Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (35): 5707-5714.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.35.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of limb and prosthesis alignment restoration after navigated total knee arthroplasty versus conventional total knee arthroplasty
Wang Zeng-liang1, 2, Zhao Li2, Zhao Jia-guo2
- 1Post-graduate College, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
2Department of Sports Medicine and Arthroscope Surgery, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China
-
Revised:2014-08-03Online:2014-08-27Published:2014-08-27 -
Contact:Zhao Li, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Sports Medicine and Arthroscope Surgery, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China -
About author:Wang Zeng-liang, Attending physician, Post-graduate College, Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; Department of Sports Medicine and Arthroscope Surgery, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Zeng-liang, Zhao Li, Zhao Jia-guo . Meta-analysis of limb and prosthesis alignment restoration after navigated total knee arthroplasty versus conventional total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(35): 5707-5714.
share this article
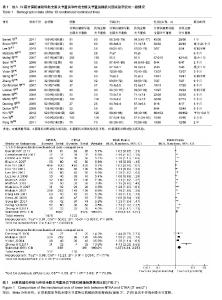
2.1 检索结果 经全面计算机及手工检索,共检索到276篇临床试验文献:PubMed检索获得文献58篇,Embase检索获得文献26篇,Cochrane CENTRAL检索获得文献21篇,ScienceDirect检索获得文献171篇,共19篇随机对照试验研究文献合格。样本总量合计2 654例(3 392膝)。各纳入研究的基本情况见表1。纳入研究的19篇文献中患者的年龄、性别比基本资料经统计学检验在基线水平上一致。文献质量等级:4篇随机对照试验为低风险,5篇随机对照试验风险不明,10篇随机对照试验为高风险。 2.2 全膝关节置换后下肢机械轴恢复情况比较的Meta分析结果 见图1。 以偏倚3°为标准:共17个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后下肢机械轴偏倚3°情况,导航全膝关节置换组1 667膝,传统全膝关节置换组1 576膝,机械轴偏倚位于3°以内发生率分别为88.54%和77.54%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=68%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后机械轴恢复精确率明显优于传统全膝关节置换[RR=1.19,95%CI(1.12-1.27),P < 0.000 01]。 以偏倚2°为标准:共4个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后下肢机械轴偏倚2°情况,导航全膝关节置换组389膝,传统全膝关节置换组291膝,机械轴偏倚位于2°以内发生率分别为81.49%和51.55%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P=0.004,I2=77%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后机械轴恢复精确率明显优于传统全膝关节置换[RR=1.67,95%CI(1.24-2.25),P=0.000 8]。 Meta分析结果稳定,倒漏斗图显示基本对称。"
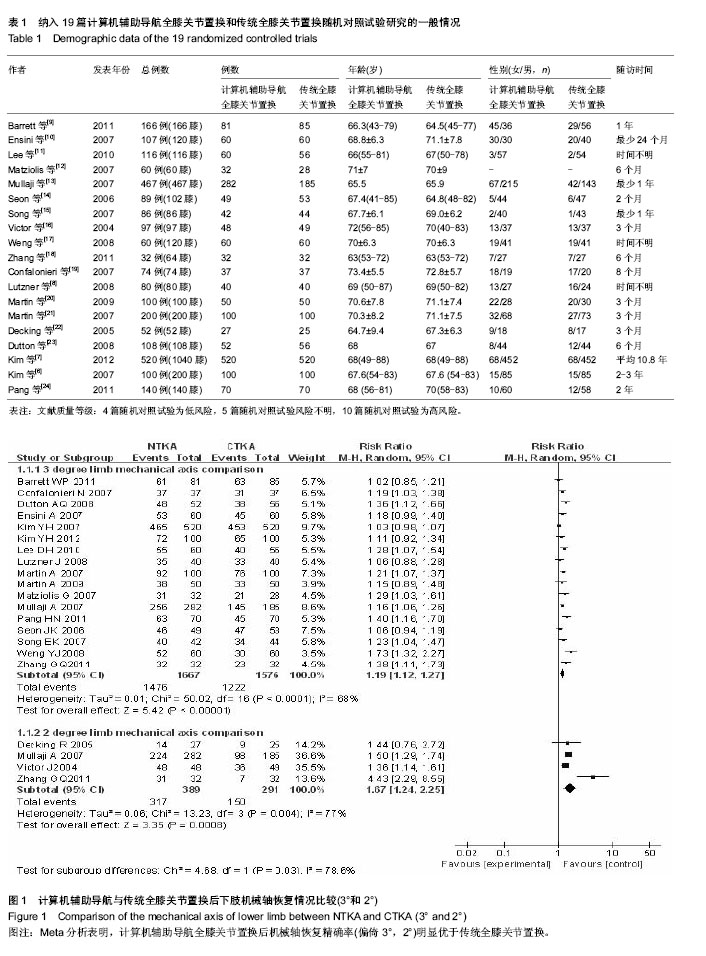
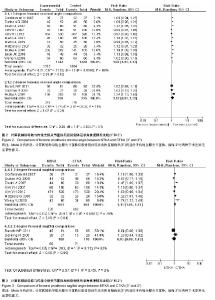
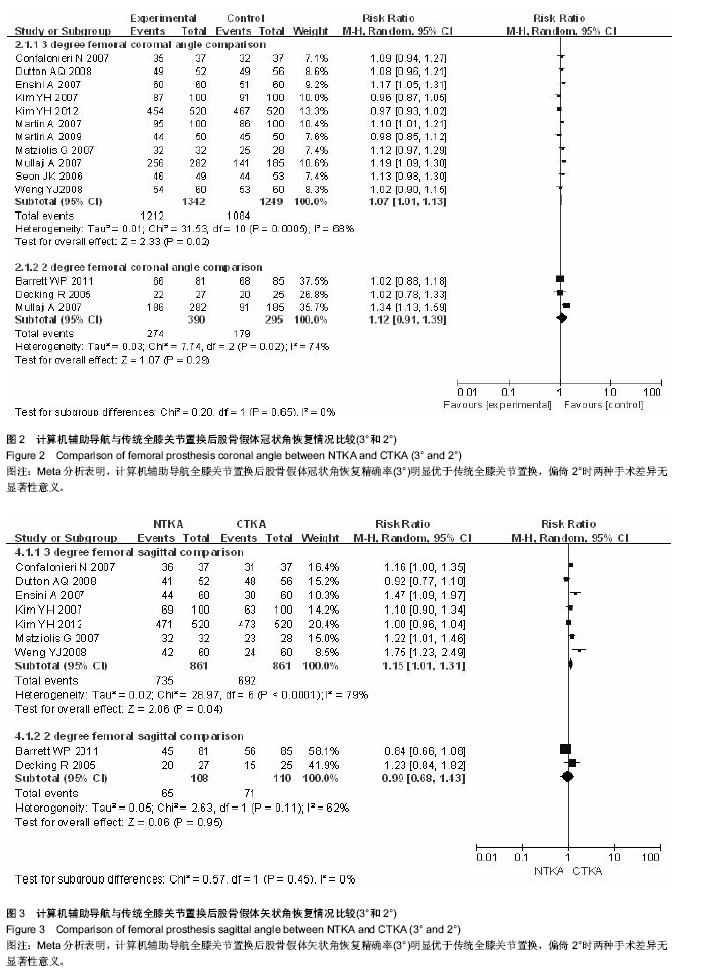
2.3 全膝关节置换后股骨假体冠状角恢复情况比较的Meta分析结果 见图2。 以偏倚3°为标准:共11个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后股骨假体冠状角偏倚3°情况,导航全膝关节置换组1 342膝,传统全膝关节置换组1 249膝,偏倚位于3°以内发生率分别为90.31%和86.79%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P=0.000 5,I2=68%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后股骨假体冠状角恢复精确率明显优于传统全膝关节置换[RR=1.07,95%CI(1.01-1.13),P=0.002]。 以偏倚2°为标准:共3个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后下肢机械轴偏倚2°情况,导航全膝关节置换组390膝,传统全膝关节置换组295膝,偏倚2°以内发生率分别为70.26%和60.68%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P=0.002,I2=74%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后股骨假体冠状角恢复精确率和传统全膝关节置换差异无显著性意义[RR=1.12,95%CI(0.91-1.39),P=0.290]。 Meta分析结果稳定,倒漏斗图显示基本对称。 2.4 全膝关节置换后股骨假体矢状角恢复情况比较的Meta分析结果 见图3。 