Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (34): 5413-5417.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.34.001
Imaging evaluation of hydroxyapatite/gel nano-composite in rabbit skull defect repair
Geng Hai-xia, Guo Xiu-juan, Qian Jun-rong, Feng Wei
- Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical College, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China
-
Revised:2014-07-16Online:2014-08-20Published:2014-08-20 -
Contact:Geng Hai-xia, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical College, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Geng Hai-xia, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical College, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2010HL046; the Scientific Development Plan of Shandong Health Bureau, No. 2011HZ018
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Geng Hai-xia, Guo Xiu-juan, Qian Jun-rong, Feng Wei . Imaging evaluation of hydroxyapatite/gel nano-composite in rabbit skull defect repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(34): 5413-5417.
share this article
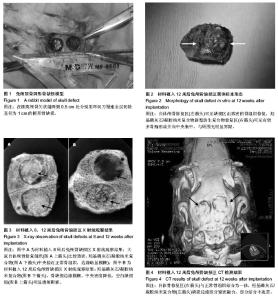
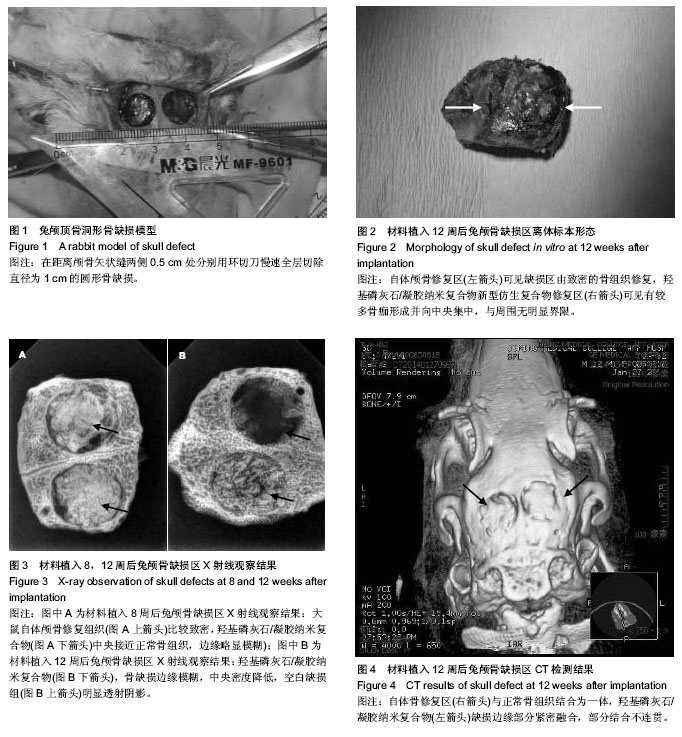
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验兔共15只,无感染和死亡,均纳入结果分析。 2.2 羟基磷灰石/凝胶纳米复合物植入后兔颅骨缺损区的一般形态 所有兔在植入后1 h内即可苏醒,植入后1 d后,精神状态有所恢复,均可自主进食,全部实验周期内实验动物无死亡,生长良好,均存活至取材。颅骨取材区及植骨区伤口均为一期愈合,植入物无脱出,无异物及免疫排斥反应。 图2是植入后12周时取材后带修复材料骨块,可以观察到,自体颅骨修复可见缺损区由致密的骨组织修复,且与周围骨组织无明显界限,羟基磷灰石/凝胶纳米复合物新型仿生复合物中央部位颜色偏黄、硬度偏低,材料表面可见有较多骨痂形成并向中央集中,其周边与骨断端之间已有较牢固的骨性连接形成,扪之有一定的强度,与周围正常骨组织也已经无明显界限。 2.3 羟基磷灰石/凝胶纳米复合物植入后兔颅骨缺损区的X射线观察结果 植入后8周:大鼠自体颅骨修复区与周围正常的骨组织形态类似;羟基磷灰石/凝胶纳米复合物修复区中央位置骨质致密,形态接近正常骨组织,边缘略显模糊,见图3A。"
| [1] Edwards PC, Ruggiero S, Fantasial J, et al. Sonic hedgehog gene enhanced tissue engineering for bone regeneration. Gene Therpay. 2005;12(4):75-86. [2] 许勇,朱立新,田京,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖复合材料与兔骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(8):1423-1426. [3] Sawyera A, Hennessyb KM, Bellisa SL, et al. Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell attachment and speading on hydroxyapatite by RGD peptides and adsorbed serum Proteins. Biomaterials. 2005;26(21):1467-1475. [4] 刘建斌.壳聚糖-明胶/β-磷酸三钙复合体作为组织工程软骨支架材料的实验研究[J],组织工程与重建外科杂志,2010,6(6):319-322. [5] Oyen ML, Ko CC. Examination of local variations in viscous, elastic, and plastic indentation responses in healing bone. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007;18(4):623-628. [6] 李瑞琦,张国平,任立中,等.纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合生物材料的特征及应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(19): 3747-3750. [7] Frmae JW. A convenient animal model for testing bone substitute materials. J Oral Surg. 1980;38(3):176-180. [8] Gosain AK. Osteogenesis in cranial defects: reassessment of the concept of critical size and the expression of TGF-[beta] isofomrs. Plast Reconsrtuct Surg. 2000;106(4): 360-371. [9] Einhorn TA. Clinically applied models of bone regeneration in tissue engineering research. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999; (367 Suppl):S59-S67. [10] Schlegel KA, Lang FJ, Donath K, et al. The monocortical critical size bone defect as an alternative experimental model in testing bone substitute materials. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;102(1):7-13. [11] Bosch C, Melsen B, Vargervik K. Importance of the critical-size bone defect in testing bone regenerating materials. J Craniofac Surg. 1998;9(4):310-316. [12] 廖文波,杨志明,邓力,等.可塑形组织工程骨修复兔颅骨缺损的组织学及力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(6): 460-463. [13] Ko CC , Michelle O, Fallgatter AM, et al. Mechanical properties and cytocompatibility of Biomimetic hydroxyapatite-gelatin nano-composites. J Mater Res. 2006;21(12):3090-3098. [14] Seong WJ, Kim UK, Swift JQ, et al. Correlations between physical properties of jawbone and dental implant initial stability. J Prosthet Dent. 2009;101(5):306-318. [15] Seong WJ, Holte JE, Holtan JR, et al. Initial stability measurement of dental implants placed in different anatomical regions of fresh human cadaver jawbone. J Prosthet Dent. 2008;99(6):425-434. [16] 彭湘红,万昆.