Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1424-1430.doi: 10.12307/2026.554
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism by which hairless gene mutation promotes white adipose tissue browning in hairless mice
Zhu Kuicheng1, Du Chunyan1, Zhang Jintao2
- 1Laboratory Animal Center, 2Henan Institute of Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-10Accepted:2025-02-13Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-15 -
Contact:Zhang Jintao, PhD, Professor, Henan Institute of Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Zhu Kuicheng, PhD, Associate professor, Laboratory Animal Center, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31372270 (to ZJT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Kuicheng, Du Chunyan, Zhang Jintao. Mechanism by which hairless gene mutation promotes white adipose tissue browning in hairless mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1424-1430.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
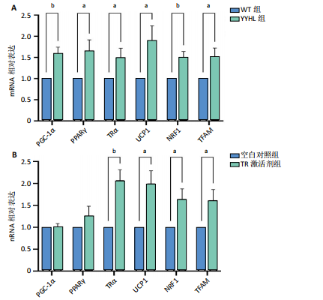
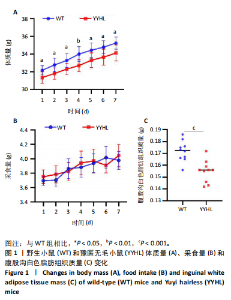
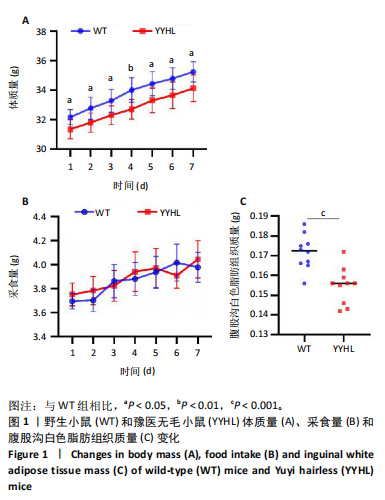
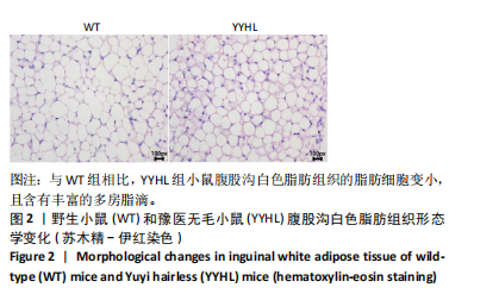
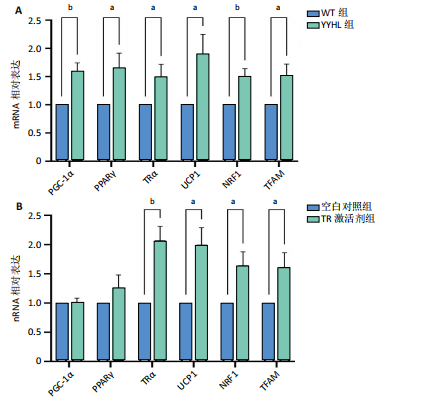
2.5 脂肪细胞褐变相关基因及蛋白表达分析 脂肪细胞褐变涉及到TRα、PPARγ及其激活因子PGC-1α、产热蛋白UCP1及线粒体生物发生基因NRF1和TFAM等。实时定量PCR结果显示,无毛基因突变小鼠脂肪组织PGC-1α、PPARγ、TRα、UCP1、NRF1和TFAM mRNA表达显著升高(P < 0.05);体外细胞实验加入TRα激动剂,结果显示,TRα、UCP1、NRF1和TFAM mRNA表达显著增加,PGC-1α、PPARγ mRNA表达与空白对照相比差异不显著。免疫荧光染色发现YYHL小鼠脂肪细胞PGC-1α及TRα蛋白阳性表达均明显增多。免疫组化染色发现YYHL小鼠脂肪细胞UCP1蛋白表达明显增多,见图4。"
| [1] APOVIAN CM, RIFFENBURG KM. Perspectives on the global obesity epidemic. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2017;24(5):307-309. [2] PICHÉ ME, TCHERNOF A, DESPRÉS JP. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ Res. 2020;126(11):1477-1500. [3] CHANDRASEKARAN P, WEISKIRCHEN R. The Role of Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-An Overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(3):1882. [4] GANGULI M, BEER JC, ZMUDA JM, et al. Aging, Diabetes, Obesity, and Cognitive Decline: A Population-Based Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(5):991-998. [5] TIAN X, CHEN S, WANG P, et al. Insulin resistance mediates obesity-related risk of cardiovascular disease: a prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21(1):289. [6] GESTA S, TSENG YH, KAHN CR. Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell. 2007;131(2):242-256. [7] JOHNSON JM, PETERLIN AD, BALDERAS E, et al. Mitochondrial phosphatidylethanolamine modulates UCP1 to promote brown adipose thermogenesis. Sci Adv. 2023;9(8):eade7864. [8] BARTELT A, HEEREN J. Adipose tissue browning and metabolic health. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10(1):24-36. [9] WALCZAK K, SIEMINSKA L. Obesity and Thyroid Axis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(18):9434. [10] MA Y, SHEN S, YAN Y, et al. Adipocyte Thyroid Hormone β Receptor-Mediated Hormone Action Fine-tunes Intracellular Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Systemic Homeostasis. Diabetes. 2023;72(5):562-574. [11] BRENT GA. Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(9):3035-3043. [12] LIU YY, SCHULTZ JJ, BRENT GA. A thyroid hormone receptor alpha gene mutation (P398H) is associated with visceral adiposity and impaired catecholamine-stimulated lipolysis in mice. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278(40):38913-38920. [13] AFFORTIT C, BLANC F, NASR J, et al. A disease-associated mutation in thyroid hormone receptor α1 causes hearing loss and sensory hair cell patterning defects in mice. Sci Signal. 