般呈球状形态,合成Ⅱ型胶原和较多的蛋白多糖。正常的关节软骨细胞外基质主要也是由丰富的胶原纤维和蛋白多糖组成。其中关节软骨的胶原以Ⅱ型胶原蛋白为主,占软骨胶原总量的90%-95%,是软骨细胞的特征性表型。Ⅱ型胶原在软骨内交织成三维网状,被聚合型蛋白多糖缠绕,起到固定蛋白多糖的作用,同时也结合一些水和阳离子为关节软骨提供抗张强度。Ⅱ型胶原蛋白除了提供张力外,还具有一些特殊的生物学功能。例如Ⅱ型胶原蛋白包被培养板在培养软骨细胞时更能维持细胞形态,延长去分化现象出现的时间,更利于细胞再分化[6]。此外宋晓娣[7]发现Ⅱ型胶原蛋白能够有效降低类风湿性关节炎模型小鼠血清中白细胞介素17、基质金属蛋白酶3和肿瘤坏死因子a等细胞因子从而达到抗关节炎作用。Lugo等[8]也发现将未变性的鸡Ⅱ型胶原蛋白对膝关节炎患者给药,结果发现Ⅱ型胶原蛋白可使患者症状明显改善,且耐受性良好。软骨中的蛋白多糖由透明质酸、蛋白多糖单体以及连接蛋白共同组成,是一种结构庞大的聚集体。由于蛋白多糖浓度很高,在胶原骨架之间形成了永合性极强的黏稠胶体,使软骨坚硬而又富有弹性[9]。此外关节软骨细胞外基质还存在数量较少的Ⅳ、Ⅵ、Ⅸ、Ⅺ、Ⅻ、Ⅻ等胶原,虽然这些小胶原只占成熟基质的一小部分,但它们不仅在关节软骨的力学性质、组织结构和形状等方面发挥着重要的结构作用,而且还发挥着特定的生物学功能[10]。例如Ⅸ型胶原通过赖氨酰氧化酶机制与Ⅱ型胶原广泛交联,形成独特的纤维网络[11]。在人类中,Ⅸ型胶原已被确认为女性髋关节骨关节炎易感位点,说明Ⅸ型胶原与髋关节骨关节炎有关。软骨中Ⅸ型胶原表达的减少可能使基质更容易受到机械力的影响,从而导致骨关节炎的发病[12]。2016年1篇文章报道Ⅸ型胶原基因多态性与儿童大骨节病的易患性有关,并推测位点rs6910140和rsll35056多态性改变了al(Ⅸ)蛋白表达的导致软骨退行性改变[13]。 2.3.2 Sox9与关节软骨细胞外基质代谢的关系 (1)Sox9与关节软骨细胞外基质合成代谢的关系: 事实上Sox9对软骨细胞外基质形成起以及软骨细胞表型的维持起着重要用。Sox9被誉为软骨发生的“主调控因子”。Ⅱ型胶原是关节软骨细胞外基质主要的胶原成分。骨关节炎早期Ⅱ型胶原量增加,但随着骨关节炎病变的发展逐渐丧失[14]。此种变化趋势与Sox9保持着着高度一致。现多项证据表明Sox9通过与Ⅱ型胶原基因的增强子结合来促进其在转录水平上表达。既往有证据表明,Sox9通过激活了位于Ⅱ型胶原基因内的第一个内含子中的48 bp软骨增强子从而促进Ⅱ型胶原基因的转 录[15]。最新的研究证据结果表明,Sox9和L-Sox5/Sox6与Ⅱ型胶原基因的内含子1、内含子6以及位于-30 kb区域的位点结合从而增强Ⅱ型胶原基因的转录,并且L-Sox5/Sox6提高了Sox9与其自身识别位点的结合效率,从而有力地增强了Sox9激活增强子的能力[16-17]。Sox9也可促进蛋白多糖基因的表达。有研究发现蛋白多糖基因4.7 kb区域包含一个高度保守的增强子,该增强子指导胚胎和成人软骨中蛋白多糖基因的表达,并且该增强子是Sox9直接结合位点,有趣的是Sox9与该增强子的结合仅发生在L-Sox5/Sox6存在的情况下[18]。Zhang等[19]发现Sox9可通过与Ⅸ胶原基因启动子区域的sox/sry结合位点(位点D和位点E)来激活Ⅸ胶原基因的转录,与Ⅱ胶原基因和蛋白多糖基因表达调控不同的是L-Sox5/Sox6不能单独或着联合刺激Ⅸ胶原基因启动子结构的转录活性。更有趣的是当L-Sox5和Sox6载体与Sox9表达载体共转染时,Ⅸ胶原基因启动子活性反而减弱。值得注意得是miR-29b在骨关节炎中扮演着重要的角色。Ⅱ型胶原基因是miR-29b的主要直接靶基因, 稳定高表达miR-29b可抑制胶原蛋白基因的翻译过程,用定量RT-PCR方法对细胞模型中miR-29b水平进行了更精确的估计,结果发现与非骨关节炎供者相比,骨关节炎患者软骨细胞miR-29b水平也显著升高(平均5.8倍)[20]。据报道,软骨形成的主转录因子Sox9通过miR-29a/b1启动子抑制miR-29a-3p和miR-29b-3p的表达,而白细胞介素1β则增加了miR-29家族在原代人软骨细胞中的表达[21]。 (2)Sox9与关节软骨细胞外基质分解代谢的关系:骨关节炎软骨的退变来源于软骨细胞外基质降解。当前认为,主要有2类酶参与关节软骨细胞外基质的降解:一类是基质金属蛋白酶,另一类是带有血小板凝血酶敏感蛋白结构域的解聚素与聚蛋白多糖酶。Sox9可抑制聚蛋白多糖酶,Zhang等[22]通过Sox9沉默实验和过表达实验证实Sox9可抑制聚蛋白多糖酶4、聚蛋白多糖酶5、聚蛋白多糖酶7、聚蛋白多糖酶12基因的mRNA生成,ChIP试验进一步证实Sox9被招募到聚蛋白多糖酶4和聚蛋白多糖酶5的启动子中,这些结果表明Sox9可通过影响聚蛋白多糖酶基因的启动子来影响聚蛋白多糖酶基因的转录。他们的试验同样也发现聚蛋白多糖酶4、聚蛋白多糖酶5、聚蛋白多糖酶7、聚蛋白多糖酶12在骨关节炎早期表达下调,随着骨关节炎进行性发展它们的表达量逐渐上升,与之相反的是Sox9在骨关节炎早期表达上调,随着骨关节炎进行性发展它的表达量逐渐下降。由此可见Sox9是聚蛋白多糖酶的抑制物,是骨关节炎早期关节软骨细胞外基质的保护器。 基质金属蛋白酶13是导致Ⅱ型胶原降解的特异性胶原酶,是软骨细胞肥大的一个显著特征[23],基质金属蛋白酶13在骨关节炎患者的关节和关节软骨中存在明显过度表达,而在正常成人关节和关节软骨组织中几乎检测不到。有研究发现Sox9的活性对基质金属蛋白酶13的表达具有负性调控作用[24]。Yun等[25]发现LEF-1与β-catenin相互作用,直接结合基质金属蛋白酶13基因的3’区,并通过改变基质金属蛋白酶13的构象而激活基质金属蛋白酶13启动子的活性。研究表明Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在骨关节炎发展过程中起着重要的促进作 用[26]。