Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (19): 3108-3116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.19.024
Modified Stoppa approach versus Ilioinguinal approach for pelvic and/or acetabular fractures: a meta-analysis
Chen Xiao, Ma Kun-long, Xu Hai-tao, Shao Gao-hai
- Department of Orthopedics, Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China
-
Online:2017-07-08Published:2017-08-10 -
Contact:Shao Gao-hai, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China -
About author:Chen Xiao, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Yongchuan Hospital, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 402160, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Xiao, Ma Kun-long, Xu Hai-tao, Shao Gao-hai. Modified Stoppa approach versus Ilioinguinal approach for pelvic and/or acetabular fractures: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 3108-3116.
share this article

2.1 纳入文献的基线特征 通过计算机与手工检索,共得到753篇文献。阅读文献标题、摘要及全文后,共排除742篇,排除原因包括:①各数据库之间重复文献和重复发表文献454篇;②非临床研究、回顾性研究、队列研究、非随机分组研究、个案报道、综述等288篇;③数据不全的研究0篇。最终纳入11个RCT研究[29-39],其中9篇为中文文献[29-37],2篇为英文文献[38-39]。共计722例患者,其中试验组(改良Stoppa入路)359例患者,对照组(髂腹股沟入路)363例患者,纳入文献的基本情况见表1。 2.2 纳入文献的质量评价 采用“Cochrane协作网的偏倚风险评估标准”对纳入的11个研究进行质量评价[29-38],纳入研究各种偏倚所占比例见图2,纳入研究质量评价及风险评估见图3。 2.3 Meta分析结果 由于KunLong Ma文献中计量资料均采用均数及其范围表示,经过联系作者本人,从而获得相关指标的均数及其标准差,进行相关统计量合并。 2.3.1 手术时间 纳入研究中11篇进行了手术时间比 较[29-38],其异质性检验显示有显著统计学意义(P < 0.000 01,I2=85%),故采用随机效应模型进行统计量合并。结果示:改良stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路2组手术时间相比较差异有非常显著性意义[MD=-46.32,95%CI(-57.84,-34.79),P < 0.000 01,见图4];通过检验评估纳入研究的发表偏倚,漏斗图结果显示无发表偏倚(见图5)。"

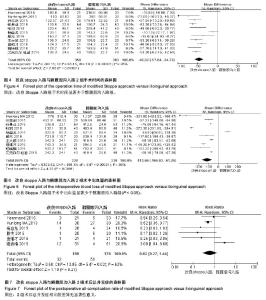
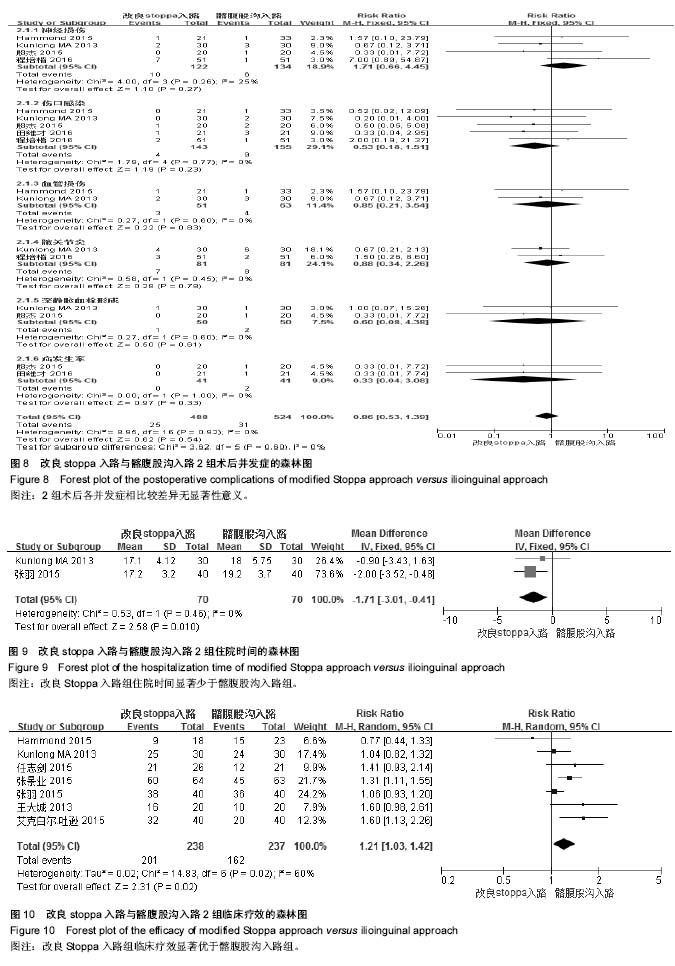
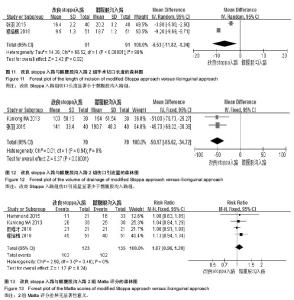
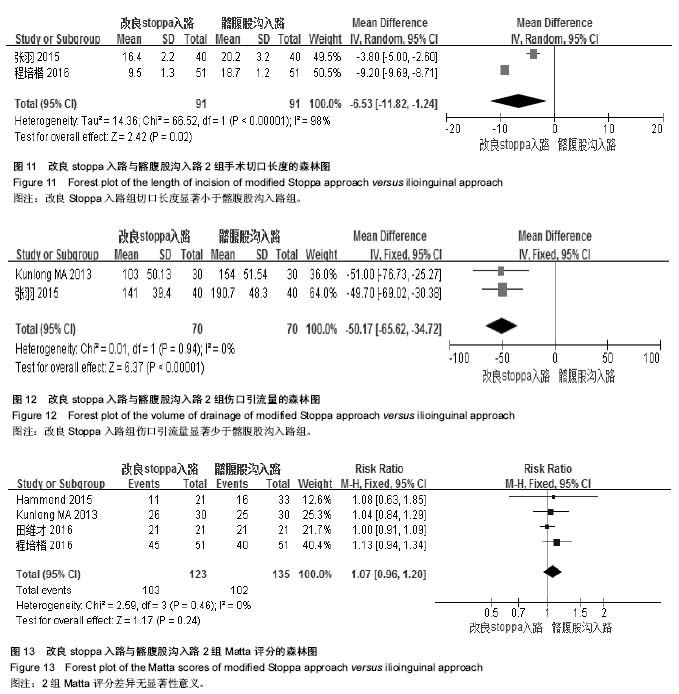
2.3.2 术中出血量 纳入研究中10篇进行了术中出血量比较[29-38],其异质性检验显示有统计学差异(P < 0.000 01,I2=99%),采用随机效应模型进行统计量合并。改良stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路2组术中出血量比较差异有显著性意义[MD=-113.66,95%CI(-166.03,-61.29),P < 0.000 1,见图6]。 2.3.3 术后并发症 纳入研究中有6篇报道了术后并发 症[29,33-34,37-39],其异质性检验有统计学差异(P=0.02,I2=62%),采用随机效应模型进行统计量合并。改良stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路2组术后总并发症相比较差异无显著性意义[RR=0.62,95%CI(0.27,1.44),P=0.27,见图7];对其进行亚组分析,各并发症指标异质性检验均差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05,I2 < 50%),均采用固定效应模型进行合并。其中5篇报道了切口感染,差异无显著性意义[RR=0.53,95%CI(0.18,1.51),P=0.23];4篇报道了神经损伤,差异无显著性意义[RR=0.1.71,95%CI(0.66,4.45),P=0.27];2篇报道了血管损伤,差异无显著性意义[RR=0.85,95%CI(0.21,3.54),P=0.83];2篇报道了髋关节炎发生率,差异无显著性意义[RR=0.88,95%CI(0.34,2.26),P=0.78];2篇报道了深静脉血栓发生率,差异无显著性意义[RR=0.60,95%CI(0.08,4.38),P=0.61];2篇报道了疝发生率,差异无显著性意义[RR=0.33,95%CI (0.04,3.08),P=0.33],详见图8。 2.3.4 住院时间 纳入研究中有2篇报道了住院时 间[36,38],其异质性检验无显著统计学意义(P=0.46,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行统计量合并。改良stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路2组住院时间相比较有统计学意义[MD=-1.71,95%CI(-3.01,-0.41),P=0.01,见图9]。 