Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (7): 1212-1219.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.07.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Glial cell responses and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in the brain of chronic vascular dementia rat models
Wang Min, Cao Bing-zhen
- Wang Min☆, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Neurology, Jinan Military General Hospital, Jinan 250031, Shandong Province, China
xmeht@163.com
-
Received:2012-05-11Revised:2012-06-18Online:2013-02-12Published:2013-03-21 -
Contact:Cao Bing-zhen, Doctor, Chief physician, Department of Neurology, Jinan Military General Hospital, Jinan 250031, Shandong Province, China cbzxia2011@163.com -
About author:Wang Min☆, Studying for doctorate, Attending physician, Department of Neurology, Jinan Military General Hospital, Jinan 250031, Shandong Province, China xmeht@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Min, Cao Bing-zhen. Glial cell responses and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in the brain of chronic vascular dementia rat models[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(7): 1212-1219.
share this article
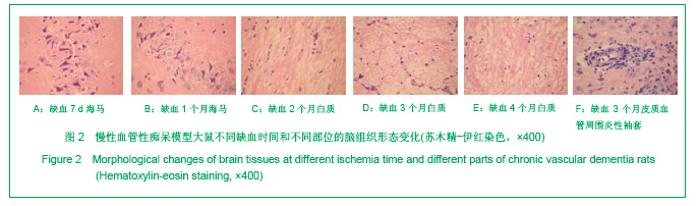
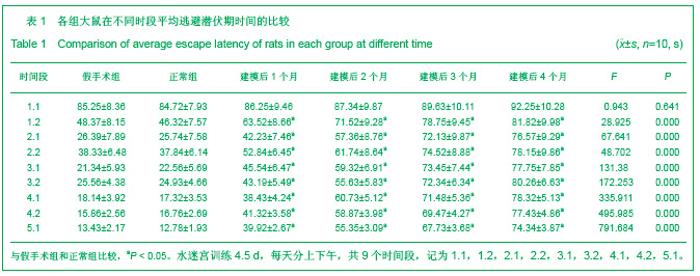
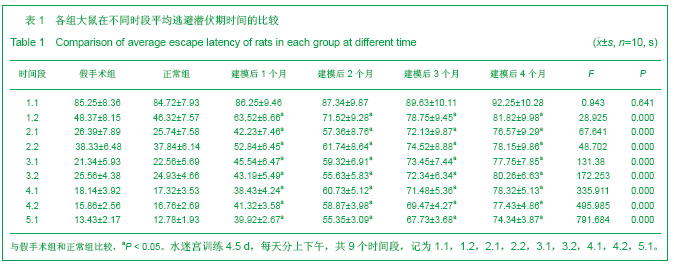
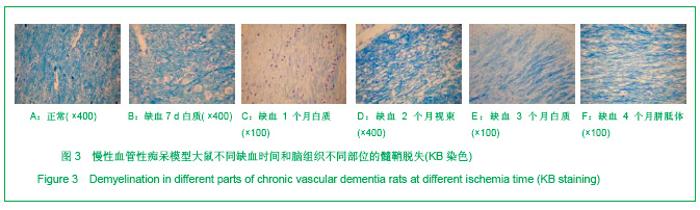
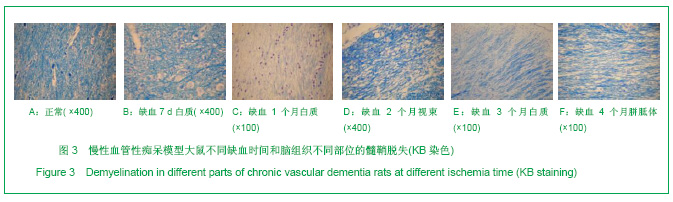
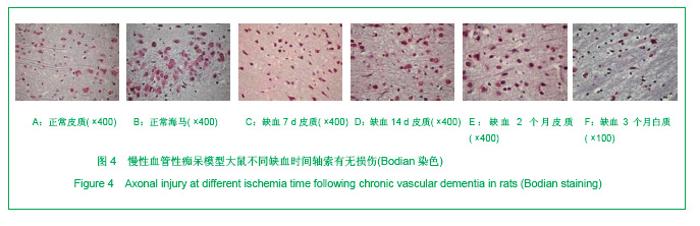
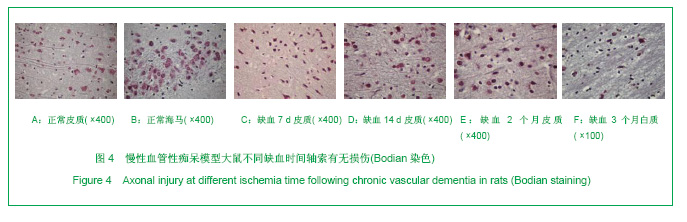
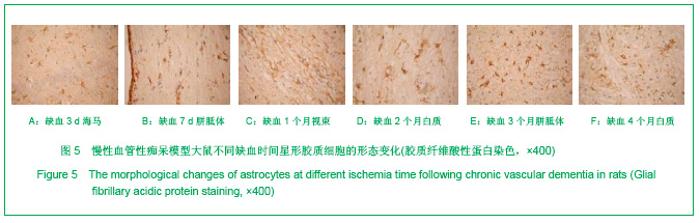
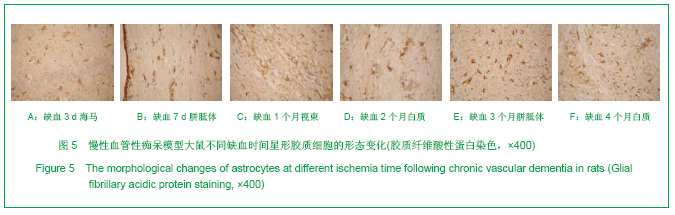
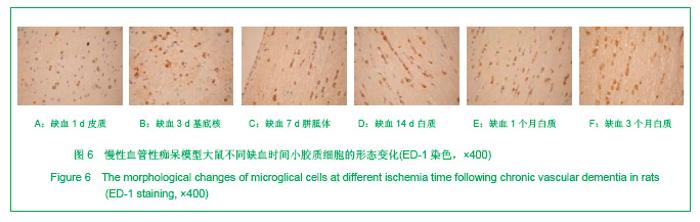
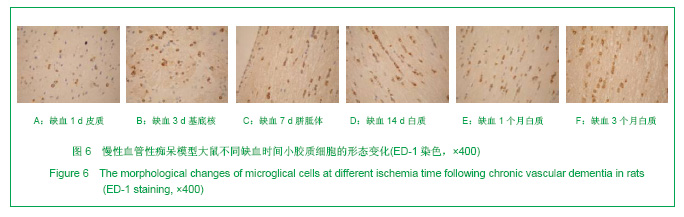
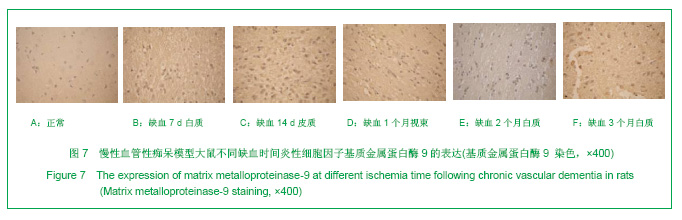
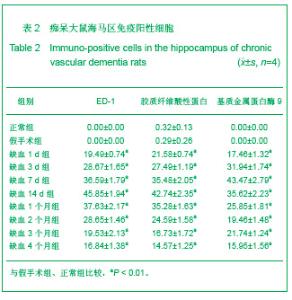
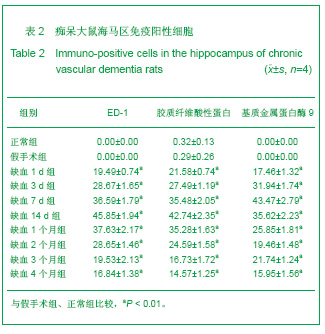
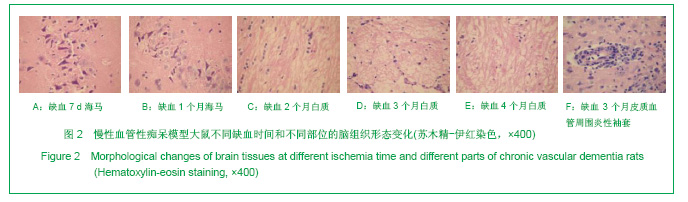
2.3 各组大鼠脑组织学观察 苏木精-伊红、KB及Bodian染色:见图2-4。模型组大鼠缺血1-3 d,额颞叶皮质及海马区锥体细胞缺血水肿呈三角形,缺血7-14 d,皮质下及脑室周围出现较多梗死灶,以海马及新皮质的3,5,6层神经细胞及尾状核等纹状体区神经细胞坏死最明显。可见较多炎性细胞浸润,主要是单核吞噬细胞,海马CA1区锥体细胞及齿状回细胞减少。缺血一两个月除上述表现外,脑室周围白质疏松呈空泡样变,海马区锥体细胞严重脱失、基质疏松及微空泡形成,星形胶质细胞明显增生,白质疏松更加明显。KB染色可见髓鞘脱失,Bodian染色示轴索连续性完好。缺血三四个月,白质疏松更加明显,髓鞘脱失明显,Bodian染色未见轴索断裂,纤维性星形胶质细胞明显增多。可见部分炎性细胞围绕小静脉周围形成袖套样改变。 免疫组织化学染色:见图5-7。正常组及假手术组大鼠未发现阳性小胶质细胞,未见基质金属蛋白酶9表达,在皮质及白质内可见散在星形胶质细胞。缺血1 d,皮质、基底节、内囊、胼胝体、海马、视束等处均有胞浆染色阳性的小胶质细胞;基质金属蛋白酶9表达在缺血3-7 d以海马CA1区增加明显;缺血7-14 d脑室周围白质小胶质细胞显著增多,梗死灶周围小胶质细胞增生明显。缺血1个月,小胶质细胞反应达到高峰,小胶质细胞和基质金属蛋白酶9的表达以室周白质最为显著,其次是皮质和海马;梗死中心区阿米巴状、圆状小胶质细胞高度聚集,梗死区周边见高分枝状小胶质细胞;缺血2-4个月后仍以室周白质及白质疏松处最显著,而海马区小胶质细胞活动则减少。胶质纤维酸性蛋白阳性星形胶质细胞在时间、空间分布及反应程度上与小胶质细胞反应相平行,形态上也经历了早期的纤维性星形胶质细胞,到胞体增大、肿胀,树突增粗,胞浆深染的反应性星形胶质细胞,后期则出现较多的纤维性星形胶质细胞。"
