Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (21): 3312-3319.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.21.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chondrogenesis of adipose tissue-derived stem cells induced by auricular chondrocytes from microtia in vivo
Cai Zhen1, Jiang Hai-yue2
- 1Department of Plastic Surgery, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; 2Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100144, China
-
Revised:2017-03-22Online:2017-07-28Published:2017-08-02 -
Contact:Jiang Hai-yue, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Professor, Chief physician, Plastic Surgery Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100144, China -
About author:Cai Zhen, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Plastic Surgery, Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences & Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cai Zhen, Jiang Hai-yue. Chondrogenesis of adipose tissue-derived stem cells induced by auricular chondrocytes from microtia in vivo[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(21): 3312-3319.
share this article
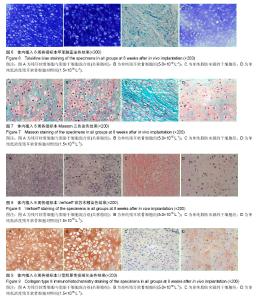
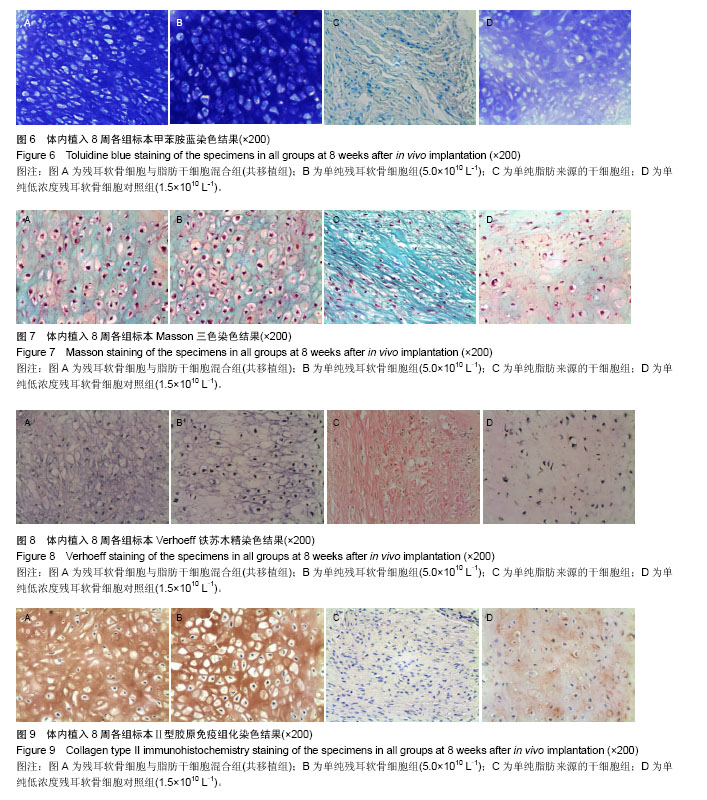
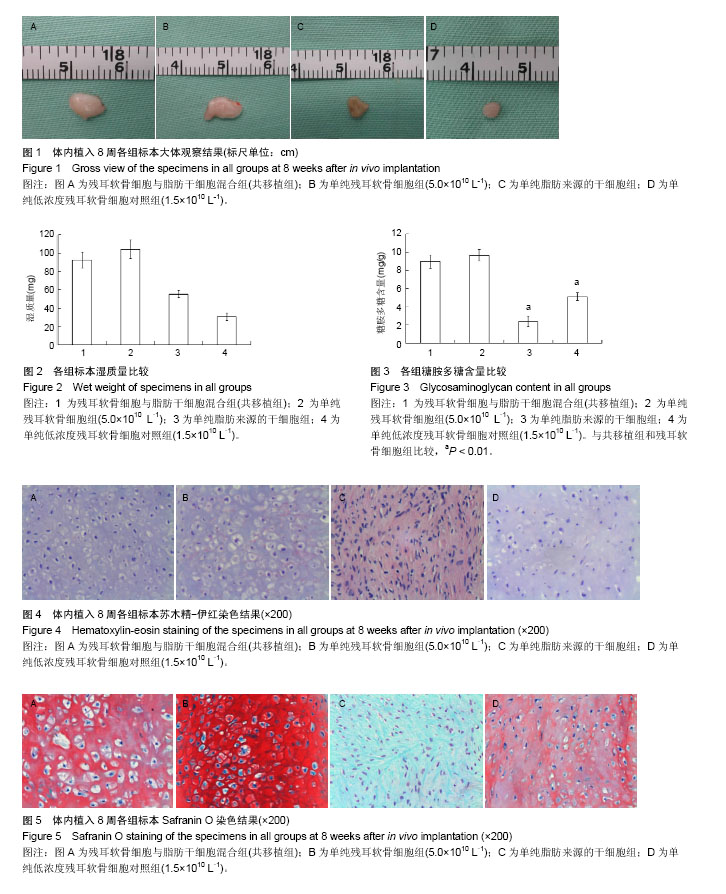
2.1 实验动物数量分析 纳入裸鼠数量24只,分4组,全部进入结果分析,无脱失。 2.2 新生组织大体观察 体内植入8周后,4组细胞- Pluronic F-127复合物均形成了较成熟的组织,新生组织周围有一层透明纤维膜包裹,纤维膜表面可见血管分支走行。共移植组与残耳软骨细胞组、低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组注射部位均有白色半透明状类似软骨组织形成,共移植组与残耳软骨细胞组标本组织外观和弹性与正常软骨极为相似,外有一层透明包膜,未见有明显的血管;低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组大部分标本表面光泽度及弹性差,脂肪干细胞组生成质软的纤维样组织,色淡黄色。各组标本大小不等,低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组标本明显小于共移植组、残耳软骨细胞组和脂肪干细胞组(见图1)。 2.3 新生组织平均湿质量与糖胺多糖含量比较 平均湿质量:共移植组的平均湿质量达到残耳软骨细胞组的80%以上;低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组平均湿质量低于残耳软骨细胞组的30%,见图2。 糖胺多糖平均含量:统计学分析结果表明,共移植组与残耳软骨细胞组的糖胺多糖含量差异无显著性意义(P=0.086 5 > 0.05),但脂肪干细胞组和低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组的糖胺多糖含量均显著低于共移植组和残耳软骨细胞组(P < 0.01),见图3。 2.4 新生组织组织学检查 2.4.1 苏木精-伊红染色 共移植组、残耳软骨细胞组与低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组组织内均有成熟的软骨陷窝形成,但陷窝大小不规则,细胞浓度与细胞排列不均匀;脂肪干细胞组为纤维样组织,未见软骨陷窝形成。低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组软骨陷窝数量较共移植组和单纯残耳软骨细胞组少,排列松散,胞外基质着色较共移植组和单纯残耳软骨细胞组淡,见图4。 2.4.2 Safranin O染色 共移植组、单纯残耳软骨细胞组与低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组组织内胞外基质均染成红色,可见大量软骨陷窝形成;单纯脂肪来源的干细胞组基质染色阴性,未见软骨陷窝形成;低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组可见胞外基质红染较共移植组和单纯残耳软骨细胞组着色浅且不均匀,且软骨陷窝排列松散,陷窝数量较共移植组与单纯残耳软骨细胞组少,见图5。 2.4.3 甲苯胺蓝染色 共移植组、单纯残耳软骨细胞组组织内均可见大量染成深蓝色的胞外基质,其间可见大量成熟的软骨陷窝;单纯脂肪来源的干细胞组基质染色阴性,未见软骨陷窝形成;低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组可见胞外基质蓝染不均匀,且软骨陷窝排列松散,陷窝数量较共移植组与单纯残耳软骨细胞组少,见图6。 2.4.4 Masson三色染色 共移植组、单纯残耳软骨细胞组与低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组软骨胞外基质有大量染成绿色的胶原存在;单纯脂肪来源的干细胞组可见大量绿色胶原纤维存在,未见软骨陷窝;低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组胞外基质中绿色胶原含量较共移植组与单纯残耳软骨细胞组明显减少,且软骨陷窝排列松散不均匀,见图7。 2.4.5 Verhoeff铁苏木精染色 共移植组、单纯残耳软骨细胞组与低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组软骨基质有染成蓝黑色的弹性纤维存在,证实有弹性软骨存在;单纯脂肪来源的干细胞组未见蓝黑色弹力纤维,可见红染的胶原纤维存在;低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组基质中蓝黑色弹性数量较共移植组与单纯残耳软骨细胞组明显减少,见图8。 2.4.6 Ⅱ型胶原免疫组化染色 共移植组、残耳软骨细胞组与低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组均可见到在成熟软骨陷窝周围有棕黄色沉淀,即Ⅱ型胶原表达;单纯脂肪来源的干细胞组未见Ⅱ型胶原表达;低浓度残耳软骨细胞对照组与共移植组和单纯残耳软骨细胞组相比,胞外基质着色浅不均匀,见图9。"
