Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (9): 1412-1417.doi: 10.12307/2022.438
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between spine-pelvic sagittal parameters and prognosis of vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Yu Chengxiang, Liu Lehong, Li Wenbo, Chen Jinshi, Ran Chunlei, Wang Zhongping
- Section III, Department of Surgery, Chongqing Sanbo Chang’an Hospital, Chongqing 400020, China
-
Received:2021-05-30Revised:2021-06-02Accepted:2021-08-09Online:2022-03-28Published:2021-12-10 -
About author:Yu Chengxiang, Master, Associate chief physician, Scetion III, Department of surgery, Chongqing Sanbo Chang’an Hospital, Chongqing 400020, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Chengxiang, Liu Lehong, Li Wenbo, Chen Jinshi, Ran Chunlei, Wang Zhongping. Correlation between spine-pelvic sagittal parameters and prognosis of vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1412-1417.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
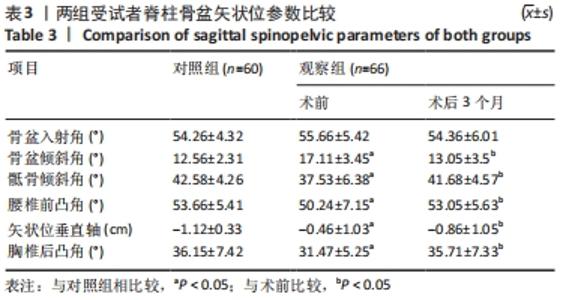
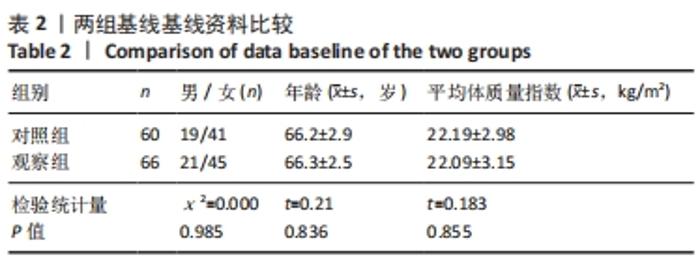
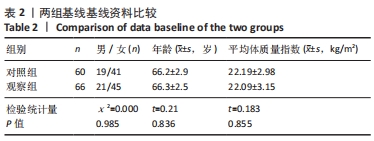
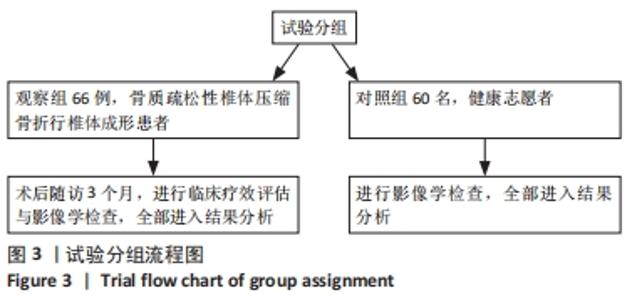
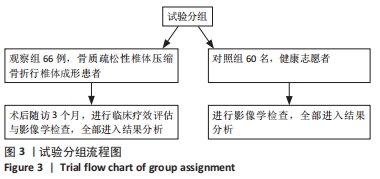
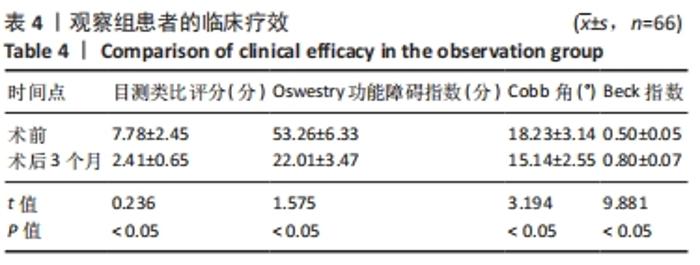
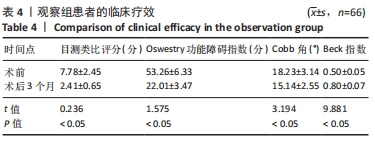
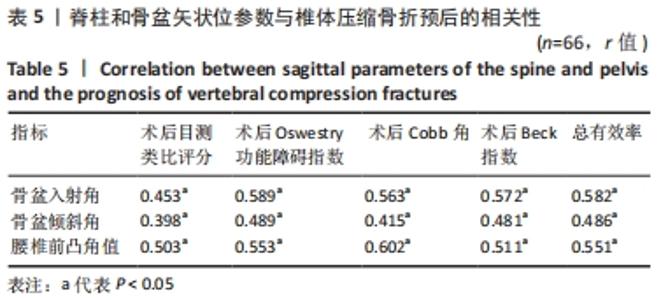
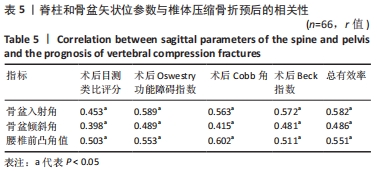
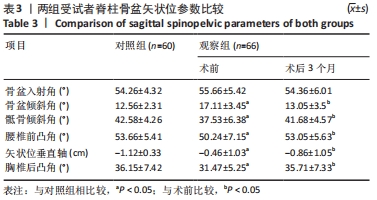
2.4 观察组患者围术期指标 66例患者都顺利完成手术,手术时间(28.26±5.23) min,术中出血量(5.31±2.49) mL,骨水泥注射量(4.51±1.22) mL。术中无并发症发生。 2.5 观察组材料宿主反应与并发症 术后发生并发症13例,发生率为9%,其中骨水泥渗漏2例,邻近椎体骨折2例,肺栓塞1例,压疮4例,下肢静脉血栓4例。试验中未发生与骨水泥材料相关的不良反应。 2.6 两组受试者脊柱和骨盆矢状位参数测量结果 观察组术前的骨盆入射角与对照组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),观察组术前与术后3个月的骨盆入射角比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);观察组患者术前的骨盆倾斜角大于对照组(P < 0.05),术前的骶骨倾斜角、腰椎前凸角、矢状位垂直轴、胸椎后凸角均小于对照组(P < 0.05);观察组患者术后3个月的骨盆倾斜角小于术前(P < 0.05,骶骨倾斜角、腰椎前凸角、矢状位垂直轴、胸椎后凸角均大于术前(P < 0.05);观察组术后3个月的上述指标与对照组比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。"
| [1] MILLER PD. Clinical Management of Vertebral Compression Fractures. J Clin Densitom. 2016;19(1):97-101. [2] KOSUKE S, TOSHINORI S, KEISUKE A, et al. Complete Fracture-Dislocation of the Thoracolumbar Spine with No Critical Neurological Deficit: A Case Report. J Med Invest. 2016;63(12):122. [3] CAMACHO JE, USMANI MF, STRICKLAND AR, et al. The use of minimally invasive surgery in spine trauma: a review of concepts. J Spine Surg. 2019;5(S1):91-100. [4] 秦琦,史晨辉,王维山,等.经皮椎体后凸成形和椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗老年骨质疏松胸腰椎压缩性骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(23):3766-3772. [5] 邹向南.高粘度骨水泥椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的椎体高度恢复情况及相关影响因素 [J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2017, 11(27):38-43. [6] BAEK SW, KIM C, CHANG H. The relationship between the spinopelvic balance and the incidence of adjacent vertebral fractures following percutaneous vertebroplasty. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(5):1507-1513. [7] CHAU L, HU Z, KO K, et al. Global sagittal alignment of the spine, pelvis, lower limb after vertebral compression fracture and its effect on quality of life. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):476. [8] 张相伟,孙建民,崔新刚,等.骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折患者脊柱矢状面的失平衡[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(26):4224-4228. [9] 郭新虎,李危石,郭昭庆,等.