Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (15): 2356-2363.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1147
Previous Articles Next Articles
Gender differences in the relationship between sit-and-reach and body composition: a survey of college students in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
Kong Cunqing, Chen Xingcai, Wu Huaqian, Chen Run, Wang Zefeng, Li Qiaoli, Tang Cheng, Zhang Wenhai,#br# Wu Yachen, Liu Peng
- (Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China)
-
Received:2018-11-21Online:2019-05-28Published:2019-05-28 -
Contact:Liu Peng, Master, Associate professor, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Kong Cunqing, Master candidate, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Chen Xingcai, Master candidate, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Kong Cunqing and Chen Xingcai contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for the College Students of Guangxi Medical University in 2018, No. 2018009 and 2018112 (both to LP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Kong Cunqing, Chen Xingcai, Wu Huaqian, Chen Run, Wang Zefeng, Li Qiaoli, Tang Cheng, Zhang Wenhai, . Gender differences in the relationship between sit-and-reach and body composition: a survey of college students in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2356-2363.
share this article
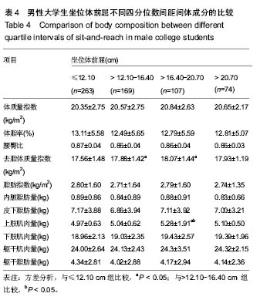
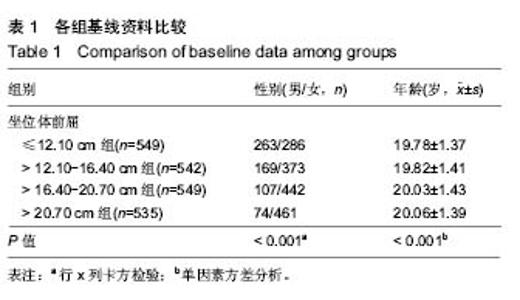
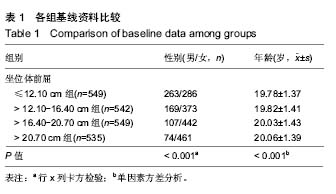
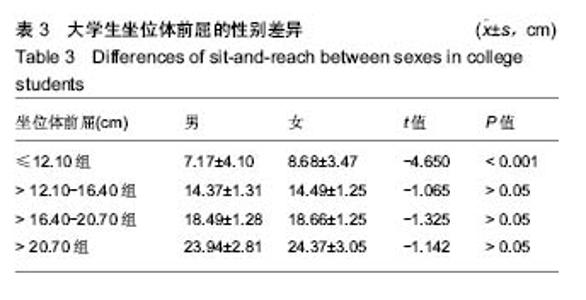
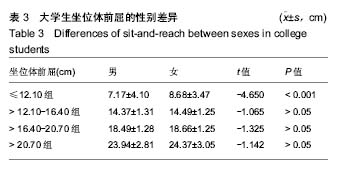
2.4 坐位体前屈不同四分位数间距间体成分的差异 2.4.1 男性大学生的比较 坐位体前屈>12.10-16.40 cm组,>16.40-20.70 cm组男大学生的去脂体质量指数与≤12.10 cm组间差异有显著性意义,且>12.10-16.40 cm 组,>16.40-20.70 cm组的去脂体质量指数大于≤12.10 cm组(P < 0.05)。此外,>16.40-20.70 cm组男性大学生的上肢肌肉量大于≤12.10 cm组、>12.10-16.40 cm组(P < 0.05)。然而,其他指标4组的比较无统计学差异。说明男性大学生柔韧性较好的其去脂体质量指数和上肢肌肉量也较高。见表4。"
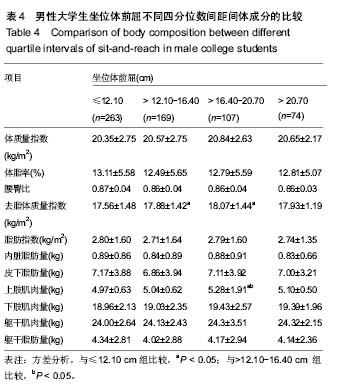
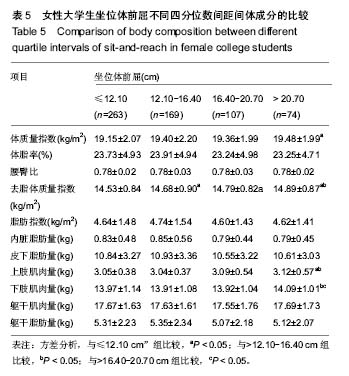
2.4.2 女性大学生的比较 坐位体前屈>20.70 cm女大学生的体质量指数显著大于≤12.10 cm组(P < 0.05);坐位体前屈>12.10-16.40 cm组,>16.40-20.70 cm组,>20.70 cm组的去脂体质量指数与≤12.10 cm组比较均有差异(P < 0.05),坐位体前屈>20.70 cm与>12.10-16.40 cm组间比较存在差异(P < 0.05);坐位体前屈>20.70 cm组的上肢肌肉量显著大于≤12.10 cm组和>12.10-16.40 cm组(P < 0.05);下肢肌肉量> 20.70 cm组显著大于>12.10-16.40 cm 组,>16.40-20.70 cm组(P < 0.05),但其他组间的比较无统计学差异。以上结果表明,与坐位体前屈较差者相比,女性大学生柔韧性较好者的体成分含量较高。见表5。"
