Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (29): 6249-6259.doi: 10.12307/2025.746
Previous Articles Next Articles
Acute effects of blood flow restriction resistance exercise on serum metabolites in obese young men
Liu Haowei, Tian Haodong, Huang Li, Yu Hanglin, Peng Li
- School of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
-
Received:2024-08-07Accepted:2024-09-15Online:2025-10-18Published:2025-03-07 -
Contact:Peng Li, MD, Professor, School of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China -
About author:Liu Haowei, Doctoral candidate, School of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China Tian Haodong, Doctoral candidate, School of Physical Education, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China Liu Haowei and Tian Haodong contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:National Social Science Foundation of China, No. 21BTY092 (to PL); Chongqing Municipal Doctoral Graduate Student Research and Innovation Project, No. CYB240087 (to THD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Haowei, Tian Haodong, Huang Li, Yu Hanglin, Peng Li. Acute effects of blood flow restriction resistance exercise on serum metabolites in obese young men[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6249-6259.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
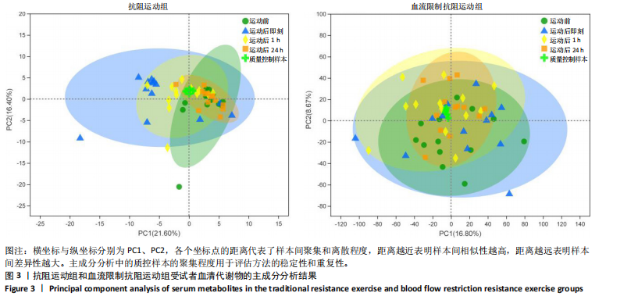
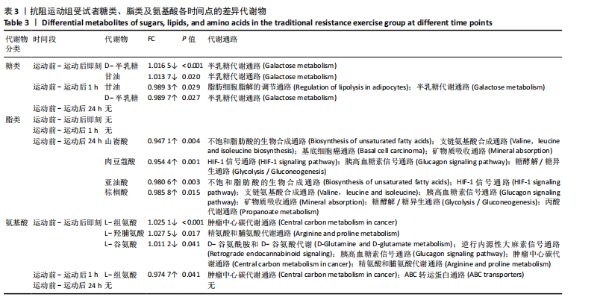
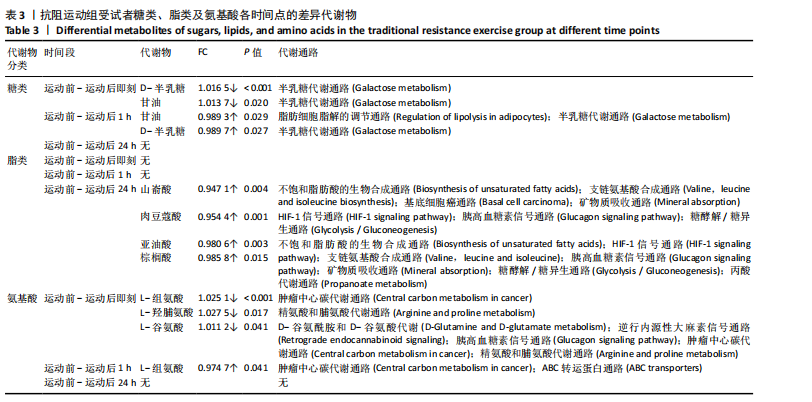
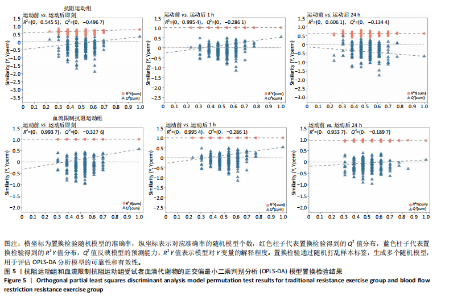
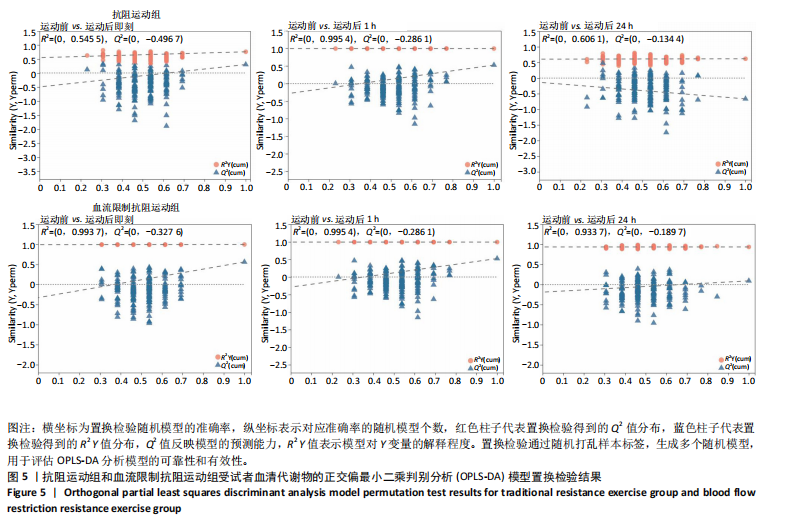
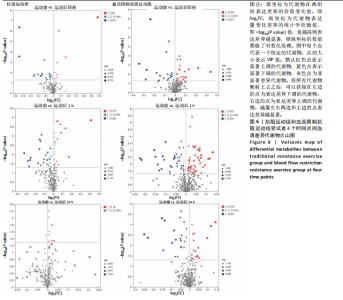
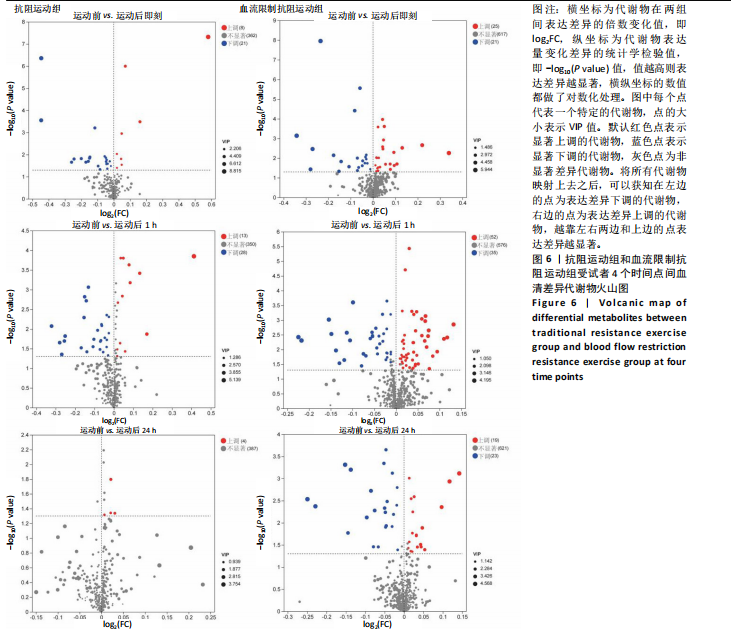
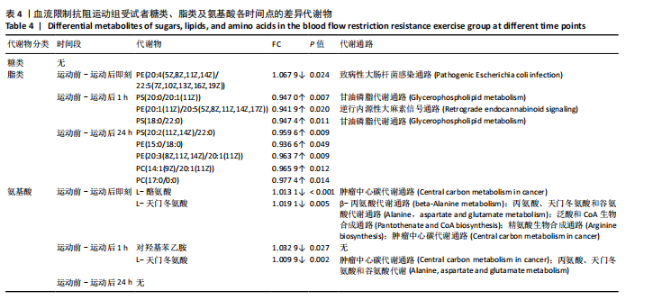
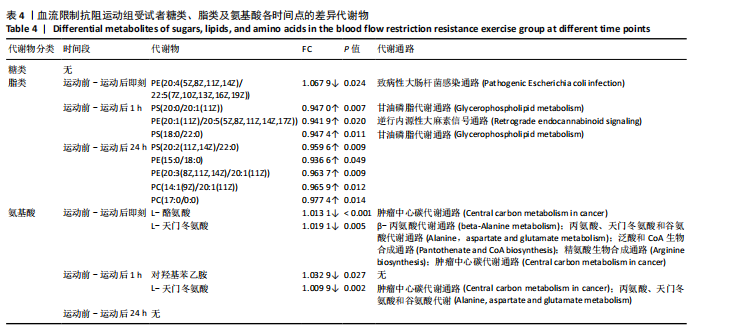
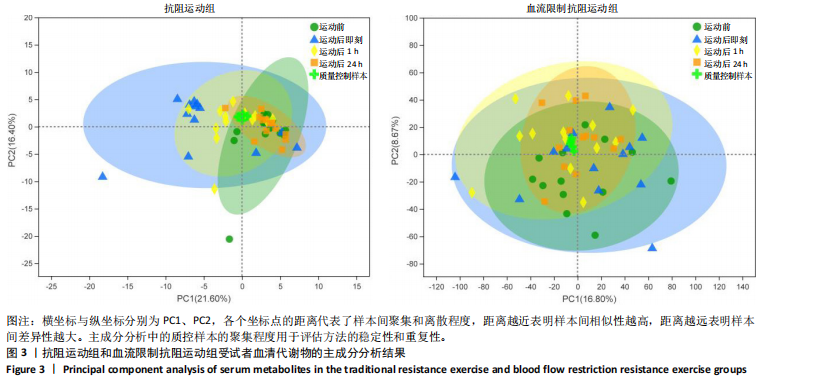
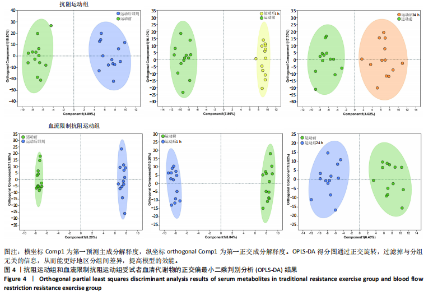
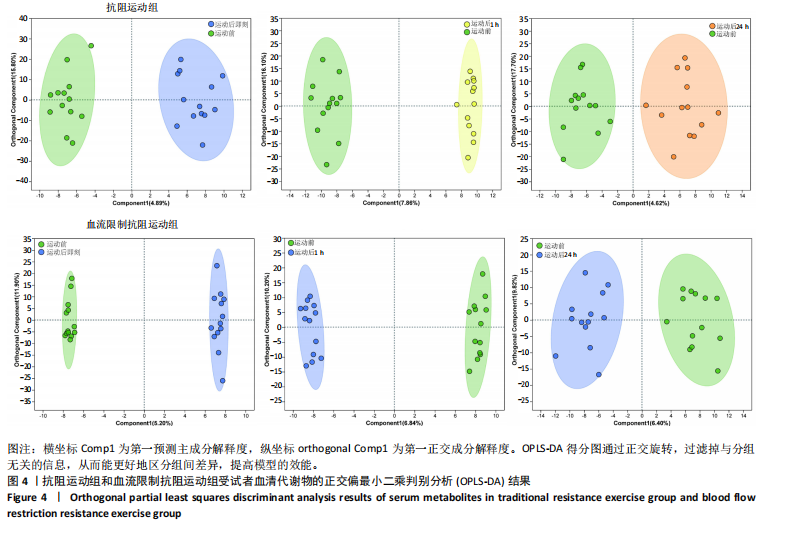
方式的运动前、运动后即刻、运动后1 h和运动后24 h均区分较明显,各组数据点有良好的聚类效果,表明数据稳定性和重复性良好,具有较高数据质量。 2.3 OPLS-DA 运用OPLS-DA建立了不同运动方式下不同时间点的分类模型(图4),结果显示两种运动方式下不同时间点之间明显相互分离,组内相互靠近。对各组的OPLS-DA模型进行置换检验(图5),结果显示R2均大于0.5且高于左侧所有点,说明模型具有较为理想的解释能力;Q2的回归线与纵轴的截距均为负,说明模型未出现过拟合,具有较为可靠的预测能力。血流限制抗阻运动在运动后即刻诱导了十分明显的代谢变化,且在随后的1 h内持续显著。抗阻运动诱导的代谢变化则从运动前持续增加,在运动后1 h达到顶峰,呈现与血流限制抗阻运动组程度相同的特征。