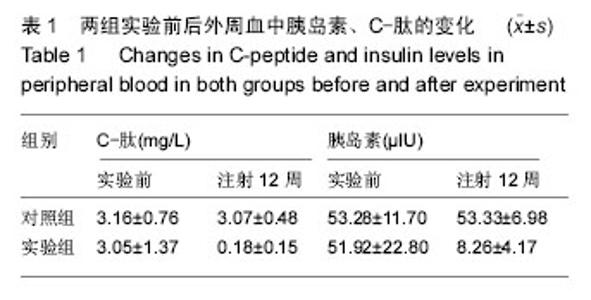
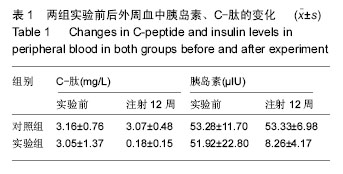
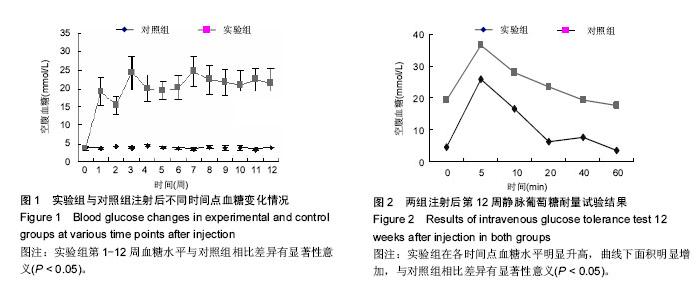
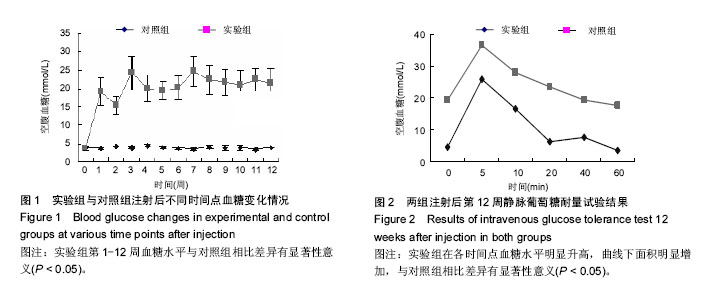
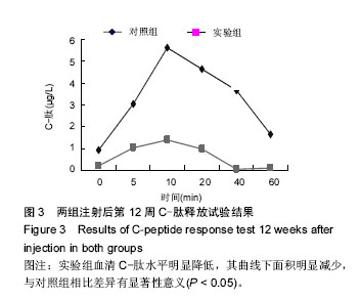
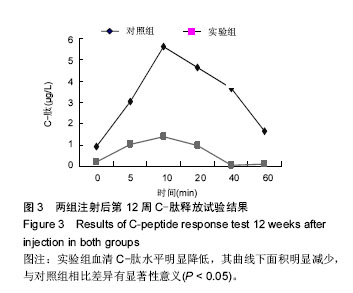
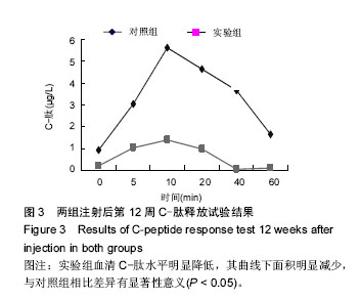
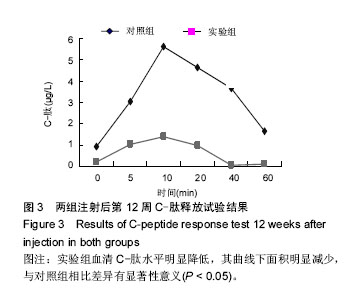
| [1] Yang W,Lu J,Weng J,et al.Prevalence of Diabetes among Men and Women in China. N Engl J Med.2010; 362(12):1090-1101.
[2] Munehiro K,Ai T,Takako N,et al.Dietary Restriction Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy through Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Regulation of the Autophagy via Restoration of Sirt1 in Diabetes Wistar Fatty (fa/fa ) Rats: A Model of Type 2 Diabetes.Exp Diabetes Res.2011;2011(9):1-11.
