Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (32): 5757-5764.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.32.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Induction ways of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into nerve cells
Chen Zeng-sheng1, Chu Qiang2, Liu Yan-feng3, Song Xuan4, Li Ping5
- 1 Department of Laboratory, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
2 Department of Ultrasound, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
3 Department of Laboratory, Sifang District Hospital, Qingdao 266033, Shandong Province, China
4 Department of Blood Transfusion, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China
5 Department of Blood Transfusion, Affiliated Hospital, Medical School of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2013-05-11Revised:2013-06-22Online:2013-08-06Published:2013-08-06 -
Contact:Li Ping, Master, Technician-in-charge, Department of Blood Transfusion, Affiliated Hospital, Medical School of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China lpxkck@126.com -
About author:Chen Zeng-sheng★, Master, Technician, Department of Laboratory, Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266071, Shandong Province, China Redapple_02@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Zeng-sheng, Chu Qiang, Liu Yan-feng, Song Xuan, Li Ping. Induction ways of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into nerve cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(32): 5757-5764.
share this article

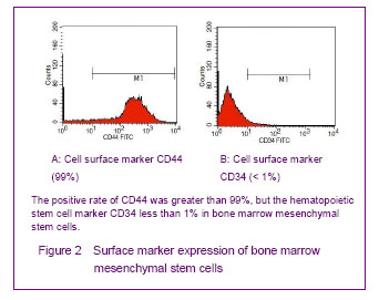
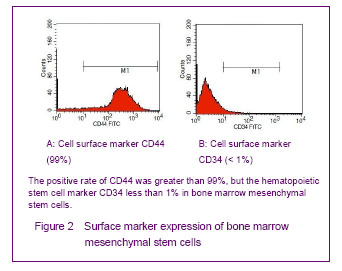
Morphology of cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells Lots of erythrocytes covered the entire bottom of culture flask with whole bone marrow culture after inoculation. A large number of blood cells were removed after low glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium was changed at the first time, scattered adherent cells could be seen in the bottom of the bottle, with fusiform or polygonal appearance, and uneven part was a whirlpool-like growth. The formation of multiple fibroblast-like cell clusters could be seen after 6 or 8 days, few round cells could be seen around the cell clusters. Fibroblast-like growth was pooled into a piece after 12 or 16 days. Adherent cells were long spindle-shaped after passage for 2-3 days. Primary cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells had a multiple differentiation potential and maintained a higher purity over 90% after repeated passages[22-23, 25-26] (Figure 1)."

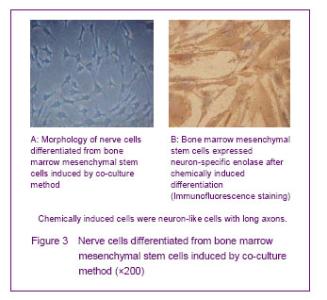
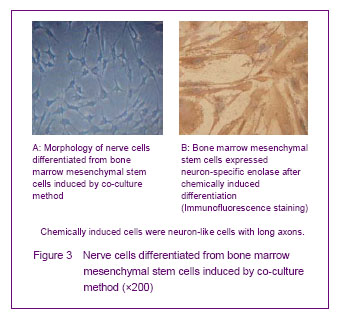
Co-culture and chemical induction methods for inducing differentiation into nerve cells Most of the cultured nerve cells grew adherent, and the cell body was full and fusiform, withshining brilliantly cytoplasm. Small protrusions were visible in the cell body for 2 or 3 days. Glial cell body was flat and had slightly larger size, and one or four short rod protrusions were around the cell body. The nerve cell bodies grew larger, and rounded protrusions around the cell body were longer and increased to form a unipolar, bipolar or multipolar projection for 6 days. Nerve cells inoculated in the 6-well plates of Transwell co-culture system, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were found to have pyknosis smaller than flat cells. Formerly, most of the cell bodies had rounded protrusion formation, and cells gradually became long stellate for 3 days. The stellate cells gradually increased, and could cross each other to form a connection with a neuron-like morphology (Figure 3) for 4 or 5 days. Neural-like cells accounted for 62.4% of the total cells. Immunofluorescence results showed Neuron-specific enolase positive rate was (60.47± 1.89)%, suggesting the performance characteristics of neurons (Figure 3). Most of the cells were still flat and wide long spindle-shaped similar as morphology characteristics of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and did not form a neuron-like morphology in the control group after cultured for 8 days. Neuron-specific enolase was also negative in the control group."
