Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (9): 1457-1463.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2472
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of radial head arthroplasty versus open reduction and internal fixation for treating radial head fractures
Cheng Caitong1, Han Pengfei1, Wu Taiyong1, Li Jian1, Fu Haijun1, Wang Yushan1, Feng Yi2
- 1Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2the Second Affiliated Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2019-04-16Revised:2019-04-22Accepted:2019-06-22Online:2020-03-28Published:2020-02-13 -
Contact:Feng Yi, MD, Associate chief physician, the Second Affiliated Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Cheng Caitong, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, No. 2015011097
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Caitong, Han Pengfei, Wu Taiyong, Li Jian, Fu Haijun, Wang Yushan, Feng Yi. Meta-analysis of radial head arthroplasty versus open reduction and internal fixation for treating radial head fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1457-1463.
share this article
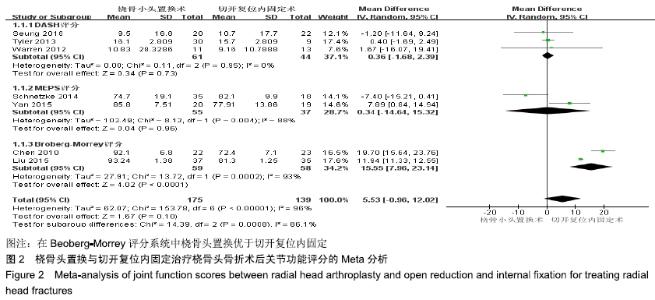
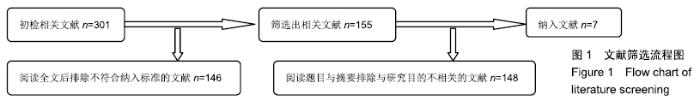
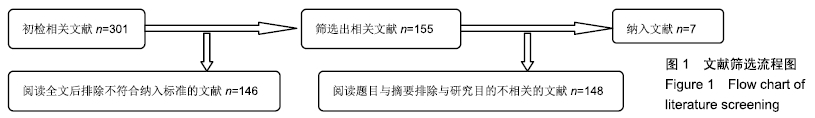
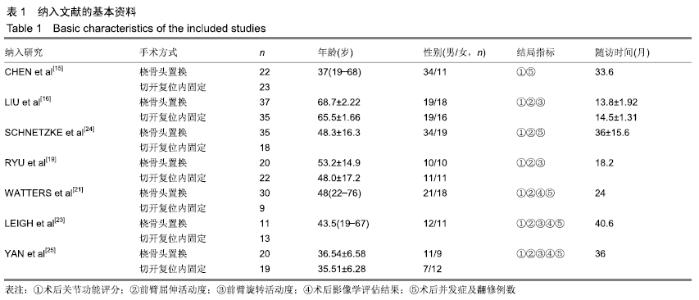
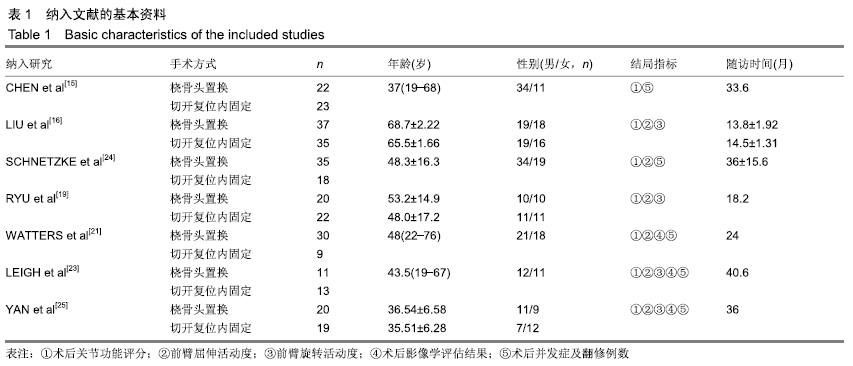
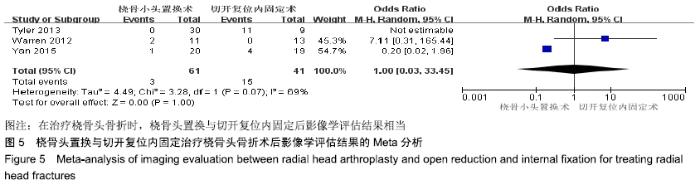
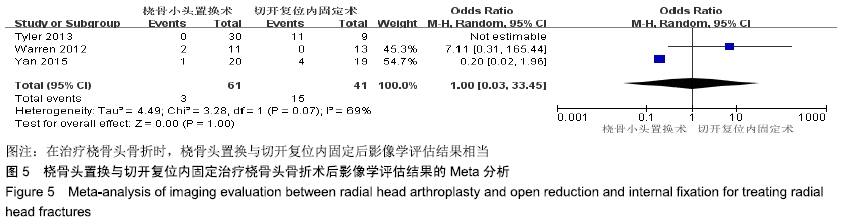
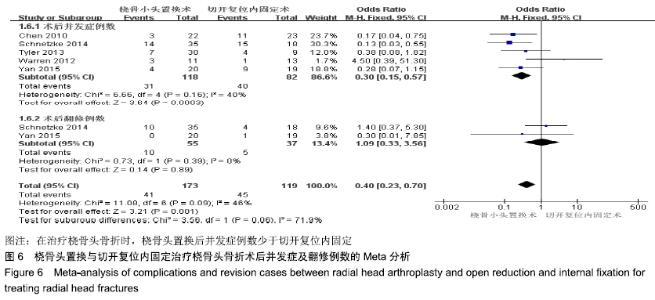
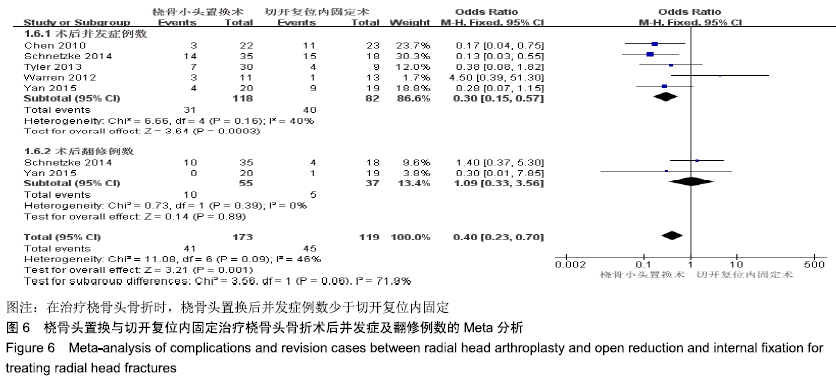