2.3.5 临床疗效 纳入研究中有7篇报道了临床疗 效[30-32,35-36,38-39],其异质性检验有显著统计学差异(P=0.02,I2=60%),采用随机效应模型进行统计量合并。改良stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路2组临床疗效相比较差异有显著性意义[RR=1.21,95%CI(1.03,1.42),P=0.02,见图10]。 2.3.6 切口长度 纳入研究中有2篇报道了手术切口长 度[36-37],其异质性检验有显著统计学差异(P < 0.000 01,I2=98%),采用随机效应模型进行统计量合并。改良stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路2组手术切口长度相比较有统计学意义[MD=-6.53,95%CI(-11.82,-1.24),P=0.02,见图11]。2.3.7 引流量 纳入研究中有2篇报道了伤口引流量[36,38],其异质性检验无统计学意义(P=0.94,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行统计量合并。改良stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路2组伤口引流量相比较差异有显著性意义[MD=-50.17,95%CI(-65.62,-34.72),P < 0.000 01,见图12]。 2.3.8 Matta评分 纳入研究中有4篇报道了Matta评 分[29,37-39],其异质性检验无统计学意义(P=0.46,I2=0%),采用固定效应模型进行统计量合并。改良stoppa入路与髂腹股沟入路2组Matta评分相比较差异无显著性意义[RR=1.07,95%CI(0.96,1.20),P=0.24,见图13]。"

| [1] Laird A, Keating JF. Acetabular fractures: a 16-year prospective epidemiological study.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2005;87(7): 969-973.[2] Balogh Z, King KL, Mackay P, et al. The epidemiology of pelvic ring fractures: a population-based study. J Trauma.2007;63(5): 1066-1073; discussion 1072-1063.[3] 柯铁. Stoppa入路联合髂骨螺钉治疗复杂骨盆骨折31例[J].福建医药杂志, 2016, 38(3): 32-34.[4] 陈明.不稳定型骨盆骨折的手术方式探讨[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013, 15(5): 445-447.[5] 周东生. 髋臼骨折的治疗进展及思考[J].中国骨伤,2016, 29(4): 293-297.[6] Guerado E, Cano JR, Cruz E. Fractures of the acetabulum in elderly patients: An update.Injury,2012, 43(SUPPL. 2): S33-S41.[7] 崔志民. 微创固定治疗不稳定骨盆骨折40例临床研究[J].中外医学研究, 2013, 11(21): 190-191.[8] 魏帅帅. 新改良Stoppa入路治疗骨盆、髋臼骨折[J].临床骨科杂志, 2012, 15(3): 264-267.[9] 钱荣勋. 改良Stoppa入路与腹股沟入路行髋臼骨折切开复位内固定术的比较[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2015, 21(9): 784-788.[10] Zha GC, Sun JY, Dong SJ. Predictors of clinical outcomes after surgical treatment of displaced acetabular fractures in the elderly.J Orthop Res. 2013;31(4):588-595.[11] Lao A, Putman S, Soenen M, et al. The ilio-inguinal approach for recent acetabular fractures: ultrasound evaluation of the ilio-psoas muscle and complications in 24 consecutive patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2014; 100(4):375-378.[12] Oh H-K, Choo SK, Kim J-J, et al. Stoppa Approach for Anterior Plate Fixation in Unstable Pelvic Ring Injury. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016;8(3):243-248.[13] Elmadag M, Uzer G, Yildiz F, et al.Safety of modified Stoppa approach for Ganz periacetabular osteotomy: A preliminary cadaveric study. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2016;50(4): 409-414.[14] Elmadag M, Guzel Y, Aksoy Y, et al. Surgical Treatment of Displaced Acetabular Fractures Using a Modified Stoppa Approach. Orthopedics.2016;39(2): e340-345.[15] Bastian JD, Savic M, Cullmann JL, et al. Surgical exposures and options for instrumentation in acetabular fracture fixation: Pararectus approach versus the modified Stoppa. Injury. 