研究发现,Sox9的N端对促进β-catenin的降解是必要和充分的,而C端则是在不影响其稳定性的情况下抑制β-catenin转录活性的,从而抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路[27]。由此可见Sox9可通过促进β-catenin降解来间接实现对于基质金属蛋白酶13基因的表达调控。 (3)Sox9对肥大标志物X型胶原表达调控:正常成人关节软骨中是不含有Ⅹ型胶原。Ⅹ型胶原是软骨细胞肥大的标志物之一。庞金辉等[28]通过Western杂交技术发现膝骨关节炎患者软骨基质中Ⅹ型胶原的含量上升。既往有研究发现Ⅹ型胶原可与Ⅱ型胶原纤维发生联系,影响关节软骨的结构和强度[29]。所以庞金辉等[28]认为膝骨关节炎患者的Ⅹ型胶原表达明显增加,这可能促使基质组分发生改变,从而加速了骨关节炎的进展。事实上Ⅹ型胶原基因近端启动子存在多个Runx2结合位点,Runx2通过与这个启动子上保守的Runx2结合位点结合而将其转录激活,但Runx2并不是单独起作用而是以Runx2为核心的复合体形式发挥作用[30- 31]。 事实上Sox9可直接或者间接影响着Runx2的功能。Zhou等[32]发现Sox9蛋白N端的HMG结构域可与Runx2的Runt结构域直接相互作用,降低了Runx2与位于X型胶原启动子上的一个特征的Runx2结合位点的结合,从而抑制了X胶原基因的转录。另外BAPX1是已知的调节Runx2表达的转录抑制因子[33]。BAPX-1被称为是一个参与调控发育后关节软骨细胞肥大表型的分子开关,它的表达与软骨细胞肥大标记物Runx2、COL10A1、软骨降解酶(基质金属蛋白酶13)的表达呈负相关[34]。Sox9直接结合了BAPX1启动子并增强了它的表达活性,从而通过促进BAPX1的表达来间接抑制Runx2基因的转录[35]。从而抑制软骨细胞肥大,维持正常软骨细胞表型。此外Runx2与软骨细胞肥大有关,肥大软骨细胞可以成为成骨细胞和成骨细胞,从而引起骨质增生,即骨赘形成[36]。 2.4 Sox9的表达调控 见图2。 2.4.1 Sox9在转录起始水平上的表达调控 考虑到Sox9在软骨细胞中的重要作用,人们相信并且已经有充分的文献证明Sox9是许多类型的调控机制的对象。Sox9是调控软骨细胞发育的主要转录因子,经遗传学研究证实Sox9的调控发生在转录水平和转录后水平[37]。如前文所述Sox9启动子包含着几个关键的顺式作用元件:低氧诱导因子1α、核因子κB成员rela、Notch信号介质RBPj、cAMP反应元件结合蛋白crb和锌指转录因子sp1。这些顺式作用元件对Sox9基因的表达起着正性或者负性调节作用。染色质免疫共沉淀显示低氧诱导因子1α与Sox9启动子结合,并上调Sox9基因的表达[38]。细胞内核因子κB结合基序结合诱导软骨Sox9启动子,促进了Sox9基因的表达[39]。Rbpj是Notch信号转导的重要介导因子,Rbpj/NICD复合物可以被招募到Sox9启动子,抑制Sox9基因的转录[40]。在Sox9启动子中发现了一个潜在的核因子κB结合位点,并确定核因子κB亚基p65通过直接与其启动子结合来正调控Sox9的表达[41]。越来越多的证据表明,表观遗传学对软骨细胞增殖、分化和功能过程中的基因表达有调节作用[42]。Kim等[43]发现Sox9启动子在骨关节炎发病过程中发生过度甲基化,导致其表达降低,此外Sox9基因进行组蛋白修饰后,其抑制性组蛋白标记(如H3K9me3和H3K27me3)水平升高,诱导组蛋白标记H3K9ac水平降低,从而抑制Sox9的表达。 2.4.2 Sox9在翻译水平上的表达调控 人Sox9 mRNA的3‘UTR具有6种不同miRNAs的识别位点:mir-101,miR-1/205,miR-590/590-3p,miR-145,miR-300和miR-384-5p。Sox9 mRNA是在胞核外的核糖体上合成Sox9蛋白,这些miRNAs通过与Sox9 mRNA碱基互补配对来影响Sox9 mRNA在核糖体上合成蛋白质。有研究已经证实miR-384-5p、miRNA-145对Sox9的调节作用[44-45]。miR-145已被确认为人类软骨细胞中关键的软骨形成调节剂Sox9的直接抑制剂,从而导致软骨细胞中Sox9的表达减少。miR-145可能通过靶向Sox9mRNA3’-UTR中位于266-288和1 386-1 408位置的2个结合点来抑制Sox9基因的翻译[46]。Sox9是miR-30b的靶基因,双荧光素酶报告试验证实miR-30b能识别Sox9 mRNA3’-UTR并与之相互作用[47]。另外IncRNA是长度在200-100 000个核苷酸之间的非编码RNA,在骨关节炎中存在差异表达。随着高通量测序芯片技术的发展,越来越多的IncRNA调控机制被发现。长非编码RNA被称为骨关节炎新的调控码[48]。越来越多的证据表明Linc-ROR对Sox9的表达调节。Wang等[49]发现Linc-ROR通过类似海绵吸附多种miRNAs,包括miR-15b,miR-33a,miR-129,miR-145和miR-206来调控Sox9的表达。Feng等[50]也发现Linc-ROR可作为miR-138和miR-145海绵来拮抗这2种miRNA的功能。 2.4.3 Sox9在蛋白水平上的表达调控 (1)乙酰化:Sox9蛋白要发挥转录因子的作用,必须位于细胞核内。如前文所述Importin-β能识别并结合Sox9的NLS来介导Sox9由胞质转运至胞核。有研究发现降低Sox9乙酰化,促进Sox9核易位,导致Sox9核移位增加[51]。SIRT1是Sox9脱乙酰的主要贡献者之一,Sox9乙酰化状态不影响蛋白质稳定性,但可以阻止Sox9核进入,Sox9的去乙酰化状态可通过增加其与Importin-β转运受体的亲和力而增强其进入胞核[52]。遗憾的是SIRT1在骨关节炎中表达下降,与关节软骨退变程度负性相关[53]。并且Sox9蛋白乙酰化水平在退变关节软骨中高于完整关节软骨[54]。 (2)磷酸化与甲基化:Sox9的磷酸化可调节其DNA结合活性和亚细胞定位。