Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (1): 146-153.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.01.026
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dental pulp stem cells in the paradigm of migration
Sidra Fahim, Pan Shuang, Zhang Lin, Niu Yu-mei
- Department of Endodontics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjinag Province, China
-
Online:2017-01-08Published:2017-03-15 -
Contact:Niu Yu-mei, M.D., Professor, Chief physician, Department of Endodontics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjinag Province, China -
About author:Sidra Fahim, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Endodontics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjinag Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81271132 and 81570963
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sidra Fahim, Pan Shuang, Zhang Lin, Niu Yu-mei. Dental pulp stem cells in the paradigm of migration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(1): 146-153.
share this article
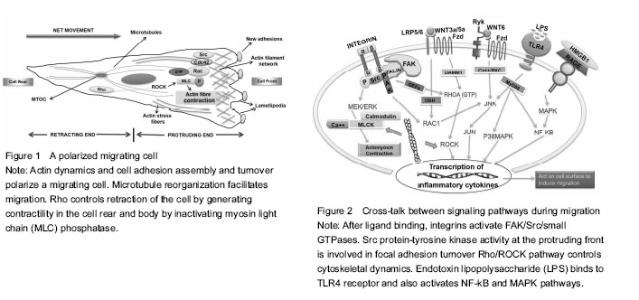
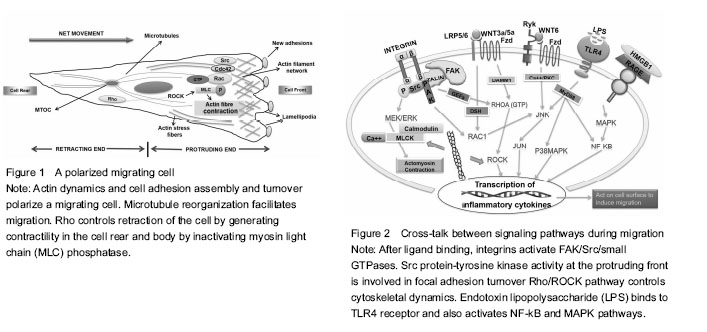
Dynamic dental stem cell niche: an underexplored arena of tissue engineering Stem cells are sustained in a niche which not only houses these stem cells but also provides physical and functional integrity. Stem cell fate is determined by specific cues generated in specific situations arising for example from sites of tissue injury. The liaison of stem cell migration with tissue regeneration phenomenon is critical for researchers in the field of tissue engineering. Cell migration is responsible for orchestrating the process of stem cell recruitment once the stem cell niche receives appropriate signals to disseminate cells to target locations. Thus understanding the fundamental mechanisms required by dental stem cells in assuming different modes of motility in physiological repair processes holds the promise for productive application of these cells in varying conditions of dental injury. Cytokines, growth factors, structural signaling proteins (cell-surface receptors) and matrix glycoproteins provide molecular interactions regulating migration of stem cells. The following sections of this review discuss the role of each of these components in migration of dental pulp stem cells directly or indirectly as evidenced by various studies. The last section of this review discusses the clinically relevant outcomes of using the enhanced migratory properties of stem cells as part of conventional treatment strategies. Cytokines and growth factors inducing motility within the realm of dental injury The inflammation caused by oral microbes generates immune response after the release of endotoxins. The bacterial invasion of pulp, as for example in pulpitis, starts an immuno-inflammatory cascade leading to well-orchestrated expression of appropriate endogenous signaling molecules which in turn causes release of cytokines followed by recruitment of stem/progenitor cells ultimately resulting in dampening of inflammation. In the course of these events, high mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1) is the protein ubiquitously produced by many cell types, particularly inflammatory cells, that acts as a cytokine when present extracellularly. Once released, it retains the potential to further induce expression of proinflammatory cytokines. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and toll-like receptor (TLR) family of receptors has been known to mediate HMGB1 signaling. One study revealed widespread expression of HMGB1 and its receptor RAGE in dental pulps undergoing inflammation where they caused reorganization of F-actin and enhanced migration of dental pulp cells in general and stem cells in particular. In this study, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation increased expression of both HMGB1 and RAGE[6]. Apart from the molecular pattern of HMGB1-RAGE interactions, there is increased expression of inflammatory cytokines in dental pulp cells, when Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria invade dental pulp successively. This cascade is initiated after stimulation from endotoxins of cariogenic bacteria like LPS (found in most gram negative bacteria) and extracts of Streptococcus mutan (S. mutans) (Gram-positive bacterium commonly found in the human oral cavity). This is only possible when reactions of innate immunity are mediated through activation of TLRs widely known for recognition of pathogenic markers and abundantly expressed in odondoblasts and dental pulp cells. However, innate immune response initiated by TLR4 when engaged by agonists of pathogenic origin is one of up-regulation of cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-8. It has been proposed that both LPS and extracts from S. mutans increase