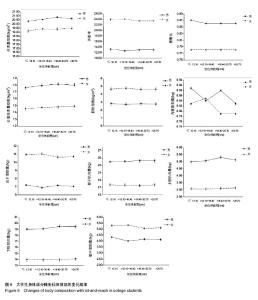
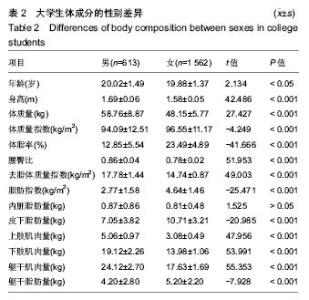
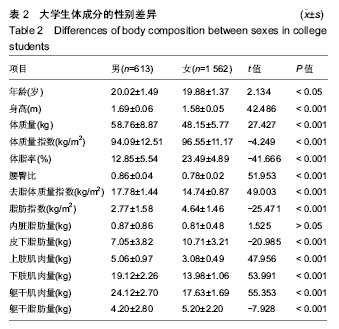
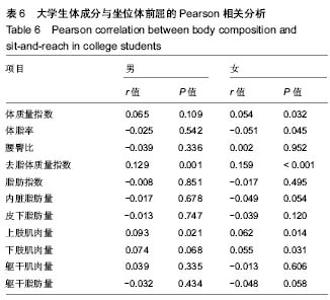
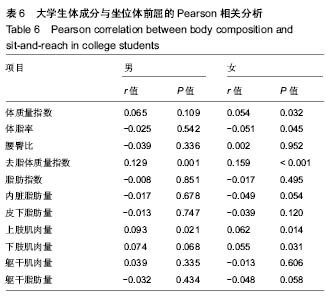
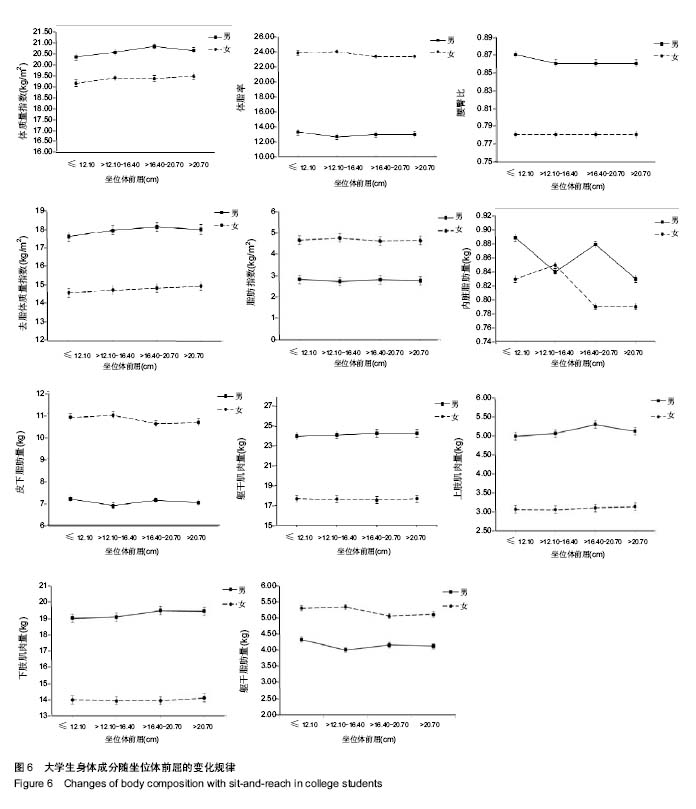
2.6 男、女性大学生体成分与坐位体前屈的变化关系 男性大学生的体质量指数、腰臀比、去脂体质量指数、躯干肌肉量、上肢肌肉量和下肢肌肉量均大于女性大学生,而女性大学生的体脂率、脂肪量指数、皮下脂肪含量和躯干脂肪量高于男性大学生。其中,男女大学生的体质量指数从坐位体前屈的下四分位数到上四分位数呈上升趋势。此外,男女大学生的内脏脂肪含量变化趋势与其他体成分指 标明显不同,男性大学生坐位体前屈>12.10-16.40 cm组的内脏脂肪含量低于女性大学生,而≤12.10 cm组,>16.40-20.70 cm组,>20.70 cm组明显高于女性大学生。男性大学生的上肢肌肉量、下肢肌肉量>16.40- 20.70 cm达到最大值,而女性在坐位体前屈下四分位数到上四分位数无明显变化趋势。总之,男、女大学生的体成分在坐位体前屈不同四分位数的变化趋势不同。见图6。"
| [1] 张慧君,于志源.对大学生身体柔韧性素质练习方法探究[J].体育世界(学术版),2014,(5):133-134.[2] 华建军.影响大学生坐位体前屈成绩因素的实验研究[J].运动. 2015, (19):64-65+71.[3] 孙庆祝,郝文亭,洪峰.体育测量与评价[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2010.[4] 方春露,周亮.不同专业背景学生的体质对比的分析——以湖南科技大学体育与非体育专业学生为例[J].体育科技, 2014,35(2): 96-97+100.[5] 马顺江,刘亮.有氧健身操对孝感市中年女性体质的影响[J].体育世界(下刊),2013,(4): 77-78.[6] 戴玉琴.瑜伽运动对更年期妇女健康体能和症状困扰的影响[D]. 衡阳:南华大学, 2013.[7] 闫丹,阮祥燕.人体成分测定方法的临床应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(24):4499-4502.[8] 李立,陈玉娟,袖山纱季.中日女大学生体成分身体形态比较[J].中国学校卫生,2013,34(2):146-148.[9] 顾芳,陈晓红,郑陆.北京市女大学生骨密度及体成分变化特征的研究[J].北京体育大学学报.2011,34(8):57-59.[10] 白静雅,何烨,海向军,等.回族大学生骨密度和体成分的变化特点[J].解剖学报,2015,46(03):410-414.[11] 黄丽仟,李俏丽,黄彬彬,等.广西在校男大学生体能测试成绩与身体肌肉参数的相关性[J].中国学校卫生, 2018,39(2): 248-251.[12] Eddy JM,Eynom D,Stephen N,et al.Impact of physical fitness prog-Am in blue-collar workplace.Health Value.1990; 14(6): 14-23.[13] Sternfield B,Wang H,Quesenberry CP JR.Physical activity and changes in weight and waist circumference in midlife women:finding from the study of women’s Health Across the Nation.Am J Epidemiol.2004;160(9):912-922.[14] Buffa R,Mereu E, Comandini O, et al. Bioelectrical impedance vector analysis(BIVA) for the assessment of two-compartment body composition.2014;68(11):1234-1240.[15] Ward LC, Müller MJ. Bioelectrical impedance analysis.2013; 67: S1.[16] Mo D, Hsieh P, Yu H, et al. The relationship between osteoporosis and body composition in pre-and postmenopausal women from different ethnic groups in China.Ethn Health.2017;22(3):295-310.[17] Bolanowski M, Nilsson BE. Assessment of human body composition using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry and bioelectrical impedance analysis. Med Sci Monit. 