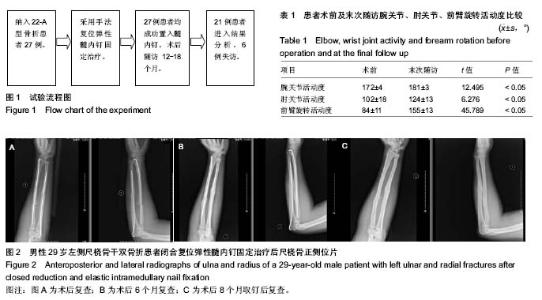
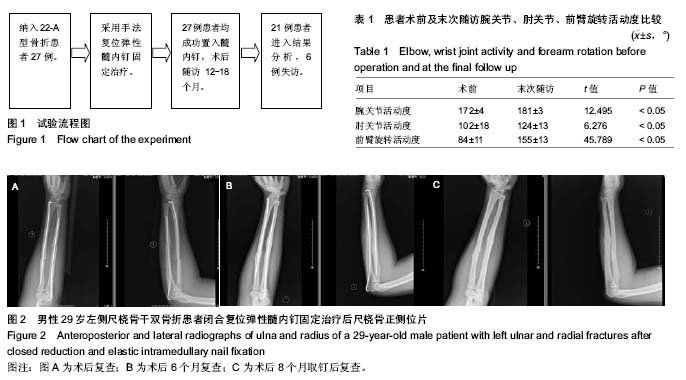
| [1] Puedi TP. 骨折治疗的AO原则[M].2版.上海:上海科学出版社, 2014:481.[2] Brooker B, Harries PC, Donnan LT,et al. Rupture of the extensor pollicis longus tendon following dorsal entry flexible nailing of radial shaft fractures in children.J Child Orthop. 2014;8(4):353-357.[3] 马一平,胡成挺,陈林,等.克氏针辅助复位弹性钉治疗儿童严重移位尺桡骨骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(10):956-958.[4] 蓝芳,林伟龙.AO钛制弹性髓内钉治疗儿童前臂不稳定性尺桡骨双骨折[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(9):49-50.[5] 张鑫,罗聪,李明,等.弹性髓内钉与钢板治疗儿童尺桡骨双骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(2):139-142.[6] 陈洪娇,彭磊,程少文.单根弹性髓内钉治疗儿童尺桡骨双骨折的疗效分析[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报, 2014,48(5):425-427.[7] 韩赛平,郑许飞,李维, 等.钛制弹性髓内钉治疗儿童前臂骨折的临床观察[J].创伤外科杂志,2017,19(1):43-45.[8] 王庆雷.弹性钉与钢板内固定治疗儿童前臂双骨折的效果观察[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(15):92-93.[9] 周连军,孙建华,刘爱春.儿童四肢长骨干闭合骨折不同治疗方法的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,5(28):428.[10] 刘国庆,王文己,时红萍,等.弹性髓内钉与钢板内固定修复前臂骨折疗效与安全性的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(26): 4248-4253.[11] Puedi TP. 骨折治疗的AO原则[M].2版.上海:上海科学出版社, 2014:55-62.[12] Anderson LD, Sick D, Tooms RE, et al. Compression-plate fixation in acute diaphyseal fractures of the radius and ulna. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975;57 (3):287-297.[13] 白晓东,张韶峰.前臂旋转功能障碍的解剖研究及其临床应用[J].中国临床康复,2006,28(7):138.[14] 赵洪,瞿玉兴,郑祖根.桡骨弓尺骨弓与前臂旋转功能的实验研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2007,22(1):28.[15] 尚天裕,吴之庆,方先之.应该怎样处理桡尺骨干双骨折[J].天津医药杂志,1959,1(5): 346.[16] 王亦璁,姜保国.骨与关节损伤[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2011:867-869.[17] 马晓春.不同治疗方法对尺桡骨干双骨折前臂功能的影响研究[J].临床医学工程,2012,19(5):738-739.[18] 何方,李国庆,叶方全. 尺桡骨骨干双骨折内固定术后前臂旋转功能障碍[J]. 中国骨伤,2004,17(4):19-20.[19] 刘晓化,赵延君,姜军,等.治疗前臂骨折畸形愈合致旋转功能障碍的体会[J].中国伤残医学,2013,21(6):117-118.[20] 常树松,王玉兰,王红,等.尺桡骨骨折术后前臂旋转功能障碍预防的疗效回顾性分析[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2010,31(4): 559.[21] 林成君,刘磊,杜学刚,等.前臂双骨折内固定方法的比较研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,1991,6(3):145.[22] 韩久卉,冯文岭,张英泽,等.内固定治疗前臂骨折疗效观察[J].河北中西医结合杂志,1993,8(3):368.[23] 李永旺.尺桡骨干双骨折的治疗[J].中国医疗前沿,2011,6(24): 30-31.[24] 马俊,赵林,夏鸿,等.重建钢板治疗尺桡骨干骨折的疗效观察[J]. 医学理论与实践,2015,28(12):1610-1612.[25] Sink EL, Gralla J, Repine M. Complications of pediatric femur fractures treated with titanium elastic nails: A comparison of fracture types. Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25: 577-580[26] 张建军,李金光.手法闭合复位与小切口复位弹性钉在儿童股骨干骨折治疗中的效果比较[J].微创医学,2016,11(5):703-705.[27] 谢亮喜. 弹性髓内钉内固定治疗儿童股骨干骨折临床研究[J]. 中国医学创新,2014,11(5):119-121.[28] 周连军,孙建华,刘爱春,等.弹性髓内钉治疗儿童长骨干骨折疗效观察[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(3):51-54.[29] 刘国庆. 弹性髓内钉与钢板内固定修复前臂骨折疗效与安全性的Meta分析[D].兰州大学,2015.[30] 谭家昌,杨有猛,徐鸿育,等.弹性髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗儿童股骨干骨折的疗效对比[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2012,27(12): 1119-1120.[31] 江剑,孙志波,禹志宏.弹性髓内钉与钢板内固定治疗儿童股骨干骨折疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2016,19(3):343-345.[32] 程少文,王伟,林忠勤,等.弹性髓内钉与锁定钢板内固定治疗儿童肱骨骨折的疗效比较[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2010,18(11): 26-28.[33] 林峰,李兵兵,陈宇.