Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (11): 1770-1775.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.11.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research advance in the biological characteristics of osteoclasts
Xie Bing-jie, Feng Jie, Han Xiang-long
- Department of Orthodontics, West China School/Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, National Key Laboratory for Oral Diseases, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Online:2017-04-18Published:2017-05-06 -
Contact:Han Xiang-long, M.D., Associate professor, Department of Orthodontics, West China School/Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, National Key Laboratory for Oral Diseases, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Xie Bing-jie, Department of Orthodontics, West China School/Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, National Key Laboratory for Oral Diseases, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81371172
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Bing-jie, Feng Jie, Han Xiang-long. Research advance in the biological characteristics of osteoclasts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1770-1775.
share this article
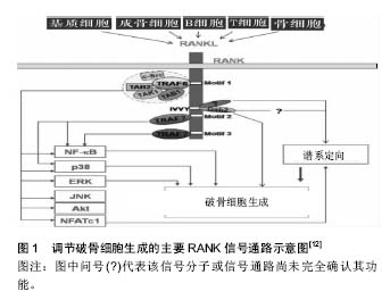
2.1 破骨细胞的来源、分化及凋亡 2.1.1 破骨细胞的来源 40多年前,不同动物模型研究均显示,与由间质细胞分化而成的成骨细胞不同,破骨细胞是由骨髓中的髓系祖细胞分化而成的单核巨噬细胞相互融合,所形成的多核巨细胞[2]。早期未成熟的增殖性单核吞噬细胞被称为破骨细胞前体,在化学因子的作用下进入血液循环,再在基底多细胞单位所释放的信号因子的作用下进入骨结构腔体,在各种化学因子、转录因子、细胞因子等信号因子的刺激下融合为多核细胞并最终活化为破骨细胞[3-4]。有研究称原发细胞如胚胎干细胞、前B细胞可形成破骨细胞,虽其生理学意义不详,但至少表明破骨细胞的来源不是单一的[5]。 2.1.2 破骨细胞的分化 许多信号分子在破骨细胞形成、分化、活化、存活、功能发挥的过程中起着积极或消极的调节作用,其中最关键的2个因子——巨噬细胞集落刺激因子与核因子κB受体激活蛋白配体(receptor activator of NF-κB ligand,RANKL)贯穿破骨细胞形成、分化、活化、发挥功能全过程[6-7]。 巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(也称为集落刺激因子1)在骨微环境中主要由成骨细胞、骨髓间质细胞和骨细胞表达。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的受体为前体细胞上的c-Fms,是一种跨膜蛋白,属酪氨酸激酶受体,其胞内段含多个酪氨酸残基。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子最关键的作用是促进核因子κB受体激活蛋白(receptor activator of NF-κB,RANK)在破骨细胞前体细胞膜上的表达,增强RANK与RANKL的结合活性。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子受体为前体细胞上的c-Fms,是一种跨膜蛋白,属酪氨酸激酶受体,其胞内段含多个酪氨酸残基,M-SCF与c-fms结合后活化其胞内的残基,引发级联反应,磷酸化DNAX-激活蛋白12以及无受体酪氨酸激酶(Syk),激活细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)、生长因子受体结合蛋白2以及丝/苏氨酸蛋白激酶/磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶(Akt/PI3K),调控破骨细胞前体的增殖、分化与存活[3]。