2001;7(5): 1029-1033. [18] Jaffrin MY, Kieffer R, Moreno MV. Evaluation of a foot-to-foot impedance meter measuring extracellular fluid volume in addition to fat-free mass and fat tissue mass. Nutrition. 2005;21(7-8): 815-824. [19] Jebb SA, Siervo M, Murgatroyd PR, et al. Validity of the leg-to-leg bioimpedance to estimate changes in body fat during weight loss and regain in overweight women:a comparison with multi-compartment models. Int J Obes (Lond). 2007;31(5):756-762. [20] National Institute of Statistics. Condizioni di salute, fattori di rischio ericorso ai servizi sanitari. 2005. [21] Thomson R, Brinkworth GD, Buckley JD, et al. Good agreement between bioelectrical impedance and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for estimating changes in body composition during weight loss in overweight young women. Clin Nutr.2007;26(6):771-777. [22] 教育部国家学生体质健康标准说明[EB/OL]. [2014-07-28]. http://www.csh.edu.cn/index.htm.[23] Institute of Medicine.Fitness measures and health outcomes in youth].Washington,DC: National Academies Press,2012.[24] 龙斌, 李丹阳.功能性训练的科学内涵[J].武汉体育学院学报, 2013,47(2):72-76.[25] 李梅.艺术体操柔韧练习过程中伤病的预防[J].运动科学,2015 (1):28-30.[26] Plowman SA.Muscular strength,endurance,and flexibility assessments[C]//Plowman SA,Meredith MD.FITNESSGRAM/ACTIVITYGRAMreference guide. 2014; 8:1-55.[27] Miyachi M,Sanada K,Yamamoto K,et al.Age, flexibility,and metabolicsyndrome.Med Sci Sports Exerc.2007;39( Suppl 5):238.[28] Fernhall B,Agiovlasitis S.Arterial function in youth: Window into cardiovascular risk. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008;105(1): 325-333. [29] Yamamoto K,Kawano H,Gando Y,et al. Poor trunk flexibility is associated with arterial stiffening. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009;297(4):H1314-H1318.[30] Farinatti PT, Brandão C, Soares PP, et al.Acute effects of stretching exercise on the heart rate variability in subjects with low flexibility levels. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(6): 1579-1585.[31] Chillón P,Castro-Piñero J,Ruiz JR,et al.Hip flexibility is the main determinant of the back-saver sit-and-reach test in adolescents.J Sports Sci.2010:28(6): 641-648.[32] De Nardi M, La Torre A, Benis R,et al.Acute effects of whole-body cryotherapy on sit-and-reach amplitude in women and men.Cryobiology.2015;71(3):511-513.