[3] Inderjeet S,Pawan KS,Shobhit B,et al.Effects of Three Different Doses of a Fruit Extract of Terminalia chebula on Metabolic Components of Metabolic Syndrome, in a Rat Model.Phytother Res.2010; 24(1):107-122.
[4] Hyun YK,Tsutomu O,Lekh RJ,et al.The protective role of amla (Emblica officinalis Gaertn.) against fructose-induced metabolic syndrome in a rat model.Br J Nutr.2010;103(4):502-512.
[5] Nakamaki S,Satoh H,Kudoh A,et al.Adiponectin reduces proteinuria in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011;236(5): 614-620.
[6] Kitamural T,Kahn CR,Accili D.Insulin receptor knockout mice.Annu Rev Physiol.2003;65(5):313-332.
[7] Graham ML,Mutch LA, Rieke EF,et al.Refining the high-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetic non-human primate model:an evaluation of risk factors and outcomes.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011;236(10): 1218-1230.
[8] Qiao CF,Tian BL,Mai G,et al.Induction of Diabetes in Rhesus Monkeys and Establishment of Insulin Administration Strategy.Transplant Proc.2009;41(1): 413-417.
[9] Pennisi E.Boom time for monkey research. Science. 2007;316(5822):216-218.
[10] Najafian B,Masood A,Mallory PC,et al.Glomerulopathy in spontaneously obese rhesus monkeys with type 2 diabetes: a stereological study.Diabetes Metab Res Rev.2011;27(4):341-347.
[11] Cooper MR,Jandeleit DK.Lipids and diabetic renal disease.Curr Dia Rep.2005;5(5):445-448.
[12] Shamekha R,Linden EH,Newcomb JD,et al. Endogenous and diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in nonhuman primates: effects of age, adiposity, and diabetes on lipoprotein profiles.Metabolism. 2011; 60(8):1165-1177.
[13] Jin X, Zeng L,He S,et al.Comparison of single high-dose streptozotocin with partial pancreatectomy combined with low-dose streptozotocin for diabetes induction in rhesus monkeys.Exp Biol Med.2010; 235(7):877-885.
[14] Kaválková P,Mraz M,Trachta P,et al.Endocrine effects of duodenal-jejunal exclusion in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Endocrinol.2016. pii:JOE-16-0206.[Epub ahead of print]
[15] Adeniyi OV,Yogeswaran P,Longo-Mbenza B,et al.Cross-sectional study of patients with type 2 diabetes in OR Tambo district, South Africa.BMJ Open.2016;6(7):e010875.doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010875.
[16] Andrews M,Leiva E,Arredondo-Olguín M.Short repeats in the heme oxygenase 1 gene promoter is associated with increased levels of inflammation, ferritin and higher risk of type-2 diabetes mellitus.J Trace Elem Med Biol.2016;37:25-30.
[17] Genser L,Casella Mariolo JR,Castagneto-Gissey L,et al.Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and the Metabolic Syndrome: Pathophysiologic Relationships and Guidelines for Surgical Intervention.Surg Clin North Am.2016;96(4):681-701.
[18] Yoshizawa S,Kodama S,Fujihara K,et al.Utility of nonblood-based risk assessment for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis.Prev Med.2016.pii: S0091-7435(16)30202-X.doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.07.026.[Epub ahead of print]
[19] Sato J,Kanazawa A,Makita S,et al.A randomized controlled trial of 130 g/day low-carbohydrate diet in type 2 diabetes with poor glycemic control.Clin Nutr. 2016. pii: S0261-5614(16)30169-8. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2016.07.003.[Epub ahead of print]
[20] Saleh Md Moin A,Dhawan S,Cory M,et al.Increased frequency of hormone negative and polyhormonal endocrine cells in lean individuals with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2016:jc20162496.[Epub ahead of print]
[21] Qiao Q,Johnsson K,Grandy S,et al.Treatment Outcomes and Tolerability Following Initiation of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients in Primary Care Practices in Germany.J Diabetes Sci Technol.2016.pii: 1932296816661349.[Epub ahead of print] |