| [1] Xie HG, Cheng LQ, Wang LN, et al.Xiandai Kangfu. 2001; 5(1):58-60. 解恒革,程流泉,王鲁宁,等.Alzheimer病和血管性痴呆患者海马杏仁核体积的MRI对照研究[J].现代康复,2001,5(1):58-60.[2] 阿部晋卫,羽生春夫,新井久之,ほか.老年期痴呆の脑循环动态に关する研究[J].日本医学会志,1996,95:103 -111. [3] Otori T, Katsumata T,Muramatsu H,Long-term measurement of cerebral blood flow and metabolism in a rat chronic hypoperfusion model.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.2003;30(4):266-272.[4] Wakita H,Tomimoto H,Akiguchi I,Axonal damage and demyelination in the white matter after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat.Brain Res..2002;924(1):63-70.[5] Ransohoff RM,Perry VH.Microglial physiology:unique stimuli,specialized responses.Annu Rev Immunol.2009;27:1l19-145.[6] Barker A J,Ullian E M.Astrocytes and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscientist.2010;16(1):40-50.[7] Halassa MM,Haydon PG.Integrated brain circuits:astrocytic networks neuronal activity and behavior.Annu Rev Physiol. 2010;172:335-355. [8] Kerever A,Schnack J,Vellinga D,et al.Novel Extracellular Matrix Structures in the Neural Stem Cell Niche Capture the Neurogenic Factor Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 from the Extracellular Milieu.Stem Cells.2007;25(9):2146-2157. [9] Muhammad S, Barakat W,Stoyanov S,et al.The HMGB1 receptor RAGE mediates ischemic brain damage.J Neurosci. 2008;28:12023-12031.[10] Qiu J,Nishimura M,Wang Y,et al.Early release of HMGB-1 from neurons after the onset of brain ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2008;28:927-938.[11] Wieraszkoa R,Ahmeda Z.Axonal release of glutamate analog,d-2,3-3H-Aspartic acid and l-14C-proline from segments of sciatic nerve following electrical and magnetie stimulation. Neurescience Letters.2009;458:19-22. [12] Wu C Y,Kaur C,Sivakumar V,et a1.Kv1.1 expression in microglia regulates production and release of proinflammatory cytokines,endothelins and nitric oxide. Neuroscience.2009;158(4):1500-1508.[13] Skaper SD.The brain as a target for inflammatory processes and neuroprotective strategies.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2007; 112(2): 23-34. [14] Kim EJ,Kown KJ,Park JY,et al.Effects of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor agonists on LPS-induced neuronal death in mixed cortical neurons:associated with iNOS and COX-2.Brain Res.2002;941(1-2):1-10.[15] Liu K,Mori S,Takahashi HK,et al. Anti-high mobility group box 1 monoclonal antibody ameliorate brain infarction induced by transient ischemia in rats.FASEB J.2007;21:3904-3916. [16] Nicholas RS,Wing MG.Compston A. Nonactivated microglia promote oligodendrocyte precursor survival and maturation through the transcription factor NF-κB.Eur J Netrosci.2001; 13:959-967. [17] Elisabetta P,Barbara M.Microglia and neuroprotection:From in vitro studies to therapeutic applications.Progress in Neurobiology. 