migration of DPSCs and decrease their proliferation, in which role of TLR4 receptor in reception and transduction of signals holds significance. Furthermore, TLR4 mediated relaying of signals leads to execution of effective immunity on the grounds that there is enhanced recruitment of DPSCs causing efficient repair and regeneration via immune modulatory processes[7]. Also, dental follicle progenitor cells (DFPCs) showing superior clonogenic capacity than bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) have been described as being able to detect Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) LPS which upregulates their migration via expression of TLR4 receptor without inducing cytotoxicity and does not cause production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in vitro to mediate this effect[8]. In order to arrest disease progress and promote healing, stem cell based therapies are being experimented upon in place of conventional treatments, but they are still largely unreliable and unpredictable. Howard et al. [9] led experiments evaluating the naturally-occurring chemotactants and extracellular matrix proteins (EMPs) that make up the milieu of an inflamed pulp. Their results provide evidence that blood-borne lipid sphingosine-1-phosphate is an extremely potent stimulator of migration in terms of chemotactic property in comparison with transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1). Among the well-characterized EMPs, laminin is the most effective of all to promote migration of DPSCs. However, when speaking of components essential for immune function, tissue repair and increasing cytokine levels, the role of an endogenously produced essential amino acid, glutamine, on the various physiological functions of human dental pulp cells has been signified. It has been proposed that glutamine, dose-dependently boosts migration through interactions with the components of WnT, bone morphogenetic protein and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways while simultaneously elevating cytokine levels. This deductive knowledge has been reinforced through the use of inhibitors for noggin, DKK-1, p38, ERK, and JNK; thereby inhibiting migration along with growth and differentiation[10]. In the context of endogenous and exogenous cytokines, in vitro models of nemosis causing the fibroblasts to activate through cell-cell interactions and terminate in programmed cell death in a necrotic-like phenotype; is the prevailing idea where the presence of fibroblasts within pulpal tissues comes into consideration. These fibroblasts have been shown to undergo a discrete phenomenon whereby normal fibroblasts if forced to cluster in a spheroid formation assume an activated pro-inflammatory response concurring with protein hydrolysis and growth factor release[11]. More so, these COX-2 producing necrotizing spheroids advance an intense inflammatory response which has been utilized to understand the nature of relationship between DPSCs and fibroblast spheroids promoting their migration[12]. Further studies investigating specific cytokines and chemokines released due to occurrence of experimentally-induced nemosis are crucial for efficient modulation of dental inflammation. Growth factors, within dentine matrix, are acquired from viable odontoblasts and pulp fibroblasts. These are released after dentine demineralization in order to provide necessary chemotactic signals required for stem cell recruitment. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is a well-known growth, morphogenic and motility factor secreted by cells of mesenchymal origin; acting in a paracrine fashion. A study by Su et al. [13] mapped out a pathway by which HGF regulated cell migration dynamics in human dental papilla cells which are the putative precursors of odontoblasts and other dental pulp cells. Their report showed that phosphorylation of paxillin resulting from activation of JNK and p38 MAP kinases leads to actin filament reorganization and enhanced cell migration in this cell line[13]. In order to understand how HCG can be utilized optimally within the microenvironment of stem cells derived from dental tissue through biochemical induction, from the standpoint of regeneration of dental tissues, further research is inevitable. Similarly, epidermal growth factor (EGF) having affinity for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) regulates various cellular functions by binding to its receptor. EGF and EGFR have been shown to influence migration and proliferation in keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Recent research potentiates the ability of EGF to facilitate migration of PDL-derived endothelial progenitor cell-like cells in an MAPK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK)- and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent fashion. In the course of this pathway, EGF down-regulates TGF-β1 induced phosphorylation of cofilin, which in turn allows for actin cytoskeletal reorganization rendering it a motility-modulating factor[14]. Needless to say, it is of prime importance to determine how EGF can become manifest in stem cells derived from dental pulp. LL37, a cathelicidin-derived peptide found in humans with broad antimicrobial activity has piqued the interest in the research on regenerative endodontics. LL37 induces transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), mediated through the heparin-binding-EGF, thus causing increased levels of phosphorylated EGFR and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK); all culminating in the migration of human pulp cells[15]. It is tempting to speculate that since neutrophils are the putative sources of LL37 within the inflamed pulp, potentiation of this effect through exogenous incorporation of this peptide in dental materials used for pulp healing and reparative dentin formation could lead us towards achieving effective reparative dentinogenesis. This necessitates clinical trials - induction strategies to utilize EGF and other growth factor ligands for EGFR in the preparation of novel dental materials acting upon mesenchymal cells and enhancing their migratory and wound-healing abilities. Modifications of molecular machinery during migration Balanced interaction of cells with extracellular matrix (ECM) causes them to assume a polarized form. At the front, attachment of a cell protrusion called lamellipodium to ECM followed by retraction of trailing edge of the migrating cell through detachment from ECM is predominantly dependent on integrin-cytoskeleton interactions. Several lines of evidence suggest involvement of Rho/ROCK pathway, MEK, JNK pathway, p38 MAP kinase, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathway, notch signaling and Eph/ephrinB interactions in modulating dental cell migration either positively or negatively[13, 14, 16-19]. The complex overlapping network of signaling pathways underlying migration comprises of an important pathway called “Rho/ROCK pathway”. It has been implicated that ROCK inhibition leads to enhanced DPC migration in vitro and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) - a bioactive phospholipid, acts synergistically with ROCK when introduced into DPCs. LPA has a chemotactic effect in multiple cell types. In DPCs, its chemotactic effect has been shown to manifest through increased cell motility via activation of Rho followed by Rac activation pathway. The additive effects of LPA and ROCK inhibition lead to lamellipodium formation, enhanced α-smooth muscle actin levels and actin cytoskeleton assembly which results in elevated migration rate[18]. Therefore, LPA acting through autocrine mechanism can be coupled with ROCK inhibition to strengthen its pro-migratory effects within the specialized microenvironment of stem cells. Integrins form a major migration promoting family of receptors and role of LPA in the activation of Rac and Rho small GTPases is accurately known. Thus how these both assist one another at the onset of migration is approaching criticality in current and future research. In human dental pulp cells α1, α2, α3, α5, α6, αv, and β1 integrin subunits are expressed which is similar to connective tissue regions in the body elsewhere. Integrin α6 has been consistently linked to migratory phenotypes in normal and malignant tissues. One research group observed that integrin α6β4 promotes LPA-initiated chemotaxis by activating RhoA, leading to subsequent activation of Rac1. Even though, integrin α6β4 signaling alone is not sufficient for this effect on RhoA&Rac, the cooperative association of LPA with integrin specifically contributes towards increased cell motility and lamellae formation[20]. Similarly, integrin engagement of ligands plays an important role in activation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK), a cytoplasmic focal adhesion associated tyrosine kinase. The relationship between FAK and spreading around of cells has been extensively researched upon in terms of its role in integrin-mediated migration, actin cytoskeleton reorganization and turnover of cell-cell or cell-substrate contacts[21]. FAK undergoes multiple molecular interactions while acting downstream of growth factors, G-protein coupled receptors and low-density lipoprotein receptors. An essential part of FAK mediated signaling is the activity of its kinase domain perpetuating regulation of Rho-family GTPase activity, phosphorylation of the type I phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase isoform-? and activation of protein tyrosine kinases of the Src family causing focal contact turnover and cell motility[22]. By using green fluorescent