此外,两组代谢变化均在运动后24 h出现明显恢复。 2.4 差异代谢物的筛选 为分析两组具体的代谢物差异,进一步以 VIP > 1、P < 0.05 和 LogFC > 1 的标准筛选了干预后各时间点差异代谢物。结果显示(图6),血流限制抗阻运动组在运动后即刻共出现46种差异代谢物,其中25种出现显著上调,21种出现显著下调;在运动后1 h共出现87种差异代谢物,其中52种显著上调,35种显著下调;在运动后24 h共出现42种差异代谢物,其中19种显著上调,23种显著下调。抗阻运动组在运动后即刻共出现29种差异代谢物,其中8种显著上调,21种显著下调;在运动后1 h共出现41种差异代谢物,其中13种显著上调,28种显著下调;在运动后24 h仅发现4种差异代谢物,均为显著上调。 2.5 两种运动方式对青年肥胖男性脂质、糖类、氨基酸代谢物及通路的影响差异 按脂质、糖类、氨基酸3类物质对各组差异代谢物进行分类,并对照KEGG数据库比对各差异代谢物参与的出现显著富集的主要代谢通路(表3,4)。结果显示,仅在抗阻运动组发现2种糖类代谢物,在运动后即刻,D-半乳糖和甘油均显著下降,显著富集在半乳糖代谢通路;在运动后1 h,D-半乳糖和甘油则显著上升,显著富集在脂肪细胞脂解的调节通路和半乳糖代谢通路。"
对于脂质代谢物,抗阻运动组仅在运动后24 h检测到4种脂类差异代谢物,包含山嵛酸、肉豆蔻酸、亚油酸、棕榈酸,显著富集在不饱和脂肪酸的生物合成通路、支链氨基酸合成通路、基底细胞癌通路、矿物质吸收通路、HIF-1信号通路、胰高血糖素信号通路、糖酵解/糖异生通路、丙酸代谢通路。在血流限制抗阻运动组中,所有时间点显著变化的脂类代谢物均为甘油磷脂。在运动后即刻,1种磷脂酰乙醇胺出现显著下降;在运动后1 h,1种磷脂酰乙醇胺、2种磷脂酰丝氨酸出现显著上升;在运动后24 h,2种磷脂酰胆碱、2种磷脂酰乙醇胺以及1种磷脂酰丝氨酸均显著上升。 对于氨基酸类代谢物,两组显著变化均只发生于运动后1 h内。在抗阻运动组中,3种氨基酸(L-组氨酸,L-羟脯氨酸和L-谷氨酸)在运动后即刻显著下降,显著富集在肿瘤中心碳代谢通路、精氨酸和脯氨酸代谢通路、D-谷氨酰胺和D-谷氨酸代谢通路、逆行内源性大麻素信号通路和胰高血糖素信号通路;L-组氨酸在运动后1 h显著上升,显著富集在肿瘤中心碳代谢通路和ABC转运蛋白通路。在血流限制抗阻运动组中,L-天门冬氨酸和L-酪氨酸在运动后即刻显著下降,显著富集在肿瘤中心碳代谢通路、β-丙氨酸代谢通路、丙氨酸、天门冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢通路、泛酸和CoA生物合成通路、精氨酸生物"
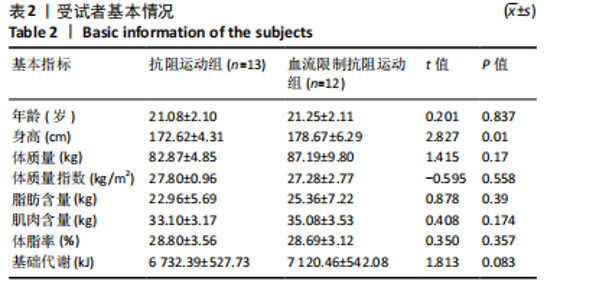
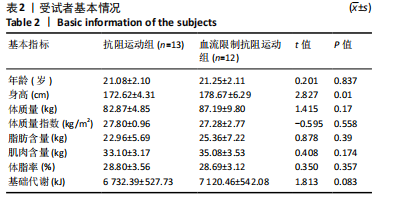
| [1] 陈伟,江华.2016年中国超重/肥胖医学营养治疗专家共识解读[J].中国实用内科杂志,2017,37(5):430-433. [2] LANDECHO MF, MARIN-OTO M, RECALDE-ZAMACONA B, et al. Obesity as an adipose tissue dysfunction disease and a risk factor for infections - Covid-19 as a case study. Eur J Intern Med. 2021;91:3-9. [3] SAGHAFI-ASL M, ALIASGHARZADEH S, ASGHARI-JAFARABADI M. Factors influencing weight management behavior among college students: An application of the Health Belief Model. PLoS One. 2020;15(2):e0228058. [4] 王祥全,姜勇,冯志钢,等.国外运动科学领域减肥研究的热点内容及发展趋向[J].武汉体育学院学报,2020,54(6):73-79. [5] 孟怡秀.不同训练方法减脂效果的比较与机理分析[J].体育科技文献通报, 2021,29(6):174-176. [6] MINNITI MC, STATKEVICH AP, KELLY RL, et al. The Safety of Blood Flow Restriction Training as a Therapeutic Intervention for Patients With Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Systematic Review. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(7):1773-1785. [7] SEGAL N, DAVIS MD, MIKESKY AE. Efficacy of Blood Flow-Restricted Low-Load Resistance Training For Quadriceps Strengthening in Men at Risk of Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2015;6(3):160-167. [8] WANG HN, CHEN Y, CHENG L, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Blood Flow Restriction Training in Patients With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022;74(1): 89-98. [9] 雷森林,张明辉,马春莲,等.加压抗阻训练的肌肉效应、量效关系及生理机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(26):4254-4264. [10] LIXANDRÃO ME, UGRINOWITSCH C, BERTON R, et al. Magnitude of Muscle Strength and Mass Adaptations Between High-Load Resistance Training Versus Low-Load Resistance Training Associated with Blood-Flow Restriction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018;48(2):361-378. [11] SAATMANN N, ZAHARIA OP, LOENNEKE JP, et al. Effects of Blood Flow Restriction Exercise and Possible Applications in Type 2 Diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021;32(2):106-117. [12] SU Y, WANG F, WANG M, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscle fitness and cardiovascular risk of obese college students. Front Physiol. 2024;14:1252052. [13] SAKAGUCHI CA, NIEMAN DC, SIGNINI EF, et al. Metabolomics-Based Studies Assessing Exercise-Induced Alterations of the Human Metabolome: A Systematic Review. Metabolites. 2019;9(8):164. [14] FATOUROS IG, CHATZINIKOLAOU A, TOURNIS S, et al. Intensity of resistance exercise determines adipokine and resting energy expenditure responses in overweight elderly individuals. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(12):2161-2167. [15] SMILIOS I, TSOUKOS P, ZAFEIRIDIS A, et al. Hormonal responses after resistance exercise performed with maximum and submaximum movement velocities. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2014;39(3):351-357. [16] WISHART DS. Metabolomics for Investigating Physiological and Pathophysiological Processes. Physiol Rev. 2019;99(4):1819-1875. [17] 郭新明,吴丽君,向欢.间歇性大强度运动前后人体血清代谢组学特征[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(9):755-761. [18] 李佳.急性大强度运动前后人体血液代谢组学特征的研究[D].太原:山西大学,2017. [19] COHEN J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. Cambrideg: Academic Press, 2013. [20] AMRHEIN V, GREENLAND S, MCSHANE B. Scientists rise up against statistical significance. Nature. 