c-Fms胞内段中,目前已知Y544,Y559,Y697,Y706, Y721,Y807,Y921,Y974这8个残基可被反氏磷酸化而作为信号分子的对接点,其中Y544,Y559,Y697, Y721,Y807,Y921对前体细胞对增殖有明确的积极作用。但这些残基在破骨细胞增殖、分化、存活过程中的作用机制仍存在争议。研究发现,缺乏巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的小鼠会患上骨硬化症,这正是由于破骨细胞缺乏所导致骨重塑失衡的表现。不表达RANK的前体细胞在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子的刺激下可形成破骨细胞,推论这是因为巨噬细胞集落刺激因子诱导了RANK的表达,经RANK/RANKL通路促进破骨细胞的形成分化[8-9]。 RANKL属肿瘤坏死因子蛋白超家族成员,可由成骨细胞谱系细胞,T、B淋巴细胞,内皮细胞表达;软骨内成骨时主要由肥厚的软骨细胞表达;在机械应力下的骨重建过程中,RANKL主要由骨细胞表达。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子作用的发挥依赖于RANKL的存在。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子主要调控破骨细胞的增殖和存活,也可通过Akt、c-Fos、ERK与RANKL作用,参与分化末期,而破骨细胞的分化过程主要由RANKL直接控制。不同于别的细胞因子,RANKL与破骨细胞上的受体RANK相连接,RANKL介导的信号分子便通过RANK的胞内信号通路诱导释放核因子,直接调控破骨细胞分化相关基因的表达[8]。RANKL分为游离形式与膜结合形式,但膜结合形式具有更高的活性[7]。大多促进破骨细胞形成和分化的因子均可诱导成骨细胞与间质细胞表达RANKL[9]。 RANK是RANKL的同源受体,可由骨髓来源的树突状细胞、活化的T细胞和破骨细胞前体表达。RANK对破骨细胞分化、淋巴结形成、B细胞发育十分关键[10]。RANK-/-小鼠显示严重的骨硬化症表型、B细胞发育受损、有明显的髓外造血,有黏膜相关的淋巴组织但无外周淋巴结[11]。RANK缺乏内源性激酶活性,不能磷酸化并激活细胞内信号分子,需通过召集肿瘤坏死因子受体激活因子发挥功能。肿瘤坏死因子受体激活因子1,2,3,5,6均可与RANK相互作用,但只有TRAF6是诱导破骨细胞分化和活化基因表达的相关信号蛋白的关键衔接分子。RANK只含有3个功能性TRAF结合基序:Motif 1、2、3可介导破骨细胞形成和功能,其中破骨细胞的存活主要由Motif 1调控。这些基序可激活6条主要信号通路(核因子кB、JNK、ERK、p38、NFATc1、Akt)调节破骨细胞形成、功能和存活[8,11-12],见图1。"
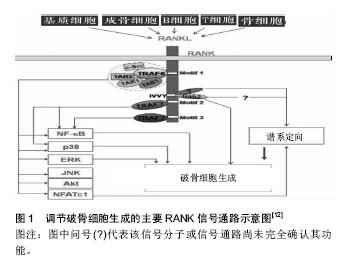
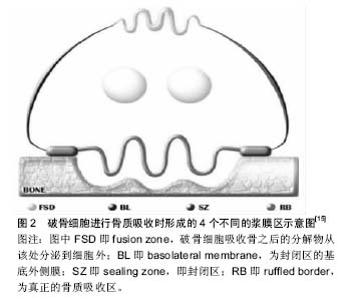
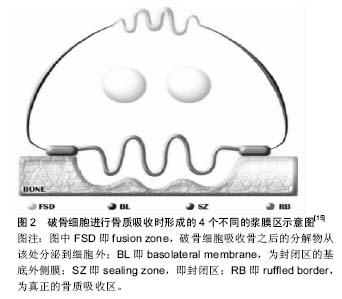
转录因子如激活T细胞核因子1(Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1,NFATc1)、核因子κB、MITF、c-Fos可激发特定基因段的转录,是破骨细胞分化相关的重要因子。NFATc1是破骨细胞分化的关键调节分子,破骨细胞前体对RANKL的最早反应即是召集RelA/p50和NFATc2至NFATc1,在钙离子的刺激下,诱导NFATc1短时的大量自我增殖、RANK活化抑制分子表达的减少,使破骨细胞生成得以发生[13]。核因子кB与NFATc2可共同诱导NFATc1的表达[3]。NFATc1可诱导积极调节子如组织蛋白酶K、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、降血钙素受体、液泡ATP酶(v-ATPase)、破骨细胞相关受体(OSCAR)、β3整合素等基因的表达,也可诱导消极调节子抑制子如B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1的表达,促进成熟破骨细胞的形成κ[11,14]。MITF可激活巨噬细胞集落刺激因子受体表达[4]。RANK诱导c-Fos的表达可活化AP-1蛋白,诱导破骨细胞的形成,c-Fos基因的缺失会造成破骨细胞和巨噬细胞间细胞系分化的转变[15]。 不同的化学因子直接或间接对破骨细胞的分化有积极或消极的影响。甲状腺素可直接作用于破骨细胞前体刺激破骨细胞分化,但具体机制不详,有学者认为部分原因是由于T3可增加破骨细胞前体c-Fos mRNA的表达[16]。脂多糖、白细胞介素1可激活前体细胞的存活和聚合;肿瘤坏死因子α在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子存在的条件下直接刺激前体细胞分化为破骨细胞。APRIL、BAFF、神经生长因子、类胰岛素生长因子Ⅰ和类胰岛素生长因子Ⅱ可代替RANKL刺激破骨细胞分化和活化[5,17]。白细胞介素6、白细胞介素11可刺激破骨细胞形成;但其机制有待进一步研究[18]。