迄今报道的Sox9唯一的磷酸化事件是cAMP依赖的蛋白激酶A(PKa)对Sox9蛋白S64和S181残基的靶向作用[55]。有研究证实,Sox9蛋白S64磷酸化可能促进Sox9二聚体形成,从而与DNA结合,而S181磷酸化则可能促进Sox9核易位和DNA结合[56-57]。体外实验表明,辅助激活剂相关的精氨酸甲基转移酶1(又称PRMT-4)在Sox9的N-端和Sox结构域(可能位于R74,R152,R177,R178和R179)上甲基化精氨酸残基,并防止Sox9与β-catenin相互作用,这些事件是否在体内发生还有待确定[58]。已经明确证实Sox9对β-catenin有抑制作用,同时β-catenin对Sox9也有抑制作用。β-catenin与Sox9的跨激活域结合而抑制Sox9的活性。一种可能的机制是β-catenin诱导Sox9降解。另一种可能是通过β-catenin与Sox9反活化结构域的结合而抑制Sox9转录复合物的形成[59]。 (3)糖基化与泛素化:糖基化是一种多步酶促过程,导致一种小的泛素类修饰蛋白与靶蛋白赖氨酸残基的共价结合。这种修饰可以调节靶蛋白的活性、稳定性、亚细胞定位和相互作用[60]。在小鼠Sox9蛋白的K61和K396中发现了2个可能的泛素类修饰蛋白位点,其中K396可能是主要的泛素类修饰蛋白位点[61]。Sox9在K396上的糖基化可影响其稳定性和活性,导致Sox9的丰度和转录活性增加[62-63]。越来越多的证据表明,Sox9水平和转录活性也受到泛素-蛋白酶体介导的降解途径的调控。泛素或相扑肽附着在特定赖氨酸残基上可促进蛋白质降解,影响蛋白质胞内转运,并改变蛋白质相互作用。E3泛素连接酶E6-AP/ UBE3A可直接泛素化Sox9 (未知残基),从而降低其体外稳定[64]。此外有研究发现Sox9泛素化和泛素类修饰蛋白化的主要位点K396的突变提高了Sox9蛋白的稳定性和转录活性[65]。综上所述,糖基化与泛素化竞争性结合Sox9-K396,从而影响Sox9的功能。Sox9泛素化和泛素类修饰蛋白化之间的平衡可能控制软骨形成过程。 "
| [1]Lefebvre V, Dvir-Ginzberg M. SOX9 and the many facets of its regulation in the chondrocyte lineage. Connect Tissue Res. 2016;58(1):2-14.[2]Südbeck P, Scherer G. Two independent nuclear localization signals are present in the DNA-binding high-mobility group domains of SRY and SOX9. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(44): 27848-27852.[3]冀全博. ADAMTS调控骨关节炎软骨退变基质降解的机制研究[D].北京:解放军医学院,2015.[4]肖瑜. 骨关节炎患者软骨在不同Outerbridge分级中SOX9、RUNX2表达的变化[D].天津:天津医科大学, 2016.[5]卓群豪,张伟娜,李舰,等. 膝关节腔内注射Sox9转染骨髓间充质干细胞修复膝关节骨关节炎[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 38(5): 736-741.[6]蒋萍,蔚芃,赵明才,等. I,Ⅱ型胶原蛋白对人软骨细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(30):4845-4850.[7]宋晓娣. 天然Ⅱ型胶原蛋白抗关节炎功能研究[D].天津:天津科技大学, 2013.[8]Lugo JP, Saiyed ZM, Lane NE. Efficacy and tolerability of an undenatured type II collagen supplement in modulating knee osteoarthritis symptoms: A muhicenter randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Nutr J. 2016;15(1): 1-15.[9]Dateki S. <i>ACAN</i> mutations as a cause of familial short stature. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2017;26(3):119-125.[10]Luo Y, Sinkeviciute D, He Y, et al. The minor collagens in articular cartilage. Protein Cell. 2017;8(8):560-572.[11]Wu JJ, Woods PE, Eyre DR. Identification of cross-linking sites in bovine cartilage type IX collagen reveals an antiparallel type II-type IX molecular relationship and type IX to type IX bonding. J Biol Chem. 1992;267(32): 23007-230014.[12]Alizadeh BZ, Njajou OT, Bijkerk C, et al. Evidence for a role of the genomic region of the gene encoding for the alpha1 chain of type IX collagen (COL9A1) in hip osteoarthritis: A population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(5): 1437-1442.