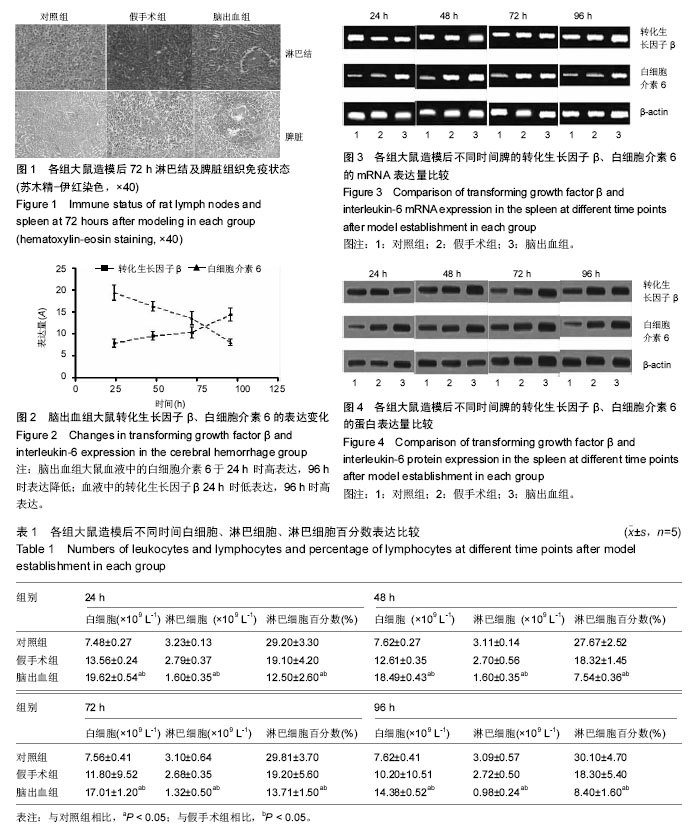
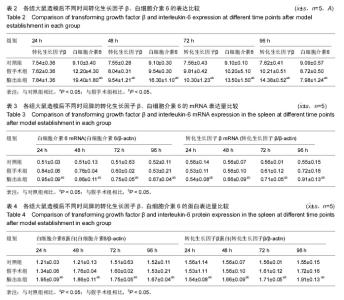
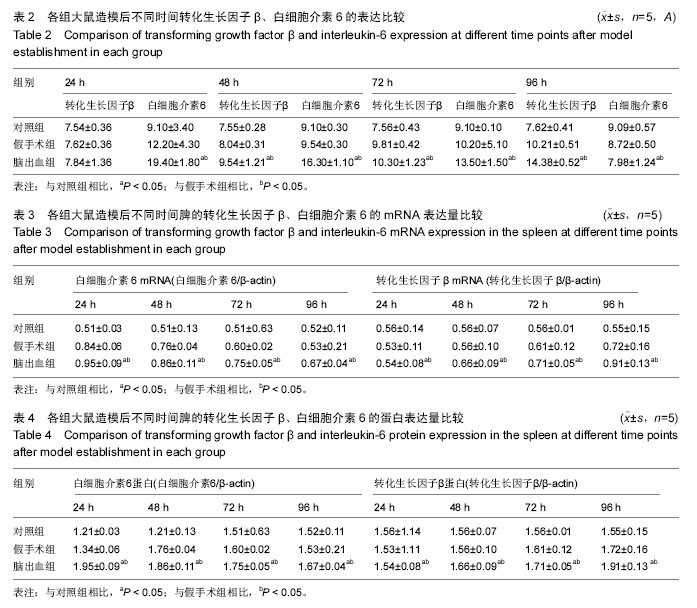
| [1] Meisel C,Prass K,Braun J,et al.Preventive antibacterial treatment improves the general medical and neurological outcome in a mouse model of stroke. Stroke. 2004;35(1):245.
[2] Chamorro A,Amaro S,TGF-Βargas M,et al. Catecholamines infection and death in acute ischemic stroke. J Nenrol Sci. 2007;252(1):29-35.
[3] Prass K,Meisel C,Hich C,et al.Stroke-induced- immunodeficiency promotes spontaneous bacterial infections and is mediated by sympathetic actiVation reVersal by posts-troke T helper cell type 1 like immunostimulation.J Exp Med. 2003;198(5):725-736.