白细胞介素34可在缺乏巨噬细胞集落刺激因子时促进RANKL诱导的破骨细胞生成。白细胞介素12、白细胞介素18可通过幼稚T细胞诱导粒细胞集落刺激生物因子,γ-干扰素等的表达抑制破骨细胞形成[3]。在关节炎性病变研究中,学者同样发现了其他路径可诱发骨吸收,而这一过程中形成破骨细胞的前体细胞来源不明确[8]。 骨保护素是骨吸收的主要抑制分子,可作为诱导受体与RANKL结合从而阻止与RANKL与RANK的相互作用,阻断破骨细胞前体向破骨细胞的分化以及成熟破骨细胞的活化。增加RANKL表达的生长因子和细胞因子也能增加骨保护素的表达,但不及RANKL强,故总体仍是促进骨质吸收。转化生长因子β、白细胞介素4、白细胞介素12、白细胞介素13、白细胞介素18可抑制破骨细胞形成分化过程[3]。降钙素可抑制破骨细胞的成熟与活化[18-20],但其抑制作用有限,可能由于随着mRNA的下调和受体的降解,破骨细胞逐渐失去对降钙素的敏感度所造成[18]。 2.1.3 破骨细胞的凋亡 破骨细胞的凋亡由2个不同的信号通路控制,一个由死亡受体(肿瘤坏死因子受体家族,含细胞内死亡结构域)开始,一个由Bcl-2家族蛋白调节。2个通路均可活化半胱天冬酶,该酶可通过裂解特异性底物诱导细胞凋亡[21]。 转化生长因子β是最早发现调控破骨细胞凋亡的因子。在骨髓细胞中表达,可通过TAK1/MEK/AKT调节破骨细胞中核因子κB的活性直接影响破骨细胞活性。也可在骨吸收过程中由骨基质释放,在破骨细胞褶皱边缘的酸性环境中被激活[3];还可吸引成骨细胞至吸收区域作为偶联因子[4]。Fas信号分子诱导破骨细胞凋亡,雌激素可通过提高破骨细胞中Fas配体的表达诱导破骨细胞凋亡,雌激素受体α可抑制调节破骨细胞活性相关基因的表达,但不影响破骨细胞前体的增殖和融合[3]。Src抑制剂导致破骨细胞凋亡,但Src-/-小鼠破骨细胞的凋亡并不增加,因有别的因子作补偿。PTH和1,25(OH)2-维生素D3可通过刺激RANKL的表达、减少骨保护素的表达防止破骨细胞凋亡,其局部浓度对决定破骨细胞的存活和形成具有重要的决定性作用[17,21]。 2.2 破骨细胞的生物学作用 2.2.1 破骨作用 破骨细胞以其骨质吸收功能为人所知晓。破骨细胞大多通过整合素玻连蛋白受体(αVβ3整合素)与kindlin-3结合连接到骨表面。kindlin-3是一种在血小板和白细胞中表达的蛋白,聚集至整合素黏附处,可在破骨细胞活化早期阶段激活β3整合素。αVβ3与其配体结合,促进Src酪氨酸激酶表达,使胞外信号进入细胞,活化多条Src依赖信号通路,将破骨细胞活化相关蛋白如Syk磷酸化。RANK可通过Src与αVβ3连接,形成复合物,激活Slp-76、Vav3、Rac、Syk后可招募磷酸化DNAX-激活蛋白12和Slp-76,形成衔接蛋白复合物,活化小Rho家族GTP酶(包括Rac)[3]。 αVβ3通过其胞内段的β3亚单位,与骨基质共同形成细胞骨架,使破骨细胞在骨-细胞界面发生极化。破骨细胞极化后,基质溶酶体分泌酸性囊性物质与基质膜相融合形成真正的吸收器官——褶皱缘膜;膜可分为内部的“吸收区”和外部的“融合区”,骨质降解后的产物通过胞饮作用从这两个功能区释放入血[12]。大量丝状肌动蛋白在膜周边的环形胞质区形成伪足结构,该区缺乏其他细胞器,称为亮区。褶皱缘膜与亮区共同形成致密的封闭区[12,15],见图2。"

破骨细胞对骨质的吸收需要先将微环境进行酸化,该过程最主要的分子机制是液泡H+-ATP酶定位到褶皱缘,将质子分泌到胞外的骨质吸收区,膜上的氯通道蛋白7氯离子通道在细胞外的酸性条件下分泌Cl-,H+和Cl-形成HCl,溶解羟基磷灰石晶体,为蛋白溶解酶降解骨基质蛋白提供酸性条件;同时破骨细胞还可产生组织蛋白酶K溶解骨基质,促进骨组织的吸收[4,22]。此时细胞内pH 的稳定可能通过基底膜上的HCO-/Cl-转换器、Na+/H+逆向转运蛋白及其他阳离子阴离子转换器完成[23]。亮区的具体作用究竟是从细胞外环境中隔离开吸收微环境,还是作为基质识别结构使整合素传递细胞外源性信号促进骨质降解仍有争议,还需进一步研究确定[22]。有体外研究显示,破骨细胞不仅表达氯通道蛋白7,其内的氯通道蛋白3也可通过细胞器酸化促进骨质吸收[24]。有研究探索质子泵抑制剂作为抗骨质吸收药物,但由于该液泡质子泵不具有破骨细胞特异性;氯离子通道抑制剂同理,故该研究临床意义并不大[15]。 Src通路涉及到的信号因子包括磷酸化DNAX-激活蛋白12(ITAM类)、Slp76、GTP酶等。除此外,有强烈促进骨吸收的因子还包括甲状旁腺激素、维他命D3、前列腺素、皮质类固醇等。而对于抑制骨吸收的机制中,目前研究较为深入的是RANKL/OPG轴。 RANKL或骨保护素可由骨细胞、成骨细胞或基质细胞表达,骨保护素与RANKL结合可阻滞破骨细胞前体的聚合和分化,其对破骨细胞功能对抑制或促进由两者间的比率所决定。当RANKL高表达时,促进破骨细胞分化并维持其生存;当骨保护素高表达时,则抑制破骨细胞生成并导致破骨细胞凋亡[4]。RANKL与骨保护素的比例可调控骨的形成和吸收,钙离子浓度可对该轴的功能进行调控。大豆提取物可以刺激成骨细胞产生骨保护素,升高OPG/RANKL比例,降低NFATc1活性而抑制RANKL介导的破骨细胞分化过程[25]。决定破骨细胞附着部位的机制曾存在疑问,现在有研究证实在出现微小裂隙的骨组织中,凋亡的骨细胞会诱导周围骨细胞产生RANKL,提高RANKL/OPG比例,诱导此处破骨细胞的形成分化并附着,参与微小裂隙的骨重塑。