Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (24): 3925-3930.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2722
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of efficacy of oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss after total knee and hip arthroplasties
Lin Jiebin1, Shi Yuling1, Gao Fenghe1, Liang Zujian1, 2
- 1Third School of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510240, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2019-11-20Revised:2019-11-22Accepted:2019-12-26Online:2020-08-28Published:2020-08-17 -
Contact:Liang Zujian, MD, Chief physician, Third School of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; the Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510240, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Lin Jiebin, Master candidate, Third School of Clinical Medicine, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2018A0303130103
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Jiebin, Shi Yuling, Gao Fenghe, Liang Zujian. Meta-analysis of efficacy of oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss after total knee and hip arthroplasties[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3925-3930.
share this article

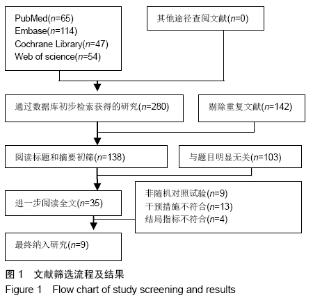
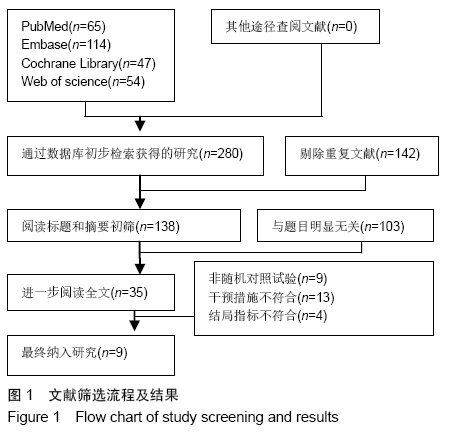
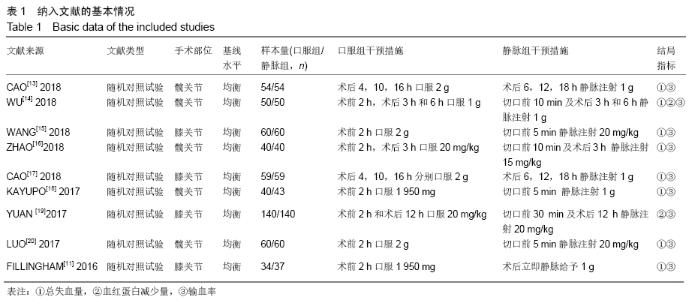
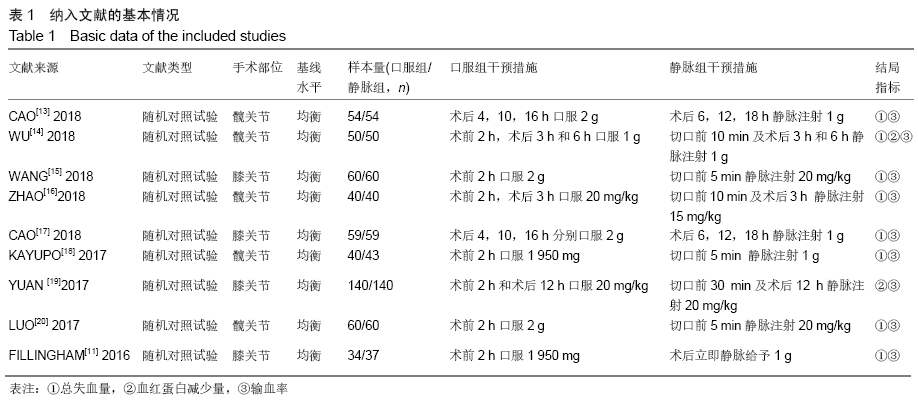
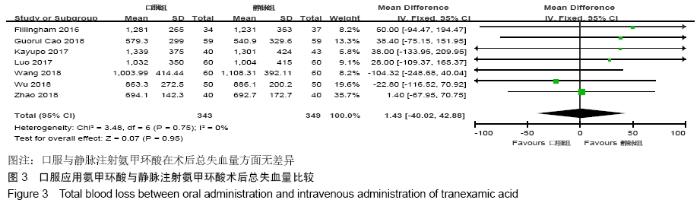
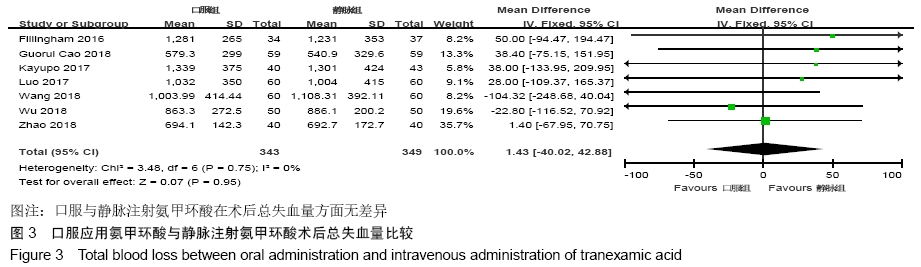
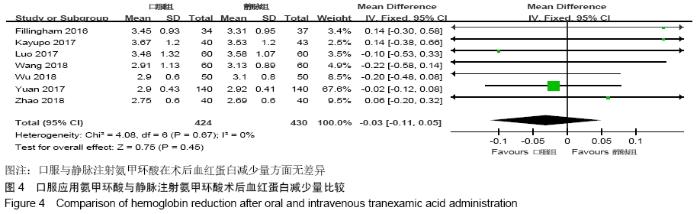
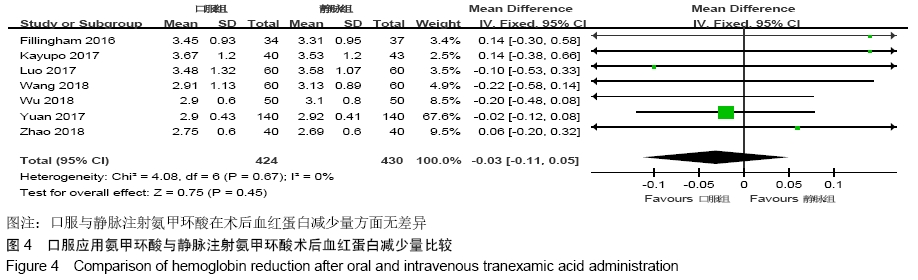
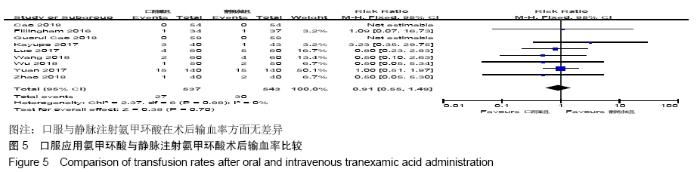
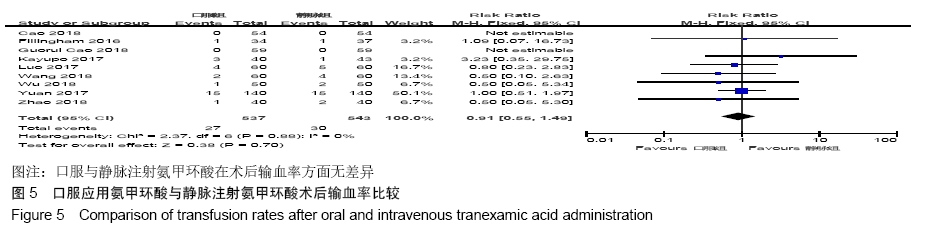
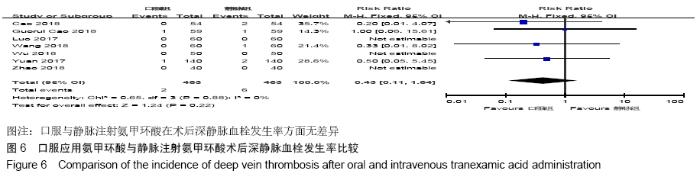
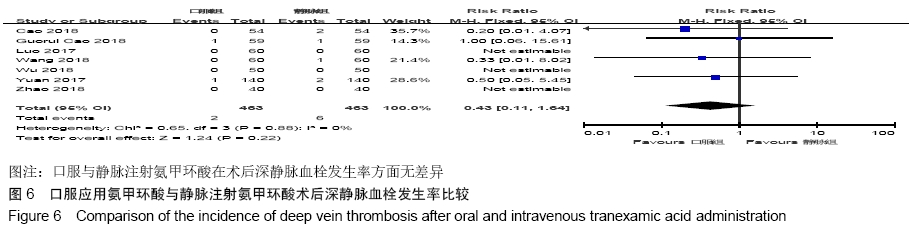
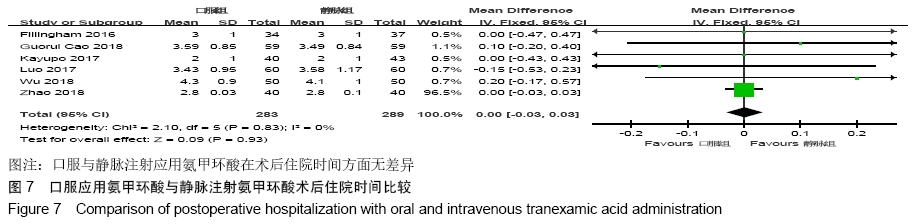
2.2 纳入文献质量总体评价 根据此次研究制定的纳入和排出标准,全面检索数据库后共纳入高质量的随机对照研究共9篇[11,13-20],包括患者1 080例,其中口服组537例,静脉组543例。纳入的研究均对患者的基线资料进行了对比,包括性别、年龄、体质量指数、基础疾病和置换前血红蛋白水平等,差异均无显著性意义。采用“Cochrane”推荐使用的偏倚风险评估工具对全部纳入的文献质量及偏倚风险进行评估。所有文献均为随机对照试验,均提及隐藏方案及实施盲法。4项为包括空白对照或局部用药的试验[15-16,19-20] ;9项研究全部提及了深静脉血栓的预防方式[11,13-20],其中6项研究使用低分子肝素预防深静脉血栓[13-17,20],2项研究使用华法林预防深静脉血栓[18,11],1项研究使用利伐沙班预防深静脉血栓[19],见图2。 "