protein, Timpson et al. particularly defined a relationship between c-Src Kinase and Rho-GTPases. They showed that after stimulation of Rho-GTPases, especially RhoA, c-Srctranslocates from the perinuclear region to the cell periphery due to formation of actin stress fibers where it becomes colocalized with focal adhesion protein vinculin. The kinase activity of c-Src is shown to be a determinant of actin remodeling involved in formation of lamellipodia and filopodia that acts in concert with Rho GTPases favoring turnover of cell adhesions required for sustained motility[23]. Some undefined mechanisms yet remain to be elucidated regarding the movement of c-Src from cell interior to periphery and incorporation alongside cell-matrix adhesions during the migratory journey of cells. Actin cytoskeletal structures regulate cellular morphology and formation of membrane protrusions like lamellipodia, filopodia and podosomes in migrating cells (Figure 1). This change in cell shape is an important feature when determining migration modifying factors. Li et al. [24] reported enhancement of actin-based motility owing to involvement of an F-actin-severing and actin capping protein “Adseverin” (belonging to gelsolin superfamily) in the migrating cells. Its expression in the DPCs influences cellular morphology regulating physiologically relevant functions of proliferation, migration and odontoblastic differentiation. Additionally, adseverin knockdown negatively regulated this pulp-wound healing cascade. Since, actin stress fibers act as inducers of cell motility, a conclusion we can draw here is that adseverin protein has a bearing on actin polymerisation and migratory ability of dental pulp cells. Bacterial LPS is a known inducer of yet another important pathway called the NF-κB pathway. When observed in vitro, LPS enhances cell migration at a threshold concentration of 1 mg/mL. It has been shown to activate NF-κB and MAPK pathways by binding to TLR4 receptors. In addition it up regulates expression of stromal cell-derived factor-1α, CXCR4, MCP-1, FGF2, MIP-1α and TGF-β1 which are crucial chemotactic factors of inflammation[19]. Hence, from the above discussion we can extrapolate the relevance of presence of endotoxins in the pulp cavity and root canals and potential initiation of indigenous repair mechanisms. In the case of mesenchymal stem cells, such as DPSCs, the role of NF-κB signaling needs further research as to whether their effect is pro- or anti-inflammatory by determining the specific molecules in cross-talk with the prototypical NF-κB pathway. Role of Wnt family of proteins in the developmental process of odontogenesis and molecular patterns associated with proliferation, migration, cell survival, and cell differentiation in the dental pulp cells is a fundamental one. Both canonical and non-canonical pathways of Wnt signaling participate via distinct intracellular pathways acting downstream of Wnt binding to either Frizzled (Fzd) or/and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein family of receptors. Wnt3a has been shown to increase migration of rat bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by imparting a strong chemotactic effect[25]. Moreover, Wnt5a, a component of non-canonical pathway, has been shown to promote motility in some cell types and inhibit migration in others. However, with regards to human dental papilla cells it mediates suppression of migration by depolymerizing microtubules and microfilaments which are vital for maximal activity in terms of cell locomotion[26]. Another study has signified interaction between Wnt6 and the JNK pathway in human dental pulp cells, thus promoting migration through activation of non-canonical pathway. Of note is the enhanced phosphorylation of JNK caused by Wnt6 which in turn provides signals affecting pronounced migration and recruitment of cells critical for tissue repair[27]. These findings gathered from recent studies have been used to compile the diagrammatic representation of some well-researched migration associated molecular processes (Figure 2). Unsurprisingly, despite extensive investigation into the mechanistic basis of generating contractile forces in cells under the effect of Wnt proteins, the shortcomings in our understanding of the precise components of molecular signaling pathways present intracellularly communicating with extracellular stimuli reflecting their specific roles in migration dynamics are potentially emerging domains for future research. Notch signaling pathway is a means of direct cell-cell communication that critically regulates proliferation, apoptosis, and fate decisions of stem/progenitor cells during development of different tissues and organs. This pathway performs its functions via five Notch ligands (Delta-like [Dll] 1, 3, 4, and Jagged 1, 2) and four