2010;92(3):293-315. [18] Ma L,Jia J,Chen SY,et al.Zhonghua Shenjing Yixue Zazhi. 2010:4(9):325-29. 马磊,贾济,陈绍洋,等.大麻素CB2受体参与电针预处理诱导的延迟相脑保护作用[J].中华神经医学杂志,2010:4(9):325-29. [19] Asya R,Ravid S,Michal S.The bright side of the glial scar in CNS repair.Nature Review Neuroscience.2009;10:235-241.[20] Ito U,Nagasao J,Kawakami E.Fate of disseminated dead neurons in the cortical ischemic penumbra:ultrastructure indicating a novel scavenger mechanism of microglia and astrocytes.Stroke.2007;38:2577-2583.[21] Eulenburg V,Gomeza J. Neurotransmitter transporters expressed in glial ce11s as regulators of synapse function. Brain Res Rev.2010;63(1-2):103-1012.[22] Yoshikawa T,Akiyoshi Y,Susumu T,et al.Ginsenoside Rbl Reduces Neurodegeneration in the Peri-infarct Area of a Thromboembolic Stroke Model in Non-human Primates.J Pharmacol Sci.2008;107(1):32-40. [23] Li J J,Wu L H,Cao Q,et al.Endothelins-1/3 and endothelin-A/B receptors expressing glial cells with special reference to activated microglia in experimentally induced cerebral ischemia in the adult rats.Neuroscience. 2010;167(3): 665-677.[24] Gasche Y,Soccal PM ,Kanemitsu M ,et al.M atrix metalloproteinases and diseases of the central nervous system with a special emphasis on ischemic brain.Front Biosci.2006;11:1289.[25] Ramos-Fernandez M,Bellolio MF, Stead LG,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase-9 as a marker for acute ischemic stroke:a systematic review.J Stroke Cerebrovaso Dis.2011;20(1): 47-54.[26] Gidday JM,Gasche YG,Copin JC,et al.Leukocyte-derived matrix metal1oproteinase-9 mediates blood-brain barrier breakdown and is proinflammatory after transient focal cerebral ischemia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2005;289: H558-H568.[27] Gu Z,Cui J,Brown S,et al.A highly specific inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-9 rescues laminin from proteolysis and neurons from apoptosis in transient focal cerebral ischemia.J Neurosci.2005;25 (27):6401-6408.[28] Rosell A, Alvarez-sabin J,Arenillas JF,et al.Matrix metalloproteinase protein array reveals a strong relation between MMP-9 and MMP-13 with diffusion-weighted in age lesion increase in human stroke.Stroke.2005;36:1415-1420.[29] Eldrup N, Gronholdt ML, Sillesen H,et al. Elevated matrix metalloproteinase-9 associated with stroke or cardiovascular death in patients with carotid stenosis.Circulation.2006;114: 1847-1854.