2022;15(738):eabj4583. [14] KUSHCHAYEVA YS, STARTZELL M, COCHRAN E, et al. Thyroid Hormone Effects on Glucose Disposal in Patients With Insulin Receptor Mutations. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105(3):e158-e171. [15] SEGOVIA JC, LIN YC, AALA W, et al. Atrichia with papular lesions in a 1-year-old girl resulting from a new homozygous nonsense pathogenic variant in the hairless gene. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2023;48(5):536-538. [16] BENAVIDES F, OBERYSZYN TM, VANBUSKIRK AM, et al. The hairless mouse in skin research. J Dermatol Sci. 2009;53(1):10-18. [17] GAO J, LI Y, GUAN Y, et al. The accelerated aging skin in rhino-like SHJHhr mice. Exp Dermatol. 2022;31(10):1597-1606. [18] BAUR R, SHANE HL, WEATHERLY LM, et al. Exposure to the immunomodulatory chemical triclosan differentially impacts immune cell populations in the skin of haired (BALB/c) and hairless (SKH1) mice. Toxicol Rep. 2022;9:1766-1776. [19] MAATOUGH A, WHITFIELD GK, BROOK L, et al. Human Hairless Protein Roles in Skin/Hair and Emerging Connections to Brain and Other Cancers. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(1):69-80. [20] BROOK L, WHITFIELD GK, HSIEH D, et al. The Mammalian Hairless Protein as a DNA Binding Phosphoprotein. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(2): 341-350. [21] LIU L, RODRIGUEZ-MATEO C, HUANG P, et al. Hairless regulates heterochromatin maintenance and muscle stem cell function as a histone demethylase antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021; 118(37):e2025281118. [22] THOMPSON CC. Thyroid hormone-responsive genes in developing cerebellum include a novel synaptotagmin and a hairless homolog. J Neurosci. 1996;16:7832-7840. [23] POTTER GB, ZARACH JM, SISK JM et al. The thyroid hormone-regulated corepressor hairless associates with histone deacetylases in neonatal rat brain. Mol Endocrinol. 2002;16(11):2547-2560. [24] MORAITIS AN, GIGUÈRE V, THOMPSON CC. Novel mechanism of nuclear receptor corepressor interaction dictated by activation function 2 helix determinants. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(19):6831-6841. [25] ENGELHARD A, CHRISTIANO AM. The hairless promoter is differentially regulated by thyroid hormone in keratinocytes and neuroblastoma cells. Exp Dermatol. 2004;13(4):257-264. [26] THOMPSON CC, BOTTCHER MC. The product of a thyroid hormone-responsive gene interacts with thyroid hormone receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(16):8527-8532. [27] POTTER GB, BEAUDOIN GM 3RD, DERENZO CL, et al. The hairless gene mutated in congenital hair loss disorders encodes a novel nuclear receptor corepressor. Genes Dev. 2001;15(20):2687-2701. [28] 王纯耀,章金涛,祝庆蕃,等.豫医无毛小鼠近交系建立及其生物学特性[J].上海实验动物科学,1999(1):67-68. [29] ZHANG JT, FANG SG, WANG CY. A novel nonsense mutation and polymorphisms in the mouse hairless gene. J Invest Dermatol. 2005; 124(6):1200-1205. [30] ZHANG H, WANG S, ZHOU Q, et al. Disturbance of calcium homeostasis and myogenesis caused by TET2 deletion in muscle stem cells. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):236. [31] CHEN LY, WANG LW, WEN J, et al. RNA-binding protein YBX3 promotes PPARγ-SLC3A2 mediated BCAA metabolism fueling brown adipogenesis and thermogenesis. Mol Metab. 2024;90:102053. [32] CÓZAR-CASTELLANO I, PERDOMO G. Assessment of Insulin Tolerance In Vivo in Mice. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2128:217-224. [33] KENNARD MR, NANDI M, CHAPPLE S, et al. The glucose tolerance test in mice: Sex, drugs and protocol. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022; 24(11):2241-2252. [34] MAFFEI M, HALAAS J, RAVUSSIN E, et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med. 1995;1(11):1155-1161. [35] PEREIRA S, CLINE DL, GLAVAS MM, et al. Tissue-Specific Effects of Leptin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. Endocr Rev. 2021;42(1):1-28. [36] PICÓ C, PALOU M, POMAR CA, et al. Leptin as a key regulator of the adipose organ. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2022;23(1):13-30. [37] STERN JH, RUTKOWSKI JM, SCHERER PE. Adiponectin, Leptin, and Fatty Acids in the Maintenance of Metabolic Homeostasis through Adipose Tissue Crosstalk. Cell Metab. 2016;23(5):770-784. [38] LI X, ZHANG D, VATNER DF, et al. Mechanisms by which adiponectin reverses high fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(51):32584-32593. [39] TANG C, ZHAO H, KONG L, et al. Probiotic Yogurt Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Lipid Accumulation and Insulin Resistance in Mice via the Adiponectin Pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 2023;71(3):1464-1476. [40] BIANCO AC, SILVA JE. Nuclear 3,5,3’-triiodothyronine (T3) in brown adipose tissue: receptor occupancy and sources of T3 as determined by in vivo techniques. Endocrinology. 1987;120(1):55-62. [41] BRÉLIVET Y, ROCHEL N, MORAS D. Structural analysis of nuclear receptors: from isolated domains to integral proteins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;348(2):466-473. [42] MUKHERJEE S, DASGUPTA S, PANJA SS, et al. Structural insight to human Retinoid X receptor alpha-Thyroid hormone receptor beta heterodimer by molecular modelling and MD-simulation studies: role of conserved water molecules. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023;41(19):9828-9839. [43] MANGELSDORF DJ, EVANS RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995;83(6):841-850. [44] TAMBONES I, LE MAIRE A. Structural Insights Into Thyroid Hormone Receptors. Endocrinology. 2024;166(1):bqae154. [45] ASTAPOVA I, HOLLENBERG AN. The in vivo role of nuclear receptor corepressors in thyroid hormone action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1830(7):3876-3881. [46] DJABALI K, CHRISTIANO AM. Hairless contains a novel nuclear matrix targeting signal and associates with histone deacetylase 3 in nuclear speckles. Differentiation. 2004;72(8):410-418. [47] SØBERG S, LÖFGREN J, PHILIPSEN FE, et al. Altered brown fat thermoregulation and enhanced cold-induced thermogenesis in young, healthy, winter-swimming men. Cell Rep Med. 2021;2(10):100408. [48] BAGON BB, LEE J, MATIENZO ME, et al. Cold-induced adaptive thermogenesis is impaired by exposure of Asian sand dust in mice. J Therm Biol. 2023;116:103675. [49] BRTKO J. Thyroid hormone and thyroid hormone nuclear receptors: History and present state of art. Endocr Regul. 2021;55(2):103-119. [50] PUIGSERVER P, WU Z, PARK CW, et al. A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell. 1998; 92(6):829-839. [51] MIRANDA CS, SILVA-VEIGA FM, SANTANA-OLIVEIRA DA, et al. PPARα/γ synergism activates UCP1-dependent and -independent thermogenesis and improves mitochondrial dynamics in the beige adipocytes of high-fat fed mice. Nutrition. 2024;117:112253. [52] SHIBATA Y, EGUCHI J, WADA J. Brown Adipose Tissue PPARγ Is Required for the Insulin-Sensitizing Action of Thiazolidinediones. Acta Med Okayama. 2023;77(3):243-254. [53] SOLMONSON A, MILLS EM. Uncoupling Proteins and the Molecular Mechanisms of Thyroid Thermogenesis. Endocrinology. 2016;157(2): 455-462. [54] LIU S, SHEN S, YAN Y, et al. Triiodothyronine (T3) promotes brown fat hyperplasia via thyroid hormone receptor α mediated adipocyte progenitor cell proliferation. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3394. [55] YAU WW, SINGH BK, LESMANA R, et al. Thyroid hormone (T3) stimulates brown adipose tissue activation via mitochondrial biogenesis and MTOR-mediated mitophagy. Autophagy. 2019;15(1):131-150. [56] WU Z, PUIGSERVER P, ANDERSSON U, et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell. 1999;98(1):115-124. [57] PILLAR TM, SEITZ HJ. Thyroid hormone and gene expression in the regulation of mitochondrial respiratory function. Eur J Endocrinol. 1997;136(3):231-239. |