[13]史晓薇,郭雄. COL9A1基因多态性与儿童大骨节病的关联分析[J]. 中国妇幼健康研究,2016,27(5):556-557.[14]陈崇伟,卫小春,向川,等. 骨性关节炎关节软骨内Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ型胶原表型的实验研究[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2006, 37(3): 248-251.[15]Bell DM, Leung KK, Wheatley SC, et al. SOX9 directly regulates the type-II collagen gene. Nat Genet. 1997;16(2): 174-180.[16]Yasuda H, Oh CD, Chen D, et al. A Novel Regulatory Mechanism of mType II Collagen Expression via a SOX9-dependent Enhancer in Intron 6. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(2):528-538.[17]Otero M, Peng H, El Hachem K, et al. ELF3 modulates type II collagen gene (COL2A1) transcription in chondrocytes by Inhibiting SOX9-CBP/p300-driven histone acetyltransferase activity. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(1):15-26.[18]Han Y, Lefebvre V. L-Sox5 and Sox6 drive expression of the aggrecan gene in cartilage by securing binding of Sox9 to a far-upstream enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28(16): 4999-5013.[19]Zhang P, Jimenez SA, Stokes DG. Regulation of human COL9A1 gene expression. Activation of the proximal promoter region by SOX9. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(1): 117-123.[20]Moulin D, Salone V, Koufany M, et al. MicroRNA-29b contributes to collagens imbalance in human osteoarthritic and dedifferentiated articular chondrocytes. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9792512. [21]Le LT, Swingler TE, Crowe N, et al. The microRNA-29 family in cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2016;94(5):583-596.[22]Zhang Q, Ji Q, Wang X, et al. SOX9 is a regulator of ADAMTSs-induced cartilage degeneration at the early stage of human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(12): 2259-2268.[23]Wei F, Zhou J, Wei X, et al. Activation of Indian Hedgehog Promotes Chondrocyte Hypertrophy and Upregulation of MMP-13 in Human Osteoarthritic Cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(7):755-763.[24]Li H, Wang D, Yuan Y, et al. New insights on the MMP-13 regulatory network in the pathogenesis of early osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19:248. [25]Yun K, Im SH. Transcriptional regulation of MMP13 by Lef1 in chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;364(4): 1009-1014.[26]唐芳,马武开,姚血明. Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与骨关节炎[J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2014,3(2):70-73.[27]Topol L, Chen W, Song H, et al. Sox9 inhibits wnt signaling by promoting β-catenin phosphorylation in the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(5):3323-3333.