Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (29): 4593-4598.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2810
Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes apoptosis in long bone-like cells via ERK1/2 signaling pathway
Shi Fangfu, Cui Hongwang, Sun Bo
- Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570102, Hainan Province, China
-
Received:2019-11-18Revised:2019-11-21Accepted:2020-02-19Online:2020-10-18Published:2020-09-11 -
Contact:Cui Hongwang, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570102, Hainan Province, China -
About author:Shi Fangfu, Attending physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570102, Hainan Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province, No. 817326
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Fangfu, Cui Hongwang, Sun Bo. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes apoptosis in long bone-like cells via ERK1/2 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4593-4598.
share this article
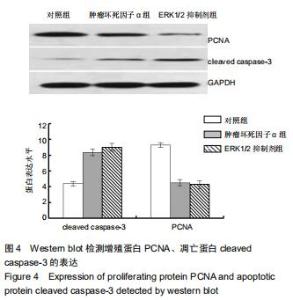
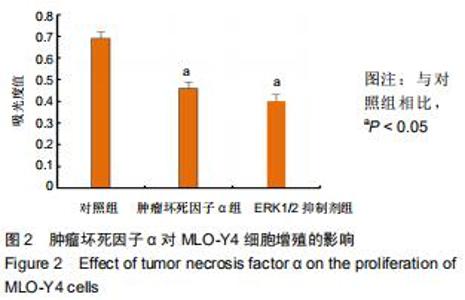
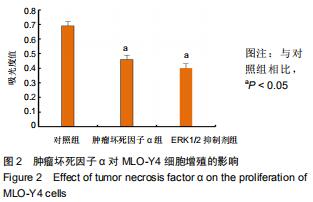
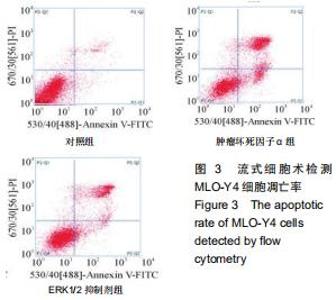
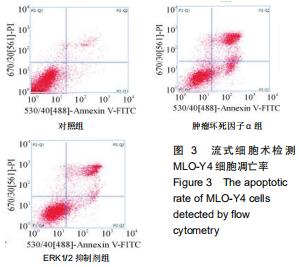
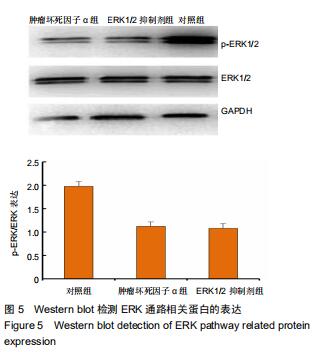
2.5 Western blot检测增殖、凋亡蛋白和ERK通路相关蛋白的表达 为了分析肿瘤坏死因子α抑制细胞增殖、促进细胞凋亡的作用机制,采用Western blot检测增殖、凋亡蛋白和ERK通路相关蛋白的表达,结果显示,与对照组相比,肿瘤坏死因子α组和ERK1/2抑制剂组细胞增殖相关蛋白PCNA的表达显著降低,细胞凋亡相关蛋白cleaved caspase-3的表达显著升高。当50 μg/L肿瘤坏死因子α和ERK1/2抑制剂组处理MLO-Y4细胞24 h可明显抑制p-ERK1/2的表达,而总蛋白ERK1/2的表达基本保持不变,与对照组比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图4,5。 "
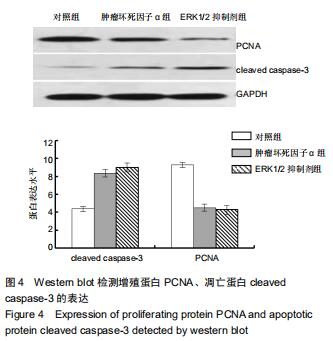
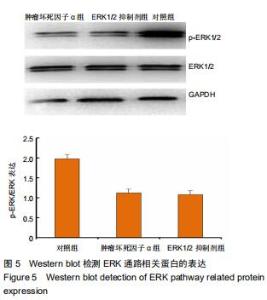
2.5 Western blot检测增殖、凋亡蛋白和ERK通路相关蛋白的表达 为了分析肿瘤坏死因子α抑制细胞增殖、促进细胞凋亡的作用机制,采用Western blot检测增殖、凋亡蛋白和ERK通路相关蛋白的表达,结果显示,与对照组相比,肿瘤坏死因子α组和ERK1/2抑制剂组细胞增殖相关蛋白PCNA的表达显著降低,细胞凋亡相关蛋白cleaved caspase-3的表达显著升高。当50 μg/L肿瘤坏死因子α和ERK1/2抑制剂组处理MLO-Y4细胞24 h可明显抑制p-ERK1/2的表达,而总蛋白ERK1/2的表达基本保持不变,与对照组比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图4,5。 "
|
[1] DIAB DL, WATTS NB. Postmenopausal osteoporosis. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013;20(6):501-509.