以偏倚3°为标准:共7个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后股骨假体矢状角偏倚3°情况,导航全膝关节置换组861膝,传统全膝关节置换组861膝,偏倚3°以内发生率分别为85.37%和80.37%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 1,I2=79%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后股骨假体矢状角恢复精确率明显优于传统全膝关节置换[RR=1.15,95% CI(1.01-1.13),P=0.040]。 以偏倚2°为标准:共2个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后股骨假体矢状角偏倚2°情况,导航全膝关节置换组108膝,传统全膝关节置换组110膝,偏倚位于2°以内发生率分别为60.19%和64.55%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P=0.110,I2=62%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后股骨假体矢状角恢复精确率和传统全膝关节置换差异无显著性意义[RR=0.99,95%CI(0.68-1.43),P=0.950]。 Meta分析结果稳定,倒漏斗图显示基本对称。"
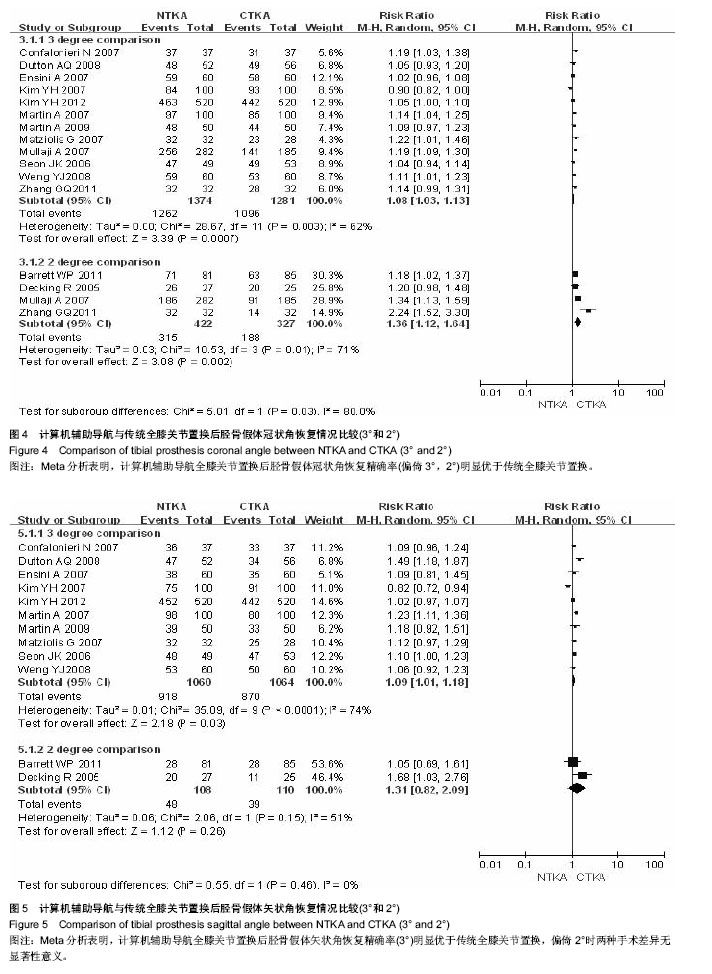
2.5 全膝关节置换后胫骨假体冠状角恢复情况比较的Meta分析结果 见图4。 以偏倚3°为标准:共12个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后胫骨假体冠状角偏倚3°情况,导航全膝关节置换组1 374膝,传统全膝关节置换组1 281膝,偏倚3°以内发生率分别为91.85%和85.56%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P=0.003,I2=62%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后胫骨假体冠状角恢复精确率明显优于传统全膝关节置换[RR=1.08,95%CI(1.03-1.13),P=0.000 7]。 以偏倚2°为标准:共4个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后胫骨假体冠状角偏倚2°情况,导航全膝关节置换组422膝,传统全膝关节置换组327膝,偏倚2°以内发生率分别为74.64%和57.49%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P=0.01,I2=71%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后胫骨假体冠状角恢复精确率明显优于传统全膝关节置换[RR=1.36,95%CI(1.12-1.64),P=0.002],Meta分析结果稳定,倒漏斗图显示基本对称。 2.6 全膝关节置换后胫骨假体矢状角恢复情况比较的Meta分析结果 见图5。 以偏倚3°为标准:共10个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后胫骨假体矢状角偏倚3°情况,导航全膝关节置换组1 060膝,传统全膝关节置换组1 064膝,偏倚3°以内发生率分别为86.60%和81.77%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 1,I2=74%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后胫骨假体矢状角恢复精确率明显优于传统全膝关节置换[RR=1.09,95%CI(1.01-1.18),P=0.030]。 以偏倚2°为标准:共2个随机对照试验报道了全膝关节置换后胫骨假体矢状角偏倚2°情况,导航全膝关节置换组108膝,传统全膝关节置换组110膝,偏倚2°以内发生率分别为44.44%和35.45%,各研究间存在统计学异质性(P=0.150,I2=51%),随机效应Meta分析表明导航组全膝关节置换后胫骨假体矢状角恢复精确率和传统全膝关节置换差异无显著性意义[RR=1.31,95%CI(0.82-2.09),P=0.260]。 Meta分析结果稳定,倒漏斗图显示基本对称。"
| [1] Feng B,Weng X,Lin J, et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Cemented Fixed-Bearing Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Chinese Population: A Survival Analysis of More Than 10 Years. J Arthroplasty. 2013. [2] Ezzet KA,Hermida JC,Steklov N, et al. Wear of polyethylene against oxidized zirconium femoral components effect of aggressive kinematic conditions and malalignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(1):116-121. [3] Wong J,Steklov N,Patil S, et al. Predicting the effect of tray malalignment on risk for bone damage and implant subsidence after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2011; 29(3):347-353. [4] Johnson DR,Dennis DA,Kindsfater KA, et al. Evaluation of total knee arthroplasty performed with and without computer navigation: a bilateral total knee arthroplasty study. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(3):455-458. [5] Sugama R,Minoda Y,Kobayashi A, et al. Conventional or navigated total knee arthroplasty affects sagittal component alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(12): 2454-2459. [6] Kim YH, Kim JS, Yoon SH. Alignment and orientation of the components in total knee replacement with and without navigation support: a prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007; 89(4):471-476. [7] Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JS. Computer-navigated versus conventional total knee arthroplasty a prospective randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(22): 2017-2024. [8] Lutzner J,Krummenauer F,Wolf C, et al. Computer-assisted and conventional total knee replacement: a comparative, prospective, randomised study with radiological and CT evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90(8):1039-1044. [9] Barrett WP,Mason JB,Moskal JT, et al. Comparison of radiographic alignment of imageless computer-assisted surgery vs conventional instrumentation in primary total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8):1273-1284. [10] Ensini A,Catani F,Leardini A, et al. Alignments and clinical results in conventional and navigated total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;457:156-162. [11] Lee DH,Park JH,Song DI, et al. Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in TKA: comparison between navigation-assisted gap balancing and conventional measured resection. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(3):381-387. [12] Matziolis G,Krocker D,Weiss U, et al. A prospective, randomized study of computer-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty. Three-dimensional evaluation of implant alignment and rotation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(2):236-243. [13] Mullaji A,Kanna R,Marawar S, et al. Comparison of limb and component alignment using computer-assisted navigation versus image intensifier-guided conventional total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, single-surgeon study of 467 knees. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(7):953-959. [14] Seon JK, Song EK. Navigation-assisted less invasive total knee arthroplasty compared with conventional total knee arthroplasty: a randomized prospective trial. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(6):777-782. [15] Song EK,Seon JK,Yoon TR, et al. Comparative Study of Stability After Total Knee Arthroplasties Between Navigation System and Conventional Techniques. J Arthroplasty. 2007; 22(8):1107-1111. [16] Victor J, Hoste D. Image-based computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty leads to lower variability in coronal alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(428):131-139. [17] Weng YJ, Hsu RW, Hsu WH. Comparison of computer-assisted navigation and conventional instrumentation for bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(5):668-673. [18] Zhang GQ,Chen JY,Chai W, et al. Comparison between computer-assisted-navigation and conventional total knee arthroplasties in patients undergoing simultaneous bilateral procedures: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(13):1190-1196. [19] Confalonieri N,Manzotti A,Pullen C, et al. Mini-incision versus mini-incision and computer-assisted surgery in total knee replacement: a radiological prospective randomised study. Knee. 2007;14(6):443-447. [20] Martin