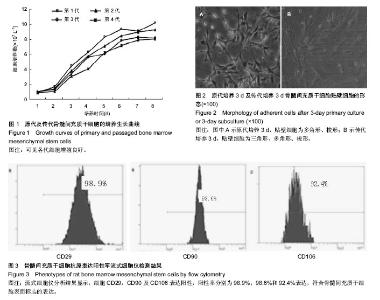
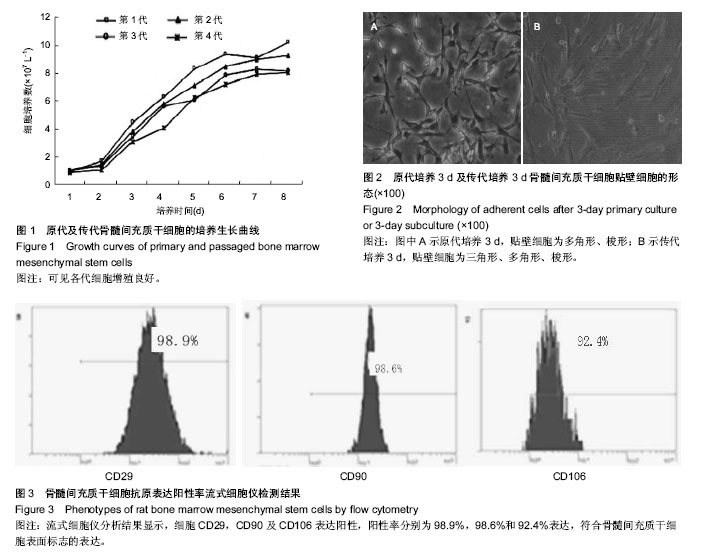
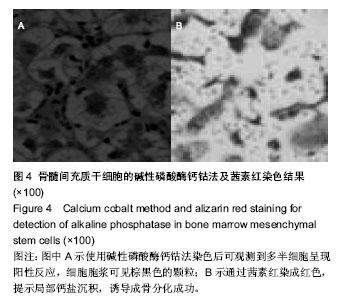
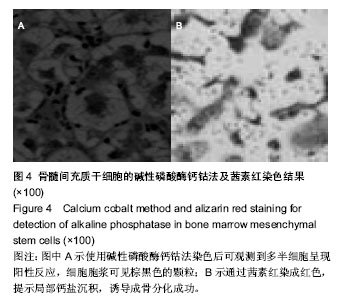
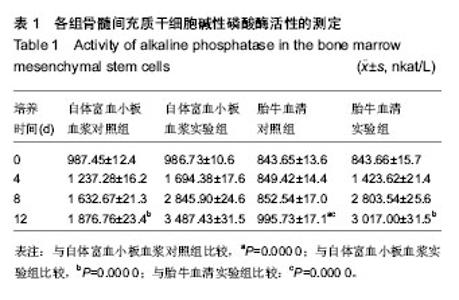
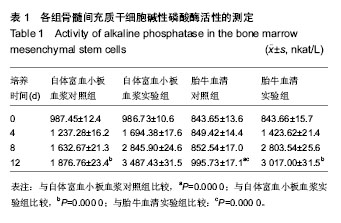
| [1] 安莹,高丽娜,杨昊,等.氯化锂对人牙周膜干细胞增殖和成骨分化的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2013,23(1):12-16.
[2] 刘银梅,张鹏.骨髓间充质干细胞对移植免疫的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(49):9264-9267.
[3] 马志兵,袁峰,冯虎.等自体富血小板血浆对兔骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(12):2211-2214.
[4] 李雪峰,刘亮,王东.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外向成骨细胞分化培养的生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(23):4185-4188.
[5] 李凌云,杜荣,范熙明.体外培养人骨髓问充质干细胞向表皮细胞分化及表皮细胞角蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(36):6661-6664.
[6] 俞猛,于方,付胜良.兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养定向诱导分化为软骨细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27): 4951-4954.
[7] 张宁,李放,罗涛.不同抗凝剂和激活剂组合在自体富血小板血浆凝胶支架促进脂肪干细胞增殖的影响[J].军医进修学院学报, 2012,33(6):113-115.
[8] Landesberg R, Roy M, Glickman RS. Quantification of growth factor levels using a simplified method of platelet-rich plasma gel preparation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(3): 297-300.
[9] Liu J,Zhu H.Human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation protects against cerebral ischemic injury and upregulates interleukin10 expression in Macaca fascicularis. Brain Res. 2010;1334:65-72.
[10] Zhang J, Li Y, Zhang ZG, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells increase oligodendrogenesis after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(6):1166-1174.
[11] 付洪海,何悦.骨髓间充质干细胞向成纤维细胞分化的研究进展[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,9(3):248-251.