| [1] KURTZ SM, ONG KL, LAU E, et al. Impact of the economic downturn on total joint replacement demand in the United States: updated projections to 2021. JBJS. 2014;96(8):624-630. [2] KURTZ S, ONG K, LAU E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. JBJS. 2007;89(4):780-785. [3] GIBON E, COURPIED JP, HAMADOUCHE M. Total joint replacement and blood loss: what is the best equation? Int Orthop. 2013;37(4): 735-739. [4] HALLSTROM B, SINGAL B, COWEN ME, et al. The Michigan experience with safety and effectiveness of tranexamic acid use in hip and knee arthroplasty. JBJS. 2016;98(19):1646-1655. [5] KIM JL, PARK JH, HAN S, et al. Allogeneic blood transfusion is a significant risk factor for surgical-site infection following total hip and knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(1): 320-325. [6] LEVINE BR, HAUGHOM B, STRONG B, et al. Blood management strategies for total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014; 22(6): 361-371. [7] BIERBAUM BE, CALLAGHAN JJ, GALANTE JO, et al. An analysis of blood management in patients having a total hip or knee arthroplasty. JBJS. 1999; 81(1): 2-10. [8] KALAIRAJAH Y, SIMPSON D, COSSEY AJ, et al. Blood loss after total knee replacement: effects of computer-assisted surgery. JBJS. 2005; 87(11):1480-1482. [9] HARRIS RN, MOSKAL JT, CAPPS SG. Does tranexamic acid reduce blood transfusion cost for primary total hip arthroplasty? A case-control study. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(2): 192-195. [10] BENONI G, LETHAGEN S, FREDIN H. The effect of tranexamic acid on local and plasma fibrinolysis during total knee arthroplasty. Thromb Res. 1997;85(3): 195-206. [11] FILLINGHAM YA, KAYUPOV E, PLUMMER DR, et al. The James A. Rand Young Investigator's Award: a randomized controlled trial of oral and intravenous tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: the same efficacy at lower cost? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(9):26-30. [12] LIN ZX, WOOLF SK. Safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness of tranexamic acid in orthopedic surgery. Orthopedics. 2016; 39(2): 119-130. [13] CAO G, HUANG Z, XIE J, et al. The effect of oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss after primary total hip arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Thromb Res. 2018;164: 48-53. [14] WU Y, ZENG Y, HU Q, et al. Blood loss and cost-effectiveness of oral vs intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty: a randomized clinical trial. Thromb Res. 2018;171:143-148. [15] WANG D, WANG HY, CAO C, et al. Tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty without tourniquet: a randomized, controlled trial of oral versus intravenous versus topical administration. