Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (19): 3110-3116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0253
Comparison of efficacy of lateral decubitus and supine position in treatment of elderly unstable intertrochanteric fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation
Lü Yang1, Wang Hai-zhou1, Zhong De-gui2, Liu Jun1, Chen Hai-yun1, Pan Jian-ke1
- 1The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine/Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Second Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2018-07-08Published:2018-07-08 -
Contact:Chen Hai-yun, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine/ Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Lü Yang, Physician, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine/ Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Project of Guangdong Province, No. 2012B061700037; the Medical Science and Technology Research Fund Project of Guangdong Province, No. A2017215; a grant from the Guangdong Provincial Finace Department, No. [2014]157; the Special Foundation for the Science and Technology Research Traditional Chinese Medicine of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. YK2013B2N19.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lü Yang, Wang Hai-zhou, Zhong De-gui, Liu Jun, Chen Hai-yun, Pan Jian-ke. Comparison of efficacy of lateral decubitus and supine position in treatment of elderly unstable intertrochanteric fractures with proximal femoral nail antirotation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(19): 3110-3116.
share this article
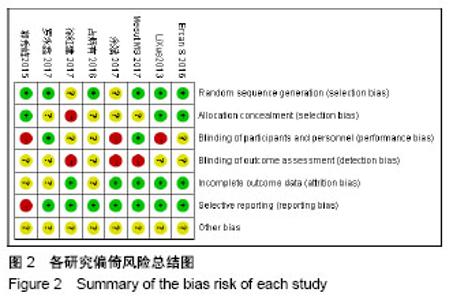
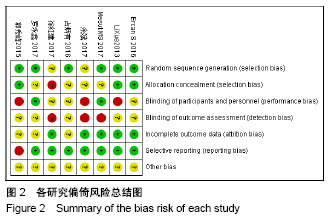
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 手术时间 共8篇文献报告了平均手术时间[9-16],由于研究间存在异质性,进行敏感性分析未见明显异常,分别对5篇纳入老年股骨转子间骨折的文献[9-12,14],以及3篇单独纳入老年股骨转子间骨折伴有肥胖的文献进行亚组分 析[13,15-16],异质性检验I2分别为0%和35%,均采用固定效应模型综合分析,分别得到[SMD=-2.92,95%CI(-3.28,-2.55),Z=15.67,P < 0.001] 和[SMD=-0.81,95%CI (-1.01,-0.61),Z=7.89,P < 0.000 1],两者差异均有显著性意义,见图3。 2.2.2 术前准备时间 共2篇报道了术前准备时间[9-10],研究存在异质性(I2=97%),而此Meta分析只纳入2个研究,不进行敏感性分析,各研究无临床异质性,纳入随机效应模型提示组间差异有显著性意义[MD=-7.58,95%CI (-14.42,-0.74),P=0.03 < 0.05],见图4。 2.2.3 术中透视次数 5个研究报道了术中平均透视相关指标[9-12,15],其中3篇文献提供了与术中平均透视次数的平均数和标准差[10,12,15],研究间存在统计学异质性(I2=87%),而此Meta分析只纳入3个研究,不进行敏感性分析,各研究无临床异质性,纳入随机效应模型提示结果具有统计学意义[MD=2.82,95%CI(0.91,4.72),P=0.004 < 0.01],见图5。其余2篇文献亦报道平卧位牵引床对术中透视时间/放射量低于平卧位人工牵引[9,11],且差异有显著性意义,但考虑两者单位不一致,未能合并进行综合分析。"
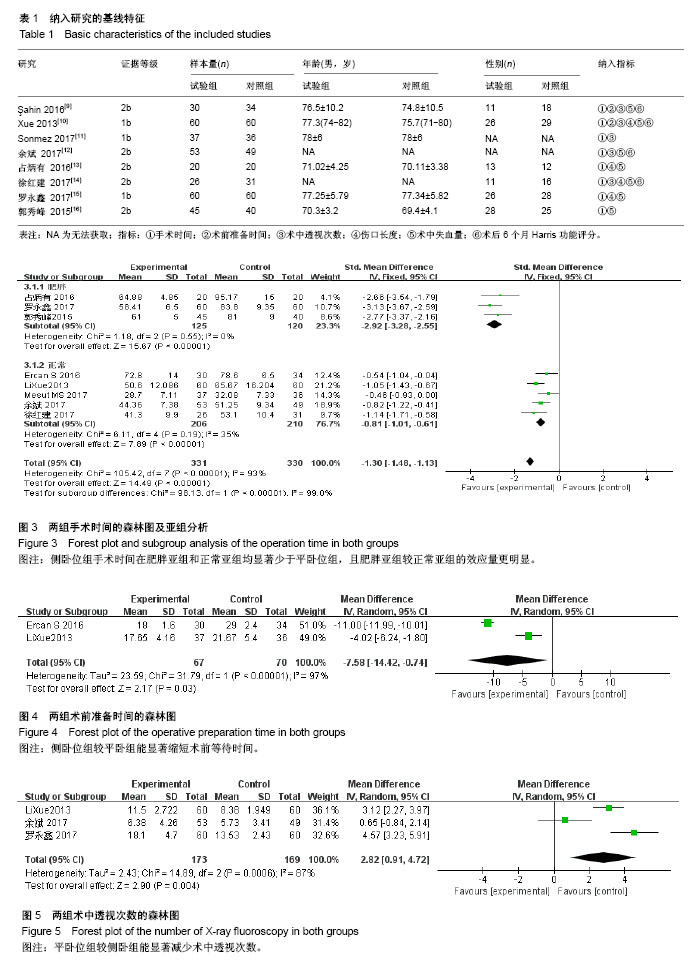
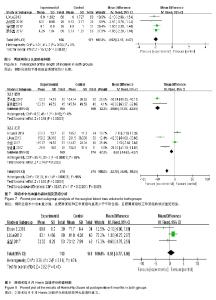
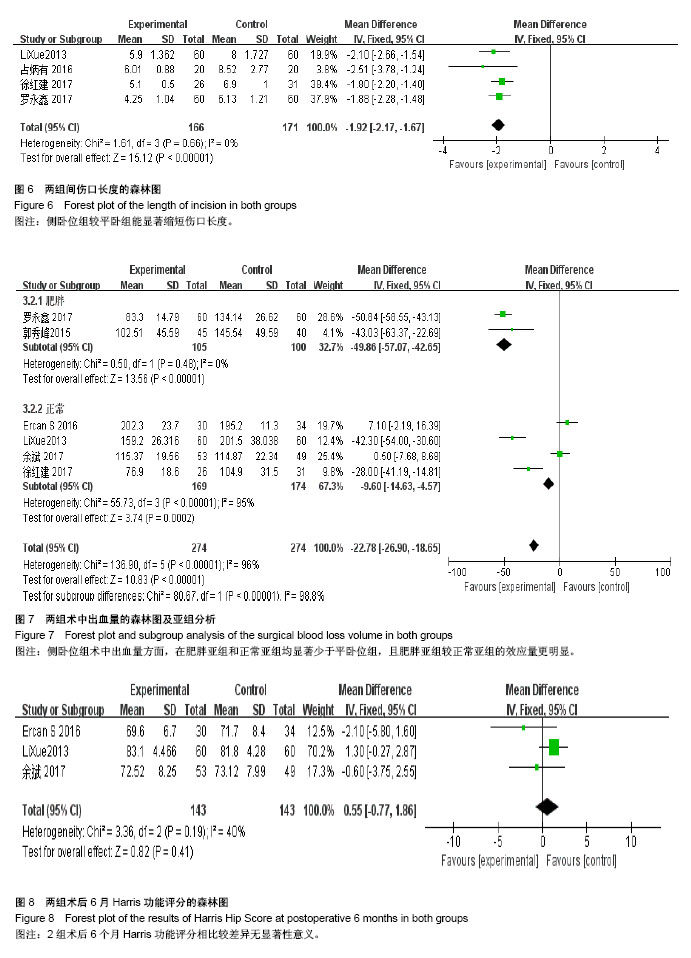