[2] CHEISHVILI D, PARASHAR S, MAHMOOD N, et al. Identification of an Epigenetic Signature of Osteoporosis in Blood DNA of Postmenopausal Women. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(11): 1980-1989. [3] COLLINS KH, HERZOG W, MACDONALD GZ, et al. Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Musculoskeletal Disease: Common Inflammatory Pathways Suggest a Central Role for Loss of Muscle Integrity. Front Physiol. 2018;9:112.
[4] ZERBINI CAF, CLARK P, MENDEZ-SANCHEZ L, et al. Biologic therapies and bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoporos Int. 2017; 28(2):429-446.
[5] MARCOVITZ PA, TRAN HH, FRANKLIN BA, et al. Usefulness of bone mineral density to predict significant coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 2005;96(8):1059-1063.
[6] FONTOVA R, GUTIÉRREZ C, VENDRELL J, et al. Bone mineral mass is associated with interleukin 1 receptor autoantigen and TNF-alpha gene polymorphisms in post-menopausal Mediterranean women. J Endocrinol Invest. 2002;25(8):684-690.
[7] PARRA-ROJAS I, RUÍZ-MADRIGAL B, MARTÍNEZ-LÓPEZ E, et al. Influence of the -308 TNF-alpha and -174 IL-6 polymorphisms on lipid profile in Mexican subjects. Hereditas. 2006;143(2006): 167-172.
[8] KATO Y, WINDLE JJ, KOOP BA, et al. Establishment of an osteocyte-like cell line, MLO-Y4. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12(12): 2014-2023.
[9] BONEWALD LF. Establishment and characterization of an osteocyte-like cell line, MLO-Y4. J Bone Miner Metab. 1999;17(1): 61-65.
[10] CHEN W, MA Y, YE H,et al. ERK1/2 is involved in cyclic compressive force-induced IL-6 secretion in MLO-Y4 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;401(3):339-343.
[11] 李洋,康倩,荣婵,等.骨碎补总黄酮对MLO-Y4细胞增殖、分化、矿化和凋亡影响的探究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(5):592-598.
[12] KITASE Y, BARRAGAN L, QING H, et al. Mechanical induction of PGE2 in osteocytes blocks glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis through both the β-catenin and PKA pathways. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(12): 2657-2668.
[13] WEHMEIER KR, KURBAN W, CHANDRASEKHARAN C, et al. Inhibition of ABCA1 Protein Expression and Cholesterol Efflux by TNF α in MLO-Y4 Osteocytes. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016;98(6): 586-595.
[14] 林煜,卢天祥,吴银生,等.健骨颗粒促进成骨细胞增殖的分子机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(15):2677-2684.
[15] KOLF CM, CHO E, TUAN RS. Mesenchymal stromal cells. Biology of adult mesenchymal stem cells: regulation of niche, self-renewal and differentiation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(1):204.
[16] TAVAZOIE M, VAN DER VEKEN L, SILVA-VARGAS V, et al. A specialized vascular niche for adult neural stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(3):279-288.
[17] 王有为.炎性因子TNF-α对SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[D].沈阳:中国医科大学, 2015.
[18] 蒙超龙,王祥,段建民,等.肿瘤坏死因子-α对人牙周膜干细胞的增殖及成骨分化的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2018,28(2):63-68.
[19] 安龙,续惠云,瓮媛媛,等.小鼠骨样细胞MLO-Y4转染方法的研究[J].生物学杂志,2010,27(6):87-90.
[20] WATERS KM, JACOBS JM, GRITSENKO MA, et al. Regulation of gene expression and subcellular protein distribution in MLO-Y4 osteocytic cells by lysophosphatidic acid: Relevance to dendrite outgrowth. Bone. 2011;48(6):1328-1335.
[21] 何银锋,赵理平,赵国阳,等.高铁环境下成骨细胞增殖和凋亡与氧化应激的关系[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2012,5(2): 125-129.
[22] LI DY, YU JC, XIAO L, et al. Autophagy attenuates the oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of Mc3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(24):5548-5556.
[23] 李冰,王军爱.ERK信号通路对人表皮干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(45):6807-6813. [24] BILAL S, JAGGI S, JANOSEVIC D, et al. ZO-1 protein is required for hydrogen peroxide to increase MDCK cell paracellular permeability in an ERK 1/2-dependent manner. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018;315(3):C422-C431.