小鼠缺乏RANKL或RANK蛋白的基因会因无法形成破骨细胞而导致骨硬化症;缺乏骨保护素的小鼠会因破骨细胞分化的增加而出现早期骨质疏松症;转基因的小鼠过度表达骨保护素会因后期破骨细胞分化的下降而导致骨硬化症。故RANKL/RANK/OPG轴在骨骼发育以及骨重建中发挥扮演着重要的角色[12]。 2.2.2 其他作用 破骨细胞是已知最主要参与骨吸收的细胞,但除此之外,破骨细胞还具有其他的生物学作用。至今所发现的分别有造血调控作用、骨形成调控作用、骨内血管生成调控作用、骨钙素的激素作用[12,26-29]。 许多破骨细胞酶(如组织蛋白酶K)通过造血干细胞调控因子如CXCL12等参与造血干细胞的维持和运动,随着局部及全身钙离子浓度的提高,破骨细胞参与造血干细胞在骨内膜的植入,但其影响机制仍需进一步研究[12,26]。研究者发现部分针对破骨细胞的疗法将会牵连到骨髓干细胞。用双磷酸盐抑制破骨细胞分化的同时,骨髓中骨髓干细胞数目将减少;而前列腺素E2可激活骨吸收,同时骨髓中骨髓干细胞数目升高。这些发现表明破骨细胞与造血干细胞相关,但其机制仍有待研究[28]。 在酶裂解和/或酸性pH形成的吸收微环境下由骨基质释放强成骨细胞合成代谢剂,大量细胞因子从骨组织中释放,如转化生长因子β、骨形成蛋白、成纤维细胞生长因子、类胰岛素生长因子Ⅰ;或由破骨细胞分泌的细胞因子,既破骨因子,如TRAcP、SLP、骨形成蛋白6、Wnt10b、肝细胞生长因子等,在骨形成部位招募成骨细胞前体,并诱导其分化,从而促进骨基质沉积和矿化。该骨生成作用始于骨吸收过程[12,26]。 破骨细胞可通过骨吸收时骨基质对转化生长因子β的释放和活化,调控内皮细胞对血管内皮生长因子的表达,通过对内皮细胞旁分泌的刺激对血管的生成进行调控,另外破骨细胞通过旁分泌途径,即核因子κB和低氧诱导因子1α通路对成骨细胞功能的调控也可间接影响血管生成[26]。 骨可维持多数外周器官的稳态,其中骨钙蛋白对于维持体内稳态尤为重要,骨钙素在破骨细胞骨吸收的酸性pH环境中脱羟基活化,从而调控能量代谢、雄性生殖以及脑部的发育。骨钙素水平可作为胰岛素分泌、敏感性以及睾丸酮水平的可靠标记。在骨改建微环境中,局部pH值降低可使骨钙蛋白去羧酸化,从而使得骨钙蛋白能够行使其功能,参与机体稳态调节。破骨细胞功能受损会使活化的骨钙素释放减少、对外周器官的影响降低[26-29]。 2.2.3 细胞间相互作用 参与骨重塑的基本细胞,包括破骨细胞、成骨细胞及骨细胞,它们之间存在着细胞间相互作用。成骨细胞可分泌RANKL及巨噬细胞集落刺激因子,它们对于破骨细胞的分化及活化有着关键作用。破骨细胞也可通过旁分泌途径产生如肝配蛋白、臂板蛋白、丛状蛋白等因子直接影响成骨细胞的形成及生理功能。骨细胞除表达RANKL和分泌巨噬细胞集落刺激因子外,还可分泌骨硬化蛋白促进破骨细胞的分化形成及破骨作用。骨硬化蛋白是WNT信号通路中的一种信号分子,该通路对所有参与骨重塑基本细胞不可或缺,在骨组织的稳态调节中有着极为重要作用。"

| [1] Kular J, Tickner J, Chim SM, et al. An overview of the regulation of bone remodelling at the cellular level. Clin Biochem. 2012;21:863-873.[2] Chambers TJ. The cellular basis of bone resorption. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;151(151): 283-293.[3] Boyce BF. Advances in osteoclast biology reveal potential new drug targets and new roles for osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res. 2013; 28(4): 711-722. [4] Boyce BF. Advances in the regulation of osteoclasts and osteoclast functions. J Dent Res. 2013;92(10): 860-867.[5] Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, et al. Modulation of Osteoclast Differentiation and Function by the New Members of the Tumor Necrosis Receptor and Ligand Families. Endocr Rev. 2013;20(3): 345-357.[6] Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423(6937):337-342.[7] Robling AG, Castillo AB, Turner CH. Biomechanical and Molecular Regulation of Bone Remodeling. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2006;8(1): 455-498.