Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (35): 5699-5706.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.35.022
Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid application in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
Liu Bing-gen1, Pang Qing-jiang2
- 1School of Medicine, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, Zhejiang Province, China
2Department of Orthopedics, Ningbo Second Hospital, Ningbo 315010, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Revised:2014-07-22Online:2014-08-27Published:2014-08-27 -
Contact:Pang Qing-jiang, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, Ningbo Second Hospital, Ningbo 315010, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Liu Bing-gen, Studying for master’s degree, School of Medicine, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, Zhejiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Bing-gen, Pang Qing-jiang . Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid application in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(35): 5699-5706.
share this article
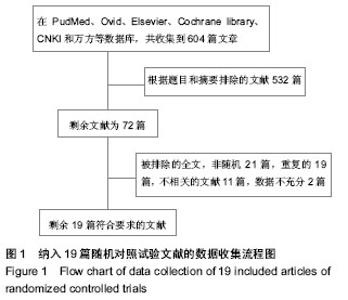
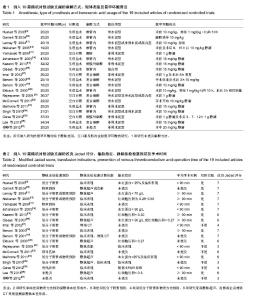
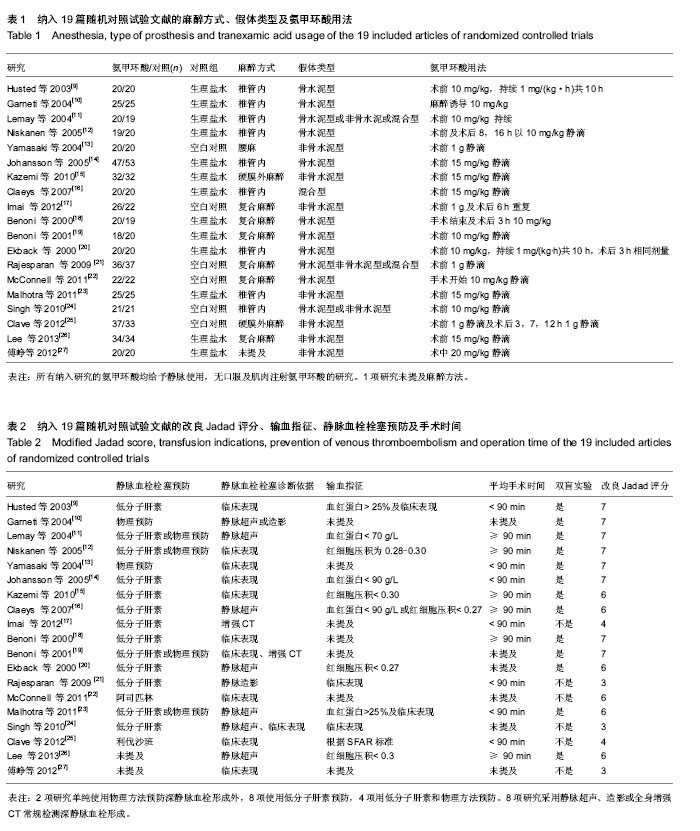
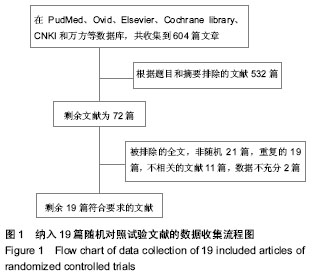
2.1 检索结果及纳入文献的质量评价 图1显示了本次研究是如何依据文献纳入和排除标准来检索相关文献。通过检索前文提到的这些数据库,一共检索出了604篇可能符合纳入标准的文献。 经过筛选,最后剩余19篇文献进入最终研究[9-27]。19篇文献多为38-100例的小样本量研究,共960例。纳入的19项随机对照试验研究中,18项研究为英文,1项研究为中文。 19项随机对照试验按照改良Jadad量表的质量评价标准进行严格的方法学质量评价,结果17项为Jadad评分大于3分,另2项Jadad评分为3分。其中14篇报道了相应方法,包括随机选择信封、随机数字表和计算机生成随机数字法等。13篇使用了双盲法,3篇使用了单盲法,16准确描述退出与失访状况的文献。 所有患者960例,其中氨甲环酸组482例,对照组478例,所有患者均接受初次全髋关节置换,置换前诊断髋关节骨关节炎为主要的病因,其他的一些病因还包括了类风湿性关节炎及股骨头缺血坏死等,每篇文献均做了患者特点的基线对比,包括年龄、性别、体质量指数、术前血红蛋白水平等。 13项研究用生理盐水作为安慰剂[9-12,14-16,18-20,23,26-27], 6项采用空白对照[13,17,21-22,24-25],所有纳入研究的氨甲环酸均为静脉使用,无口服及肌肉注射氨甲环酸的研究,静脉给予氨甲环酸剂量和给药方式有多种,剂量有10-20 mg/kg,1 g,1 mg/(kg•h)泵入。给药时间也有多种,包括术前给药、手术结束时给药、持续静脉泵入给药及术后追加第二剂等方式。 6项研究采用全身+硬膜外麻醉[17-19,21-22,26],1项腰 麻[13],2项硬膜外麻醉[15,25],1项未提及麻醉方法[27],其余均采用椎管内麻醉。 7项研究使用骨水泥型假体[10,12,14,18-20,22],3项使用非骨水泥型假体[13,15,17,23,25-27],1项使用混合型假体[16],2项为非骨水泥或骨水泥型[9,24],2项为非骨水泥或骨水泥型或混合型假体[11,21]。 2项研究单纯使用物理方法预防深静脉血栓形成 外[10,13],8项使用低分子肝素预防[9,14-17,19-20],4项用低分子肝素和物理方法预防[10-12,18],2项用其他的方法预防,2项未提及预防方法[26-27]。 8项研究采用静脉超声、造影或全身增强CT常规检测深静脉血栓形成[10-11,16-17,19-20,22,26],余11项根据临床表现对可疑病例进行辅助检查。 8项研究平均手术时间< 90 min [9,13-14,17-18,21,23,25],院6项平均手术时间≥90 min[11-12,15-16,18,26],5项未提及[19,20,22,24,27]。纳入研究的一般资料见表1,2。"
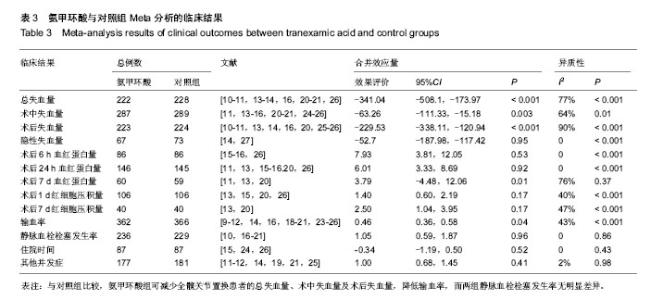