[33] 任拴锁.青少年标枪运动员柔韧性训练[J].青少年体育,2018, (3):115+65.[34] Mookerjee S,McMahon MJ. Electromyographic analysis of muscle activation during sit-and-reach flexibility tests. J Strength Cond Res. 2014;28(12):3496-3501.[35] 张葆欣,周道宏.健身关节操对中老年群体柔韧素质的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007,11(52):10522-10523+ 10542.[36] Davis DS,Quinn RO,Whiteman CT,et al.Concurrent validity of four clinical tests used to measure hamstring flexibility.J Strength Cond Res.2008;22(2):583-588.[37] Lemmink KA,Kemper HC,de Greef MH,et al.The validity of the sit-and-reach test and the modified sit-and-reach test in middle-aged to older men and women.Res Q Exerc Sport. 2003; 74(3):331-336.[38] López-Miñarro PA,Andújar PS,Rodrñguez-Garcña PL.A comparison of the sit-and-reach test and the back-saver sit-and-reach test in university students. J Sports Sci Med. 2009;8(1):116-122.[39] Mier CM. Accuracy and feasibility of video analysis for assessing hamstring flexibility and validity of the sit-and-reach test. Res Q Exerc Sport. 2011;82(4):617-623.[40] López-Miñarro PA,Rodríguez-García PL.Hamstring muscle extensibility influences the criterion-related validity of sit-and-reach and toe-touch tests.J Strength Cond Res. 2010; 24(4):1013-1018.[41] Liemohn W,Sharpe GL,Wasserman JF.Criterion related validity of the sit-and-reach test.J Strength Cond Res. 1994(8):91-94.[42] 肖红克,王莉,胡精超.河南省大学生体质状况以及影响体质健康的因素研究——基于2016年河南省高校体测数据的分析[J].吉林体育学院学报,2018,34(4):97-103.[43] Manire JT, Kipp R,Spencer J,et al. Diurnal variation of hamstring and lumbar flexibility.J Strength Cond Res. 2010; 24(6):1464-1471.[44] Chillón P,Castro-Piñero J,Ruiz JR,et al. Hip flexibility is the main determinant of the back-saver sit-and-reach test in adolescents.J Sports Sci.2010;28(6):641-648.[45] Miñarro PA,Andújar PS,García PL,et al.A comparison of the spine posture among several sit-and-reach test protocols. J Sci Med Sport.2007;10(6):456-462.[46] Kawano MM,Ambar G,Oliveira BI,et al.Influence of the gastrocnemius muscle on the sit-and-reach test assessed by angular kinematic analysis. Rev Bras Fisioter.2010;14(1): 10-15.[47] Youdas JW,Krause DA,Hollman JH.Validity of hamstring muscle length assessment during the sit-and-reach test using an inclinometer to measure hip joint angle.J Strength Cond Res.2008;22(1):303-309.