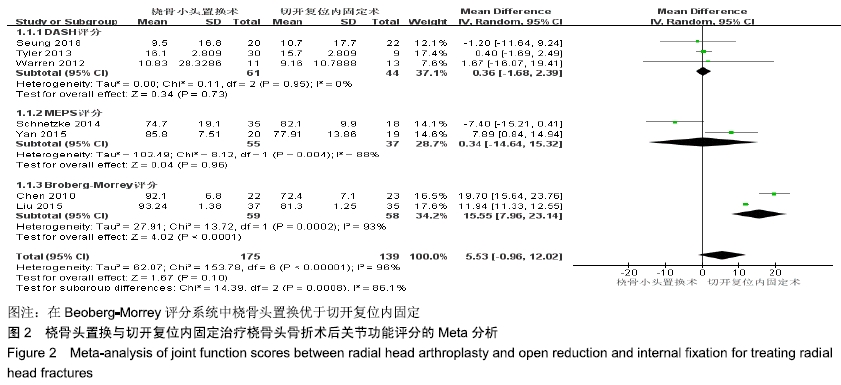
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 术后关节功能评分 根据功能评分系统的不同,将纳入的7篇文献分为上肢功能评分、Mayo肘关节功能评分和Beoberg-Morrey评分3个亚组[15-16,19,21,23-25],对于桡骨头置换与切开复位内固定治疗桡骨头骨折的疗效进行比较,因为各亚组及研究结果间存在异质性(I2 > 50%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示,在Beoberg-Morrey评分系统中桡骨头置换优于切开复位内固定[95%CI(7.96,23.14),P < 0.000 1],但是在上肢功能评分[95%CI(-1.68,2.39),P=0.73]和Mayo肘关节功能评分[95%CI(-14.64,15.32),P=0.96]方面2组相当,其差异无显著性意义,见图2。 "
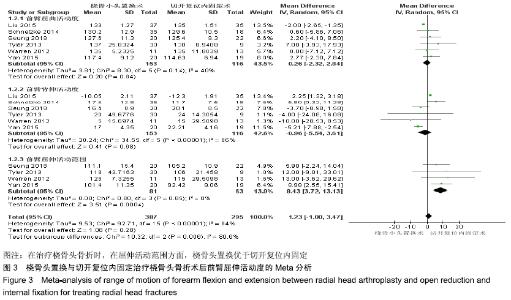
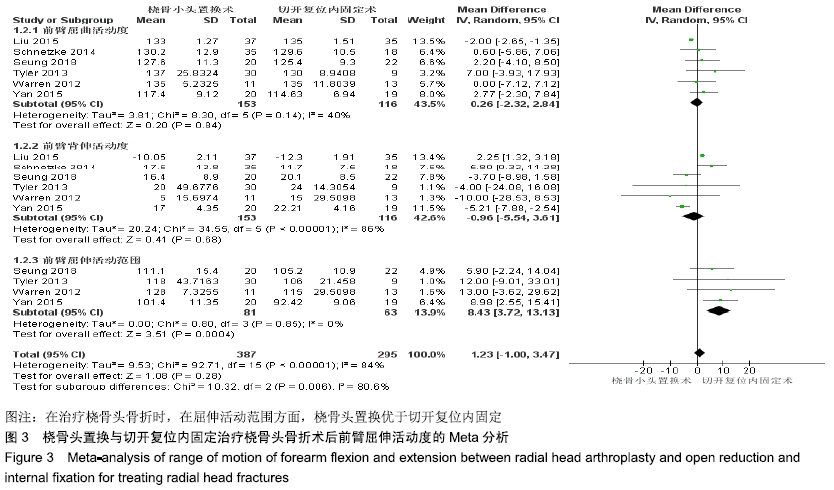
2.2.2 前臂屈伸活动度 根据前臂屈曲、背伸以及屈伸活动范围的不同,将纳入的6篇文献分为3个亚组[16,19,21,23-25],对于桡骨头置换与切开复位内固定治疗桡骨头骨折的疗效进行比较,因为各亚组及研究结果间存在异质性(I2 > 50%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示,在治疗桡骨头骨折时,在屈伸活动范围方面,桡骨头置换优于切开复位内固定[95%CI(3.72,13.13),P=0.000 4],但是在前臂屈曲活动度[95%CI(-2.32,2.84),P=0.84]和前臂背伸活动度[95%CI(-5.54,3.61),P=0.68]上2组相当,其差异无显著性意义,见图3。 "
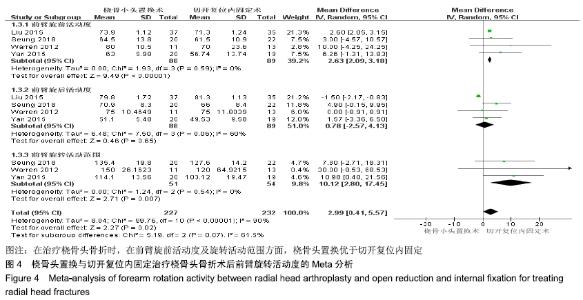
2.2.3 前臂旋转活动度 根据前臂旋前、旋后以及旋转活动范围的不同,将纳入的4篇文献分为3个亚组[16,19,23,25],对于桡骨头置换与切开复位内固定治疗桡骨头骨折的疗效进行比较,因为各亚组及研究结果间存在异质性(I2 > 50%),故采用随机效应模型进行Meta分析。结果显示,在治疗桡骨头骨折时,在前臂旋前活动度[95%CI(2.09,3.18),P < 0.000 01]及旋转活动范围方面[95%CI(2.80,17.45),P=0.007],桡骨头置换术优于切开复位内固定术,其差异有显著性意义;但是在前臂旋后活动度上2组相当[95%CI(-2.57,4.13),P=0.65],其差异无显著性意义,见图4。 "

| [1] DUCKWORTH AD, CLEMENT ND, JENKINS PJ, et al. The epidemiology of radial head and neck fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(5):112-119. [2] 张欣凯,孙纯森,刘建军,等.不同入路切开复位内固定术对AO 23-C2型桡骨远端骨折患者骨折愈合效果及腕关节功能的影响分析[J].医学理论与实践,2019,32(8):1187-1189. [3] 罗成,杨林,陈波,等.