| [1] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [2] | Tao Yunfei, Peng Li. Acute effects of blood flow restriction in low-intensity resistance training on endothelial function-related inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1184-1195. |
| [3] | Liu Chenchen, Liu Ruize, Bao Mengmeng, Fang Li, Cao Liquan, Wu Jiangbo. Blood flow restriction training intervention in the elderly with sarcopenic obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6963-6970. |
| [4] | Liu Haowei, Tian Haodong, Huang Li, Yu Hanglin, Peng Li. Acute effects of blood flow restriction resistance exercise on serum metabolites in obese young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6249-6259. |
| [5] |
Yang Fengying, Zhao Yuqing, You Huijuan, Zhang Pengyi, Chen Yan, Wang Qinglu, Liu Yingying .
Macrophage efferocytosis: a new target for the treatment of obesity-related metabolic diseases #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 430-440.
|
| [6] | Kong Luming, Zhao Diqian, Bai Wenzhe, Li Nianhu. Association between obesity and diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3705-3712. |
| [7] | Chen Cong, , , Wu Huijuan, , Hu Yue, , Zhou Huanghao, , Huang Chunxiu. Aerobic exercise promotes remodeling of the energy metabolism network in the skeletal muscle of mice with sarcopenic obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3596-3604. |
| [8] | Zhao Yanan, Lu Donglei, Tan Sijie, . Exercise intervention for sarcopenic obesity in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3657-3667. |
| [9] | Zhao Yuqing, Wang Wei, You Huijuan, Chen Liyuan, Chen Yan, Wang Qinglu, Yang Fengying. Relationship between macrophage subtypes in obese adipose tissue and metabolic diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2832-2841. |
| [10] | Li Xiupeng, Su Yuying, Wang Yuetong, Peng Liang, Wang Yida, Jing Wen. Effect of low-volume high-intensity interval training on cardiovascular risk factor in obese or overweight populations: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2590-2604. |
| [11] | Zhu Peng, Li Yingyu, Lu Xiaoqian, Wu Qiong. Anti-obesity effect of insulin-like growth factor 1 in naturally aging mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2536-2543. |
| [12] | Zhang Wenli, Zhao Ziqi, Liang Leichao, Tang Yunqi, Wang Yong. Differences in dynamic stability across different height barriers between obese and average men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2319-2326. |
| [13] | Guo Xinfeng, Liang Zhidong, Chen Huiyu, Li Yang. Effects of training modalities and training cycles on visceral and subcutaneous fat in recessively obese individuals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2340-2346. |
| [14] | Wang Weiqing, Zhou Yue. Chronic inflammation regulates adipose tissue fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1307-1312. |
| [15] | Hong Weihao, Tian Hang, Luan Yisheng, Ma Yixuan, Xiong Yingzhe, Zhang Bing. Effects of moderate-intensity continuous training and high-intensity interval training on obesity-related muscle atrophy in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5618-5623. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||