[30] Rosell A,Cuadrado E,Ortega-Aznar A,et al MMP-9- positive neutrophil infiltration is associated to blood-brain barrier breakdown and basal lamina type IV collagen degradation during hemorrhagic transformation after human ischemic stroke. Stroke.2008;39(4):1121-1126.[31] Cuadrado E,Ortega L, Hernandez-Guillamon M,et al.Tissue plasminogen activator(t-PA)promotes neutrophil degranulation and MMP-9 release.J Leukoc Biol.2008;84(1): 207-214.[32] Kong XM,Yan HM,Wang YL,et al.Zhongguo Xueye Liubianxue Zazhi. 2010;20(2):209-211. 孔小明,阎红梅,王玉林,等.急性脑出血患者中基质金属蛋白酶-9的临床意义[J].中国血液流变学杂志,2010,20(2):209-211. [33] Lucivero V,Prontera DM,Mezzapesa M,et a1.Different roles of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and-9 after human iscbaemic stroke.Neurol Sci.2007;28(4):165-170.[34] Lee JK, Kwak HJ, Piao MS,et al.Quercetin reduces the elevated matrix metalloproteinases-9 level and improves functional outcome after cerebral focal ischemia in rats. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011;153(6):1321-1329. |
| [1] | Chen Ju, Zheng Jinchang, Liang Zhen, Huang Chengshuo, Lin Hao, Zeng Li. Effect and mechanism of beta-caryophyllene in mice with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347. |
| [2] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [3] | Li Linzhen, Jiao Hongzhuo, Chen Weinan, Zhang Mingzhe, Wang Jianlong, Zhang Juntao. Effect of icariin-containing serum on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in human chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [4] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [5] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [6] | Lyu Xiaofan, Huang Yi, Ding Liucheng . Mitochondrial mechanism and intervention therapy in diabetic cystopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1508-1515. |
| [7] | Cao Xinyan, Yu Zifu, Leng Xiaoxuan, Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Liu Xihua. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation on motor function and gait in children with cerebral palsy: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1539-1548. |
| [8] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [9] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [10] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [11] | Zhang Jiuxuan, Zhang Jinnan, Sui Xiaofan, Pei Xiaxia, Wei Jianhong, Su Qiang, Li Tian. Effects of ammonia poisoning on cognitive behavior and hippocampal synaptic damage in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1122-1128. |
| [12] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [13] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [14] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [15] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||