2.2.4 伤口长度 共4篇报道了平均伤口长度[10,13-15],人工牵引组与牵引床牵引进行Meta分析,研究间不存在异质性(I2=0%),纳入固定效应模型提示结果差异有显著性意义[MD=-1.92,95%CI(-2.17,-1.67),P < 0.000 1],见图6。 2.2.5 术中出血量 共6篇报道了平均伤口长度[9-10,12,14-16],2组研究间存在异质性(I2=96%),进行敏感性分析未见异常,分别对2篇单独纳入老年股骨转子间骨折伴有肥胖的文献[12-13],以及4篇纳入老年股骨转子间骨折的文献进行亚组分析[9,10,12,14],异质性检验I2分别为0%和95%,前者使用固定效应模型得到[MD=-49.86,95%CI(-57.07,-42.65),Z=13.58,P < 0.000 1],后者使用随机效应模型得到[MD=-22.90,95%CI(-14.63,-4.57),Z=3.74,P=0.000 2],两者差异均有显著性意义,见图7。 2.2.6 术后6个月Harris功能评分 共4篇报道了术后6个月Harris功能评分[9-10,12,14],研究存在异质性(I2=79%),敏感性分析剔除其中1个无临床异质性的研究[14],剩余研究间不存在异质性(I2=0%),纳入固定效应模型提示结果差异无显著性意义[MD=0.55,95%CI(-0.77,1.86),P > 0.05],见图8。"
| [1] 李岩,王东,孙海钰,等. 髓内与髓外系统骨钉置入治疗不稳定股骨转子间骨折的综合效果评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(35): 6254-6260.[2] 张立峰,林创鑫,冯卫,等. 斯氏针辅助复位在股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定治疗不稳定型股骨转子间骨折中的应用[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2017, 19(2): 127-132.[3] Sharma A, Mahajan A, John B. A Comparison of the clinico-radiological outcomes with proximal femoral nail (PFN) and proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in fixation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(7): C5-C9.[4] Doruk H, Mas MR, Yildiz C, et al. The effect of the timing of hip fracture surgery on the activity of daily living and mortality in elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2004;39(2):179-185.[5] Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Klaassen CD, et al. Alteration of bile acid and cholesterol biosynthesis and transport by perfluorononanoic acid (PFNA) in mice. Toxicol Sci.2017.[6] Bartonicek J, Dousa P, Jehlicka D. History of intramedullary nailing. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2001;68(1): 59-62.[7] Davis PH, Frymoyer JW. The lateral position in the surgical management of intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1969;51(6):1128-1134.[8] B P, Ball C, Sackett D. Levels of evidence and grades of recommendation. Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine. 2015.[9] ?ahin E, Songür M, Kalem M, et al. Traction table versus manual traction in the intramedullary nailing of unstable intertrochanteric fractures: A prospective randomized trial. Injury. 2016;47(7): 1547-1554.[10] Xue L, Zha L, Chen Q, et al. Randomized controlled trials of proximal femoral nail antirotation in lateral decubitus and supine position on treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Scientific World J.2013;2013: 1-7.[11] Sonmez MM, Camur S, Erturer E, et al. Strategies for proximal femoral nailing of unstable intertrochanteric fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(3): e37-e44.[12] 余斌,王敏,彭党兵,等. 非牵引床手法复位PFNA内固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折临床疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017,32(10): 1019-1021.[13] 占炳有. 不同手术体位在PFNA治疗股骨粗隆间骨折中的应用效果比较[J]. 中国当代医药, 2016,23(19):106-108.[14] 徐红建,周荣. 仰卧位与侧卧位行PFNA内固定治疗不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折的临床疗效对比[J]. 浙江创伤外科, 2017,22(1):103-106.[15] 罗永鑫,陈敬忠,余华伟,等. 不同体位下PFNA治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折疗效比较[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2017,23(2):154-157.