2016; 47(3):695-701. [16] Letournel E. Acetabulum fractures: classification and management.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1980;(151): 81-106.[17] Matta JM. Operative treatment of acetabular fractures through the ilioinguinal approach. A 10-year perspective. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1994;(305):10-19.[18] Briffa N, Pearce R, Hill AM, et al. Outcomes of acetabular fracture fixation with ten years' follow-up[J]. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery - Series B.2011;93B(2): 229-236.[19] Rocca G, Spina M. Anterior combined endopelvic (ACE) approach for the treatment of the acetabular and pelvic ring fractures: A new proposal. Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 6:S9-S15. [20] Matta JM. Fractures of the acetabulum: accuracy of reduction and clinical results in patients managed operatively within three weeks after the injury.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1996;78(11):1632-1645.[21] Kothe M, Lein T, Weber AT, et al. [Morel-Lavallee lesion. A grave soft tissue injury]Unfallchirurg.2006;109(1): 82-86.[22] Cole JD, Bolhofner BR.Acetabular fracture fixation via a modified Stoppa limited intrapelvic approach. Description of operative technique and preliminary treatment results. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1994;(305):112-123.[23] Hirvensalo E, Lindahl J, Bostman O. A new approach to the internal fixation of unstable pelvic fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1993;(297): 28-32.[24] Shazar N, Eshed I, Ackshota N, et al. Comparison of acetabular fracture reduction quality by the ilioinguinal or the anterior intrapelvic (modified Rives-Stoppa) surgical approaches. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(6):313-319.[25] Andersen RC, O'Toole RV, Nascone JW, et al.Modified stoppa approach for acetabular fractures with anterior and posterior column displacement: Quantification of radiographic reduction and analysis of interobserver variability. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(5):271-278.[26] Sagi HC, Afsari A, Dziadosz D. The anterior intra-pelvic (modified rives-stoppa) approach for fixation of acetabular fractures.J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(5):263-270.[27] Archdeacon MT,Kazemi N,Guy P,et al.The modified stoppa approach for acetabular fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011 Mar;19(3):170-175.[28] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1): 1-12.[29] 田维才. 改良Stoppa入路在髋臼及骨盆骨折手术治疗中的应用[J].大家健康(下旬版),2016, 10(8): 111-111.[30] 王大城. 经改良Stoppa入路治疗骨盆髋臼骨折的疗效观察[J].中国医药指南, 2013,11(23):103-104.[31] 艾克白尔•吐逊. 改良Stoppa入路手术用于髋臼骨折中的有效性及可行性[J].中国伤残医学, 2015, 23(18): 47-48.[32] 任志剑. 经改良Stoppa入路治疗骨盆髋臼骨折的效果分析[J].中外医学研究, 2015, 13(3): 19-20.[33] 杨自龙. 改良Stoppa入路方式在骨盆骨折、髋臼骨折治疗中的应用效果探讨[J]. 当代医学, 2015, 21(3): 81-82.[34] 殷杰. 改良Stoppa入路手术方法治疗骨盆髋臼骨折的临床疗效分析[J].陕西医学杂志, 2015, (9): 1224-1226.