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):13579. [16] ZHAO HY, XIANG MY, XIA YY, et al. Efficacy of oral tranexamic acid on blood loss in primary total hip arthroplasty using a direct anterior approach: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2018; 42(11):2535-2542. [17] CAO G, XIE J, HUANG Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of multiple boluses of oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid at reducing blood loss after primary total knee arthroplasty without a tourniquet: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Thromb Res. 2018;171: 68-73. [18] KAYUPOV E, FILLINGHAM YA, OKROJ K, et al. Oral and intravenous tranexamic acid are equivalent at reducing blood loss following total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. JBJS. 2017;99(5): 373-378. [19] YUAN X, LI B, WANG Q, et al. Comparison of 3 routes of administration of tranexamic acid on primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled study. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9): 2738-2743. [20] LUO ZY, WANG HY, WANG D, et al. Oral vs intravenous vs topical tranexamic acid in primary hip arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, controlled study. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(3):786-793. [21] PANTELI M, PAPAKOSTIDIS C, DAHABREH Z, et al. Topical tranexamic acid in total knee replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee. 2013;20(5):300-309. [22] RONDAY HK, TE KOPPELE JM, GREENWALD RA, et al. Tranexamic acid, an inhibitor of plasminogen activation, reduces urinary collagen cross-link excretion in both experimental and rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol.1998;37(1):34-38. [23] KONIG G, HAMLIN BR, WATERS JH. Topical tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion rates in total hip and total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(9): 1473-1476. [24] FU DJ, CHENG C, LIN G, et al. Use of intravenous tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Chin J Traumatol. 