高度发育不良性腰椎滑脱复位程度与脊柱-骨盆矢状位参数变化的关系 [J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020, 12(28):345-348. [10] ZHANG YL, SHI LT, TANG PF, et al. Correlation analysis of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and spinal sagittal imbalance. Orthopade. 2017;46(3):249. [11] HUSSAIN S, ZARKAR A, ELMODIR A, et al. Vertebral compression fracture rate following stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for spine oligometastases: a UK experience. J Radiother Pract. 2021;22(2):1-5. [12] 王福兵,张夏琦,彭庆辉,等. L5~S1椎间融合术对腰椎矢状位参数和邻近节段退变的影响[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2019, 39(7): 1028-1033. [13] 邢润麟,张顺聪,江晓兵,等.脊柱矢状面失衡对骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折椎体成形术疗效的影响 [J].脊柱外科杂志,2017,15(2): 106-110. [14] OH HS, KIM TW, KIM HG, et al. Gradual Height Decrease of Augmented Vertebrae after Vertebroplasty at the Thoracolumbar Junction. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2016;12(1):18-21. [15] DU PLESSIS AM, GREYLING LM, et al. Differentiation and classification of thoracolumbar transitional vertebrae. J Anat. 2018;232(5): 850-856. [16] PARK SK, PARK JG, KIM BS, et al. Thoracolumbar junction: morphologic characteristics, various variants and significance. Br J Radiol. 2016; 89(64):766-784. [17] ANWAR HA, BUTLER JS, YARASHI T, et al. Segmental Pelvic Correlation (SPeC): a novel approach to understanding sagittal plane spinal alignment. Spine J. 2015;15(12):2518-2523. [18] SHARIFNEZHAD A, RAISSI GR, FOROGH B, et al. The Validity and Reliability of Kinovea Software in Measuring Thoracic Kyphosis and Lumbar Lordosis. Iran Rehabil J. 2021;19(2):129-136. [19] NASTO LA, PEREZ-ROMERA AB, SHALABI ST, et al. Correlation between preoperative spinopelvic alignment and risk of proximal junctional kyphosis after posterior-only surgical correction of Scheuermann kyphosis. Spine J. 2016;15(12):21-26. [20] PORTO AB, OKAZAKI VHA. Thoracic Kyphosis and Lumbar Lordosis Assessment by Radiography and Photogrammetry: A Review of Normative Values and Reliability. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2018; 41(8):712-723. [21] RABEI R, PATEL K, GINSBURG M, et al. Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation for Vertebral Compression Fractures: National Trends in the Medicare Population (2005–2015). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019; 44(2):123-133. [22] HONG JY, CHOI SW, KIM GD, et al. Reliability Analyses of Radiographic Measures of Vertebral Body Height Loss in Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2019;129:e191-e198. [23] 许九生,王俊魁,刘宏建,等.T1骨盆角与胸腰椎骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折脊柱-骨盆矢状位平衡的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2017,34(4):697-699. [24] FARUQI S, TSENG CL, WHYNE C, et al. Vertebral Compression Fracture After Spine Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: A Review of the Pathophysiology and Risk Factor. Neurosurgery. 2018;83(3):314-322. [25] WEI X, GENGWU L, CHAO C, et al. Correlations between the sagittal plane parameters of the spine and pelvis and lumbar disc degeneration. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):137-139. [26] STAUDE V, RADZISHEVSKA Y, ZLATNYK R. Radiometric parameters of the sacrum and pelvis, affecting the spine and pelvic balance in the frontal plane, in healthy volunteers. Ortop Travmatol Protez. 