Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (32): 5227-5233.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.32.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Signaling pathways in secondary injuries following spinal cord injury
Yang Yong-dong1, Zhao He1, Yu Xing1, Tang Xiang-sheng2, Hu Zhen-guo1, Chen Si-xue1, Liu Tao1, Xu Lin1
- (1Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China; 2Department of Orthopaedics, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China)
-
Received:2017-09-25Online:2017-11-18Published:2017-11-15 -
Contact:Yu Xing, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China -
About author:Yang Yong-dong, M.D., Attending physician, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China Zhao He, Studying for doctorate, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China Yang Yong-dong and Zhao He contributed equally to this work.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yong-dong1, Zhao He1, Yu Xing1, Tang Xiang-sheng2, Hu Zhen-guo1, Chen Si-xue1, Liu Tao1, Xu Lin1. Signaling pathways in secondary injuries following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(32): 5227-5233.
share this article
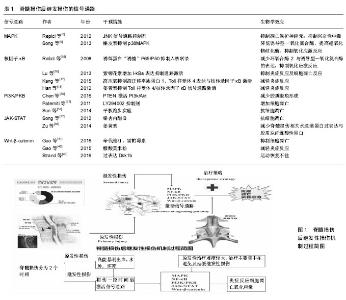
2.1 MAPK信号通路 2.1.1 概述及组成 以MAPK为代表的信号转导通路统称为MAPK通路。该通路主要特点是MAPK逐级磷酸化后入核,在核内对转录因子及其他效应分子进行磷酸化修饰从而产生以细胞增殖、分化、炎症、凋亡及应激为主的生物学效应[1]。MAPK在哺乳动物中已证实至少有5个亚家族,其中起主导作用的有3个亚家族成员,分别是细胞外信号调节激酶、c-Jun N端激酶/应激激活的蛋白激酶(JNK/SAPK)、p38MAPK。其中细胞外信号调节激酶参与构成经典Ras/MAPK信号转导途径,在细胞增殖与分化调控中具有重要作用,如酪氨酸激酶受体(Trk)A/B、表皮生长因子受体、成纤维生长因子受体、血小板衍生生长因子受体等多种受体均需要细胞外信号调节激酶的活化来完成信号转导过程。JNK/SAPK与p38MAPK两者均参与细胞对辐射、渗透压及温度变化等应激反应过程使靶细胞发生"

| [1] Spencer JP, Vafeiadou K, Williams RJ, et al. Neuroinflammation: modulation by flavonoids and mechanisms of action. Mol Aspects Med. 2012; 33(1):83-97. [2] Blanc A1, Pandey NR, Srivastava AK. Synchronous activation of ERK 1/2, p38mapk and PKB/Akt signaling by H2O2 in vascular smooth muscle cells: potential involvement in vascular disease. Int J Mol Med. 2003; 11(2):229-234.[3] Arthur JS, Ley SC. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13(9):679-692.[4] Liu T, Cao FJ, Xu DD, et al. Upregulated Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling pathway: a new hope in the repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(5):792-796. [5] Lawrence MC, Jivan A, Shao C, et al. The roles of MAPKs in disease. Cell Res. 2008; 18(4):436-442. [6] Choi DC, Lee JY, Lim EJ. Inhibition of ROS-induced p38MAPK and ERK activation in microglia by acupuncture relieves neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 2012;236(2):268-282. [7] Gantke T, Sriskantharajah S, Sadowski M. IκB kinase regulation of the TPL-2/ERK MAPK pathway. Immunol Rev. 2012 ; 246(1):168-182. [8] Repici M, Chen X, Morel MP. Specific inhibition of the JNK pathway promotes locomotor recovery and neuroprotection after mouse spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis. 2012; 46(3):710-721. [9] Song Y, Liu J, Zhang F, et al. Antioxidant effect of quercetin against acute spinal cord injury in rats and its correlation with the p38MAPK/iNOS signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2013; 92(24-26):1215-1221. [10] Kim KT, Kim HJ, Cho DC, et al. Substance P stimulates proliferation of spinal neural stem cells in spinal cord injury via the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Spine J. 2015; 15(9):2055-2065. [11] Ting AT, Bertrand MJ. More to Life than NF-κB in TNFR1 Signaling. Trends Immunol. 2016; 37(8):535-545. [12] Han X, Wang SY, Zhang Z, et al. BMS-345541 inhibited nuclear factor kappa B expression and improved locomotor function recovery in rats after acute spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2011;6: 1775-1779.[13] Napetschnig J, Wu H. Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling.Annu Rev Biophys. 2013; 42:443-468. [14] Sasaki K, Iwai K.Roles of linear ubiquitinylation, a crucial regulator of NF-κB and cell death, in the immune system.Immunol Rev. 2015; 266(1):175-189. [15] Rafati DS, Geissler K, Johnson K, et al. Nuclear factor-kappa B decoy amelioration of spinal cord injury-induced inflammation and behavior outcomes. J Neurosci Res. 2008; 86(3):566-580.[16] Lu M, Wang S, Han X, et al. Butein inhibits NF-κB activation and reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells and apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2013; 542:87-91. [17] Kang N, Hai Y, Yang J,et al. Hyperbaric oxygen intervention reduces secondary spinal cord injury in rats via regulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8(2):1141-1153. [18] Han X, Lu M, Wang S, et al. Targeting IKK/NF-κB pathway reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells and apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurosci Lett. 2012;511(1):28-32. [19] Ni H, Jin W, Zhu T, et al. Curcumin modulates TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway following traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. J Spinal Cord Med. 2015;38(2):199-206. [20] Yarar-Fisher C, Bickel CS, Kelly NA, et al. Heightened TWEAK-NF-κB signaling and inflammation-associated fibrosis in paralyzed muscles of men with chronic spinal cord injury.