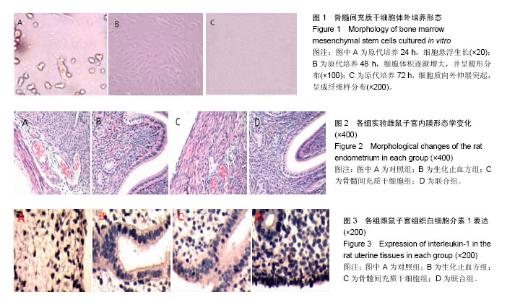
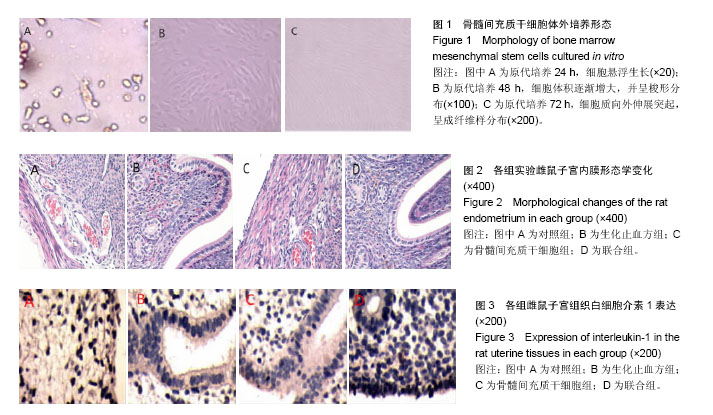
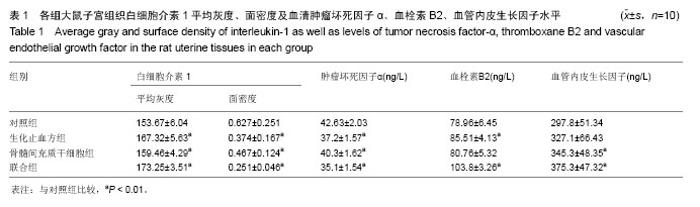
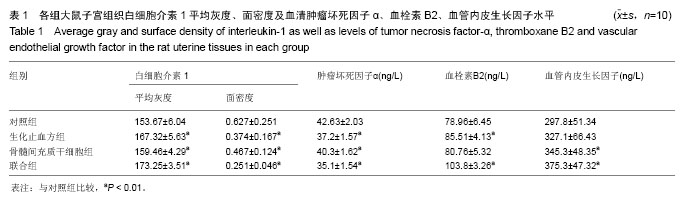
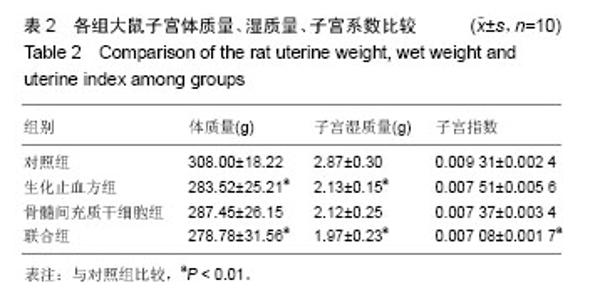
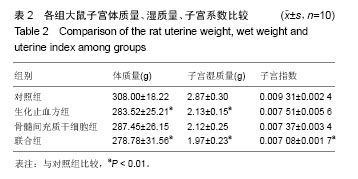
| [1] 乐杰.妇产科学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:77-82.[2] Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, et al. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968;6(2):230-247.[3] 韩冉,戴宁,林韵,等.妇科养坤丸与骨髓间充质干细胞移植修复薄型子宫内膜[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(1):65-69.[4] 刘滋康,具星爱,靳继德,等.肝细胞生长因子基因修饰的人骨髓间充质干细胞促进大鼠肢体血管新生[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2010,6(2):61-65.[5] 雷香丽.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的体外培养及体内移植实验性研究[D].广州:南方医科大学, 2012.[6] 曾晶,尤昭玲,查亚萍,等.妇科止血消痛颗粒对产后子宫复旧不全大鼠模型子宫MMP-9、TIMP-1mRNA表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2010, 17(6):31-33.[7] Gargett CE, Schwab KE, Zillwood RM, et al. Isolation and culture of epithelial progenitors and mesenchymal stem cells from human endometrium. Biol Reprod. 2009;80(6): 1136-1145.[8] Ito Y, Goldschmeding R, Kasuga H, et al. Expression patterns of connective tissue growth factor and of TGF-beta isoforms during glomerular injury recapitulate glomerulogenesis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010;299(3):F545-558.[9] Leask A, Holmes A, Abraham DJ. Connective tissue growth factor: a new and important player in the pathogenesis of fibrosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002;4(2):136-142.[10] 王永刚. 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向子宫内膜细胞分化的体外实验[D].长沙:中南大学, 2012.[11] 张雯碧,程明军,徐丛剑.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向子宫内膜上皮细胞方向分化的体外实验[J].现代妇产科进展, 2010,19(4): 257-260.[12] Li CD, Zhang WY, Yuan CL, et al. Simulated uterus microenvironment induced human placental mesenchymal stem cells differentiation to uterus smooth muscle cells in vitro. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;88(45):3200-3204.[13] 韦伟,郑飞云,杨孝军.骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进大鼠子宫创伤修复[J].基础医学与临床, 2012, 32(7):727-733.[14] 张晓磊, 卢美松. 骨髓间充质干细胞与子宫内膜再生[J].国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2015,34(5):433-436.[15] McLaren J. Vascular endothelial growth factor and endometriotic angiogenesis. Hum Reprod Update. 2000; 6(1):45-55.[16] Merighi S, Benini A, Mirandola P, et al. Adenosine modulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression via hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in human glioblastoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72(1):19-31.[17] Jing Z, Qiong Z, Yonggang W, et al. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve regeneration of thin endometrium in rat. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(2):587-594.[18] 李霞,陈飞虎,袁凤来,等.益母草碱对药物流产后大鼠子宫的作用研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2009,14(5):481-486.[19] 梁晋如.山茱萸的化学成分及其生物活性研究[D]. 西安:西北大学,2014.[20] 赵娜,郭治昕,赵雪,等.丹参的化学成分与药理作用[J]. 现代药物与临床,2007,22(4):155-160.[21] 窦红霞,高玉兰.防风的化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J].中医药信息,2009,26(2):15-17.[22] 刘兆平,卢承前,陈君石.子宫实验和E-SCREEN实验在检测雌激素活性中的相关性[J].卫生研究,2004,33(4):458-460.[23] Goebeler M, Gillitzer R, Kilian K, et al. Multiple signaling pathways regulate NF-kappaB-dependent transcription of the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene in primary endothelial cells. Blood. 2001;97(1):46-55. |