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 术中失血量 10篇文献报道了全髋关节置换中失血量[11,13-16,20-21,24-26]。各研究间有统计学异质性(I2=64%,P=0.003),故采用随机效应模型,结果显示氨甲环酸组术中失血量显著低于对照组[WMD=-63.26,95%CI (-111.33,-15.18),P=0.01,表3]。 对纳入的每项研究剔除1次,剩余研究做合并分析,此敏感性分析显示单项研究对结果影响较小,WMD的范围为-86.71[95%CI(-147.39,-26.04)]到-44.90[95%CI(-87.36,-2.45)]。以上分析说明Meta分析结果的稳定性较好。 2.2.2 术后失血量 8篇文献报道了全髋关节置换后失血量[10-11,13-14,16,20,25-26]。各研究间有统计学异质性(I2=90%, P < 0.000 1),故采用随机效应模型,结果显示氨甲环酸组术后失血量显著低于对照组[WMD=-229.53,95%CI (-338.11,-120.94),P < 0.0001,表3]。 对纳入的每项研究剔除1次,剩余研究做合并分析,此敏感性分析显示单项研究对结果影响较小,WMD的范围为-269.38 [95%CI(-381.03,-157.72)]到-166.20[95%CI (-230.36,-102.04)]。以上分析说明Meta分析结果的稳定性较好。 2.2.3 总失血量 共有8篇文献报道了全髋关节置换总失血量[10-11,13-14,16,20-21,26]。各研究间有统计学异质性(I2=77%, P ,故采用随机效应模型,结果显示氨甲环酸组总失血量显著低于对照组[WMD=-341.04,95%CI(-508.10,-173. 97),P < 0.001,表3]。< 0.001) 对纳入的每项研究剔除1次,剩余研究做合并分析,此敏感性分析显示单项研究对结果影响较小,WMD的范围为-387.13[95%CI(-546.43,-227.84)]到-289.42[95%CI (-421.66,-157.17)]。以上分析说明Meta分析结果的稳定性较好。 2.2.4 隐性失血量 2篇文献报道了全髋关节置换隐性失血量[14,27]。各研究间无统计学异质性(I2=0,P=0.95),故采用固定效应模型,结果显示氨甲环酸组隐性失血量显著低于对照组[WMD=-52.70,95%CI(-187.98,-117.42),P < 0.001,表3]。 2.2.5 异体输血率 18篇文献提供了患者的异体输血率,其中14篇数据可用[9-12,14,16,18-21,23-26],无统计学异质性(I2=42%,P=0.04),采用固定效应模型。氨甲环酸组异体输血率显著低于对照组[RR=0.45,95%CI(0.35,0.57), P < 0.000 1,表3]。 对纳入的每项研究剔除1次,剩余研究做合并分析,此敏感性分析显示单项研究对结果影响较小,WMD的范围为0.47[95%CI(0.37,0.60)]到0.38 [95%CI (0.29,0.49)]。以上分析说明Meta分析结果的稳定性较好。 2.2.6 静脉血栓栓塞发生率 17篇文献提供了静脉血栓栓塞的发生率,其中7篇数据可用[10,16-21],对静脉血栓栓塞的各研究间无统计学异质性(I2=0,P=0.88),采用固定效应模型,氨甲环酸组与安慰剂组静脉血栓的发生率差异无显著性意义[RR=1.30,95%CI(0.62,2.73),P=0.48,表3]。 对纳入的每项研究剔除1次,剩余研究做合并分析,此敏感性分析显示单项研究对结果影响较小,WMD的范围为1.47[95%CI(0.67,3.24)]到1.04[95%CI(0.47,2.30)]。以上分析说明Meta分析结果的稳定性较好。"

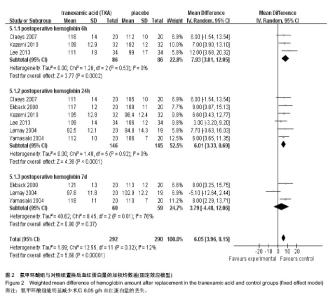
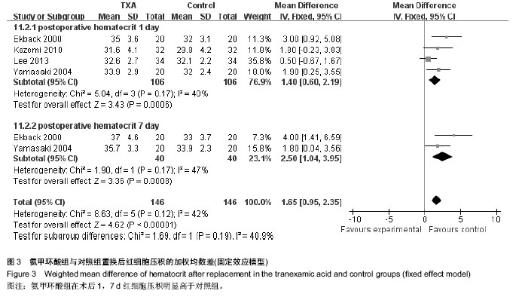
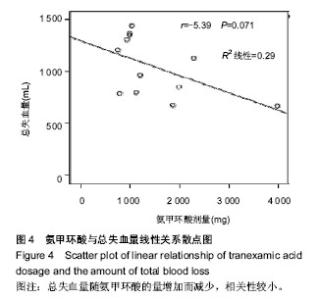
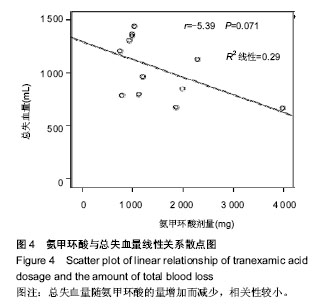
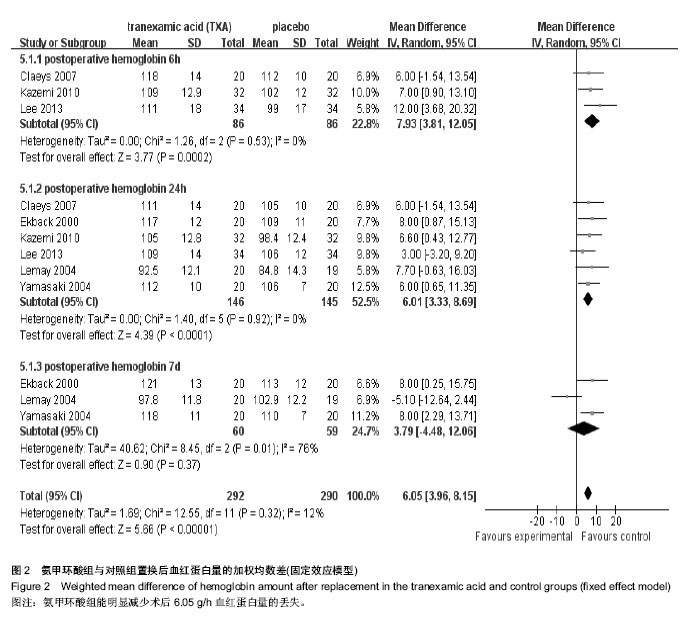
2.2.7 术后血红蛋白及红细胞压积 10篇文章报道了术后血红蛋白和红细胞压积变化值[11,13-16,18,20,21,24,26]。其中6篇数据可用[11,13,15-16,20,26],见表3。 使用氨甲环酸组能明显显著改善术后血红蛋白下降值[95%CI(3.90,8.15),P < 0.001,图2]和红细胞压积下降值[95%CI(1.42,3.16),P < 0.001,图3)。 按照时间进行亚组分析,观察术后6 h、1 d和7 d血红蛋白变化值,和术后1,7 d红细胞压积的变化值,红细胞压积变化值在术后1 d和7 d的比较中,氨甲环酸组均高于对照组;血红蛋白变化值在术后6 h和1 d的比较中,氨甲环酸组均高于对照组。而术后7 d血红蛋白变化值两组差异无显著性意义。根据以上的结果,氨甲环酸能够减缓血红蛋白丢失量和红细胞压积下降量。 2.2.8 住院时间 3篇文献提供了住院时间[15,25-26],各研究间无统计学异质性(I2=0,P=0.52),故采用固定效应模型,结果[WMD=-0.34,95%CI(-1.19,0.50),P=0.43,表3],氨甲环酸组与对照组比较,氨甲环酸组并没有增加住院时间。 2.2.9 其他并发症 6篇文献提供了其他并发症的发生率(如伤口感染、呕心、胸痛等)[11-12,14,19,21,25],各研究间无统计学异质性(I2=2%,P=0.41),故采用固定效应模型,氨甲环酸组与安慰剂组其他并发症的发生率差异无显著性意义[RR=1.00,95%CI(0.68,1.45),P=0.98,表3]。 2.3 氨甲环酸与总失血量的关系 有11篇文献报道了不同氨甲环酸的剂量及总失血量[11-18,20-21,25]。以氨甲环酸为横坐标,总失血量为纵坐标的散点图,线性相关系数r=-0.539,氨甲环酸与总失血量有一定的相关性(r=-0.539,P=0.071,图4),提示患者髋关节置换后总失血量随氨甲环酸的量增加而减少。"
