Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (24): 5263-5271.doi: 10.12307/2025.758
Previous Articles Next Articles
Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: data analysis of serum metabolite and inflammatory factor in the European population
Zhang Yibo1, Lu Jianqi2, Mao Meiling1, Pang Yan1, Dong Li1, Yang Shangbing1, Xiao Xiang1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Cardiology, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-10-10Accepted:2024-11-16Online:2025-08-28Published:2025-02-06 -
Contact:Lu Jianqi, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Cardiology, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Yibo, Master’s candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China Regional Fund, No. 82160887 (to LJQ); The Second Batch of Scientific Research Projects for the Business Construction of the National Clinical Research Base of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. JDZX2015146 (to LJQ); National Traditional Chinese Medicine Inheritance and Innovation Center Project, No. 2023019-10 (to LJQ); Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2021GXNSFAA220111 (to LJQ); Guangxi Qihuang Scholar Training Project, No. 2024005-06-02 (to LJQ); Guangxi Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Self-funded Research Project, No. GXZYA20230065 (to LJQ); Key Discipline of High-Level Traditional Chinese Medicine in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region - Traditional Chinese Medicine Cardiology, No. 2024016-02-02 (to LJQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: data analysis of serum metabolite and inflammatory factor in the European population[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5263-5271.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
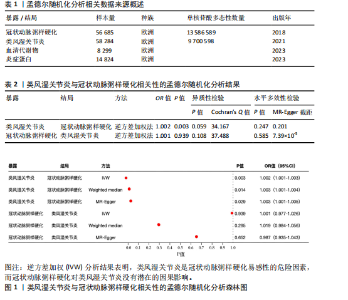
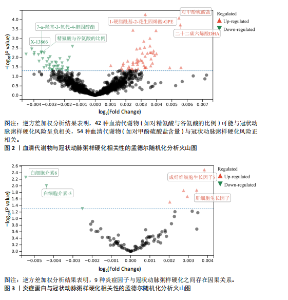
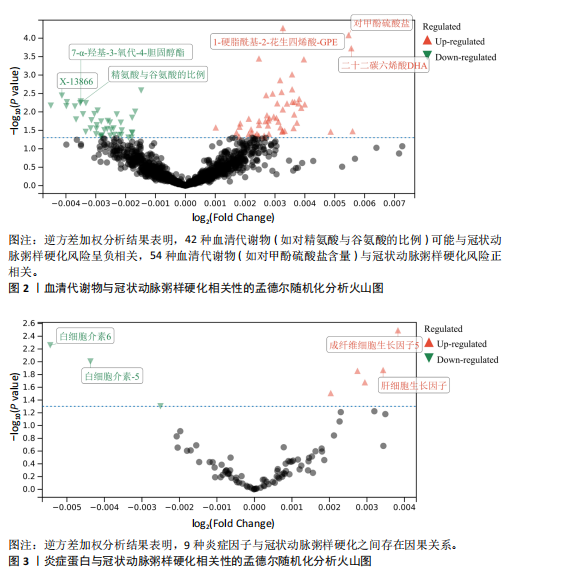
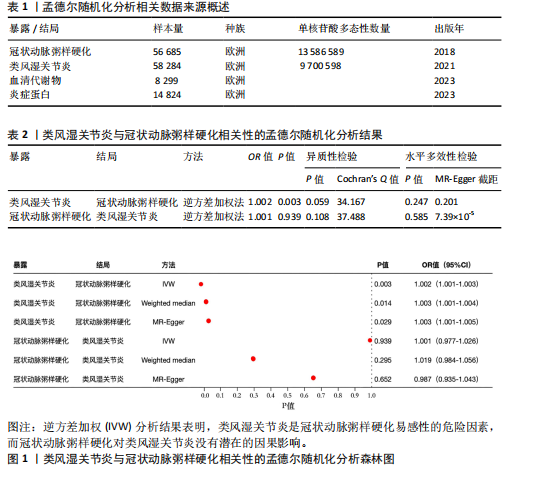
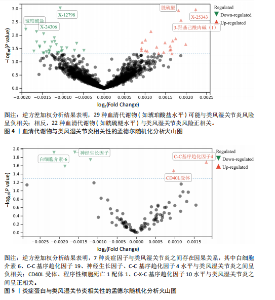
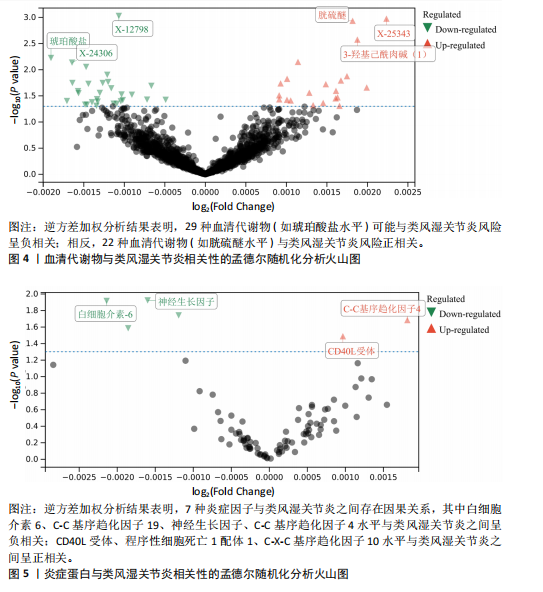