| [1] Patel SA, Bhrany AD, Murakami CS, et al. Autologous costochondral microtia reconstruction. Facial Plast Surg. 2016;32(2):188-198.[2] Zhou J, Pan B, Yang Q, et al.Three-dimensional autologous cartilage framework fabrication assisted by new additive manufactured ear-shaped templates for microtia reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;69(10): 1436-1444.[3] Balaji SM.Two stage ear/microtia reconstruction using costal cartilage. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2015;5(2):163-167.[4] Xu Z, Xu F, Zhang R, et al. A New Classification of Helix Fabrication Methods with Autogenous Costal Cartilage in Microtia Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017.[5] Yang M, Jiang H, Yu X, et al. Sternal Development and Variations and Anomalies in Patients With Microtia: Evaluation Using 3-Dimensional Computed Tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2017.[6] Zhou L, Ding R, Li B, et al. Cartilage engineering using chondrocyte cell sheets and its application in reconstruction of microtia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(1):73-80. [7] Melgarejo-Ramírez Y, Sánchez-Sánchez R, García-López J, et al. Characterization of pediatric microtia cartilage: a reservoir of chondrocytes for auricular reconstruction using tissue engineering strategies. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016;17(3): 481-489.[8] Roato I, Alotto D, Belisario DC, et al. Adipose Derived- Mesenchymal Stem Cells Viability and Differentiating Features for Orthopaedic Reparative Applications: Banking of Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:4968724.[9] Bielli A, Scioli MG, Gentile P,et al. Adipose-derived stem cells in cartilage regeneration: current perspectives. Regen Med. 2016;11(7):693-703.[10] Jang Y, Jung H, Ju JH. Chondrogenic Differentiation Induction of Adipose-derived Stem Cells by Centrifugal Gravity.J Vis Exp. 2017.[11] Im GI, Kim DY, Shin JH, et al. Repair of cartilage defect in the rabbit with cultured mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83(2):289-294.[12] Solchaga LA, Gao J, Dennis JE, et al. Treatment of osteochondral defects with autologous bone marrow in a hyaluronan-based delivery vehicle. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(2): 333-347.[13] Ko CY, Ku KL, Yang SR, et al. In vitro and in vivo co-culture of chondrocytes and bone marrow stem cells in photo cross linked PCL-PEG-PCL hydrogels enhances cartilage formation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(10):E485-E496.[14] Leyh M, Seitz A, Dürselen L, et al. Subchondral bone influences chondrogenic differentiation and collagen production of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):453.[15] Chen Y, Chen Y, Zhang S,et al. Parathyroid Hormone-Induced Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Chondrogenic Differentiation and its Repair of Articular Cartilage Injury in Rabbits. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2016;22:132-145.