Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1341-1347.doi: 10.12307/2025.995
Effect and mechanism of beta-caryophyllene in mice with osteoarthritis
Chen Ju1, Zheng Jinchang2, Liang Zhen2, Huang Chengshuo1, Lin Hao2, Zeng Li1
- 1Faculty of Chinese Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao Special Administrative Region 999078, China; 2Orthopedic Center, the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-30Accepted:2024-12-31Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-12 -
Contact:Zeng Li, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Faculty of Chinese Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao Special Administrative Region 999078, China -
About author:Chen Ju, PhD, Faculty of Chinese Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Quality Research in Chinese Medicine, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao Special Administrative Region 999078, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Science and Technology Program, No. 2023A1414020048 (to CJ [project participant]); Guangdong Medical Science and Technology Research Fund, Nos. B2024006 (to LZ) and B2024110 (to ZJC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Ju, Zheng Jinchang, Liang Zhen, Huang Chengshuo, Lin Hao, Zeng Li. Effect and mechanism of beta-caryophyllene in mice with osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1341-1347.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
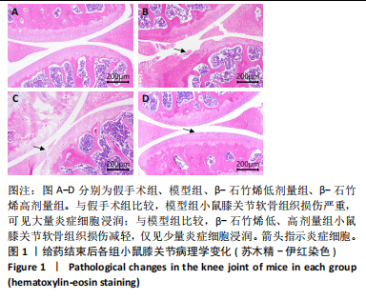
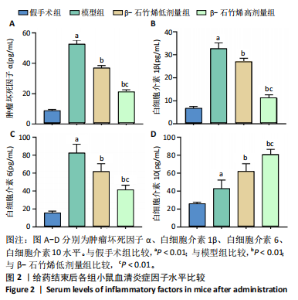
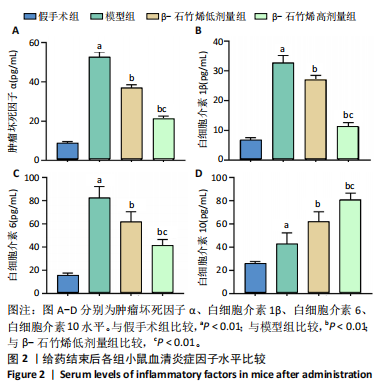
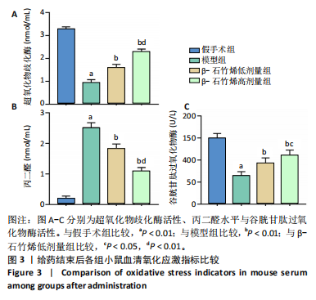
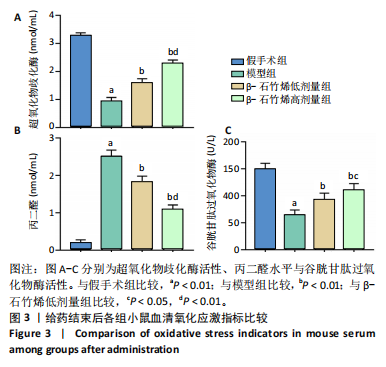
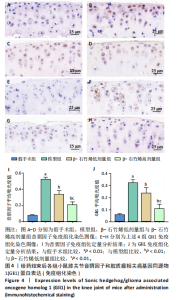
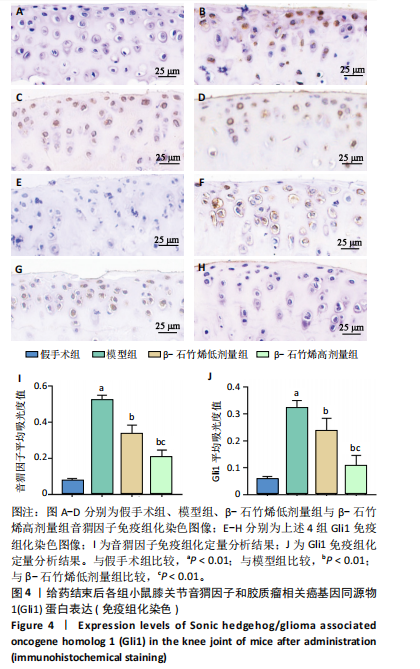
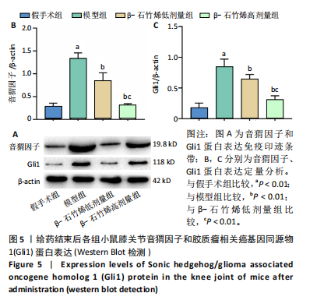
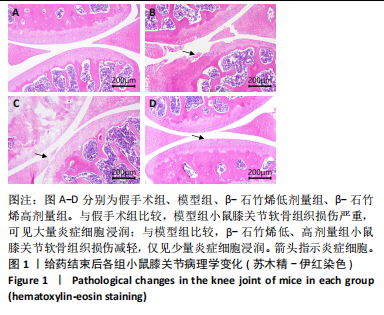
2.1 实验动物数量分析 40只小鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 β-石竹烯改善膝骨关节炎小鼠膝关节损伤 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,与假手术组比较,模型组小鼠膝关节软骨组织损伤严重,可见大量炎症细胞浸润;与模型组比较,β-石竹烯低、高剂量组小鼠膝关节软骨组织损伤减轻,仅见少量炎症细胞浸润,见图1。 2.3 β-石竹烯降低膝骨关节炎小鼠血清炎症因子水平 与假手术组比较,模型组小鼠血清肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素10水平升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,β-石竹烯低、高剂量组小鼠血清肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6水平降低(P < 0.01),白细胞介素10水平升高(P < 0.01);与β-石竹烯低剂量组比较,β-石竹烯高剂量组小鼠血清肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6水平降低(P < 0.01),白细胞介素10水平升高(P < 0.01),见图2。 2.4 β-石竹烯改善膝骨关节炎小鼠血清氧化应激指标 与假手术组比较,模型组小鼠血清超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性明显降低(P < 0.01),丙二醛水平明显升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,β-石竹烯低、高剂量组小鼠血清超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性明显升高(P < 0.01),丙二醛水平明显降低(P < 0.01);与β-石竹烯低剂量组比较,β-石竹烯高剂量组小鼠血清超氧化物歧化酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),丙二醛水平降低(P < 0.01),见图3。 2.5 β-石竹烯下调膝骨关节炎小鼠膝关节音猬因子和Gli1蛋白表达 免疫组化染色结果显示,与假手术组比较,模型组小鼠膝关节音猬因子和Gli1蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,β-石竹烯低、高剂量组小鼠膝关节音猬因子和Gli1蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01);与β-石竹烯低剂量组比较,β-石竹烯高剂量组小鼠膝关节音猬因子和Gli1蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01),见图4。 Western Blot检测结果显示,与假手术组比较,模型组小鼠膝关节音猬因子和Gli1蛋白相对表达升高(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,β-石竹烯低、高剂量组小鼠膝关节音猬因子和Gli1蛋白相对表达降低(P < 0.01);与β-石竹烯低剂量组比较,β-石竹烯高剂量组小鼠膝关节音猬因子和Gli1蛋白相对表达降低(P < 0.01),见图5。"