2.1 工具变量 最初提取与类风湿关节炎和冠状动脉粥样硬化相关的所有单核苷酸多态性,然后根据工具变量的特定标准进行筛选,排除潜在的数据偏差,最终54个单核苷酸多态性被纳入工具变量。以血清代谢物作为暴露,确定了33 421个与冠状动脉粥样硬化相关的单核苷酸多态性和32 268个与类风湿关节炎相关的单核苷酸多态性关于炎症因子,选择了2 695个与冠状动脉粥样硬化相关的单核苷酸多态性和2 719个与抑郁症相关的单核苷酸多态性。 2.2 孟德尔随机化分析结果 2.2.1 类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化的相关性 类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化相关性的孟德尔随机化结果,见图1所示。逆方差加权分析结果表明,类风湿关节炎是冠状动脉粥样硬化易感性的危险因素(OR=1.002,95%CI=1.001-1.003,P=0.003),加权中位数法(OR=1.003,95%CI= 1.001-1.004,P=0.014)、MR-Egger方法(OR=1.003,95%CI=1.001-1.005,P= 0.029)分析结果也表明类风湿关节炎是冠状动脉粥样硬化易感性的危险因素。另外还进行了反向孟德尔随机化研究,以探讨冠状动脉粥样硬化与类风湿关节炎之间是否存在相关性,逆方差加权分析结果表明,冠状动脉粥样硬化对类风湿关节炎没有潜在的因果影响(OR=1.001,95%CI=0.977-1.026,P=0.939),见表2。 2.2.2 血清代谢物与冠状动脉粥样硬化的相关性 逆方差加权分析结果表明,42种血清代谢物(如对精氨酸与谷氨酸的比例)(P=0.006,OR=0.996,95%CI=0.994-0.999)可能与冠状动脉粥样硬化风险呈负相关,54种血清代谢物(如对甲酚硫酸盐含量)(P= 8.28×10-5,OR=11.005,95%CI=1.003-1.008)与冠状动脉粥样硬化风险正相关,见图2。 2.2.3 炎症蛋白与冠状动脉粥样硬化的相关性 逆方差加权分析结果表明,9种炎症因子与冠状动脉粥样硬化之间存在因果关系,其中成纤维细胞生长因子5(P=0.003,OR=1.004,95%CI=1.001-1.006)、肝细胞生长因子(P=0.014,OR=1.003,95%CI=1.001-1.006)、Fms相关酪氨酸激酶3配体(P=0.014,OR=1.003,95%CI=1.001-1.005)、C-C基序趋化因子28 (P=0.021,OR=1.003,95%CI=1.000-1.006)、C-C基序趋化因子4 (P=0.021,OR=1.003,95%CI=1.000-1.006)、抑瘤素M(P=0.031,OR=1.004,95%CI=1.000-1.008)水平可增加冠状动脉粥样硬化患病风险;白细胞介素6 (P=0.006,OR=0.995,95%CI=0.991-0.998)、白细胞介素5 (P=0.010,OR=0.996,95%CI=0.992-0.999)、青蒿素(P=0.050,OR=0.998,95%CI=0.995-0.100)水平可在基因水平上降低冠状动脉粥样硬化患病风险,见图3。 2.2.4 血清代谢物与类风湿关节炎的相关性 逆方差加权分析结果表明,29种血清代谢物(如琥珀酸盐水平,P=0.006,OR=0.998,95%CI=0.997-0.100)可能与类风湿关节炎风险呈负相关;相反,22种血清代谢物(如胱硫醚水平,P=0.001,OR=1.002,95%CI=1.001-1.003)与类风湿关节炎风险正相关,见图4。"
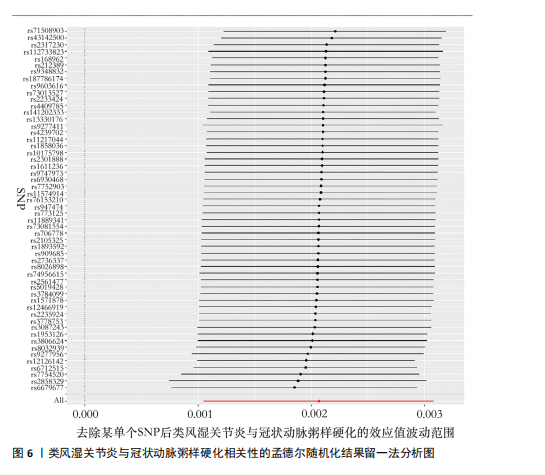
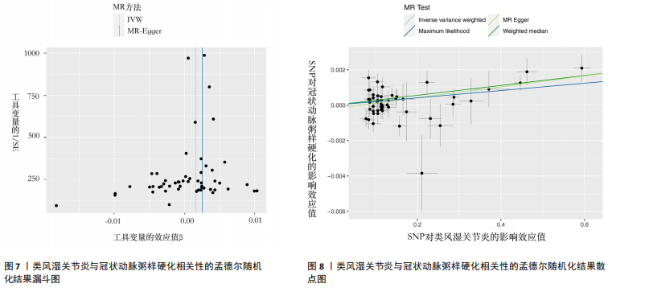
2.2.5 炎症蛋白与类风湿关节炎的相关性 逆方差加权分析结果表明,7种炎症因子与类风湿关节炎之间存在因果关系,见图5。其中,4种炎症因子与类风湿关节炎之间呈负向因果关系,白细胞介素6(P=0.012,OR=0.998,95%CI=0.996-0.100)、C-C基序趋化因子19(P=0.026,OR=0.998,95%CI= 0.997-0.100)、神经生长因子(P=0.012,OR=0.998,95%CI=0.997-0.100)、C-C基序趋化因子4(P=0.018,OR=0.999,95%CI=0.998-0.100)水平与类风湿关节炎之间呈负相关。CD40L受体(P=0.032,OR=1.001,95%CI=1.000-1.002)、程序性细胞死亡1配体1(P=0.021,OR=1.002,95%CI=1.000-1.003)、C-X-C基序趋化因子10(P=0.015,OR=1.002,95%CI= 1.000-1.003)水平与类风湿关节炎之间呈正相关。 2.3 敏感性分析结果 2.3.1 类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化相关性的敏感性分析结果 采用MR-Egger法的截距项对水平多效性进行评估,结果显示类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化相关性的孟德尔随机化分析中未获得水平多效性的证据(P=0.247,MR-Egger截距=0.201)。