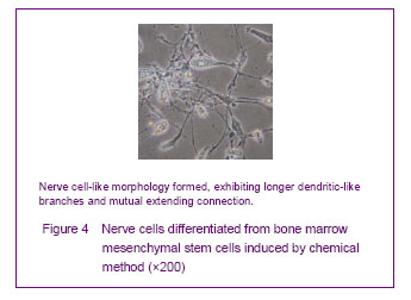
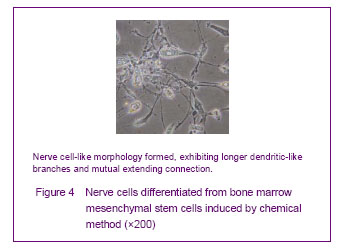
Chemically induced culture results Cells showed adherent growth after 1-3 days in the chemically induced group, and no obvious morphological changes were observed. The cell body significantly shrank and a circle or a triangle extended at 4 days. Some cells formed longer dendritic-like branches, and mutual extending connection; some cells were similar to neurons, and the long axons appeared to render the nerve cell-like morphology (Figure 4) at 5-6 days. Nerve cells accounted for 50.4% of the total cells, and the positive rate for neuron-specific enolase was (40.91± 1.63)%."
| [1] Lin L, Fu X, Zhang X, et al. Rat adipose-derived stromal cells expressing BMP4 induce ectopic bone formation in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2006;27(12): 1608-1615.[2] Tao H, Rao R, Ma DD. Cytokine-induced stable neuronal differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a serum/feeder cell-free condition. Dev Growth Differ. 2005;47(6):423-433.[3] Tang Y, Yasuhara T, Hara K, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived stem cells: a promising therapy for stroke. Cell Transplant. 2007;16(2):159-169.[4] Bang OY, Lee JS, Lee PH, et al. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in stroke patients. Ann Neurol. 2005; 57(6):874-882.[5] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[6] Sanchez-Ramos J, Song S, Cardozo-Pelaez F, et al. Adult bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neural cells in vitro. Exp Neurol. 2000;164(2):247-256.[7] Kopen GC, Prockop DJ, Phinney DG. Marrow stromal cells migrate throughout forebrain and cerebellum, and they differentiate into astrocytes after injection into neonatal mouse brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(19): 10711-10716.[8] Buzańska L, Machaj EK, Zab?ocka B, et al. Human cord blood-derived cells attain neuronal and glial features in vitro. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 10):2131-2138.[9] Lei Z, Yongda L, Jun M, et al. Culture and neural differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 2007;31(9):916-923. [10] Jin K, Mao XO, Batteur S, et al. Induction of neuronal markers in bone marrow cells: differential effects of growth factors and patterns of intracellular expression. Exp Neurol. 2003;184(1):78-89.[11] Choong PF, Mok PL, Cheong SK, et al. Generating neuron-like cells from BM-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Cytotherapy. 2007;9(2):170-183.[12] Li Y, Chopp M, Chen J, et al. Intrastriatal transplantation of bone marrow nonhematopoietic cells improves functional recovery after stroke in adult mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000;20(9):1311-1319.[13] Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Therapeutic benefit of intracerebral transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurol Sci. 2001;189(1-2): 49-57.[14] Chopp M, Zhang XH, Li Y, et al. Spinal cord injury in rat: treatment with bone marrow stromal cell transplantation. Neuroreport. 2000;11(13):3001-3005.[15] Mahmood A, Lu D, Yi L, et al. Intracranial bone marrow transplantation after traumatic brain injury improving functional outcome in adult rats. J Neurosurg. 2001;94(4):589-595.[16] Schwarz EJ, Alexander GM, Prockop DJ, et al. Multipotential marrow stromal cells transduced to produce L-DOPA: engraftment in a rat model of Parkinson disease. Hum Gene Ther. 1999;10(15):2539-2549.[17] Mezey E, Chandross KJ, Harta G, et al. Turning blood into brain: cells bearing neuronal antigens generated in vivo from bone marrow. Science. 2000;290(5497):1779-1782.[18] Brazelton TR, Rossi FM, Keshet GI, et al. From marrow to brain: expression of neuronal phenotypes in adult mice. Science. 2000;290(5497):1775-1779.[19] Park KW, Eglitis MA, Mouradian MM. Protection of nigral neurons by GDNF-engineered marrow cell transplantation. Neurosci Res. 2001;40(4):315-323.