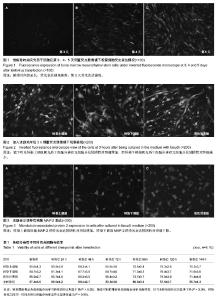
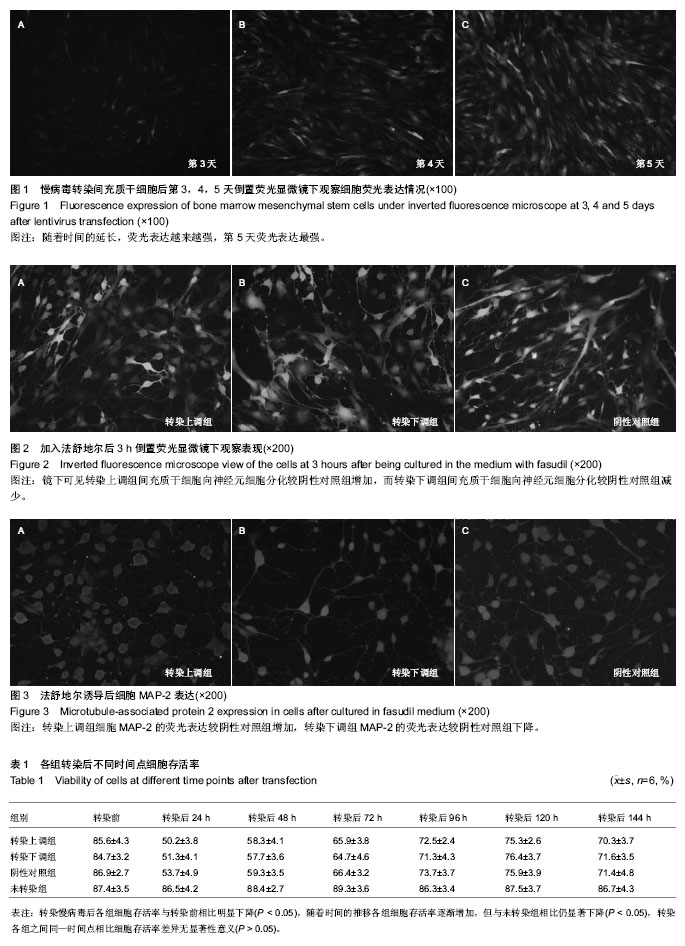
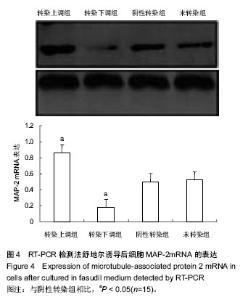
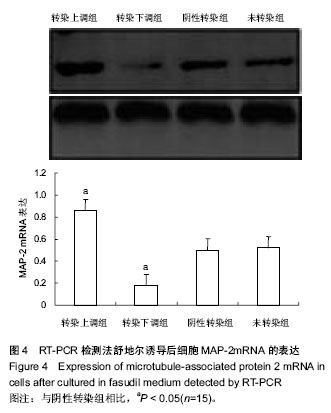
| [1] Thornton JE, Gregory RI.How does Lin28 let-7 control development and disease.Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(9): 474-482.
[2] Sugaya K.Possible use of autologous stem cell therapies for Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2005;2(3):367-376.
[3] Sugaya K, Merchant S.How to approach Alzheimer's disease therapy using stem cell technologies.J Alzheimers Dis. 2008; 15(2):241-254.
[4] Inui M, Martello G, Piccolo S.MicroRNA control of signal transduction.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(4):252-263.
[5] Guo L, Zhao RC, Wu Y.The role of microRNAs in self-renewal and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Exp Hematol. 2011;39(6):608-616.
[6] Laine SK, Hentunen T, Laitala-Leinonen T.Do microRNAs regulate bone marrow stem cell niche physiology?Gene. 2012; 497(1):1-9.
[7] Wulczyn FG, Smirnova L, Rybak A,et al.Post-transcriptional regulation of the let-7 microRNA during neural cell specification. FASEB J. 2007;21(2):415-426.