敏感性Cochran’s Q检验结果表明,类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化相关性的孟德尔随机化分析中不存在异质性(基于逆方差加权法P= 0.059、Q=34.167,基于MR-Egger法P=0.074,Q=49.842),见表2。 反向孟德尔随机化分析结果显示,冠状动脉粥样硬化与类风湿关节炎相关性的孟德尔随机化分析中未获得水平多效性的证据(P=0.585,MR-Egger截距=7.39×10-5)。敏感性Cochran’s Q 检验结果表明,冠状动脉粥样硬化与类风湿关节炎相关性的孟德尔随机化分析中不存在异质性(基于逆方差加权法P=0.108、Q=37.488,基于MR-Egger法P=0.094、Q=37.069),见表2。 通过留一法逐个剔除,未见明显影响结果的单核苷酸多态性,见图6。漏斗图显示代表因果关系的效应点呈对称分布,见图7,表示受潜在偏倚影响的可能性较少;此外,散点图(图8)和漏斗图排除了潜在异常值和水平多效性的可能性。敏感性分析进一步"

排除了异质性和水平多效性的影响,证明了结果的稳健性。 2.3.2 血清代谢物与冠状动脉粥样硬化相关性的敏感性分析结果 采用MR-Egger法的截距项对水平多效性进行评估,结果显示鞘磷脂(P=0.029,MR-Egger截距=0.002)、二十二碳六烯酸DHA(P=0.036,MR-Egger截距=-0.001)、1-硬脂酰基-2-吲哚甲酰基-GPI (P=0.036,MR-Egger截距= 0.001)、N-乙酰基异嘌呤(P=0.039,MR-Egger截距=-0.001)、N-乙酰牛磺酸(P=0.040,MR-Egger截距=-0.001)水平存在潜在水平多效性,其余血清代谢物均不存在水平多效性。敏感性Cochran’s Q 检验结果表明,27种代谢物存在异质性(基于逆方差加权法P < 0.05),其余69种代谢物不存在异质性,表明所选工具变量具有可靠性。 2.3.3 炎症蛋白与冠状动脉粥样硬化相关性的敏感性分析结果 采用MR-Egger法的截距项对水平多效性进行评估,未发现水平多效性的存在。敏感性Cochran’s Q 检验结果表明,成纤维细胞生长因子5(基于逆方差加权法P=3.03×10-8、Q=95.546,基于MR-Egger 法P=1.71×10-8、Q=95.505)、抑瘤素M(基于逆方差加权法 P= 0.010、Q=42.879,基于MR-Egger法 P=0.011、Q=41.408)、Fms相关酪氨酸激酶3配体(基于逆方差加权法P= 0.045、Q=61.090,基于MR-Egger法P=0.043、Q=60.198)水平存在异质性,仅有3种炎症蛋白存在潜在异质性,表明结果仍具有稳健性。 2.3.4 血清代谢物与类风湿关节炎相关性的敏感性分析结果 采用MR-Egger法的截距项对水平多效性进行评估,结果显示2-甲氧基间苯二酚硫酸盐含量(P=0.009,MR-Egger截距=-0.000)、1-硬脂酰基-2-油酰基-GPI(P=0.018,MR-Egger截距=-0.001)、胱氨酸(P=0.032,MR-Egger截距= 0.000)、5-α-孕烷-3-β,2-β二醇单硫酸盐1(P=0.038,MR-Egger截距= 0.000)水平存在潜在水平多效性,其余血清代谢物均不存在水平多效性。敏感性Cochran’s Q检验结果表明,3-(4-羟基苯基)乳酸(基于逆方差加权法P=0.016、Q=41.188,基于MR-Egger法 P=0.013、Q=40.750)、1-硬脂酰-2-油酰基-GPI(基于逆方差加权法P=0.016、Q=41.188,基于法MR-Egger P=0.122、Q=27.497)水平存在异质性,其余血清代谢物均不存在异质性,证明了结果的可靠性。 2.3.5 炎症蛋白与类风湿关节炎相关性的敏感性分析结果 采用MR-Egger法的截距项对水平多效性进行评估,程序性细胞死亡1配体1 (P=0.050,MR-Egger截距=-0.000)水平存在潜在水平多效性,其余炎症蛋白均不存在水平多效性。敏感性Cochran’s Q检验结果表明,C-C基序趋化因子19(基于逆方差加权法 P=8.36×10-8、Q=99.094,基于MR-Egger法P=3.06×10-7、Q=93.584)、C-C基序趋化因子10(基于逆方差加权法P=0.001、Q=61.901,基于MR-Egger法P=0.001、Q=60.594)、C-C基序趋化因子4(基于逆方差加权法P=0.005、Q=56.294,基于MR-Egger法P=0.004、Q=56.244)水平存在异质性,程序性细胞死亡1配体1、白细胞介素6、CD40L受体、神经生长因子水平均不存在显著的异质性。"