[4] 史焕昌.卒中诱导的免疫抑制与卒中相关性感染[J]. 国际脑血管病杂志,2012,20(11): 862-865.
[5] 任瑞芳,黄良国,蒋国红,等.脑源性神经营养因子基因重组慢病毒转染骨髓间质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑出血的实验研究[J].中华神经科杂志,2013,46(4):257-264.
[6] Howard RJ,Simmons RL.Acquired immunologic deficiencies after trauma and surreal procedures.Surg Gyneeol Obstet. 1974;139(5):771-782.
[7] 毛新发.血清CRP、LP(a)、IL-6在老年急性脑梗死患者中的表达及意义[J].医学临床研究,2015(5): 954-955, 956.
[8] 郭志强,吕清泉,张劲松.脑卒中后免疫抑制的相关研究[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2012,11(3):164-167.
[9] 刘杨,马少林,沈桢巍.脑卒中后免疫抑制[J].中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2010,17(4):297-299.
[10] 马嘉,闫福岭.白介素-10在脑卒中后免疫抑制中的作用[J].中华脑血管病杂志(电子版),2011,5(5):49-52.
[11] Xin JH,Zhao JF,Wang LB,et al.Influence of beta-endorphin on function of immune system of patients with cerebral hemorrhage. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003;83(16):1409-1412.
[12] Kochanek PM, Yonas H. Subarachnoid hemorrhage, systemic immune response syndrome, and MODS: is there cross-talk between the injured brain and the extra-cerebral organ systems? Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Crit Care Med. 1999;27(3):454-455.
[13] 张英,段轶轩,黄俊涛,等.不同时间电针对急性脑出血大鼠炎性免疫反应的影响[J].中医药信息,2011,28(01): 84-87.
[14] Klebe D, McBride D, Flores JJ, et al. Modulating the Immune Response Towards a Neuroregenerative Peri-injury Milieu After Cerebral Hemorrhage. J Neur Pharmacol. 2015;10(4):576-586.
[15] 张轶丹,赵建军,金曦,等.破血化瘀填精补髓方剂对脑出血大鼠模型神经营养因子BDNF表达的影响[J].中国中医急症,2015,24(1):1-3,23.
[16] 王琦,李建远.脑出血患者红细胞免疫功能的研究[J].宁夏医学院学报,2001,23(1):9-10.
[17] 李晓明,蔡军,刘宁,等.环孢菌素A对脑细胞移植治疗大鼠实验性脑出血免疫反应的影响[J].临床神经病学杂志, 2006,19(4):284-286.
[18] 周路球,马真,石小峰,等.脑出血患者细胞免疫功能变化研究[J].现代预防医学,2012,39(14):3659-3660,3664.
[19] 章文斌,卜博,周定标.脑出血患者红细胞免疫及T细胞亚群的变化[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(19):3790-3791.
[20] 贺文彬,楚世峰,陈乃宏.丹参总酚酸对大鼠缺血性脑卒中后免疫抑制现象的改善作用[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2015,29(3):391-397.
[21] 金鑫,赵涵,王俊芳,等.β内啡肽对脑出血患者免疫系统功能的影响[J]. 中华医学杂志,2003,83(16):1409-1412.
[22] 祁大勇,王景丰.脑出血患者的免疫功能研究[J].现代预防医学,2015,42(24):4508-4510.
[23] 李孝生,刘址忠,陈鹏,等.脑穿刺损伤并局部注药大鼠模型的构建初探[J].南昌大学学报(医学版),2011,51(6):1-5.
[24] Kocaogullar Y, Esen IK. Preventive effects of intraperitoneal selenium on cerebral vasospasm in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2010;22(1):53-58.
[25] 罗晓红,万东君, 吴兵,等.老龄急性缺血性脑卒中后多器官功能障碍综合征模型大鼠的免疫功能变化[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(42):64-66.
[26] 李中华,张贺,刘冰,等.不同压力高压氧对实验性脑出血大鼠模型血肿周围水肿及MMP-9和TIMP-1表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2014,34(19):5501-5503. |