[16] 郭秀峰. 侧卧位与平卧位下股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗肥胖患者股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 大家健康(中旬版), 2015, 9(10): 64-65.[17] 隋福革,汪群,王东军,等. 无牵引床下仰卧位与侧卧位股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013, 15(5): 447-449.[18] 王宏亮,李丹,李学军,等. 不同体位下股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折的临床研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(16): 1523-1525.[19] Turgut A, Kalenderer O, Karapinar L, et al. Which factor is most important for occurrence of cutout complications in patients treated with proximal femoral nail antirotation? Retrospective analysis of 298 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(5): 623-630.[20] Takigami I, Ohnishi K, Ito Y, et al. Acetabular perforation after medial migration of the helical blade through the femoral head after treatment of an unstable trochanteric fracture with proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA): a case report. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(9): e86-e89.[21] Jiamton C, Boernert K, Babst R, et al. The nail-shaft-axis of the of proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) is an important prognostic factor in the operative treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017.[22] Hu SJ, Chang SM, Ma Z, et al. PFNA-II protrusion over the greater trochanter in the Asian population used in proximal femoral fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2016;50(6):641-646.[23] Hong JB, Dan Y, Ouyang L, et al. Biomechanical study on different lengths of PFNA fixation for unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2017;17(4): 299-302.[24] 丁树伟,徐学振,张寿强,等. 侧卧位与仰卧位PFNA内固定治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2015, 30(6): 636-637.[25] Jiamton C, Boernert K, Babst R, et al. The nail-shaft-axis of the of proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) is an important prognostic factor in the operative treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017.[26] Shin WC, Seo JD, Lee SM, et al. Radiographic outcomes of osteosynthesis using proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) system in intertrochanteric femoral fracture: Has PFNA II Solved All the problems? Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(2): 104-112.[27] Shin YS, Chae JE, Kang TW, et al. Prospective randomized study comparing two cephalomedullary nails for elderly intertrochanteric fractures: Zimmer natural nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation II. Injury. 2017;48(7): 1550-1557.[28] Brunner A, Buttler M, Lehmann U, et al. What is the optimal salvage procedure for cut-out after surgical fixation of trochanteric fractures with the PFNA or TFN: A multicentre study. Injury. 2016;47(2): 432-438.