| [1] ZENG C, DOHERTY M, PERSSON MSM, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of acetaminophen, topical and oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for knee osteoarthritis: evidence from a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and real-world data. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021;29(9):1242-1251. [2] BUCHANAN WW, KEAN CA, KEAN WF, et al. Osteoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology. 2024;32(1):13-22. [3] BRAATEN JA, BANOVETZ MT, DEPHILLIPO NN, et al. Biomarkers for osteoarthritis diseases. Life (Basel). 2022;12(11):1799. [4] GRÄSSEL S, ZAUCKE F, MADRY H. Osteoarthritis: novel molecular mechanisms increase our understanding of the disease pathology. J Clin Med. 2021;10(9):1938. [5] LI H, KONG W, LIANG Y, et al. Burden of osteoarthritis in china, 1990-2019: findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(3):1189-1197. [6] HU S, LI Y, ZHANG X, et al. Increasing burden of osteoarthritis in china: trends and projections from the global burden of disease study 2019. Med Sci Monit. 2024;30:e942626. [7] KULKARNI P, MARTSON A, VIDYA R, et al. Pathophysiological landscape of osteoarthritis. Adv Clin Chem. 2021;100:37-90. [8] JADIDI S. A review of non-surgical pain management in osteoarthritis. Cureus. 2020;12(10):e10829. [9] RICHARD MJ, DRIBAN JB, MCALINDON TE. Pharmaceutical treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023;31(4):458-466. [10] BRUMAT P, KUNŠIČ O, NOVAK S, et al. The surgical treatment of osteoarthritis. life (Basel). 2022;12(7):982. [11] GRESS K, CHARIPOVA K, AN D, et al. Treatment recommendations for chronic knee osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2020; 34(3):369-382. [12] EMAMI A, NAMDARI H, PARVIZPOUR F, et al. Challenges in osteoarthritis treatment. Tissue Cell. 2023;80:101992. [13] LIAO B, GUAN M, TAN Q, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound inhibits fibroblast-like synoviocyte proliferation and reduces synovial fibrosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Orthop Translat. 2021;30:41-50. [14] ZHU R, FANG H, WANG J, et al. Inflammation as a therapeutic target for osteoarthritis: A literature review of clinical trials. Clin Rheumatol. 2024;43(8):2417-2433. [15] ATIK I, GUL E, ATIK S. Evaluation of the relationship between Knee Osteoarthritis and Meniscus Pathologies. Malawi Med J. 2024;36(1):48-52. [16] COLLINS JA, KAPUSTINA M, BOLDUC JA, et al. Sirtuin 6 (SIRT6) regulates redox homeostasis and signaling events in human articular chondrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;166:90-103. [17] CHOI M, MIN JS, MOON SW, et al. Mitoregulin modulates inflammation in osteoarthritis: Insights from synovial transcriptomics and cellular studies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024;734:150652. [18] FANG Z, HU Q, LIU W. Vitamin B6 alleviates osteoarthritis by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):447. [19] HU Q, ZUO T, DENG L, et al. β-Caryophyllene suppresses ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia reperfusion via activation of the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway in MCAO/R rats. Phytomedicine. 2022;102: 154112. [20] SANTOS NA, MARTINS NM, SISTI FM, et al. The cannabinoid beta-caryophyllene (BCP) induces neuritogenesis in PC12 cells by a cannabinoid-receptor-independent mechanism. Chem Biol Interact. 