A,Sheinkop MB,Langhenry MM, et al. Accuracy of side-cutting implantation instruments for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009; 17(4):374-381. [21] Martin A,Wohlgenannt O,Prenn M, et al. Imageless navigation for TKA increases implantation accuracy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;460:178-184. [22] Decking R,Markmann Y,Fuchs J, et al. Leg axis after computer-navigated total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized trial comparing computer-navigated and manual implantation. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(3):282-288. [23] Dutton AQ,Yeo SJ,Yang KY, et al. Computer-assisted minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty compared with standard total knee arthroplasty. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(1):2-9. [24] Pang HN,Yeo SJ,Chong HC, et al. Computer-assisted gap balancing technique improves outcome in total knee arthroplasty, compared with conventional measured resection technique. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011; 19(9): 1496-1503. [25] Anderson KC, Buehler KC, Markel DC. Computer Assisted Navigation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Comparison With Conventional Methods. J Arthroplasty. 2005; Suppl 3: 132-138. [26] Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(5): 709-714. [27] Buechel FF Sr. Long-term followup after mobile-bearing total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(404):40-50. [28] Berend ME,Ritter MA,Meding JB, et al. Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(428):26-34. [29] Molfetta L, Caldo D. Computer navigation versus conventional implantation for varus knee total arthroplasty: a case-control study at 5 years follow-up. Knee. 2008;15(2): 75-79. [30] Hetaimish BM,Khan MM,Simunovic N, et al. Meta-analysis of navigation vs conventional total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):1177-1182. [31] Fu Y,Wang M,Liu Y, et al. Alignment outcomes in navigated total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(6):1075-1082. [32] Kuzyk PR,Higgins GA,Tunggal JA, et al. Computer navigation vs extramedullary guide for sagittal alignment of tibial components: radiographic study and meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(4):630-637. |
| [1] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [2] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [3] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [4] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [5] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [6] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [7] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [8] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [9] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [10] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [11] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [12] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [13] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [14] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [15] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||