[29] Shin YS, Chae JE, Kang TW, et al. Prospective randomized study comparing two cephalomedullary nails for elderly intertrochanteric fractures: Zimmer natural nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation II. Injury. 2017;48(7): 1550-1557.[30] 黄晋,杨松杰,罗勤瑜,等. 侧卧位与平卧位下股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗肥胖患者股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014, 16(4): 364-366.[31] 胡炳炎,艾金伟,陈琼,等. 系统评价和Meta分析股骨近端髓内钉与防旋型股骨近端髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的差异[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(53): 8010-8021.[32] Macheras GA, Koutsostathis SD, Galanakos S, et al. Does PFNA II avoid lateral cortex impingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(11): 3067-3076.[33] Turgut A, Kalenderer O, Gunaydin B, et al. Fixation of intertrochanteric femur fractures using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) in the lateral decubitus position without a traction table. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(5): 513-520.[34] Tao YL, Ma Z, Chang SM. Does PFNA II avoid lateral cortex impingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(4): 1393-1394.[35] 林少胜,谢扬,黄铿. 侧卧位和仰卧位PFNA治疗肥胖患者股骨转子间骨折的临床疗效对比研究[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2017,19(2): 102-105.[36] 邱志杰,杨惠林,魏立. PFNA治疗老龄不稳定股骨转子间骨折76例的临床疗效分析[J]. 重庆医学, 2010, 39(17): 2270-2272.[37] Kini SG, Hin LC, Haniball J. Lateral cortex blowout during PFNA blade insertion in a subtrochanteric fracture---Should bone quality determine the type of nail used? Chin J Traumatol. 2015;18(2): 116-119.[38] Turgut A. Fixation of intertrochanteric femur fractures using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) in the lateral decubitus position without a traction table. Acta Orthopaedica et Traumatologica Turcica. 2014;48(5): 513-520.[39] 黄凤琪,肖小注,邓建龙,等. 两种体位下PFNA治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的临床比较[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2015,21(5): 448-450.[40] 陈伟,魏宁,杜晨光,等. 顺势双反牵引复位和牵引床复位对手术治疗老年股骨转子间骨折疗效的影响[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2017, 33(4): 332-337. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [3] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [4] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [5] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [6] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [7] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [8] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [9] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [10] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [11] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [12] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [13] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [14] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [15] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||