2019;567(7748):305-307. [21] BIAU DJ, KERNÉIS S, PORCHER R. Statistics in brief: the importance of sample size in the planning and interpretation of medical research. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(9):2282-2288. [22] 中华医学会内分泌学分会,中华中医药学会糖尿病分会,中国医师协会外科医师分会肥胖和糖尿病外科医师委员会,等.基于临床的肥胖症多学科诊疗共识(2021年版)[J].中华消化外科杂志,2021,20(11):1137-1152. [23] BULL FC, AL-ANSARI SS, BIDDLE S, et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br J Sports Med. 2020; 54(24):1451-1462. [24] BORG G. Borg’s Perceived Exertion and Pain Scales. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, 1998. [25] AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SPORTS MEDICINE. ACSM’s exercise testing and prescription[M]. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams, 2023. [26] (美)哈夫, (美)特里普利特.NSCA-CSCS美国国家体能协会体能教练认证指南[M]. 北京:人民邮电出版社,2021. [27] 魏佳,李博,冯连世,等.血流限制训练的方法学因素及潜在安全性问题[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(3):3-12. [28] MADARAME H, NEYA M, OCHI E, et al. Cross-transfer effects of resistance training with blood flow restriction. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2008;40(2):258-263. [29] LOENNEKE JP, FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, et al. Effects of cuff width on arterial occlusion: implications for blood flow restricted exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(8):2903-2912. [30] REN Y, YU G, SHI C, et al. Majorbio Cloud: A one-stop, comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses. Imeta. 2022;1(2):e12. [31] MORVILLE T, SAHL RE, MORITZ T, et al. Plasma Metabolome Profiling of Resistance Exercise and Endurance Exercise in Humans. Cell Rep. 2020;33(13):108554. [32] KNUIMAN P, HOPMAN MT, MENSINK M. Glycogen availability and skeletal muscle adaptations with endurance and resistance exercise. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015;12:59. [33] 崔益玮,王利敏,戴志远,等.脂质组学在食品科学领域的研究现状与展望[J].中国食品学报,2019,19(1):262-270. [34] 倪致雅,唐苗苗,夏瑢.基于色谱质谱联用技术的中医痰湿体质的代谢组学研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2017,35(4):918-923. [35] MILLER JM, COYLE EF, SHERMAN WM, et al. Effect of glycerol feeding on endurance and metabolism during prolonged exercise in man. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1983;15(3):237-242. [36] VAN ROSENDAL SP, OSBORNE MA, FASSETT RG, et al. Physiological and performance effects of glycerol hyperhydration and rehydration. Nutr Rev. 2009; 67(12):690-705. [37] YOON SY, AHN D, JI YH, et al. Linoleic acid exerts antidiabetic effects by inhibiting protein tyrosine phosphatases associated with insulin resistance. J Funct Foods. 2021;83:104532. [38] MARANGONI F, AGOSTONI C, BORGHI C, et al. Dietary linoleic acid and human health: Focus on cardiovascular and cardiometabolic effects. Atherosclerosis. 2020;292:90-98. [39] YANG L, GUAN G, LEI L, et al. Palmitic acid induces human osteoblast-like Saos-2 cell apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018;23(6):1283-1294. [40] AMINE H, BENOMAR Y, TAOUIS M. Palmitic acid promotes resistin-induced insulin resistance and inflammation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):5427. [41] 刘如灿,金青哲,单良,等.山嵛酸低热量油脂的可用热量及安全性评价[J].中国粮油学报,2011,26(8):26-30. [42] IWATA K, SAKAI H, TAKAHASHI D, et al. Myristic acid specifically stabilizes diacylglycerol kinase δ protein in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2019;1864(7):1031-1038. [43] SAKAI H, MATSUMOTO KI, URANO T, et al. Myristic acid selectively augments β-tubulin levels in C2C12 myotubes via diacylglycerol kinase δ. FEBS Open Bio. 2022;12(10):1788-1796. [44] TREEDE I, BRAUN A, SPARLA R, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of phosphatidylcholine. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(37):27155-27164. [45] LAGACE TA. Phosphatidylcholine: Greasing the Cholesterol Transport Machinery. Lipid Insights. 2016;8(Suppl 1):65-73. [46] XIAO D, CHANG W. Phosphatidylserine in Diabetes Research. Mol Pharm. 2023; 20(1):82-89. [47] TIAN S, ZHAO Y, QIAN L, et al. DHA-enriched phosphatidylserine alleviates high fat diet-induced jejunum injury in mice by modulating gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2023;14(3):1415-1429. [48] WILLIS SJ, MILLET GP, BORRANI F. Insights for Blood Flow Restriction and Hypoxia in Leg Versus Arm Submaximal Exercise. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2020;15(5):714-719. [49] 吴鹤云,张悦,蒋帅,等.木糖和葡萄糖共发酵生产L-组氨酸[J].食品与发酵工业,2020,46(16):115-120. [50] BROSNAN ME, BROSNAN JT. Histidine Metabolism and Function. J Nutr. 2020; 150(Suppl 1):2570S-2575S. [51] VICENT D, GARCIA-MARTINEZ JA, VILLANUEVA-PEÑACARRILLO ML, et al. Stimulation of insulin secretion and potentiation of glibenclamide-induced insulin release by the dimethyl ester of glutamic acid in anaesthetized rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1995;27(1):27-30. [52] POORTMANS JR, CARPENTIER A, PEREIRA-LANCHA LO, et al. Protein turnover, amino acid requirements and recommendations for athletes and active populations. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2012;45(10):875-890. [53] 李宝成,张怡,熊正英.补充酪氨酸对运动能力影响的可能机制[J].北京体育大学学报,2007(1):68-70. [54] 贾青慧,陈莉,王珍,等.薏米及薏米糠氨基酸组成分析及营养评价[J].食品工业,2017,38(4):185-188. [55] 李登光,倪伟,高伟.天门冬氨酸钾镁消除运动疲劳的作用机制[J].首都体育学院学报,2005(6):52-54. |
| [1] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [3] | Zhou Ying, Tian Yong, Zhong Zhimei, Gu Yongxiang, Fang Hao. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 regulates mTORC1/ULK1 signaling and promotes autophagy to improve myocardial injury in sepsis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6434-6440. |
| [4] | Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Central anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of tea polyphenols in exercise fatigue model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6474-6481. |
| [5] | Sun Rongyan, Xu Luchun, Jiang Guozheng, Song Jiawei, Ma Yukun, Fan Jiaojiao, Wang Guanlong, Yang Yongdong, Yu Xing. Du Meridian electroacupuncture inhibits ferroptosis and promotes neurorepair in rats with acute cervical spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6228-6238. |
| [6] | Chen Lijuan, Gao Xinxue, Wu Jin, Du Ying, Lyu Meijun, Sui Guoyuan, Jia Lianqun, Pan Guowei. Construction and evaluation of spleen-deficiency hyperlipidemia mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6237-6242. |
| [7] | Du Juan, Zhang Yi, Hao Quanshui. Effects of exercise on activation of microglia and astrocytes and neuronal apoptosis in depressed rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6243-6248. |