[28]庞金辉,刘明轩,石文俊,等. X型胶原在膝骨关节炎软骨中的表达[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2012, 16(15):44-46.[29]van der Kraan PM, Stoop R, Meijers TH, et al. Expression of type X collagen in young and old C57Bl/6 and Balb/c mice. Relation with articular cartilage degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9(2):92-100.[30]Amano K, Densmore M, Nishimura R, et al. Indian Hedgehog Signaling Regulates Transcription and Expression of Collagen Type X via Runx2/Smads Interactions. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(36):24898-24910.[31]Li F, Lu Y, Ding M, et al. Runx2 contributes to murine Col10a1 gene regulation through direct interaction with its cis-enhancer. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(12):2899-2910.[32]Zhou G, Zheng Q, Engin F, et al. Dominance of SOX9 function over RUNX2 during skeletogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(50):19004-19009.[33]Lengner CJ, Hassan MQ, Serra RW, et al. Nkx3.2-mediated repression of Runx2 promotes chondrogenic differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(16):15872-15879.[34]Caron MM, Emans PJ, Surtel DA, et al. BAPX-1/NKX-3.2 acts as a chondrocyte hypertrophy molecular switch in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67(11):2944-2956.[35]Yamashita S, Andoh M, Ueno-Kudoh H, et al. Sox9 directly promotes Bapx1 gene expression to repress Runx2 in chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(13):2231-2240.[36]Yang L, Tsang KY, Tang HC, et al. Hypertrophic chondrocytes can become osteoblasts and osteocytes in endochondral bone formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(33): 12097-12102.[37]Akiyama H, Chaboissier MC, Martin JF, et al. The transcription factor Sox9 has essential roles in successive steps of the chondrocyte differentiation pathway and is required for expression of Sox5 and Sox6. Genes Dev. 2002; 16(21):2813-2828.[38]Amarilio R, Viukov SV, Sharir A, et al. HIF1alpha regulation of Sox9 is necessary to maintain differentiation of hypoxic prechondrogenic cells during early skeletogenesis. Development. 2007;134(21):3917-3928.[39]Ushita M, Saito T, Ikeda T, et al. Transcriptional induction of SOX9 by NF-kappaB family member RelA in chondrogenic cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(8):1065-1077.[40]Chen S, Tao J, Bae Y, et al. Notch gain of function inhibits chondrocyte differentiation via Rbpj-dependent suppression of Sox9. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(3):649-659.