[8] Pederson L, Ruan M, Westendorf JJ, et al. Regulation of bone formation by osteoclasts involves Wnt/BMP signaling and the chemokine sphingosine-1-phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(52):20764-20769.[9] Boyce BF, Xing L. Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;473 (2): 139-146.[10] Dougall WC, Glaccum M, Charrier K, et al. RANK is essential for osteoclast and lymph node development. Genes Dev. 1999; 13(18):2412-2424.[11] Nakashima T, Takayanagi H. New regulation mechanisms of osteoclast differentiation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;1240(1): E13-18.[12] Xu F, Teitelbaum SL. Osteoclasts: New Insights. Bone Res. 2013; 1(1): 11-26.[13] Asagiri M, Takayanagi H. The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 2007; 40(2):251-264.[14] Tetsuro Y, Jun H, Hiroyuki A, et al. Epigenetic regulation of osteoclast differentiation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011;26(11): 2665-2671.[15] Vaananen K. Mechanism of osteoclast mediated bone resorption--rationale for the design of new therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57(7): 959-971.[16] Kanatani M, Sugimoto T, Sowa H, et al. Thyroid hormone stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of RANKL-RANK interaction. J Cell Phys. 2004; 201(1): 17-25.[17] Katagiri T, Takahashi N. Regulatory mechanisms of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Oral Dis. 2002;8(8): 147-159.[18] Quinn JM, Gillespie MT. Modulation of osteoclast formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(3): 739-745.[19] Chambers TJ. The birth of the osteoclast. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192(1): 19-26.[20] Tsuda E, Goto M, Mochizuke S, et al. Isolation of a Novel Cytokine from Human Fibroblasts That Specifically Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997; 234(1): 137-142.[21] Xing L, Boyce BF. Regulation of apoptosis in osteoclasts and osteoblastic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328 (3): 709-720.[22] Teitelbaum SL. Bone Resorption by Osteoclasts. Science. 2000;289(5484): 1504-1508.[23] Rousselle AV, Heymann D. Osteoclastic Acidi?cation Pathways During Bone Resorption. Bone. 2002;30(4): 533-540.[24] Okamoto F, Kajiya H, Toh K, et al. Intracellular ClC-3 chloride channels promote bone resorption in vitro through organelle acidification in mouse osteoclasts. Am J Phys Cell Phys. 2008;294(1): 693-701.