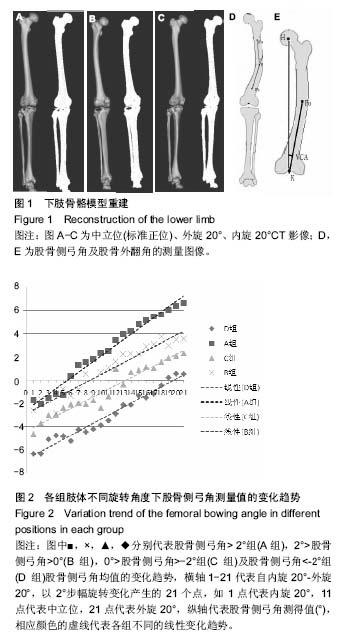
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (11): 1764-1769.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.11.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of femoral bowing angle on the lower limb alignment in different positions based on CT three-dimensional reconstruction
Wu Wei1, 2, Guo Wan-shou1, 2, Li Chuan-dong3, Liu Zhao-hui2, Zhang Qi-dong2, Cheng Li-ming2
- 1Graduate School of Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China; 2Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, 3Department of Radiology, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
-
Online:2017-04-18Published:2017-05-06 -
Contact:Guo Wan-shou, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Graduate School of Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China; Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Wu Wei, Studying for doctorate, Associate chief physician, Graduate School of Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100730, China; Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China -
Supported by:the Capital Special Research Project of Health Development, No. 2016-2-4062
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Wei, Guo Wan-shou, Li Chuan-dong, Liu Zhao-hui, Zhang Qi-dong, Cheng Li-ming. Effect of femoral bowing angle on the lower limb alignment in different positions based on CT three-dimensional reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1764-1769.
share this article
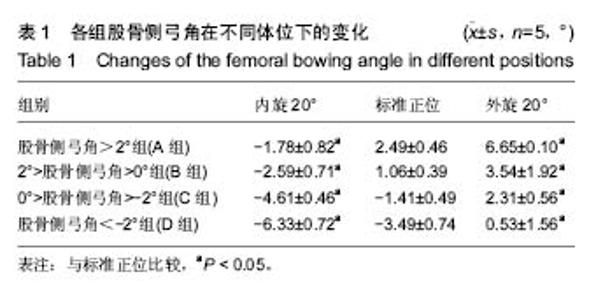
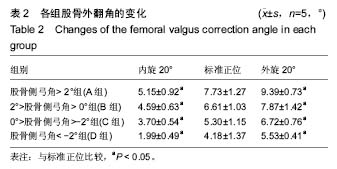
2.1 受试者数量分析 共收集83例患者166侧下肢,其中男51例,女32例,根据前述纳入标准,最终入选20例,确认其标准正位股骨侧弓角,分为4组,股骨侧弓角 > 2°组(A组),2° > 股骨侧弓角 > 0°(B组),0°> 股骨侧弓角 > -2°组(C组),股骨侧弓角 < -2°组(D组),每组5例。 2.2 受试者基线分析 入选的4组病例资料显示在年龄,身高,体质量方面特征的差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.3 各组股骨侧弓角的变化 以4组模型的内旋20°,标准正位,外旋20°为典型位置,它们在各典型位置下股骨侧弓角的测量均值见表1,图2,各组分别在内旋20°时股骨侧弓角显著减小(P < 0.05)和外旋20°位置时显著增大(P < 0.05)。"
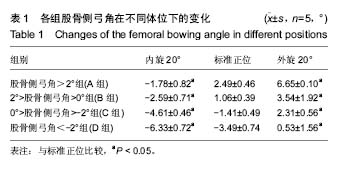
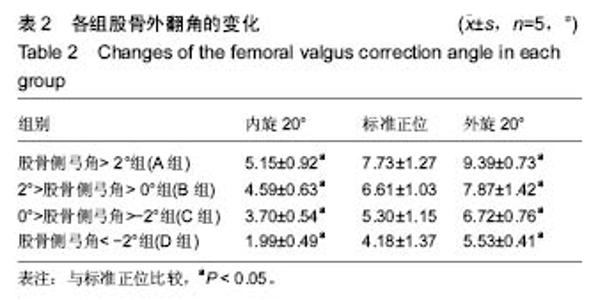
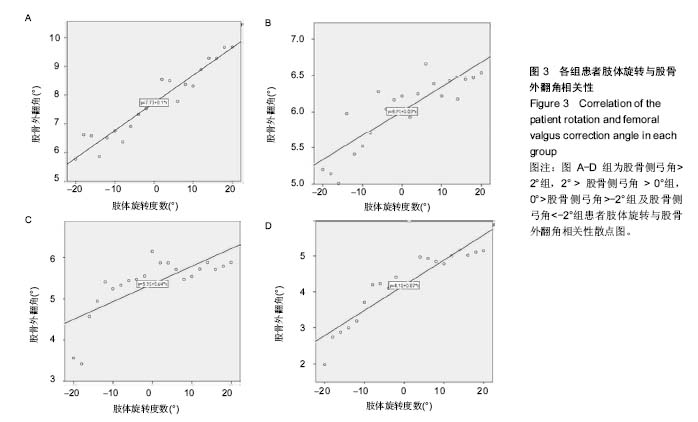
肢体内旋可以使各组病例股骨侧弓角测得值均值基于标准正位测量值,呈逐渐减小的趋势,外旋使股骨侧弓角测得值均值基于标准正位测量值均值呈逐渐增大趋势,4组直线回归方程分别为:A组y=0.47x-2.60,B组y=0.34x-2.91,C组y=0.33x-4.41,D组y=0.35x-6.34。由此可见,标准正位股骨侧弓角较大的A组的变化趋势较剧烈回归系数0.47,标准正位股骨侧弓角绝对值较小的B,C组的变化趋势较和缓,回归系数分别为0.34,0.33,D组回归系数0.35(图3)。 2.4 各组股骨外翻角的变化 各组5例病例在各自21个体位下所测得的股骨外翻角见表2,变化趋势同股骨侧弓角检测结果。"

2.5 相关性分析结果 分别绘制各组病例的股骨外翻角与体位变化相关性的散点图,并于图中添加拟合线及其拟合回归方程,图3显示,将横轴0°位对应的纵坐标看为各自组的股骨相对于下肢力线的外翻真实度数,其他各角度所测量的股骨外翻角均认作为不规范体位下所摄X射线片所测得的数据,各组股骨外翻角与旋转度数的回归系数分别为0.1(A组),0.03(B组),0.04(C组)和0.07(D组)。由各自的线性方程可知每有1°的旋转,可以分别产生平均0.1°(A组),0.03°(B组),0.04°(C组)和0.07°(D组)的测量误差;A组病例在存在20°体位旋转时即可对股骨外翻角测得值产生2°的误差,也可以认为股骨侧弓因旋转对整个下肢力线产生2°的误差,而要达到这一相同大小的误差,B组需要67°的下肢旋转偏差,C组需要50°的下肢旋转偏差,而D组则需要29°的下肢旋转偏差。 实验进一步对不同体位下股骨侧弓(股骨侧弓角)测得值与股骨外翻角相关性(股骨外翻角)测得值进行分析,得出二者相关性程度,结果4组病例所得股骨侧弓角与股骨外翻角的相关系数分别为0.86,0.80,0.88,0.85,P < 0.001。 可见在肢体旋转自-20°至20°,股骨侧弓角与股骨外翻角间始终存在显著正相关性,说明由于不同体位会引起股骨侧弓的变化,股骨外翻角测得值也会随之发生相应的变化。"
| [1] Luo CF. Reference axes for reconstruction of the knee. Knee. 2004;(11):251-257. [2] Winter A. Ferguson K. Syme B, et al. Pre-operative analysis of lower limb coronal alignment-a comparison of supine MRI versus standing full-length alignment radiographs. Knee. 2014; 21(6):1084-1087.[3] Alghamdi A, Rahmé M, Lavigne M, et al. Tibia valga morphology in osteoarthritic knees: importance of preoperative full limb radiographs in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(8):1671-1676. [4] Gbejuade HO, White P, Hassaballa M, et al. Do long leg supine CT scanograms correlate with weight-bearing full-length radiographs to measure lower limb coronal alignment? Knee. 2014;21(2):549-552. [5] Fakhrai N, Widhalm P, Chiari C, et al. Automatic assessment of the knee alignment angle on full-limb radiographs. Eur J Radiol. 