[41]Ushita M, Saito T, Ikeda T, et al. Transcriptional induction of SOX9 by NF-kappaB family member RelA in chondrogenic cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17:1065-1075.[42]Duan L, Liang Y, Ma B, et al. Epigenetic regulation in chondrocyte phenotype maintenance for cell-based cartilage repair. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(11):2127-2140.[43]Kim KI, Park YS, Im GI. Changes in the epigenetic status of the SOX-9 promoter in human osteoarthritic cartilage. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(5):1050-1060.[44]Zhang W, Cheng P, Hu W, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-384-5p alleviates osteoarthritis through its effects on inhibiting apoptosis of cartilage cells via the NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting SOX9. Cancer Gene Ther. 2018;25(11-12):326-338.[45]康菲,杨波,闫演飞,等. miR-145在间充质干细胞来源软骨细胞肥大化中的作用[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2013, 35(11): 1058-1061. [46]Martinez-Sanchez A, Dudek KA, Murphy CL. Regulation of human chondrocyte function through direct inhibition of cartilage master regulator SOX9 by microRNA-145 (miRNA-145). J Biol Chem. 2011;287(2):916-924.[47]Wa Q, He P, Huang S, et al. miR-30b regulates chondrogenic differentiation of mouse embryo-derived stem cells by targeting SOX9. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(6):6131-6137.[48]Cen X, Huang XQ, Sun WT, et al. Long noncoding RNAs: a new regulatory code in osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2017; 9(11):4747-4755. [49]Wang L, Yu X, Zhang Z, et al. Linc-ROR promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through the derepression of SOX9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017; 36(1):182. [50]Feng L, Shi L, Lu YF, et al. Linc-ROR Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Functioning as a Competing Endogenous RNA for miR-138 and miR-145. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;11:345-353.[51]Chen LY, Lotz M, Terkeltaub R, et al. Modulation of matrix metabolism by ATP-citrate lyase in articular chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(31):12259-12270.[52]Bar Oz M, Kumar A, Elayyan J, et al. Acetylation reduces SOX9 nuclear entry and ACAN gene transactivation in human chondrocytes. Aging Cell. 2016;15(3):499-508.[53]伍平. SIRT1在骨关节炎关节软骨中的表达及其意义[D]. 长沙:中南大学, 2010.[54]Bar Oz M, Kumar A, Elayyan J, et al. Acetylation reduces SOX9 nuclear entry and ACAN gene transactivation in human chondrocytes. Aging Cell. 2016;15(3):499-508.