[12] 郑有华,何滔,匡世军,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外分离培养及其生物学特性[J].国际医卫生导报,2010,16(2):129-134.
[13] 邹翰林,郭永飞,刘岩.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中的微小RNA及Wnt通路[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(10):1896-1900.
[14] 胡苏,逄曙光,崔莹,等.链脲佐菌素诱导糖尿病大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[J].山东大学学报(医学版), 2013,51(8):7-12.
[15] 王斌,罗毅文,胡年宏.补肾填精法对兔骨折后不同时相骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].安徽中医学院学报,2013,32(1): 66-69.
[16] 陆细红,邓敏,贺洪辉,等.miR-125b通过靶向抑制Smad4调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2013, 38(4):341-346.
[17] 邬培红,华子义,赵秀娟.姜黄素促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中活性氧表达变化研究[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(18): 24-26,29.
[18] 李文宝,李刚.补肾中药诱导干预骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化研究进展[J].实用中医药杂志,2013,29(4):324-326.
[19] 严瀚,徐绘华,郭奇峰,等.重组腺病毒体外诱导山羊骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究[J].中华显微外科杂志,2013, 36(2): 156-160.
[20] 曹钰,杜娟,范志朋.BCOR基因敲除促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究[J].北京口腔医学,2013,21(2):61-64.
[21] 张新昌,张西正.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化相关通路的研究进展[J].医学综述,2013,19(21):3853-3856.
[22] 汤军,蔡建平,张贤.中药提取物诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J].山东中医药大学学报,2013,37(3):257-258.
[23] 刘燕,张文杰,张秀丽,等.含锶锌黄长石涂层钛表面促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的初步研究[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2013, 22(2):66-70.
[24] 虞冀哲,杨勇,刘朝旭,等.共培养条件下电磁场干预对大鼠成骨细胞及骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].中华物理医学杂志, 2013,35(4):250-255.
[25] 张兴安,吴蜀江,卢海彬,等.自体富血小板血浆修复面神经损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(28):5145-5150.
[26] 邓茜,吴小蔚,刘闺男.脂肪干细胞和自体富血小板血浆载体复合物体内构建血管化组织工程脂肪的可行性及疗效分析[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(29):24-27.
[27] 张健,姜鑫,张洪亮.自体富血小板血浆对兔前交叉韧带重建后腱骨愈合组织学影响[J].辽宁医学院学报,2013,34(2):23-26.
[28] 孟繁星,李放,白煜,等.不同方法制备兔自体富血小板血浆凝胶支架促进脂肪干细胞增殖比较[J].军医进修学院学报,2013,34(6): 635-639.
[29] 王虎,李凡,单臣.自体富血小板血浆注射治疗跟痛症的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(13):3160-3161.
[30] 贝朝涌,唐际存,王锐英,等.感染骨灭活原位移植自体富血小板血浆复合骨髓治疗慢性骨髓炎[J].实用医学杂志,2012,28(4): 558-561.
[31] 黎洪棉,柳大烈,赵培冉,等.脂肪干细胞与自体富血小板血浆载体复合物体内构建血管化组织工程脂肪[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(45):8424-8429.
[32] 胡新锋,王宸,芮云峰.自体富血小板血浆干预兔早期椎间盘退变的初步研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(8):977-983.
[33] 王昕,陈小平,林金德,等.自体富血小板血浆-脂肪颗粒填充矫治唇部软组织缺损畸形的临床观察[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2012,23(9):544-547.
[34] 张宁,李放,罗涛.不同抗凝剂和激活剂组合在自体富血小板血浆凝胶支架促进脂肪干细胞增殖的影响[J].军医进修学院学报, 2012,33(6):659-661,671.
[35] 高悠水,朱珍宏,胡斌,等.低氧张力下骨髓间充质干细胞增殖与成骨分化特点及研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(5): 318-320.
[36] 原工杰,刘琳,肖云鹤,等.孕酮对人牙周膜细胞增殖及成骨分化的调控作用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2011,27(10):598-602.
[37] 匡威,谭家莉,张红梅,等.miR146a参与炎症条件下骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的降低及其机制研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2011, 27(11):643-645.
[38] 王悦,杨旭芳,周延民,等.富血小板血浆对人脂肪间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化能力的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2011,27(9): 786-789.
[39] 孙昊,王旭东,沈国芳,等.Dlx2在MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化过程中的作用[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2011,9(3):189-194.
[40] 彭飞,郑亚东,徐西强,等.620nm低能量红光对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].激光生物学报,2011,20(3):285-288.
[41] 赵丹,罗进勇.BMP9促进间充质干细胞C3H10T1/2成骨分化的研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2011,10(16):1225-1226,1230. |