[16] 周广东,王晓云,刘天一,等.软骨细胞诱导骨髓基质细胞体内软骨形成[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,3(22):272-274.[17] Zhang L, He A, Yin Z, et al. Regeneration of human-ear- shaped cartilage by co-culturing human microtia chondrocytes with BMSCs. Biomaterials. 2014;35(18): 4878-4887.[18] De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A, et al. Comparison of multilineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174 (3): 101-109.[19] Davies OG, Cooper PR, Shelton RM, et al. A comparison of the in vitro mineralisation and dentinogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue, bone marrow and dental pulp.J Bone Miner Metab. 2015;33(4): 371-382.[20] Lotfy A, Salama M, Zahran F, et al. Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells derived from rat bone marrow and adipose tissue: a comparative study.Int J Stem Cells. 2014; 7(2):135-142.[21] Ogawa R, Mizuno H, Watanabe A, et al. Osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation by adipose-derived stem cells harvested from GFP transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;313(4): 871-874.[22] Dragoo JL, Samimi B, Zhu M, et al. T issue-engineered cartilage and bone using stem cells from human infrapatellar fat pads. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(5): 740-747.[23] Awad HA, Wickham MQ, Leddy HA, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived adult stem cells in agarose, alginate, and gelatin scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2004;25(16): 3211-3222.[24] Bhaumick B. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding proteins and insulin-like growth factor secretion by cultured chondrocyte cells: identification, characterization and ontogeny during cell differentiation. Regul Pept. 1993;48: 113-122.[25] Hennig T, Lorenz H, Thiel A. Reduced chondrogenic potential of adipose tissue derived stromal cells correlates with an altered TGFbeta receptor and BMP profile and is overcome by BMP-6. J Cell Physiol. 2007;211(3): 682-691.[26] Sailor LZ, Hewick RM, Morris EA, et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 maintains the articular chondrocyte phenotype in long-term culture, J Orthop Res. 1996;14:937-945.[27] Wei Y, Hu Y, Lv R, et al. Regulation of adipose-derived adult stem cells differentiating into chondrocytes with the use of rhBMP-2. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(6): 570-579.[28] Estes BT, Wu AW, Guilak F. Potent induction of chondrocytic differentiation of human adipose-derived adult stem cells by bone morphogenetic protein 6. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(4): 1222-1232.[29] Verbruggen G, Wang J, Wang L, et al. Analysis of chondrocyte functional markers and pericellular matrix components by flow cytometry. Methods Mol Med. 2004;100: 183-208.[30] Olney RC, Wang J, Sylvester J E, et al. Growth factor regulation of human growth plate chondrocyte proliferation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;317: 1171-1182.[31] Almalki SG, Agrawal DK. ERK signaling is required for VEGF-A/VEGFR2-induced differentiation of porcine adipose-derivedmesenchymal stem cells into endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):113.