[35] 张景业. 改良Stoppa入路治疗骨盆髋臼骨折的临床观察[J].当代医学, 2015, 21(33): 32-33.[36] 张羽. 髂腹股沟入路和改良Stoppa入路治疗髋臼骨折的效果对比[J]. 当代医学, 2015, 21(20): 75-76.[37] 程培楷. 新型改良Stoppa入路治疗髋臼骨折合并同侧骨盆骨折的临床效果[J]. 牡丹江医学院学报, 2016, 37(3): 84-85.[38] Ma K, Luan F, Wang X, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of the modified Stoppa versus the ilioinguinal approach for acetabular fractures. Orthopedics.2013;36(10): e1307-1315.[39] Hammad AS,El-Khadrawe TA.Accuracy of reduction and early clinical outcome in acetabular fractures treated by the standard ilio-inguinal versus the Stoppa/iliac approaches. Injury.2015;46(2): 320-326.[40] Xu Y,Lin C,Zhang L,et al.Anterograde fixation module for posterior acetabular column fracture: Computer-assisted determination of optimal entry point, angle, and length for screw insertion. Medical Science Monitor. 2016; 22: 3106-3112.[41] Elmada M, Güzel Y, Ali Acar M, et al.The Stoppa approach versus the ilioinguinal approach for anterior acetabular fractures: A case control study assessing blood loss complications and function outcomes. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(6):675-680.[42] 李坤. 改良Stoppa入路和髂腹股沟入路治疗髋臼骨折临床疗效的Meta分析[J]. 大连医科大学硕士学位论文,2015.[43] 王小健, 苏云星, 郭秀生,等. 经髂腹股沟入路与+Stoppa+入路治疗移位型髋臼骨折临床疗效的+Meta+分析[J].中华解剖与临床杂志, 2016, 21(5): 426-431[44] Nayak SB, Deepthinath R, Prasad AM, et al.A South Indian cadaveric study on obturator neurovascular bundle with a special emphasis on high prevalence of 'venous corona mortis'.Injury.2016;47(7): 1452-1455.[45] Darmanis S, Lewis A, Mansoor A, et al. Corona mortis: An anatomical study with clinical implications in approaches to the pelvis and acetabulum. Clinical Anatomy.2007;20(4): 433-439.[46] 王钢. Stoppa入路在骨盆髋臼骨折中的应用及典型病例分析[C].第五届上海国际骨科前沿技术与临床转化学术会议论文集,上海:2011:134,133. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [3] | Yu Chengxiang, Liu Lehong, Li Wenbo, Chen Jinshi, Ran Chunlei, Wang Zhongping. Correlation between spine-pelvic sagittal parameters and prognosis of vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1412-1417. |
| [4] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [5] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [6] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [7] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [8] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [9] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [10] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [11] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [12] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [13] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [14] | Cui Xing, Sun Xiaoqi, Zheng Wei, Ma Dexin. Huangqin Decoction regulates autophagy to intervene with intestinal acute graft-versus-host disease in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1057-1062. |
| [15] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||