2010;74(1):236-240. [6] Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT, et al. The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA. 2001;286:188-195. [7] Chang A, Hayes K, Dunlop D, et al. Thrust during ambulation and the progression of knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3897-3903. [8] Sharma L, Song J, Dunlop D, et al. Varus and valgus alignment and incident and progressive knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1940-1945. [9] Huang TW, Hsu WH, Peng KT, et al. Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane: a comparison of conventional and computerassisted surgery in an Asian population. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2011;93:345. [10] Lee CY, Huang TW, Peng KT, et al. Variability of distal femoral valgus resection angle in patients with end-stage osteoarthritis and genu varum deformity: radiographic study in an ethnic asian population. Biomed J. 2015. [11] Mullaji AB, ShettyGM, Lingaraju AP, et al. Which factors increase risk ofmalalignment of the hip-knee-ankle axis in TKA? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471:134. [12] Lasam MP, Lee KJ, Chang CB, et al. Femoral lateral bowing and varus condylar orientation are prevalent and affect axial alignment of TKA in Koreans. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471:1472.[13] Brouwer RW, Jakma TS, Brouwer KH, et al. Pitfalls in determining knee alignment: a radiographic cadaver study. J Knee Surg. 2007;20(3):210-215. [14] Brouwer RW, Jakma TS, Bierma-Zeinstra SM, et al. The whole leg radiograph: standing versus supine for determining axial alignment. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74:565-568.[15] Rinonapoli E, Mancini GB, Corvaglia A, et al. Tibial osteotomy for varus gonarthrosis. A 10- to 21-year follow-up study. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;353:185-193.[16] Wang JW, Wang CJ. Total knee arthroplasty for arthritis of the knee with extra-articular deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84-A(10):1769-1774.[17] Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, et al. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;356:144-153.[18] Jiang CC, Insall JN. Effect of rotation on the axial alignment of the femur: pitfalls in the use of femoral intramedullary guides in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(248): 50-56.[19] Swanson KE, Stocks GW, Warren PD, et al. Does axial limb rotation affect the alignment measurements in deformed limbs. Clin Orhop. 2000;371:246-252.[20] 吴蔚,许建中,郭漳生.成人正常股骨解剖测量及其在膝关节置换的临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(3):200-202.[21] Tang WM, Chiu KY, Kwan MFY. Sagittal bowing of the distal femur in Chinese patients who require total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2005;(23):41-45.[22] Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM, et al. Coronal bowing of the femur and tibia in Chinese: its incidence and effects on total knee arthroplasty planning. J Orthop Surg. 2007;15(1):32-36.[23] Mullaji AB, Marawar SV, Mittal V. A comparison of coronal plane axial femoral relationships in Asian patients with varus osteoarthritic knees andhealthy knees. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(6):861-867.[24] Radtke K, Becher C, Noll Y, et al. Effect of limb rotation on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(4):451-457.25.