2017;(2):52-61. [27] KOTELNIKOV AO, RYABYKH SO, BURTSEV AV. Postural changes of the vertebral-pelvic balance in patients with Hip-Spine syndrom. Genij Ortop. 2020;26(1):206-211. [28] DREISCHARF M, PRIES E, BASHKUEV M, et al. Differences between clinical “snap-shot” and “real-life” assessments of lumbar spine alignment and motion – What is the “real” lumbar lordosis of a human being? J Biomech. 2016;49(5):638-644. [29] LE HUEC JC, GILLE O, FABRE T. Sagittal balance and spine-pelvis relation: A French speciality? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(5):551-554. [30] LAOUISSAT F, SEBAALY A, GEHRCHEN M, et al. Classification of normal sagittal spine alignment: refounding the Roussouly classification. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(8):2002-2011. [31] HAN F, WEISHI L, ZHUORAN S, et al. Sagittal plane analysis of the spine and pelvis in degenerative lumbar scoliosis. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(1):4741-4746. [32] HAFFER H, ADL AMINI D, PERKA C, et al. The Impact of Spinopelvic Mobility on Arthroplasty: Implications for Hip and Spine Surgeons. J Clin Med. 2020;9(8):552-556. [33] MERRILL RK, KIM JS, LEVEN DM, et al. Differences in Fundamental Sagittal Pelvic Parameters Based on Age, Sex, and Race. Clin Spine Surg. 2018;31(2):109-114. [34] ARIMA H, DIMAR JR, GLASSMAN SD, et al. Differences in lumbar and pelvic parameters among African American, Caucasian and Asian populations. Eur Spine J. 2018;27(12):2990-2998. [35] YOSHIKI A, SHUNJI T, HIROYUKI O, et al. Sagittal spino-pelvic alignment in adults: The Wakayama Spine Study. PloS One. 2017;12(6):e0178697. [36] ZHOU S, SUN Z, LI W, et al. The standing and sitting sagittal spinopelvic alignment of Chinese young and elderly population: does age influence the differences between the two positions? Eur Spine J. 2020;29(3): 405-412. [37] LI Y, SHEN Z, HUANG M, et al. Stepwise resection of the posterior ligamentous complex for stability of a thoracolumbar compression fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(35):342-346. [38] FILARDI V, SIMONA P, CACCIOLA G, et al. Finite element analysis of sagittal balance in different morphotype: Forces and resulting strain in pelvis and spine. J Orthop. 2017;14(2):268-275. [39] RADCHENKO V, SKIDANOV A. Changes in the paravertebral muscles in patients with degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine. Ortop Travmatol Protez. 2018;10(3):50-56. [40] LONG Y, YI W, YANG D. Advances in Vertebral Augmentation Systems for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Res Manag. 2020;12(7):3947-3954. [41] HU KZ, CHEN SC, XU L. Comparison of percutaneous balloon dilation kyphoplasty and percutaneous vertebroplasty in treatment for thoracolumbar vertebral compression fractures. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(1 Suppl):96-102. [42] CHANG DG, HA KY, KIM YH, et al. Spinopelvic Alignment by Different Surgical Methods in the Treatment of Degenerative Sagittal Imbalance of the Lumbar Spin. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30(4):390-397. |
| [1] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [2] | Liu Yuhang, Zhou Jianqiang, Xu Xuebin, Qu Xingyue, Li Ziyu, Li Kun, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Zhang Shaojie. Establishment and validation of finite element model of lower cervical spine in 6-year-old children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 870-874. |