[48] Mier CM, Shapiro BS.Sex differences in pelvic and hip flexibility in men and women matched for sit-and-reach score. J Strength Cond Res. 2013; 27(4): 1031-1035.[49] 尹亚晶,朱妹.瑜伽对中年女性体成分和平衡能力的影响[J].福建体育科技2011,33 (5):42-46.[50] Sharon Ann Plowman.儿童青少年骨骼肌相关体适能测试的10大研究问题[J].北京体育大学学报,2015,38(12):55-67.[51] 刘建国,周直模.太极拳和交谊舞对中老年人骨密度及柔韧性的对比研究[J].湖北体育科技,2012,31(3):325-326+330.[52] 魏燕玲,王子.高原大学生与平原大学生体质特征的对比分析[J].吉林体育学院学报,2017,33(4):82-88.[53] 马小明,樊蓉芸.高原低氧环境对人体适应性的影响探析[J].成都体育学院学报,2015, 41(3):94-97. [54] 许永东.青海省汉族中学生的体质现状和发展趋势[J].才智, 2012, (9):295. [55] 刘卫,李丰祥.大学生身体成分特征与运动能力及体质健康的关系[J].体育学刊,2004,11(1):52-55.[56] 张照萍.杭州市成年人体脂率与体质健康的相关性研究[D]. 金华:浙江师范大学,2014.[57] 杨梦利,娄晓民,彭玉林,等.大学生BMI与身体素质指标的相关性[J].中国学校卫生,2013,34(9):1093-1098.[58] 吴秀琴,周晓东,葛林伟,等.体脂分布类型与身体机能、素质的关系:福建省3个城市7614人调查[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(33):6550-6553.[59] 朱婉宁,李绍军,刘璐玮.大学生瘦体质量与运动能力的相关性研究[J].运动,2012, (13): 62-63.[60] 欧阳荣,夏云.论健美操柔韧性的训练[J].内江科技, 2011,32(10): 178-179.[61] 徐苏.瑜伽练习对青年女性体成分、柔韧性和静态平衡能力的影响[J].体育科技文献通报,2018,26(3):116-118.[62] 杨羿帆,陈玉凤.体育专业学生身体脂肪与运动能力的相关性研究[J].当代体育科技,2017,7(4):87-89.[63] 王小雷.瑜伽对青年女性身体功能及睡眠质量的影响研究[D]. 上海:上海师范大学,2016. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Shu Wenbo, Chen Mengchi, Li Hua, Huang Liqian, Huang Binbin, Zhang Wenhai, Wu Yachen, Wang Zefeng, Li Qiaoli, Liu Peng. Correlation between body fat distribution and characteristics of daily physical activity in college students [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1277-1283. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Wu Gang, Chen Jianwen, Wang Shilong, Duan Xiaoran, Liu Haijun, Dong Jianfeng. Simple HyProCure subtalar stabilization in treatment of adolescent flexible flatfoot combined with painful accessory navicular bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| [5] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Li Jun, Zuo Xinhui, Liu Xiaoyuan, Zhang Kai, Han Xiangzhen, He Huiyu, . Effect of over expression of miR-378a on osteogenic and vascular differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4939-4944. |
| [13] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [14] | Jiang Xiaoyan, Zhu Haifei, Lin Haiqi, Lin Wentao. Cold therapy promotes self-limited recovery of delayed-onset muscle soreness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3609-3613. |
| [15] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||