| [8] | Zhang Ziyu, Chen Longhao, Sheng Wei, Lyu Hanzhe, Shen Ying, Wang Binghao, Lyu Zhizhen, Lyu Lijiang. Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation: evolution towards standardization, efficiency, and precision of diagnosis and treatment methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6269-6276. |
| [9] | Chai Jinlian, Sun Tiefeng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Li Guangzheng, Zhou Zhongqi, Liang Xuezhen, Wang Ping. Therapeutic effect of Cornus Cervi Colla on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rat models: fecal metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6187-6197. |
| [10] | Wu Xiaochou, Wang Huiying, Wang Jie, Zhang Caifeng, Hou Yanyun, Jin Bo. Protective mechanism of tanshinone IIA in mouse ovarian cryopreservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6198-6204. |
| [11] | Song Yuting, Wen Chunlei, Li Yi, Bai Xue, Gao Hong, Hu Tingju, Wang Zijun, Yan Xu. Effects of myocardial extracellular matrix remodeling on connexin 43 and its Ser368 phosphorylation and electrical conduction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6212-6218. |
| [12] | Liu Ruojing, Zhao Xue, Zhu Yizhen, Fu Lingling, Zhu Junde. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in mice by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6219-6227. |
| [13] | Chen Xiaoqing, Gong Yunzhao, Chen Wei. Association of the controlling nutritional status score and systemic immune-inflammation index with postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5071-5078. |
| [14] | Wang Zhifeng, Yang Jiao, Xi Yujiang, Xu Shuangfeng, Shi Ting, Lan Junfeng, Hao Zhihui, He Pengfen, Yang Aiming, Pan Pan, Wang Jian. Biomarkers affecting the progression of mild to moderate cognitive impairment after stroke: #br# a non-targeted metabolomics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5116-5126. |
| [15] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: data analysis of serum metabolite and inflammatory factor in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5263-5271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||