2017;261:86-95. [21] FIDYT K, FIEDOROWICZ A, STRZĄDAŁA L, et al. β-caryophyllene and β-caryophyllene oxide-natural compounds of anticancer and analgesic properties. Cancer Med. 2016;5(10):3007-3017. [22] ESPINOZA-GUTIÉRREZ HA, LÓPEZ-SALIDO SC, FLORES-SOTO ME, et al. Angiotensinergic effect of β-Caryophyllene on Lipopolysaccharide- induced systemic inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024; 719:150081. [23] 周智华,杜琼颖,郅青.β-石竹烯激活自噬减轻小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤的作用及机制[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2021,13(11): 1379-1382,1389. [24] FU C, QIU Z, HUANG Y, et al. Protective role of Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides against chondrocyte extracellular matrix degeneration through lncRNA GAS5 in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2022;24(2):532. [25] SU H, YAN Q, DU W, et al. Calycosin ameliorates osteoarthritis by regulating the imbalance between chondrocyte synthesis and catabolism. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024;24(1):48. [26] LEFEBVRE V, SMITS P. Transcriptional control of chondrocyte fate and differentiation. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2005;75(3):200-12. [27] GENG Y, BLANCO FJ, CORNELISSON M, et al. Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in normal human articular chondrocytes. J Immunol. 1995;155(2):796-801. [28] PELLETIER JP, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, ABRAMSON SB. Osteoarthritis, an inflammatory disease: potential implication for the selection of new therapeutic targets. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(6):1237-1247. [29] ZHEN G, GUO Q, LI Y, et al. Mechanical stress determines the configuration of TGFβ activation in articular cartilage. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1706. [30] 杨博,刘峻承,郑德勇,等.骨关节炎模型构建的研究进展[J].河北医药,2023,45(16):2515-2519. [31] CHEN X, LI Z, HONG H, et al. Xanthohumol suppresses inflammation in chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111238. [32] QIN R, SUN J, WU J, et al. Pyrroloquinoline quinone prevents knee osteoarthritis by inhibiting oxidative stress and chondrocyte senescence. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(3):1460-1472. [33] YEATER TD, CRUZ CJ, CRUZ-ALMEIDA Y, et al. Autonomic nervous system dysregulation and osteoarthritis pain: mechanisms, measurement, and future outlook. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2022;24(6):175-183. [34] WANG Y. Novel drug discovery approaches for MMP-13 inhibitors in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2024;114:130009. [35] KHAN NM, HASEEB A, ANSARI MY, et al. Dataset of effect of Wogonin, a natural flavonoid, on the viability and activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in IL-1β-stimulated human OA chondrocytes. Data Brief. 2017;12:150-155. [36] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42. [37] MORRIS G, GEVEZOVA M, SARAFIAN V, et al. Redox regulation of the immune response. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19(10):1079-1101. [38] AHMAD N, ANSARI MY, HAQQI TM. Role of iNOS in osteoarthritis: Pathological and therapeutic aspects. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(10):6366-6376. [39] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452. [40] BALDISSERA MD, SOUZA CF, GRANDO TH, et al. Hypolipidemic effect of β-caryophyllene to treat hyperlipidemic rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017;390(2):215-223. [41] LIU M, NIU W, OU L. β-Caryophyllene ameliorates the Mycoplasmal pneumonia through the inhibition of NF-κB signal transduction in mice. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(8):4240-4246. [42] 涂仕娟,杨红亚,李桃,等.吴茱萸碱调节Shh/Gli1信号通路对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨损伤的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2024,53(9): 827-833. [43] FENG M, LIU W, DING J, et al. Sonic hedgehog induces mesenchymal stromal cell senescence-associated secretory phenotype and chondrocyte apoptosis in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:716610. [44] HU Z, CHEN Y, ZHU S, et al. Sonic hedgehog promotes proliferation and migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via rho/rock signaling. J Immunol Res. 2022;2022:3423692. |
| [1] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [2] | Li Linzhen, Jiao Hongzhuo, Chen Weinan, Zhang Mingzhe, Wang Jianlong, Zhang Juntao. Effect of icariin-containing serum on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory damage in human chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Wen Guangwei, Zhen Yinghao, Zheng Taikeng, Zhou Shuyi, Mo Guoye, Zhou Tengpeng, Li Haishan, Lai Yiyi. Effects and mechanisms of isoginkgetin on osteoclastogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [4] | Lyu Guoqing, Aizimaitijiang·Rouzi, Xiong Daohai. Irisin inhibits ferroptosis in human articular chondrocytes: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1359-1367. |
| [5] | Peng Zhiwei, Chen Lei, Tong Lei. Luteolin promotes wound healing in diabetic mice: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1398-1406. |
| [6] | Zhu Kuicheng, Du Chunyan, Zhang Jintao. Mechanism by which hairless gene mutation promotes white adipose tissue browning in hairless mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1424-1430. |
| [7] | Li Hao, Tao Hongcheng, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu, Ding Qiang, Niu Chicheng, Huang Kai, Kang Hongyu. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway regulates the development of osteoarthritis: guiding targeted therapy with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1476-1485. |
| [8] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [9] | Hu Jing, Zhu Ling, Xie Juan, Kong Deying, Liu Doudou. Autophagy regulates early embryonic development in mice via affecting H3K4me3 modification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1147-1155. |
| [10] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [11] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [12] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [13] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [14] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [15] | Gu Fucheng, Yang Meixin, Wu Weixin, Cai Weijun, Qin Yangyi, Sun Mingyi, Sun Jian, Geng Qiudong, Li Nan. Effects of Guilu Erxian Glue on gut microbiota in rats with knee osteoarthritis: machine learning and 16S rDNA analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1058-1072. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||