2013;16(2):67-76. [25] LEE QJ, CHANG WYE, WONG YC. Blood-sparing efficacy of oral tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017; 32(1):139-142. [26] VEIEN M, SØRENSEN JV, MADSEN F, et al. Tranexamic acid given intraoperatively reduces blood loss after total knee replacement: a randomized, controlled study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2002;46(10): 1206-1211. [27] HIIPPALA S, STRID L, WENNERSTRAND M, et al. Tranexamic acid (Cyklokapron) reduces perioperative blood loss associated with total knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth.1995;74(5):534-537. [28] CAMARASA MA, OLLÉ G, SERRA-PRAT M, et al. Efficacy of aminocaproic, tranexamic acids in the control of bleeding during total knee replacement: a randomized clinical trial. Br J Anaesth. 2006; 96(5):576-582. [29] BENONI G, FREDIN H. Fibrinolytic inhibition with tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and blood transfusion after knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomised, double-blind study of 86 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1996;78(3):434-440. [30] SEOL YJ, SEON JK, LEE SH, et al. Effect of tranexamic acid on blood loss and blood transfusion reduction after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2016;28(3):188-193. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [4] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [5] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [6] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [7] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [8] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [9] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [10] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [11] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [12] | Yuan Jun, Yang Jiafu. Hemostatic effect of topical tranexamic acid infiltration in cementless total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 873-877. |
| [13] | Liu Lihua, Sun Wei, Wang Yunting, Gao Fuqiang, Cheng Liming, Li Zirong, Wang Jiangning. Type L1 steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through femoral head and neck junction decompression by fenestration: a single-center prospective clinical study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 906-911. |
| [14] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [15] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||