[55]Huang W, Zhou X, Lefebvre V, et al. Phosphorylation of SOX9 by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A enhances SOX9's ability to transactivate a Col2a1 chondrocyte-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(11):4149-4158.[56]Kamachi Y, Kondoh H. Sox proteins: regulators of cell fate specification and differentiation. Development. 2013;140(20): 4129-4144.[57]Malki S, Nef S, Notarnicola C, et al. Prostaglandin D2 induces nuclear import of the sex-determining factor SOX9 via its cAMP-PKA phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2005;24(10): 1798-1809.[58]Ito T, Yadav N, Lee J, et al. Arginine methyltransferase CARM1/PRMT4 regulates endochondral ossification. BMC Dev Biol. 2009.[59]Akiyama H, Lyons JP, Mori-Akiyama Y, et al. Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004;18(9):1072-1087.[60]Flotho A, Melchior F. Sumoylation: a regulatory protein modification in health and disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2013;82:357-385.[61]Oh HJ, Kido T, Lau YF. PIAS1 interacts with and represses SOX9 transactivation activity. Mol Reprod Dev. 2007;74(11): 1446-1455.[62]Hattori T, Eberspaecher H, Lu J, et al. Interactions between PIAS proteins and SOX9 result in an increase in the cellular concentrations of SOX9. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(20): 14417-14428.[63]Hattori T, Eberspaecher H, Lu J, et al. Interactions between PIAS proteins and SOX9 result in an increase in the cellular concentrations of SOX9. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(20):14417-14428.[64]Hattori T, Kishino T, Stephen S, et al. E6-AP/UBE3A protein acts as a ubiquitin ligase toward SOX9 protein. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(49):35138-35148.[65]Akiyama H, Kamitani T, Yang X, et al. The transcription factor Sox9 is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system and stabilized by a mutation in a ubiquitin-target site. Matrix Biol. 2005;23(8):499-505. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [4] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [5] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [6] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [7] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [8] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [9] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [10] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [11] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [12] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [13] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [14] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [15] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||