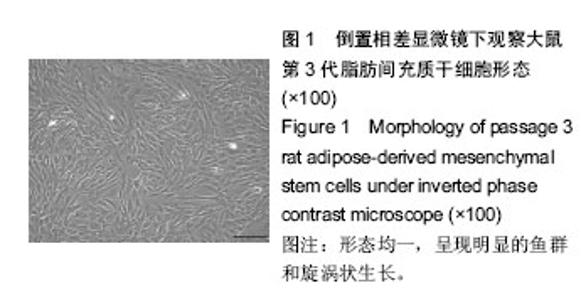
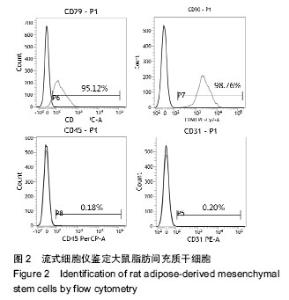
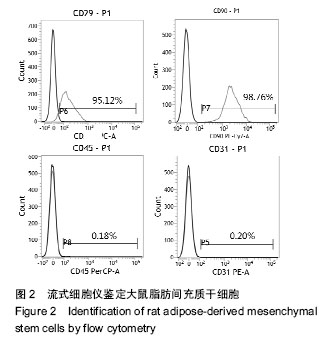
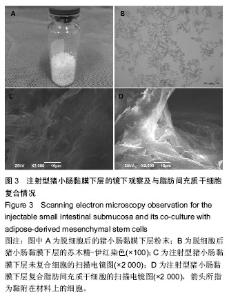
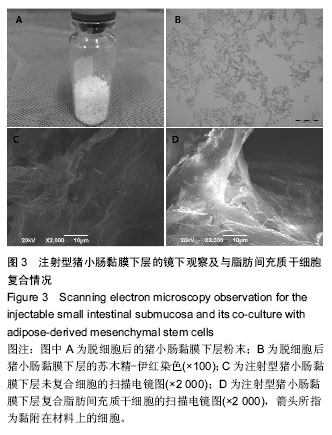
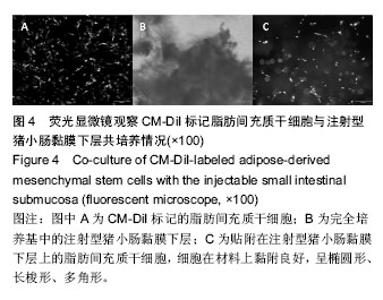
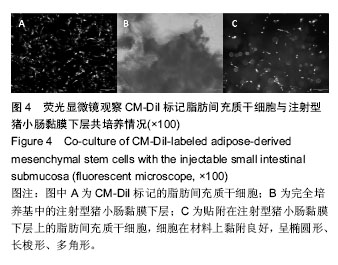
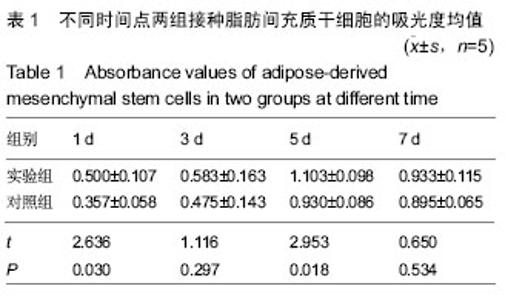
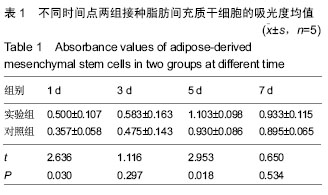
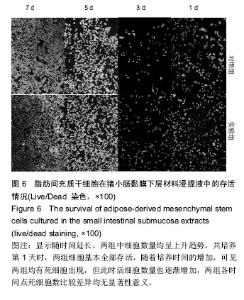
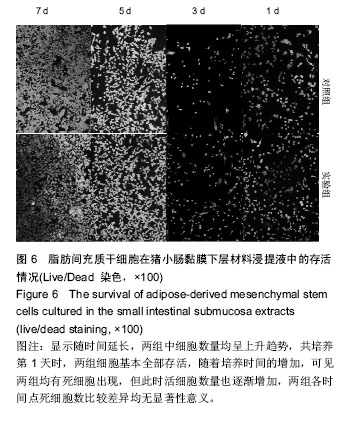
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (38): 5730-5736.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.38.016
Previous Articles Next Articles
Injectable small intestinal submucosa is co-cultured with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro
- 1Department of Plastic and Burn Surgery, 2Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2016-08-19Online:2016-09-16Published:2016-09-16 -
Contact:Tan Mei-yun, Associate professor, Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Guo Xing, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Plastic and Burn Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31271049
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Xing, Zhou Hong, Li Dan, Gao Xiao-chun, Dai Lei, Huang Hai-jun, Tan Mei-yun.