| [1] CAI Y, ZHANG J, LIANG J, et al. The Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Findings from the 2019 Global Burden of Diseases Study and Forecasts for 2030 by Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort Analysis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(4):1291. [2] BACKLUND RT, DRAKE I, BERGSTROM U, et al. Adherence to Dietary Guidelines, and the Risk of Developing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from a Nested Case-control Study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024;63(2):407-413. [3] GU P, PU B, LIU T, et al. Appraising Causal Risk and Protective Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Bone. Joint Res. 2023;12(9):601-614. [4] ALEXANDRE A, SA-COUTO D, BRANDAO M, et al. Subclinical Left Ventricular Dysfunction in. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Findings from the Prospective Porto-RA Cohort. Clin Res Cardiol. 2024. doi:10.1007/s00392-024-02548-6. [5] LYU Q, MA L, LIU H, et al. Meta-analysis of Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(45): e35912. [6] VOS TLS AC. Global Incidence, Prevalence, Years Lived with Disability (YLDs), Disability-adjusted Life-years (DALYs), and Healthy Life Expectancy (HALE) for 371 Diseases and Injuries in 204 Countries and Territories and 811 Subnational Locations, 1990-2021: a Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet. 2024; 403(10440):2133-2161. [7] CORRAO S, CALVO L, GIARDINA A, et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis, Cardiometabolic Comorbidities, and Related Conditions: Need to Take Action. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1421328. [8] POUDEL S, GHIMIRE M, SHRESTHA K, et al. Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on Hospitalized. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: Study of Demographics, Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes. Cureus. 2024;16(7):e65011. [9] KLINGENBERG R, LUSCHER TF. Rheumatoid Arthritis and Coronary Atherosclerosis: Two Cousins. Engaging in a Dangerous Liaison. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(48):3423-3425. [10] LOVERGROVE CE, HOWLES SA, FURNISS D, et al. Causal Inference in Health and Disease: a Review of the Principles and Applications of Mendelian Randomization. J Bone Miner Res. 2024;39(11):1539-1552. [11] MARCHEV AS, VASILEVA LV, AMIROVA KM, et al. Metabolomics and Health: from Nutritional Crops. and Plant-based Pharmaceuticals to Profiling of Human Biofluids. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(19-20): 6487-6503. [12] PSYCHOGIOS N, HAU DD, PENG J, et al. The Human Serum Metabolome. PLoS One. 2011;6(2):e16957. [13] GUPTA V, WALIA GK, SACHDEVA MP. ‘Mendelian Randomization’: an Approach for Exploring Causal. Relations in Epidemiology. Public Health. 2017;145:113-119. [14] BURGESS S, CRONJE HT. Incorporating Biological and Clinical Insights into Variant Choice for Mendelian Randomisation: Examples and Principles. eGastroenterology. 2024;2(1):e100042. [15] CAO Y, YANG Y, HU Q, et al. Identification of Potential Drug Targets for Rheumatoid Arthritis from Genetic Insights: a Mendelian Randomization Study. J Transl Med. 2023; 21(1):616. [16] ARNETT FC, EDWORTHY SM, BLOCH DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 Revised. Criteria for the Classification of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31(3):315-324. [17] CHEN Y, LU T, PETTERSSON-KYMMER U, et al. Genomic Atlas of the Plasma Metabolome Prioritizes. Metabolites Implicated in Human Diseases. Nat Genet. 2023;55(1):44-53. [18] ZHAO JH, STACEY D, ERIKSSON N, et al. Author Correction: Genetics of Circulating Inflammatory. Proteins Identifies Drivers of Immune-mediated Disease Risk and Therapeutic Targets. Nat Immunol. 2023; 24(11):1960. [19] BURGESS S, SMALL DS, THOMPSON SG. A Review of Instrumental Variable Estimators for Mendelian. Randomization. Stat Methods Med Res. 2017;26(5):2333-2355. [20] DALAL T, PATEL CJ. PYPE: A Pipeline for Phenome-wide Association and Mendelian Randomization in Investigator-driven Biobank Scale Analysis. Patterns (N Y). 2024; 5(6):100982. [21] TIAN H, PATEL A, BURGESS S. Estimating Time-Varying Exposure Effects Through Continuous-Time. Modelling in Mendelian Randomization. Stat Med. 2024.doi: 10.1002/sim.10222. [22] GRANT AJ, BURGESS S. A Bayesian Approach to Mendelian Randomization Using Summary Statistics in the Univariable and Multivariable Settings with Correlated Pleiotropy. Am J Hum Genet. 2024;111(1):165-180.