[25] LIU D, LIANG X, ZHANG H. Effects of High Glucose on Cell Viability and Differentiation in Primary Cultured Schwann Cells: Potential Role of ERK Signaling Pathway. Neurochem Res. 2016; 41(6):1281-1290.
[26] 钟海波,郭祥,黄琳惠.葛根素通过ERK1/2和p38 MAPK信号通路刺激成骨分化和骨形成的机制[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2019,29(2):78-83.
[27] WU X, LI S, XUE P, et al. Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, facilitates osteogenic proliferation and differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells through phosphoinositide 3-kinase(PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT), extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)1/2, and cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathways involving β-catenin. Exp Cell Res. 2017;360(2):281-291.
[28] BLAGOSKLONNY MV, SCHULTE T, NGUYEN P, et al. Taxol-induced apoptosis and phosphorylation of Bcl-2 protein involves c-Raf-1 and represents a novel c-Raf-1 signal transduction pathway. Cancer Res. 1996;56(8):1851-1854.
[29] WANG W, GOU X, XUE H, et al. Ganoderan (GDN) Regulates The Growth, Motility And Apoptosis Of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through ERK Signaling Pathway In Vitro And In Vivo. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:8821-8832.
[30] YEH YH, LIANG CY, CHEN ML, et al. Apoptotic effects of hsian-tsao (Mesona procumbens Hemsley) on hepatic stellate cells mediated by reactive oxygen species and ERK, JNK, and caspase-3 pathways. Food Sci Nutr. 2019;7(5):1891-1898.
[31] LOU M, ZHANG LN, JI PG, et al. Quercetin nanoparticles induced autophagy and apoptosis through AKT/ERK/Caspase-3 signaling pathway in human neuroglioma cells: In vitro and in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84:1-9.
[32] TSUDA Y, KANJE M, DAHLIN LB. Axonal outgrowth is associated with increased ERK 1/2 activation but decreased caspase 3 linked cell death in Schwann cells after immediate nerve repair in rats. BMC Neurosci. 2011;12:12.
[33] TIAN C, CHANG H, LA X, et al. Wushenziye Formula Inhibits Pancreatic β Cell Apoptosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via MEK-ERK-Caspase-3 Signaling Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2018;2018:4084259.
[34] HU Y, LIU K, BO S, et al. Inhibitory effect of puerarin on vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation induced by oxidised low-density lipoprotein via suppressing ERK 1/2 phosphorylation and PCNA expression. Pharmazie.2016;71(2):89-93.
[35] LI B, WANG F, LIU N, et al. Astragaloside IV inhibits progression of glioma via blocking MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;491(1):98-103.
[36] ZHENG W, SUN R, YANG L, et al. Daidzein inhibits choriocarcinoma proliferation by arresting cell cycle at G1 phase through suppressing ERK pathway in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(4):2518-2524.
[37] ZHANG J, XIONG L, TANG W, et al. Hypoxic culture enhances the expansion of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells via the regulatory pathways of cell division and apoptosis. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018;54(9):666-676.
[38] LI B, LI C, ZHU M, et al. Hypoxia-Induced Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Exhibit an Enhanced Therapeutic Effect on Radiation-Induced Lung Injury in Mice due to an Increased Proliferation Potential and Enhanced Antioxidant Ability. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(4):1295-1310.
[39] PARK B, YIM JH, LEE HK, et al. Ramalin inhibits VCAM-1 expression and adhesion of monocyte to vascular smooth muscle cells through MAPK and PADI4-dependent NF-kB and AP-1 pathways. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2015;79(4):539-552. [40] WANG Z, NIU Q, PENG X, et al. Mitofusin 2 ameliorates aortic remodeling by suppressing ras/raf/ERK pathway and regulating mitochondrial function in vascular smooth muscle cells. Int J Cardiol. 2015;178:165-167. |
| [1] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [2] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [3] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [5] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [6] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [7] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [8] | Zhang Wenwen, Jin Songfeng, Zhao Guoliang, Gong Lihong. Mechanism by which Wenban Decoction reduces homocysteine-induced apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [9] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [10] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [11] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [12] | Zhou Jihui, Yao Meng, Wang Yansong, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Influence of novel nanoscaffolds on biological behaviors of neural stem cells and the related gene expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 532-536. |
| [13] | Su Liping, Lu Ziyang, Liu Li, Zhang Wei, Su Tianyuan, Hu Xiayun, Pu Hongwei, Han Dengfeng. C-jun, Cytc and Caspase-9 in the apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons induced by diacetylmorphine in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3943-3948. |
| [14] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [15] | Zhou Wu, Wang Binping, Wang Yawen, Cheng Yanan, Huang Xieshan. Transforming growth factor beta combined with bone morphogenetic protein-2 induces the proliferation and differentiation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3630-3635. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||