| [1] Mednick RE, Alvi HM,Krishnan V,et al. Factors Affecting Readmission Rates Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2014;96(14):1201-1209. [2] Zhou XD, Tao LJ, Li J, et al.Do we really need tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of nineteen randomized controlled trials. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(7):1017-1027. [3] Alshryda S, Mason J,Sarda P,et al.Topical (intra-articular) tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates following total hip replacement: a randomized controlled trial(TRANX-H).J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(21):1969- 1974. [4] Bruce W,Campbell D,Daly D,et al.Practical recommendations for patient blood management and the reduction of perioperative transfusion in joint replacement surgery. ANZ J Surg. 2013;83(4):222-229. [5] Zhao J, Li J, Zheng W, et al. Low Body Mass Index and Blood Loss in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: Results from 236 Consecutive Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:742393. [6] Watts CD, Pagnano MW. Minimising blood loss and transfusion in contemporary hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(11 Suppl A):8-10. [7] Cardone D, Klein AA. Perioperative blood conservation. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009;26(9):722-729 [8] Samujh C, Falls TD, Wessel R. Decreased Blood Transfusion Following Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty Using Tranexamic Acid. J Arthroplasty. 2014. pii: S0883-5403(14)00335-0. [9] Husted H, Blond L, Sonne-Holm S, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and blood transfusions in primary total hip arthroplasty: a prospective randomized double-blind study in 40 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 2003;74:665-669. [10] Garneti N, Field J. Bone bleeding during total hip arthroplasty after administration of tranexamic acid. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(4):488-492. [11] Lemay E, Guay J, Côté C, et al. Tranexamicacidreduces the need for allogenic red blood cell transfusions in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Can J Anaesth. 2004; 51(1): 31-37. [12] Niskanen RO, Korkala OL. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in cemented hip arthroplasty: a randomized, doubleblind study of39patients with osteoarthritis. Acta Orthop. 