[23] QIAN Y, HE Z, ZHAO SS, et al. Genetically Determined Circulating Levels of Cytokines and the Risk of. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Genet. 2022;13:802464. [24] BURGESS S, BOEDEN J, FALL T, et al. Sensitivity Analyses for Robust Causal Inference from Mendelian. Randomization Analyses with Multiple Genetic Variants. Epidemiology. 2017;28(1):30-42. [25] KARPOUZAS GA, ESTIS J, REZAEIAN P, et al. High-sensitivity Cardiac Troponin I is a Biomarker for. Occult Coronary Plaque Burden and Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(6):1080-1088. [26] LOGSTRUP BB, OLESEN K, MASIC D, et al. Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on Major Cardiovascular Events in Patients with and without Coronary Artery Disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(9):1182-1188. [27] AMBROSINO P, LUPOLI R, DI MINNO A, et al. Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Patients with Rheumatoid. Arthritis. A Meta-analysis of Literature Studies. Thromb Haemost. 2015;113(5):916-930. [28] BEDEKOVIC D, BOSNJAK I, ŠARIC S, et al. Role of Inflammatory Cytokines in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Development of Atherosclerosis: A Review. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(9):1550. [29] BOETERS DM, BURGERS LE, TOES RE, et al. Does Immunological Remission, Defined as Disappearance of Autoantibodies, Occur with Current Treatment Strategies? A Long-term Follow-up Study in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients who Achieved Sustained DMARD-free Status. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019; 78(11):1497-1504. [30] PACCOU J, BOUDOT C, RENARD C, et al. Total Calcium-sensing Receptor Expression in Circulating Monocytes is Increased in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Severe Coronary Artery Calcification. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):412. [31] MANGONI AA, TOMMASI S, SOTGIA S, et al. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine: a Key Player in the Pathophysiology of Endothelial Dysfunction, Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis? Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(18):2131-2140. [32] KIM EY, MOUDGIL KD. Immunomodulation of Autoimmune Arthritis by Pro-inflammatory Cytokines. Cytokine. 2017;98: 87-96. [33] SERDAR CC, CIHAN M, YUCEL D, et al. Sample size, Power and Effect Size Revisited: Simplified and. Practical Approaches in Pre-clinical, Clinical and Laboratory Studies. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2021;31(1):10502. [34] AIT-OUFELLA H, LIBBY P. Inflammation and Atherosclerosis: Prospects for Clinical Trials. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2024; 44(9):1899-1905. [35] OISHI Y, MANABE I. Macrophages in Age-related Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2016;2:16018. [36] WANG C, LIU S, YANG Y, et al. Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-17 are Associated with Coronary Artery Disease. Clin Cardiol. 2024; 47(2):e24188. [37] HANNA A, FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines as Therapeutic Targets in Heart Failure. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2020;34(6):849-863. [38] BLAGOV AV, CHUROV AV, GOLOVYUK AL, et al. The Role of Metabolic Disorders in the Development of Atherosclerosis. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2024;70(9):148-155. [39] SOLER PB, ESTRADA-CAPETILLO L, IZQUIERDO E, et al. Macrophages from the Synovium of Active. Rheumatoid Arthritis Exhibit an Activin A-dependent Pro-inflammatory Profile. J Pathol. 2015; 235(3):515-526. [40] CHEN W, FANG Y, WANG H, et al. Role of Chemokine Receptor 2 in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Research. Update. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;116:109755. [41] PARK E, IQBAL R, GILES JT, et al. Use of Methotrexate and TNF Inhibitors in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis-associated Interstitial Lung Disease: a Survey of Rheumatologists. Clin Rheumatol. 