壳聚糖/纳米多层结构羟基磷灰石/明胶复合膜的性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(14):2777-2779. [17] Ronald EJ, Roger Z, Franz EW, et al. Evaluation of an in situ formed synthetic hydrogel as a biodegradable membrane for guided bone regeneration. Clin Oral Impl Res. 2006;17(4): 426-433. [18] Luo TJM, Ko CC, Chiu CK, et al. Aminosilane as an effective binder for hydroxyapatite-gelatin nanocomposites. J Sol Gel Sci Tech. 2010;53:459-465. [19] Park SB, Ko CC, Son WS, et al. Influence of flowable resins on the shear bone strength of orthodontic brackets. Dent Mater J. 2009;28(6):730-734. [20] Oyen ML, Ko CC. Modeling the indentation variability of natural nanocomposite materials. J Mater Res. 2008;23(3): 760-767. [21] Ferreira JN, Ko CC, Myers S, et al. Evaluation of surgically retrieved temporomandibular joint alloplastic implantspilot study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;66(6):1112-1124. [22] Huang HL, Hsu JT, Fuh LJ, et al. Bone stress and interfacial sliding analysis of implant designs on an immediately loaded maxillary implant: a non-linear finite element study. J Dent. 2008,36(6):409-417. [23] 朱凌云,王彦平,石宗利,等.聚磷酸钙纤维/明胶软骨组织工程支架复合材料的制备及性能表征[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(47):9265-9268. [24] de Melo Mde F, Melo SL, Zanet TG, et al. Digital radiographic evaluation of the midpalatal suture in patients submitted to rapid maxillary expansion. Indian J Dent Res. 2013;24(1): 76-80. [25] Önem E, Baks BG, Sogur E. Changes in the fractal dimension, feret diameter, and lacunarity of mandibular alveolar bone during initial healing of dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(5):1009-1013. [26] Patel S, Wilson R, Dawood A, et al. The detection of periapical pathosis using digital periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography-part 2: a 1-year post-treatment follow-up. Int Endod J. 2012;45(8):711-723. [27] Ersev H, Yilmaz B, Dinçol ME, et al. The efficacy of ProTaper Universal rotary retreatment instrumentation to remove single gutta-percha cones cemented with several endodontic sealers. Int Endod J. 2012;45(8):756-762. [28] Lee AH, Cheung GS, Wong MC. Long-term outcome of primary non-surgical root canal treatment. Clin Oral Investig. 2012;16(6):1607-1617. [29] Calvo-Guirado JL, Gómez-Moreno G, López-Marí L, et al. Crestal bone loss evaluation in osseotite expanded platform implants: a 5-year study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(12): 1409-1414. [30] Artzi Z, Kohen J, Carmeli G, et al. The efficacy of full-arch immediately restored implant-supported reconstructions in extraction and healed sites: a 36-month retrospective evaluation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010;25(2): 329-335. [31] Calvo-Guirado JL, Ortiz-Ruiz AJ, López-Marí L, et al. Immediate maxillary restoration of single-tooth implants using platform switching for crestal bone preservation: a 12-month study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(2):275-281. [32] Crespi R, Capparè P, Gherlone E. Magnesium-enriched hydroxyapatite compared to calcium sulfate in the healing of human extraction sockets: radiographic and histomorphometric evaluation at 3 months. J Periodontol. 2009;80(2):210-218. [33] Christiansen R, Kirkevang LL, Hørsted-Bindslev P, et al. Randomized clinical trial of root-end resection followed by root-end filling with mineral trioxide aggregate or smoothing of the orthograde gutta-percha root filling-1-year follow-up. Int Endod J. 2009;42(2):105-114. [34] Yoshioka T, Kobayashi C, Suda H, et al. An observation of the healing process of periapical lesions by digital subtraction radiography. J Endod. 