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016;310(9):E754-761. [21] Kaltschmidt C, Kaltschmidt B, Neumann H, et al. Constitutive NF-kappa B activity in neurons. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14(6): 3981-3992.[22] Pizzi M, Goffi F, Boroni F, et al. Opposing roles for NF-kappa B/Rel factors p65 and c-Rel in the modulation of neuron survival elicited by glutamate and interleukin-1beta.J Biol Chem. 2002;277(23):20717-20723.[23] Lipton SA. Janus faces of NF-kappa B: neurodestruction versus neuroprotection.Nat Med. 1997;3(1):20-22.[24] Jiménez-Garza O, Camacho J, Ibarra A, et al. Early effects of modulating nuclear factor-kappaB activation on traumatic spinal cord injury in rats.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1053:148-150.[25] Martini M, De Santis MC, Braccini L, et al. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and cancer: an updated review. Ann Med. 2014; 46(6):372-383. [26] Hemmings BA, Restuccia DF. The PI3K-PKB/Akt pathway.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(4). pii: a026609. [27] Porta C, Paglino C, Mosca A.Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling in Cancer.Front Oncol. 2014;4:64. [28] Chappell WH, Steelman LS, Long JM, et al. Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR inhibitors: rationale and importance to inhibiting these pathways in human health. Oncotarget. 2011;2(3):135-164.[29] Zheng B, Ye L, Zhou Y, et al. Epidermal growth factor attenuates blood-spinal cord barrier disruption via PI3K/Akt/Rac1 pathway after acute spinal cord injury.J Cell Mol Med. 2016;20(6):1062-1075. [30] Chen CH, Sung CS, Huang SY,et al. The role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in glial scar formation following spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2016;278:27-41. [31] Paterniti I, Esposito E, Mazzon E. Evidence for the role of PI(3)-kinase-AKT-eNOS signalling pathway in secondary inflammatory process after spinal cord compression injury in mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2011; 33(8):1411-1420.[32] Sun Y, Dae YK, Tae YY, et al. Treadmill exercise reduces spinal cord injury?induced apoptosis by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in rats. Exp Ther Med. 2014; 7: 587-593.[33] Zhang P, Zhang L, Zhu L, et al. The change tendency of PI3K/Akt pathway after spinal cord injury. Am J Transl Res. 2015; 7(11):2223-2232. eCollection 2015.[34] Nicolas CS, Amici M, Bortolotto ZA, et al. The role of JAK-STAT signaling within the CNS.JAKSTAT. 2013;2(1): e22925. [35] He G, Karin M. NF-κB and STAT3-key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011;21(1):159-168. [36] Kiu H, Nicholson SE. Biology and significance of the JAK/STAT signalling pathways.Growth Factors. 2012;30(2):88-106. [37] Song Y, Zeng Z, Jin C. Protective effect of ginkgolide B against acute spinal cord injury in rats and its correlation with the JAK/STAT signaling pathway.Neurochem Res. 2013; 38(3):610-619. [38] Zu J, Wang Y, Xu G,et al. Curcumin improves the recovery of motor function and reduces spinal cord edema in a rat acute spinal cord injury model by inhibiting the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Acta Histochem. 2014;116(8):1331-1336. [39] Huelsken J, Vogel R, Erdmann B. Beta-Catenin controls hair follicle morphogenesis and stem cell differentiation in the skin.Cell. 2001;105(4):533-545.[40] Clevers H, Nusse R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149(6):1192-1205. [41] Gao K, Shen Z, Yuan Y, et al. Simvastatin inhibits neural cell apoptosis and promotes locomotor recovery via activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway after spinal cord injury. J Neurochem. 2016;138(1):139-149. [42] Gao K, Wang YS, Yuan YJ,et al. Neuroprotective effect of rapamycin on spinal cord injury via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(6):951-957.[43] Strand NS, Hoi KK, Phan TM, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes regeneration after adult zebrafish spinal cord injury.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;477(4):952-956. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [3] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [4] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [5] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [6] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [7] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [8] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [9] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [10] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [11] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [12] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [13] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [14] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [15] | Li Xuan, Sun Yimin, Li Longbiao, Wang Zhenming, Yang Jing, Wang Chenglin, Ye Ling. Manufacturing of nano-modified polycaprolactone microspheres and its biological effects in dental pulp cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1530-1536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||