2024; 43(9):3029-3032. [42] KARPOUZAS GA, ORMSETH SR, HERNANDEZ E, et al. Impact of Cumulative Inflammation, Cardiac. Risk Factors, and Medication Exposure on Coronary Atherosclerosis Progression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(3):400-408. [43] YIN X, ZHANG Y, ZOU J, et al. Association of the Systemic Immune-inflammation Index with All-cause and Cardiovascular Mortality in Individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):15129. [44] FERT-BOBER J, DARRAH E, ANDRADE F. Insights into the Study and Origin of the Citrullinome in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2020;294(1):133-147. [45] ALMEIDA-SANTIAGO C, QUEVEDO-ABELEDO JC, HERNANDEZ V, et al. Circulating Interleukin-6 and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Low Disease Activity due to Active Therapy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2023;41(7):1537-1543. [46] ROUBILLE C, RICHER V, STARNINO T, et al. The Effects of Tumour Necrosis Factor Inhibitors, Methotrexate, Mon-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Corticosteroids on Cardiovascular Events in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(3):480-489. [47] ZHANG J, XIE F, YUN H, et al. Comparative Effects of Biologics on Cardiovascular Risk among Older Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(10): 1813-1818. [48] FERRAZ-AMARO I, GONZALEZ-GAY MA, GARCRIA -DOPICO JA, et al. Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2013; 40(7):1040-1047. [49] BARBATI C, VOMERO M, COLASANTI T, et al. TNFα Expressed on the Surface of Microparticles Modulates Endothelial Cell Fate in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):273. [50] ZIMMERMAN MC, CLEMENS DL, DURYEE MJ, et al. Direct Antioxidant Properties of Methotrexate: Inhibition of Malondialdehyde-acetaldehyde-protein Adduct Formation and Superoxide Scavenging. Redox Biol. 2017;13:588-593. [51] DAVIDA L, PONGRACZ V, MOHAMED EA, et al. A Prospective, Longitudinal Monocentric Study on Laser Doppler Imaging of Microcirculation: Comparison with Macrovascular Pathophysiology and Effect of Adalimumab Treatment in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2020; 40(3):415-424. |
| [1] | Zou Rongji, Yu Fangfang, Wang Maolin, Jia Zhuopeng. Triptolide inhibits ferroptosis and improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model of cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 873-881. |
| [2] | Chen Xiaoqing, Bian Luyao, Lu Xingyu, Yang Tao, Li Xiang Hai. Thread embedding pretreatment at Xinshu (BL 15) improves cardiac function of acute myocardial ischemia rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 882-891. |
| [3] | Wang Mingqi, Feng Shiya, Han Yinhe, Yu Pengxin, Guo Lina, Jia Zixuan, Wang Xiuli. Construction and evaluation of a neuralized intestinal mucosal tissue engineering model in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 892-900. |
| [4] | Wang Jie, Huang Rui, Zhang Ye, Shou Zhaoxi, Yao Jie, Liu Chenxi, Liao Jian. Role and mechanism of probiotics in peri-implantitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 901-907. |
| [5] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [6] | Yu Shiyu, Yu Sutong, Xu Yang, Zhen Xiangyan, Han Fengxuan. Advances in research and application of tissue engineering therapeutic strategies in oral submucous fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 936-948. |
| [7] | Jin Zhiyong, Wang Yufeng, Zhao Binjie, Xiong Minquan, Yan Li. Effects of inter-limb asymmetry on athletic performance from the perspective of bilateral limb control strategy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 949-963. |
| [8] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [9] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [10] | Yan Chengbo, Luo Qiuchi, Fan Jiabing, Gu Yeting, Deng Qian, Zhang Junmei. Effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on orthodontic tooth movement and bone microstructure parameters on the tension side in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 824-831. |
| [11] | Xu Shencong, Fang Zifei, Ji Mingyi, Xu Chengrui, Li Binhong, Cao Jiayu, Xu Junfeng. Application of Onlay bone grafts from mandibular lateral oblique line in implant restoration of bone defects in upper anterior teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 841-848. |
| [12] | Ma Hong, Ding Xueling, Wang Qi, Lyu Hui, Asya Albusm, Cheng Xinyi, Ma Xiang. Expression and significance of tumor necrosis factor alpha, nuclear factor kappaB and ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule-1 in the hippocampus of mice with aortic dissection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 858-863. |
| [13] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [14] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [15] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||