[32] Feng C, Luo X, He N, et al. Efficacy and persistence of allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with hyaluronic acid in osteoarthritis after intra-articular injection in a sheep model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2017.0039. [33] Zhang J, Neoh KG, Kang ET. Electrical Stimulation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Endothelial Cells Co-cultured in a Conductive Scaffold for Potential Orthopedic Applications. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017. doi: 10.1002/term.2441.[34] Ohta Y, Hamaguchi A, Ootaki M, et al. Intravenous infusion of adipose-derived stem/stromal cells improves functional recovery of rats with spinal cord injury. Cytotherapy. 2017. pii: S1465-3249(17)30544-3. [35] Aji K, Zhang Y, Aimaiti A,et al. MicroRNA-145 regulates the differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells to smooth muscle cells via targeting Krüppel-like factor 4. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(6):3787-3795. [36] Jin R, Shen M, Yu L, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Suppress Inflammation Induced by IL-1β through Down-Regulation of P2X7R Mediated by miR-373 in Chondrocytes of Osteoarthritis. Mol Cells. 2017;40(3): 222-229. [37] Clark KC, Fierro FA, Ko EM, et al. Human and feline adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells have comparable phenotype, immunomodulatory functions, and transcriptome. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):69. [38] Hoseini SJ, Ghazavi H, Forouzanfar F, et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor 1-Transfected Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Angiogenic Proliferation. DNA Cell Biol. 2017;36(5):401-412.[39] Linh NT, Abueva CD, Lee BT. Enzymatic in situ formed hydrogel from gelatin-tyramine and chitosan-4-hydroxylphenyl acetamide for the co-delivery of human adipose-derived stem cells and platelet-derived growth factor towards vascularization. Biomed Mater. 2017; 12(1):015026. [40] Almalki SG, Llamas Valle Y, et al. MMP-2 and MMP-14 Silencing Inhibits VEGFR2 Cleavage and Induces the Differentiation of Porcine Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Endothelial Cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017; 6(5):1385-1398.[41] 蔡震,潘博,林琳,等.残耳软骨细胞诱导脂肪来源干细胞体外软骨形成实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(1):83-88.[42] 苗春雷,周广东,刘天一,等.软骨细胞与骨髓基质细胞共培养体内构建软骨的初步研究[J].上海第二医科大学学报,2004,24(4): 246-249. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [5] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [6] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [7] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [8] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [9] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [10] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [11] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [12] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [13] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [14] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [15] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||