2002;28(8):589-591. [35] Göhring TN, Schmidlin PR, Lutz F. Two-year clinical and SEM evaluation of glass-fiber-reinforced inlay fixed partial dentures. Am J Dent. 2002;15(1):35-40. [36] Saad AY, al-Nazhan S. Radiation dose reduction during endodontic therapy: a new technique combining an apex locator (Root ZX) and a digital imaging system (RadioVisioGraphy). J Endod. 2000;26(3):144-147. [37] Chong BS, Ford TR, Wilson RF. Radiological assessment of the effects of potential root-end filling materials on healing after endodontic surgery. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1997;13(4): 176-179. |
| [1] | Zhang Yun-ge, Song Ke-guan. Periprosthetic osteolysis induced by wear particles: research progress of calcineurin/activated T cell nuclear factor signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1115-1122. |
| [2] | Liu Wei, Huang Jian. Applied research and progress of three-dimensional printing technology in joint replacement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1123-1130. |
| [3] | Xi Li-cheng, Li Hong-yu. Research progress of the influence of alcohol on the local microenvironment of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1137-1142. |
| [4] | Yang Bao-jia, Yang Kai-shun, Yao Ru-bin. Correlation of nicotine dose and lumbar posterolateral fusion rate: imaging and biomechanical testing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7251-7260. |
| [5] | Wu Xiao-guang, Qiu Zhi-fu, Meng Jie, Zu Bing-xue, Li Meng-meng, Miao Hui. Effects of Buyanghuanwu decoction on the protein expression of PI3K, Akt, Bcl-2 and BAX in brain tissue of a rat model of cerebral hemorrhage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5933-5938. |
| [6] | Zhang Jian-jun, Shi Huan-chang. Immunosuppressed rat model of cerebral hemorrhage: construction and assessment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5939-5945. |
| [7] | Fu Feng, Zhao Ming-liang, Li Xiao-hong, Chen Chong, Wang Li-na, Sun Hong-tao, Tu Yue, Zhang Sai . Dynamic changes of brain cavity in rats after traumatic brain injury detected by MRI-based three-dimensional reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5946-5952. |
| [8] | Yu Yu-qin, Hu Nian-chun, Duan Ji-an, Li Da-peng, Liu Chang. Neuroprotective effects of sufentanil preconditioning on spinal cord injury in mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5966-5972. |
| [9] | Wang Zhan, Li Hao-peng, He Xi-jing, Hao Ding-jun, Zhang Kun, Chen Ming-xia, Lei Ting. Pathological changes in the spinal cord of a model of acute cauda equina compression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5973-5978. |
| [10] | Zhao Yan-rui, Lv Wen-rui, Wang Dong, Zhou Jun-lin. Effects of carbonyl sulfide in a rat model of limb ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 5994-6000. |
| [11] | Chen Wei-hua, Lv Guo-hua, Zhou Bin, Kang Yi-jun. Establishment of a dog model of pyogenic spinal infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6014-6020. |
| [12] | Ge Run, Yang Lan. Protective effects of piperine on alveolar bone and collagen in a periodontitis model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6034-6040. |
| [13] | Song Qiao-qiao, Zhou Hui-liang, Zhen Hai-tao, Wang Na, Deng Jing, Wang Jin-xiang, Pan Xing-hua . Establishment and evaluation of a rhesus monkey model of experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6048-6053. |
| [14] | Pan Lei, Zhang Jin-biao, Cui Rong-gang, Zhao Bao-hui, Li Hua, Zhang Zhong-yong, Wang Xu-chu. Establishment of nonalcoholic fatty liver C57BL/6 mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6054-6059. |
| [15] | Wang Shi-jun, Li Yu-ting, Li Chun-de. Establishment, application and progression of an animal model of cervical spondylosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6067-6073. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