Notch receptors (Notch 1-4) which are type I transmembrane proteins with extra-cellular and intra-cellular domains. Notch signaling has been shown to regulate mice bone marrow-derived MSC migration and function via the upregulation of CXCR4 expression in response to stromal cell-derived factor-1α both in vitro and in vivo [28]. Moreso, Notch signaling plays an important role in wound healing as shown by experiments on cultured vascular endothelial cells, keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Enhanced dermal wound healing and tissue repair potential has been observed in vivo in mice under the regulatory effects of activating notch signaling[29]. Migration-altering behavior of the components of the notch signaling axis is also evident from in vivo and in vitro studies on tumor cells describing stimulation of migration of breast cancer cells[30] and regulation of hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration[31]. These findings suggest that notch-signaling could serve as a potential pharmacological target and may provide a novel approach for the treatment of dental injuries where stem cells are employed. By determining specific factors interacting with NOTCH signaling we can fully understand the role of NOTCH in human DPSC migration which could build upon our knowledge of migratory characteristics in this stem cell line. Treatment protocols promoting/inhibiting migration Dental materials have long been setting restorative trends seeking successful treatment outcomes. With the introduction of stem cells’ based therapies and endless boundaries of technological advancement in dental science, the use of conventional treatments is beginning to phase out. However, some dental materials have continued to evolve in their properties drawing on existing methods of tooth repair and regeneration, leading to better predictability even when used with stem cells. MTA has been providing a promising treatment in tooth repair and regeneration procedures for over a decade now. Through considerable amount of research work its benefits related to biocompatibility have already been brought to light. More so, a study by D'Antò et al. demonsrated the upregulating effect of MTA on the migration of bone marrow derived human mesenchymal stem cells. MTA cement, when made to interact with hMSCs, it enhanced their migratory ability significantly[32]. In context of the study reported herein, know-how of implementing useful pro-migratory influence of MTA on the DPSCs, a type of mesenchymal stem cells, is crucial to improve the results of stem-cell based therapy in dental settings. Zhu et al. [33] did a comparative study on BioAggregate® (aluminium-free bioceramic material) and ProRoot® MTA employed as part of restorative and root canal treatment protocols in endodontics. Their work demonstrated better biocompatibility of BioAggregate in comparison to MTA owing to enhanced stress fiber formation in mesenchymal cells, thus leading to enhanced cytoskeletal reorganization and significantly pronounced migration. Therefore, improved migratory capacities of the dental pulp stem cells with the use of BioAggregate® in vitro, has led researchers to place it above MTA as a material of choice in terms of efficient clinical applications. Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate (HEMA) has been shown to inhibit migration of DPSCs at concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, and 2.5 mmol/L without affecting cell viability. This suppression of migration is orchestrated through a decrease in FAK phosphorylation at Tyr397 and phosphorylation of p38 MAP kinase signaling pathways[34]. Contrary to this, a previous study reported that increased p38 signaling was related to increased FAK phosphorylation and cell migration[35]. Whatever the relation may be between components downstream of FAK and p38 signaling pathways, we need to go even deeper and identify how biocompatible hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) really is at the ultrastructural level, and whether inclusion of this chemical in resin-based dental materials and dentine adhesive systems is more of a hindrance than help in pulpal wound healing and dentin regeneration, needs definitive characterization. Luo et al. evaluated the effect of bioactive tricalcium silicate cement Biodentine™ on cellular migration which has been manufactured with active biosilicate technology. It has been gaining reputation as a superior material with versatile indications in clinical settings. Biodentine™ has been reported to work on the migratory behavior of DPSCs in a positive manner possibly through upscaling of chemokines[36]. Under the effect of Biodentine™, exactly what combination of signaling molecules is involved in the propagation of proliferation, migration and adhesion of DPSCs, when