2005; 76(6):829-832. [13] Yamasaki S, Masuhara K, Fuji T. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss after cementless total hip arthroplasty- prospective randomized study in 40cases. Int Orthop. 2004;28(2):69-73. [14] Johansson T, Pettersson LG, Lisander B. Tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplastysaves blood and money: a randomized, double- blind study in 100 patients. Acta Orthop. 2005;76(3): 314-319. [15] Kazemi SM,Mosaffa F,Eajazi A,et al. The Effect of tranexamic acid on reducing Blood Loss in cementless total hip arthroplastyunder epidural anesthesia. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(1):1124-1130. [16] Claeys MA, Vermeersch N, Haentjens P. Reduction of blood loss with tranexamic acids in primary total hip replacement surgery. Acta Chir Belg. 2007;107(4):397-401. [17] Imai N, Dohmae Y, Suda K, et al. Tranexamic acid for reduction of blood loss during total hip arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(10):1838-1842. [18] Benoni G, Lethagen S, Nilsson P, et al.Tranexamic acid,given at the end of the operation,does not reduce postoperative blood loss in hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71: 250-254. [19] Benoni G, Fredin H, Knebel R, et al. Blood conservation with tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind study in 40 primary operations. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001;72:442-448. [20] Ekback G, Axelsson K, Ryttberg L, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss in total hip replacement surgery. Anesth Analg. 2000;91:1124-1130. [21] Rajesparan K, Biant LC, Ahmad M, et al. The effect of an intravenous bolus of tranexamic acid on blood loss in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009;91:776-783. [22] McConnell JS, Shewale S, Munro NA, et al . Reduction of blood loss in primary hip arthroplasty with tranexamic acid or fibrin spray. Acta Orthop. 2011;82:660-663. [23] Malhotra R, Kumar V, Garg B. The use of tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss in primary cementless total hip arthroplasty. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2010;21:101-104. [24] Singh J, Ballal MS, Mitchell P, et al. Effects of tranexamic acid on blood loss during total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg. 2010; 18:282-286. [25] Clave A, Fazilleau F, Dumser D, et al. Efficacy of tranexamic acid on blood loss after primary cementless total hip replacement with rivaroxaban thromboprophylaxis: a case-control study in 70 patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98:48-490. [26] Lee YC, Park SJ, Kim JS, et al. Effect of tranexamic acid on reducing postoperative blood loss in combined hypotensive epidural anesthesia and general anesthesia for total hip replacement. J Clin Anesth.2013;25(5):393-398. [27] 傅峥,张健,姚海.