[25] Lonner JH, Laird MT, Stuchin SA. Effect of rotation and knee flexion on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(331):102-106.[26] Kawakami H, Sugano N, Yonenobu K, et al. Effects of rotation on measurement of lower limb alignment for knee osteotomy. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(6):1248-1253.[27] Kim JM, Hong SH, Kim JM, et al. Femoral shaft bowing in the coronal plane has more significant effect on the coronal alignment of TKA than proximal or distal variations of femoral shape. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(7): 1936-1942. [28] Lee CY, Huang TW, Peng KT, et al. Variability of distal femoral valgus resection angle in patients with end stage osteoarthritis and genu varum deformity:radiographic study in an ethnic asian population. Biomed J. 2015;38(4):350-355. [29] Gugenheim JJ, Probe RA, Brinker MR. The effects of femoral shaft malrotation on lower extremity anatomy. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18:658-664.[30] Thippanna RK, Kumar MN. Lateralization of femoral entry point to improve the coronal alignment during total knee arthroplasty in patients with bowed femur. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9):1943-1948.[31] 吴长福,郑祖高,陈宣煌,等.基于3D打印股骨远端骨折标准件库接骨板的数字化内固定[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(13): 1895-1903. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Xu Xinzhong, Wu Zhonghan, Yu Shuisheng, Zhao Yao, Xu Chungui, Zhang Xin, Zheng Meige, Jing Juehua. Biomechanical analysis of different ways of inserting Steinmann Pins into the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [3] | Wei Guoqiang, Li Yunfeng, Wang Yi, Niu Xiaofen, Che Lifang, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Shi Guopeng, Bai Ling, Mo Kai, Zhang Chenchen, Xu Yangyang, Li Xiaohe. Biomechanical analysis of non-uniform material femur under different loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [4] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [5] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [6] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [7] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [8] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [9] | Li Shuo, Su Peng, Zhang Li, Wu Qiulong, Hu Xiangyu, Lai Yuliang. Positive effect of supracondylar femoral osteotomy on the correction of knee varus based on three-dimensional reconstruction and finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 858-863. |
| [10] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [11] | Wei Xing, Liu Shufang, Mao Ning. Roles and values of blood flow restriction training in the rehabilitation of knee joint diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 774-779. |
| [12] | Chen Xiaoxu, Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Yang Kun. Preparation and application of acellular scaffold in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 591-596. |
| [13] | Kang Kunlong, Wang Xintao. Research hotspot of biological scaffold materials promoting osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 597-603. |
| [14] | Shen Jiahua, Fu Yong. Application of graphene-based nanomaterials in stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 604-609. |
| [15] | Zhang Tong, Cai Jinchi, Yuan Zhifa, Zhao Haiyan, Han Xingwen, Wang Wenji. Hyaluronic acid-based composite hydrogel in cartilage injury caused by osteoarthritis: application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 617-625. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||