| [3] | Li Yuqiao, Sun Tianwei, Ma Bin, Zhou Zhaohong, Dong Runbei, Wu Haiyang. A comparative study of imaging parameters and quality of life scores between subtypes of lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 943-948. |
| [4] | Li Jian, Bao Zhengqi, Zhou Pinghui, Zhu Ruizhi, Li Zhixiang, Wang Jinzi. Effects of posterior single open-door laminoplasty and anterior cervical corpectomy fusion on cervical sagittal balance parameters in the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 949-953. |
| [5] | Yi Xinrong, Jia Fuquan, He Xin, Zhang Shaojie, Ren Xiaoyan, Li Zhijun. Establishment of cervical bone age equation for male adolescents aged 8-16 years old in Hohhot based on thin-slice CT [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 954-958. |
| [6] | Ou Liang, Kong Dezhong, Xu Daoqing, Ni Jing, Fu Xingqian, Huang Weichen. Comparative clinical efficacy of polymethyl methacrylate and self-solidifying calcium phosphate cement in vertebroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 649-656. |
| [7] | Shen Song, Xu Bin. Diffuse distribution of bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty reduces the incidence of refracture of adjacent vertebral bodies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 499-503. |
| [8] | Hou Wanxing, Li Hongwei, Zheng Xin, Zhu Xianren. Correlation between preoperative magnetic resonance imaging findings and bone cement leakage after percutaneous vertebral augmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 504-509. |
| [9] | Kou Bowen, Han Ye, Hao Yiguang, Xu Haoxiang, Wen Wangqiang, Zhang Zepei, Lan Jie, Miao Jun. Morphological changes and strain characteristics of lumbar intervertebral disc during sitting in forward flexion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(36): 5792-5797. |
| [10] | Huang Taosheng, Chen Jianquan, Lin Xinyuan, Lyu Zhouming, Chen Maoshui. 3D printing percutaneous puncture guide plate assisted vertebroplasty for single-level osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture with active registration location combined with anatomic marker localization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(36): 5819-5825. |
| [11] | Xiong Hengheng, Nie Weizhi. Accurate simulation of stress state in bone joint and related soft tissue injury by three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(36): 5875-5880. |
| [12] | He Yujie, Li Pei, Xue Mingming, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Wang Xing, Gao Mingjie, Wu Chao, Kang Zhijie, Zhang Shaojie, Wang Haiyan. Establishment and validation of finite element model of cervical facet joint in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5265-5270. |
| [13] | Bi Jingwei, Ren Jiabin, Liu Xin, Sun Ning, Li Rui, Li Yuefei, Sun Zhaozhong. 3D-CT-guided unilateral biportal endoscopic localization of L5 and S1 nerve roots and intervertebral space [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5283-5289. |
| [14] | Liu Jin, Yin Hongkun, Chen Guo, Zhang Yu, Gu Zuchao, Tang Jing. A machine learning prediction model based on MRI radiomics for refracture of thoracolumbar segments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5323-5328. |
| [15] | Cai Feng, Yu Bo, Zeng Duo, Chen Qincan, Liao Qi. Cortical bone trajectory in elderly patients with osteoporosis of lumbar disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 403-407. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||