氨甲环酸对全髋关节置换术隐性失血的影响[J]. 重庆医科大学学报,2012,37(4):359-361. [28] Jadad AR,Moore RA,Carroll D.Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?Control Clin Trials. 1996;17: 1-12. [29] Dunn CJ,Goa KL. Tranexamie acid: a review of its use in surgery and other indications. Drugs. 1999;57: 1005-1032. [30] Hiippala S,Strid L,Wennerstrand M,et al. Tranexmic acid(cyklokapron) reduces perioperative blood loss associated with total knee arthreplasty. Br J Anacsth. 1995;74: 534-537. [31] Sukeik M, Alshryda S, Haddad FS, et al.Systematic review and meta-analysis of the use of tranexamic acid in total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2011;93:39-46. [32] Liu X,Zhang X,Chen Y,et al. Hidden blood loss after total hip arthoplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26: 1100-1105. [33] Hynes MC, Calder P, Rosenfeld P, et al. The use of tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss duringtotal hip arthroplasty: an observational study. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2005;87(2):99-101. [34] Ralley FE, Berta D, Binns V, et al. One intraoperative dose of tranexamicacid for patients having primary hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(7):1905-1911. |
| [1] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [2] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [6] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [7] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [8] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [9] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [10] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [11] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [12] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [13] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [14] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [15] | Lü Zexiang, Wu Jutai, Jiang Jian, Feng Xiao, Li Tengfei, Wang Yehua. Effect of tranexamic acid combined with carbazochrome sodium sulfonate on blood loss and safety after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 386-390. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||