used as a pulp capping agent, that results in efficient dentin bridge formation and diminished pulpal inflammation is yet another area of potential research which is not completely understood. Some researchers demonstrated the effect of calcium-hydroxide on the efficacy of autologously transplanted DPSCs when these two were applied in combination to treat teeth where dentin regeneration was required for restoration of structure and function. Their results showed that DPSCs performed better in the presence of calcium hydroxide in terms of recruitment, migration, proliferation and mineralization leading to dentine deposition[37]. It can, thus be, gleaned from this experimental evidence that this popular pulp capping material in dental practice is as reliable with stem cell based therapies as with those undertaken prior to use of stem cells for biomimetically restoring teeth. However, a protocol for using stem cells with calcium hydroxide or other pulp capping materials now being used with some bioactive molecules added to them needs to be devised, before upregulation of dentine regeneration can come to fruition in a clinically relevant way. Virtually all kinds of cells, including stem cells, rely on the ion channels to regulate diverse cellular processes such as proliferation, migration, differentiation, which respond to cytoplasmic signals through influx of ions. Recently, identification of a protein called transient receptor potential cation channel (TRPM7), containing an ion channel associated with a serine/threonine protein kinase, has set a new path for researchers. Cui et al. [38] demonstrated expression of TRPM7 in the cytoplasm of DPSCs. Their data suggest that TRPM7 channels participate in migration dynamics by controlling influx of Ca2+ ions and homoeostasis of Mg2+ ions. Whether the role of Mg2+ ions or Ca2+ ions is more important in eliciting directional cell movement in DPSCs and whether these ion channels negatively or positively regulate cations in response to external stimuli are the questions which need conclusive answers by way of further investigations. Moreover, additional studies are indispensable in revealing mechanisms underlying immune response of stem cells and factors modulating their response via receptor-ligand interactions."
| [1] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630. [2] Smith AJ, Lesot H. Induction and regulation of crown dentinogenesis: embryonic events as a template for dental tissue repair. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2001;12(5): 425-437. [3] About I, Bottero MJ, de Denato P, et al. Human dentin production in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2000;258(1):33-41. [4] Téclès O, Laurent P, Zygouritsas S, et al. Activation of human dental pulp progenitor/stem cells in response to odontoblast injury. Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50(2):103-108. [5] Mathieu S, El-Battari A, Dejou J, et al. Role of injured endothelial cells in the recruitment of human pulp cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50(2):109-113. [6] Zhang X, Jiang H, Gong Q, et al. Expression of high mobility group box 1 in inflamed dental pulp and its chemotactic effect on dental pulp cells. Biochem Bioph Res Commun. 2014;450(4):1547-1552.[7] Liu Y, Gao Y, Zhan X, et al. TLR4 activation by lipopolysaccharide and Streptococcus mutans induces differential regulation of proliferation and migration in human dental pulp stem cells. J Endodont. 2014;40(9): 1375-1381. [8] Chatzivasileiou K, Lux CA, Steinhoff G, et al. Dental follicle progenitor cells responses to Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(6):766-773. [9] Howard C, Murray PE, Namerow KN. Dental pulp stem cell migration. J Endodont. 2010;36(12):1963-1966. [10] Kim DS, Jue SS, Lee SY, et al. Effects of glutamine on proliferation, migration, and differentiation of human dental pulp cells. J Endodont. 2014;40(8):1087-1094. [11] Bizik J, Kankuri E, Ristimäki A, et al. Cell–cell contacts trigger programmed necrosis and induce cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11(2):183-195. [12] Zhai S, Wang Y, Jiang W, et al. Nemotic human dental pulp fibroblasts promote human dental pulp stem cells migration. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(10):1544-1552. [13] Su Y, Xie W, Wang C, et al. JNK/P38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Used for Hepatocyte Growth Factor–induced Proliferation, Differentiation, and Migration in Human Dental Papilla Cells. J Endodont. 2012;38(9): 1207-1213. [14] Kimura H, Okubo N, Chosa N, et al. EGF positively regulates the proliferation and migration, and negatively regulates the myofibroblast differentiation of periodontal ligament-derived endothelial progenitor cells through MEK/ERK-and JNK-dependent signals. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(4):899-914. [15] Kajiya M, Shiba H, Komatsuzawa H, et al. The antimicrobial peptide LL37 induces the migration of human pulp cells: a possible adjunct for regenerative endodontics. J Endodont. 2010;36(6):1009-1013.[16] Arthur A, Koblar S, Shi S, et al. Eph/ephrinB mediate dental pulp stem cell mobilization and function. J Dental Res. 2009; 88(9):829-834. [17] Mitsiadis T, Feki A, Papaccio G, et al. Dental pulp stem cells, niches, and notch signaling in tooth injury. Adv Dent Res. 2011;23(3):275-279. [18] Cheng R, Cheng L, Shao MY, et al. Roles of lysophosphatidic acid and the Rho-associated kinase pathway in the migration of dental pulp cells. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(6):1019-1027. [19] Li D, Fu L, Zhang Y, et al. The effects of LPS on adhesion and migration of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro. J Dent. 2014;42(10):1327-1334. [20] O'Connor KL, Chen M, Towers LN. Integrin α6β4 cooperates with LPA signaling to stimulate Rac through AKAP-Lbc-mediated RhoA activation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2012;302(3):C605-C614. [21] Schaller MD. Biochemical signals and biological responses elicited by the focal adhesion kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1540(1):1-21. [22] Schlaepfer DD, Mitra SK. Multiple connections link FAK to cell motility and invasion. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2004;14(1): 92-101. [23] Timpson P, Jones GE, Frame MC, et al. Coordination of cell polarization and migration by the Rho family GTPases requires Src tyrosine kinase activity. Curr Biol. 2001;11(23): 1836-1846. [24] Li X, Jiang H, Huang Y, et al. Expression and function of the actin-severing protein adseverin in the proliferation, migration, and differentiation of dental pulp cells. J Endodont. 2015;41(4):493-500. [25] Shang YC, Xiong F, Li Y, et al. Wnt3a signaling promotes proliferation, myogenic differentiation, and migration of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2007;28(11):1761-1774.[26] Peng L, Ye L, Dong G, et al. WNT5A inhibits human dental papilla cell proliferation and migration. Biochem Bioph Res Common. 2009;390(3):1072-1078. [27] Li R, Wang C, Tong J, et al. WNT6 promotes the migration and differentiation of human dental pulp cells partly through c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway. J Endodont. 2014;40(7):943-948.[28] Xie J, Wang W, Si JW, et al. Notch signaling regulates CXCR4 expression and the migration of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Immunol. 2013;281(1):68-75. [29] Chigurupati S, Arumugam TV, Son TG, et al. Involvement of notch signaling in wound healing. PLoS One. 2007;2(11): e1167. [30] Bolós V, Mira E, Martínez-Poveda B, et al. Notch activation stimulates migration of breast cancer cells and promotes tumor growth. Breast Cancer Res. 2013;15(4):1. [31] Sahlgren C, Gustafsson MV, Jin S, et al. Notch signaling mediates hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration and invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(17): 6392-6397. [32] D'Antò V, Di Caprio MP, Ametrano G, et al. Effect of mineral trioxide aggregate on mesenchymal stem cells. J Endodont. 2010;36(11):1839-1843. [33] Zhu L, Yang J, Zhang J, et al. A comparative study of BioAggregate and ProRoot MTA on adhesion, migration, and attachment of human dental pulp cells. J Endodont. 2014;40(8):1118-1123. [34] Williams DW, Wu H, Oh JE, et al. 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate inhibits migration of dental pulp stem cells. J Endodont. 2013;39(9):1156-1160. [35] Lee J, Jung ID, Chang WK, et al. p85 β-PIX is required for cell motility through phosphorylations of focal adhesion kinase and p38 MAP kinase. Exp Cell Res. 2005;307(2): 315-328. [36] Luo Z, Li D, Kohli MR, et al. Effect of Biodentine™ on the proliferation, migration and adhesion of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent. 2014;42(4):490-497. [37] Ji YM, Jeon SH, Park JY, et al. Dental stem cell therapy with calcium hydroxide in dental pulp capping. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(6):1823-1833. [38] Cui L, Xu S, Ma D, et al. The effect of TRPM7 suppression on the proliferation, migration and osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. Int Endod J. 2014;47(6): 583-593. |
| [1] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [5] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [6] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [7] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [11] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [12] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [13] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [14] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [15] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||