share this article
| [1]Wilson A,Butler PE,Seifalian AM.Adipose-derived stem cells for clinical applications: A review.Cell Prolif. 2011; 44(1):86-98. [2]Hong SJ,Jia SX,Xie P,et al.Topically delivered adipose derived stem cells show an activated-fibroblast phenotype and enhance granulation tissue formation in skin wounds. PloS One.2013;8(1):e55640. [3]Dong Y,Hassan WU,Kennedy R,et al.Performance of an in situ formed bioactive hydrogel dressing from a peg-based hyperbranched multifunctional copolymer.Acta Biomaterialia. 2014;10(5):2076-2085. [4]Gugerell A,Neumann A,Kober J,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells cultivated on electrospun l-lactide/glycolide copolymer fleece and gelatin hydrogels under flow conditions-aiming physiological reality in hypodermis tissue engineering. Burns.2015;41(1):163-171. [5]Haubner F,Gassner HG.Potential of adipose-derived stem cells concerning the treatment of wound healing complications after radiotherapy. HNO. 2015;63(2): 111-117. [6]Ozpur MA,Guneren E,Canter HI,et al.Generation of skin tissue using adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Plast Reconstr Surg.2016;137(1):134-143. [7]Shalaby SM,Sabbah NA,Saber T,et al.Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate the immune response in chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model.IUBMB Life.2016;68(2): 106-115. [8]Zuk PA,Zhu M,Mizuno H,et al.Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng.2001;7(2):211-228. [9]Park BS,Jang KA,Sung JH,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells and their secretory factors as a promising therapy for skin aging.Dermatol Surg. 2008;34(10):1323-1326. [10]Taha MF,Hedayati V.Isolation, identification and multipotential differentiation of mouse adipose tissue-derived stem cells.Tissue Cell. 2010;42(4): 211-216. [11]Gimble JM,Katz AJ,Bunnell BA.Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine.Circ Res.2007;100(9): 1249-1260. [12]Yamane S,Iwasaki N,Majima T,et al.Feasibility of chitosan-based hyaluronic acid hybrid biomaterial for a novel scaffold in cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2005;26(6):611-619. [13]Lutolf MP,Hubbell JA.Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering.Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(1):47-55. [14]Shi L,Ronfard V.Biochemical and biomechanical characterization of porcine small intestinal submucosa (sis): A mini review.Int J Burns Trauma.2013;3(4): 173-179. [15]Davies OG,Cooper PR,Shelton RM,et al.Isolation of adipose and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells using cd29 and cd90 modifies their capacity for osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation.J Tissue Eng.2015;6:2041731415592356. [16]Nie C,Yang D,Xu J,et al.Locally administered adipose-derived stem cells accelerate wound healing through differentiation and vasculogenesis.Cell Transplant.2011;20(2):205-216. [17]Kang KN,Kim da Y,Yoon SM,et al.In vivo release of bovine serum albumin from an injectable small intestinal submucosa gel.Int J Pharm.2011;420(2): 266-273. [18]Kim K,Kim MS.An injectable hydrogel derived from small intestine submucosa as a stem cell carrier.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2015.doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33504. [Epub ahead of print] [19]Guo X,Xia B,Lu XB,et al.Grafting of mesenchymal stem cell-seeded small intestinal submucosa to repair the deep partial-thickness burns.Connect Tissue Res. 2016:1-10. [20]Cowles EA,Brailey LL,Gronowicz GA. Integrin-mediated signaling regulates ap-1 transcription factors and proliferation in osteoblasts. J Biomed Mater Res.2000;52(4):725-737. [21]Andree B,Bar A,Haverich A,et al.Small intestinal submucosa segments as matrix for tissue engineering: Review.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2013;19(4):279-291. [22]杨浩,吴迪,李世和,等.猪小肠黏膜下层基质支架材料复合脂肪基质干细胞的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(3):415-418. [23]房艳,倪伟民,单伟,等.海绵状的小肠粘膜下层促进成骨样细胞增殖分化[J].中国生物工程杂志,2013,33(6):18-23. [24]田伟,王效杰.猪小肠黏膜下层海绵的三维重建、表面修饰和细胞黏附性[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014,34(14):3949- 3951. [25]Choi JW,Park JK,Chang JW,et al.Small intestine submucosa and mesenchymal stem cells composite gel for scarless vocal fold regeneration.Biomaterials. 2014;35(18):4911-4918. [26]Zonari A,Martins TM,Paula AC,et al. Polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate structures loaded with adipose stem cells promote skin healing with reduced scarring.Acta Biomaterialia. 2015;17: 170-181. [27]Zeng Y,Zhu L,Han Q,et al.Preformed gelatin microcryogels as injectable cell carriers for enhanced skin wound healing.Acta Biomaterialia. 2015;25: 291-303. [28]Kono H,Teshirogi T.Cyclodextrin-grafted chitosan hydrogels for controlled drug delivery.Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;72:299-308. [29]Kwon JS,Yoon SM,Shim SW,et al.Injectable extracellular matrix hydrogel developed using porcine articular cartilage.Int J Pharm.2013;454(1):183-191. [30]Naderi-Meshkin H,Andreas K,Matin MM,et al. Chitosan-based injectable hydrogel as a promising in situ forming scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Cell Biol Int.2014;38(1):72-84. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [7] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [8] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [9] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [10] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [11] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [12] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [13] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [14] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [15] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||