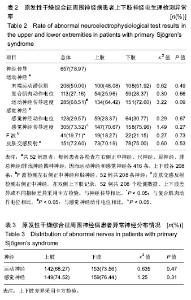
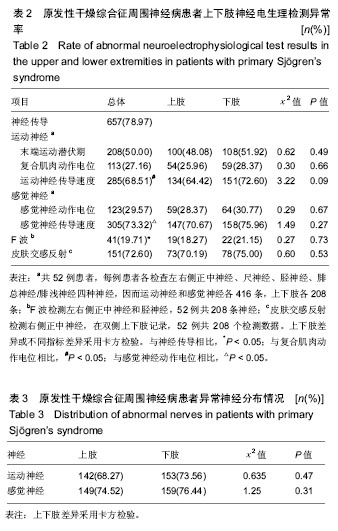
| [1] Brito-Zerón P, Baldini C, Bootsma H, et al. Sjögren syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16047.[2] 陈璟珠,钟南山,陆再英.内科学[M].8版.北京:人民卫生出版社. 2013:826-829.[3] Mellgren SI, Conn DL, Stevens JC, et al. Peripheral neuropathy in primary Sjögren's syndrome. Neurology. 1989;39(3):390-394.[4] Grant IA, Hunder GG, Homburger HA, et al. Peripheral neuropathy associated with sicca complex. Neurology. 1997; 48(4):855-862.[5] Cao BZ, Cao XB, Chang GF, et al. Clinicopathological analysis on neurological injuries in Sjögren syndrome. Zhonghua Shenjing Ke Zazhi. 2005;38:434-437.[6] Goransson LG, Herigstad A, Tjensvoll AB, et al. Peripheral neuropathy in primary sjogren syndrome: a population-based study. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(11):1612-1615.[7] Tobón GJ, Pers JO, Devauchelle-Pensec V, et al. Neurological Disorders in Primary Sjögren's Syndrome. Autoimmune Dis. 2012;2012:645967.[8] Mellgren SI, Göransson LG, Omdal R. Primary Sjögren's syndrome associated neuropathy. Can J Neurol Sci. 2007; 34(3):280-287.[9] 孟肃,何志义.以周围神经病变为首发症状的干燥综合征3例临床分析及文献回顾[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2014,31:451-452.[10] 程新旺,郭洁,汪志云.以周围神经损害为首发表现的干燥综合征1例报告[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2013,30:660-661.[11] Gemignani F, Marbini A, Pavesi G, et al. Peripheral neuropathy associated with primary Sjögren's syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994;57(8):983-986.[12] Wakasugi D, Kato T, Gono T, et al. Extreme efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for severe burning pain in a patient with small fiber neuropathy associated with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Modern rheumatology. 2009; 19(4):437-440.[13] Sandroni P, Low PA. Autonomic peripheral neuropathies: clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. J Clin Neuromuscul Dis. 2001;2(3):147-157.[14] Gorson KC, Ropper AH. Positive salivary gland biopsy, Sjögren syndrome, and neuropathy: clinical implications. Muscle Nerve. 2003;28(5):553-560.[15] Rodier G, Weber JC. Involvements of the peripheral nervous system and primary Gougerot-Sjogren syndrome. Rev Med Interne. 1996;17(7):558-562.[16] 崔丽英.简明肌电图学手册[M].北京:科学出版社.2006. [17] David C, Preston MD. Electromyography and Neuromuscular Disorders. 2013: Elsevier Inc.[18] Morgen K, Mcfarland HF, Pillemer SR. Central nervous system disease in primary Sjogrens syndrome: the role of magnetic resonance imaging. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 34(3):623-630.[19] Qi XK, Dong QW. The clinical symptoms and treatment of connective tissue disease involving the nervous system. Zhognguo Shiyong Neike Zazhi. 2012;32(11):842-845.[20] Li YX, Wu LJ, Chen QT. Clinical and pathological changes of neuromuscular complications in 7 Sjogren's syndrome cases. Zhonghua Shenjing Ke Zazhi. 2001;34(6):344-346. |