[8] Marson A, Levine SS, Cole MF,et al.Connecting microRNA genes to the core transcriptional regulatory circuitry of embryonic stem cells.Cell. 2008;134(3):521-533.
[9] Wilbert ML, Huelga SC, Kapeli K,et al.LIN28 binds messenger RNAs at GGAGA motifs and regulates splicing factor abundance.Mol Cell. 2012;48(2):195-206.
[10] Viswanathan SR, Daley GQ, Gregory RI.Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28.Science. 2008; 320 (5872):97-100.
[11] Rybak A, Fuchs H, Smirnova L,et al.A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment.Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10(8):987-993.
[12] Wright JE, Ciosk R.RNA-based regulation of pluripotency. Trends Genet. 2013;29(2):99-107.
[13] Viswanathan SR, Daley GQ.Lin28: A microRNA regulator with a macro role.Cell. 2010;140(4):445-449.
[14] 周燕,陈奎生,高剑波,等. miR-124-1 促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞神经分化的实验研究[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2012,14(3): 215-220.
[15] 景黎君,贾永林,鲁晶晶,等. MicroRNA-9-1慢病毒载体的构建及其对小鼠骨髓间质干细胞诱导分化为神经细胞的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(2):326-331.
[16] Simmons A, Whitehead RP, Kolokoltsov AA,et al.Use of recombinant lentivirus pseudotyped with vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein G for efficient generation of human anti-cancer chimeric T cells by transduction of human peripheral blood lymphocytes in vitro.Virol J. 2006;3:8.
[17] Solomon A, Mian Y, Ortega-Cava C,et al.Upregulation of the let-7 microRNA with precocious development in lin-12/Notch hypermorphic Caenorhabditis elegans mutants.Dev Biol. 2008; 316(2):191-199.
[18] Zhu H, Shyh-Chang N, Segrè AV,et al.The Lin28/let-7 axis regulates glucose metabolism.Cell. 2011;147(1):81-94.
[19] Whelan JT, Hollis SE, Cha DS,et al.Post-transcriptional regulation of the Ras-ERK/MAPK signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(3):1235-1241.
[20] Connick P, Kolappan M, Patani R,et al.The mesenchymal stem cells in multiple sclerosis (MSCIMS) trial protocol and baseline cohort characteristics: an open-label pre-test: post-test study with blinded outcome assessments.Trials. 2011;12:62.
[21] Connick P, Kolappan M, Crawley C,et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: an open-label phase 2a proof-of-concept study.Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(2):150-156.
[22] Gu W, Zhang F, Xue Q,et al.Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reduces lesion volume and induces axonal regrowth of injured spinal cord.Neuropathology. 2010; 30(3):205-217.
[23] Zhang C,He XJ,Li HP,et al. Chondroitinase ABC plus bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(11): 965-974.
[24] Zhang CL, Zou Y, He W,et al.A role for adult TLX-positive neural stem cells in learning and behaviour.Nature. 2008; 451(7181):1004-1007.
[25] Li S, Sun G, Murai K,et al.Characterization of TLX expression in neural stem cells and progenitor cells in adult brains.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43324.
[26] Shi Y, Chichung Lie D, Taupin P,et al. Expression and function of orphan nuclear receptor TLX in adult neural stem cells. Nature. 2004;427(6969):78-83.
[27] Shi Y, Sun G, Zhao C,et al.Neural stem cell self-renewal.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008;65(1):43-53.
[28] Zhao C, Sun G, Ye P,et al.MicroRNA let-7d regulates the TLX/microRNA-9 cascade to control neural cell fate and neurogenesis.Sci Rep. 2013;3:1329.
[29] 彭涛,滕军放,关文娟,等.盐酸法舒地尔体外诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化的可行性[J].郑州大学学报:医学版, 2010,45(4):559-562.
[30] 赵二义,王留东,文全庆,等.Notch信号在盐酸法舒地尔诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元分化过程中的作用[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2010,26(4):428-432. |