[20] Ogawa S. Biochemical and immunological laboratory findings in Kawasaki disease. Nihon Rinsho. 2008;66(2):315-320.[21] Azizi SA, Stokes D, Augelli BJ, et al. Engraftment and migration of human bone marrow stromal cells implanted in the brains of albino rats--similarities to astrocyte grafts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(7):3908-3913.[22] Yang NL, Yang F, Xu LL. Differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neurons induced by neural cells by co-culture method. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;11(29):5611-5614.[23] Kuo CK, Tuan RS. Tissue engineering with mesenchymal stem cells. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2003;22(5):51-56.[24] Jia XJ, Sun XJ, Xu LL. Differentiation of hnman bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes under a cerltain inicroenvironment. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(34):6635-6638.[25] Shin M, Yoshimoto H, Vacanti JP. In vivo bone tissue engineering using mesenchymal stem cells on a novel electrospun nanofibrous scaffold. Tissue Eng. 2004;10 (1-2):33-41.[26] Lu P, Blesch A, Tuszynski MH. Induction of bone marrow stromal cells to neurons: differentiation, transdifferentiation, or artifact? J Neurosci Res. 2004;77(2):174-191.[27] Xu LL, Yang NL. Differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts in vitro. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12 (38): 7483-7486.[28] Wu B, Wu YC, Zheng QX, et al. The proliferation, adhesion and induced differentiation into neurocytes of bone marrow stromal cells on IKVAV peptide nanofiber gel. Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2007;9(8):740-744.[29] Chu K, Kim M, Park KI, et al. Human neural stem cells improve sensorimotor deficits in the adult rat brain with experimental focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2004;1016(2): 145-153.[30] Andrews EM, Tsai SY, Johnson SC, et al. Human adult bone marrow-derived somatic cell therapy results in functional recovery and axonal plasticity following stroke in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2008;211(2):588-592. [31] Castro RF, Jackson KA, Goodell MA, et al. Failure of bone marrow cells to transdifferentiate into neural cells in vivo. Science. 2002;297(5585):1299.[32] Terada N, Hamazaki T, Oka M, et al. Bone marrow cells adopt the phenotype of other cells by spontaneous cell fusion. Nature. 2002;416(6880):542-545. [33] Park KS, Lee YS, Kang KS. In vitro neuronal and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood. J Vet Sci. 2006;7(4):343-348.[34] Battula VL, Bareiss PM, Treml S, et al. Human placenta and bone marrow derived MSC cultured in serum-free, b-FGF-containing medium express cell surface frizzled-9 and SSEA-4 and give rise to multilineage differentiation. Differentiation. 2007;75(4):279-291. [35] Kögler G, Sensken S, Airey JA, et al. A new human somatic stem cell from placental cord blood with intrinsic pluripotent differentiation potential. J Exp Med. 2004;200(2):123-135.[36] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [3] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [4] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [5] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [6] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [7] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [8] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [9] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [10] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [11] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [12] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [13] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [14] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [15] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||