锁定钛板结合弹性髓内钉内固定治疗成人胫腓骨下段骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(8):876-877.[34] Aksoy C,Caosor O,Yazycy M,et al.Pediatric femoral fractures: a comparison of compression-plate fixation and flexible intramedullary nail fixation. Bone Joint Surg. 2003;85: 263.[35] Flynn JM, Luedtke LM, Ganley TJ, et al. Comparison of titanium elastic nails with traction and a spica cast to treat femoral fractures in children. Bone Surg. 2004;86:770-771.[36] 王庆雷.不同内固定方式治疗大龄儿童尺桡骨双骨折的临床效果比较[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(13):68-69.[37] Sayed M, Abulsaad M, Elhad M, et al. Reconstruction plate fixation of subtrochanteric femoral fractures in children. Acta Orthop Belg. 2007;73(4):484-490.[38] Sandders JO, Browne RH, Mooney JF, et al. Treatment of femora fracture in children by pediatric orthopedists results of a 1998 survey. Pediatr Orthop. 2001;21(8):436.[39] 李豹,林光锚,潘展鹏.钛制弹性髓内钉治疗小儿尺桡骨不稳定双骨折18例[J].浙江中医药大学报,2011,34(6):875.[40] Mahar AT, Lee SS, Lalonde FD, et al. Biomechanical comparison of stainless steel and titanium nails for fixation of simulated femoral fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2004;24(6): 638-641.[41] Huang YC, Renn JH, Tarng YW. The titanium elastic nail serves as an alternative treatment for adult proximal radial shaft fractures: a cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1): 10.[42] ?ahin N, Akal?n Y, Türker O, et al. ESIN and K-wire fixation have similar results in pediatric both-bone diaphyseal forearm fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2017;23(5): 415-420. [43] Heare A, Goral D, Belton M, et al. Intramedullary implant choice and cost in the treatment of pediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(10):e334-e338.[44] Lu D, Lin Z, Zhang JD, et al. Treatment of pediatric forearm midshaft fractures: Is there a difference between types of orthopedic surgeon? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017; 103(1):119-122.[45] Lyman A, Wenger D, Landin L. Pediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures: epidemiology and treatment in an urban population during a 10-year period, with special attention to titanium elastic nailing and its complications. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2016; 25(5):439-446. [46] Cai H, Wang Z, Cai H. Prebending of a titanium elastic intramedullary nail in the treatment of distal radius fractures in children. Int Surg. 2014;99(3):269-275.[47] Sinikumpu JJ, Keränen J, Haltia AM, et al. A new mini-invasive technique in treating pediatric diaphyseal forearm fractures by bioabsorbable elastic stable intramedullary nailing: a preliminary technical report. Scand J Surg. 2013;102(4):258-264. [48] Furlan D, Pogoreli? Z, Bio?i? M, et al. Elastic stable intramedullary nailing for pediatric long bone fractures: experience with 175 fractures. Scand J Surg. 2011;100(3): 208-215.[49] Kravel T, Sher-Lurie N, Ganel A. Extensor pollicis longus rupture after fixation of radius and ulna fracture with titanium elastic nail (TEN) in a Child: a case report. J Trauma. 2007; 63(5):1169-1170. [50] Mendoza-Balta RJ, Bello-González A, Rosas-Cadena JL. Treatment of shaft fractures in children with elastic titanium nails. Acta Ortop Mex. 2009;23(5):286-291. |