[25] Park K, Ju WC, Yeo JH, et al. Increased OPG/RANKL ratio in the conditioned medium of soybean-treated osteoblasts suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 2014;33(1):178.[26] Cappariello A, Maurizi A, Veeriah V, et al. Reprint of: The Great Beauty of the osteoclast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;561(65): 13-21.[27] Ferron M, Wei J, Yoshizawa T, et al. Insulin signaling in osteoblasts integrates bone remodeling and energy metabolism. Cell. 2010;142(2): 296-308.[28] Lymperi S, Ersek A, Ferraro F, et al. Inhibition of osteoclast function reduces hematopoietic stem cell numbers in vivo. Blood. 2011;117(5): 1540-1549.[29] Oury F, Ferron M, Huizhen M, et al. Osteocalcin regulates murine and human fertility through a pancreas-bone-testis axis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(12): 2421-2433. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [5] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [6] | He Yunying, Li Lingjie, Zhang Shuqi, Li Yuzhou, Yang Sheng, Ji Ping. Method of constructing cell spheroids based on agarose and polyacrylic molds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
| [7] | He Guanyu, Xu Baoshan, Du Lilong, Zhang Tongxing, Huo Zhenxin, Shen Li. Biomimetic orientated microchannel annulus fibrosus scaffold constructed by silk fibroin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 560-566. |
| [8] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [9] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [10] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [11] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| [12] | Li Hui, Chen Lianglong. Application and characteristics of bone graft materials in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 626-630. |
| [13] | Gao Cangjian, Yang Zhen, Liu Shuyun, Li Hao, Fu Liwei, Zhao Tianyuan, Chen Wei, Liao Zhiyao, Li Pinxue, Sui Xiang, Guo Quanyi. Electrospinning for rotator cuff repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 637-642. |
| [14] | Guan Jian, Jia Yanfei, Zhang Baoxin , Zhao Guozhong. Application of 4D bioprinting in tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 446-455. |
| [15] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||