用闭合复位外固定术和切开复位内固定术治疗老年单侧桡骨远端闭合性骨折的效果对比[J].当代医药论丛, 2019,17(5):96-97. [4] KAAS L, VAN RIET RP, VROEMEN JP, et al. The epidemiology of radial head fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(6):520-523. [5] 李彬,刘丹,李冀.假体置换与微型钢板内固定治疗伴有桡骨头粉碎骨折的肘关节三联征的临床效果分析[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2018,21(5):498-501. [6] KAAS L, STRUIJS PA, RING D, et al. Treatment of Mason type II radial head fractures without asso- ciated fractures or elbow dislocation: a systematic review. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(1):1416-1421. [7] 袁文峰,易华云,吴师骥.闭合复位与切开复位内固定术治疗桡骨远端骨折对比研究[J]. 当代医学,2018,24(17):60-62. [8] BRUINSMA W, KODDE I, DE MUINCK KEIZER RJ, et al. A randomized controlled trial of nonoperative treatment versus open reduction and internal fixa- tion for stable, displaced, partial articular fractures of the radial head: the RAMBO trial BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014; 6(15):140-147. [9] DELCLAUX S, LEBON J, FARAUD A, et al. Complications of radial head prostheses. Int Orthop. 2015; 39(7):907-913. [10] 吴家盛.桡骨头假体置换治疗桡骨头粉碎性骨折临床观察[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2018,28(14):100-102. [11] HALL JA, MCKEE MD. Posterolateral rotatory instability of the elbow following radial head resection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 8(3):1571-1579. [12] 李嘉.成人桡骨头骨折采用切开复位内固定术治疗的效果分析[J].中国医药指南,2017,15(35):104-105. [13] ALLIEU Y, WINTER M, PEQUIGNOT JP. Radial head replace-ment with a pyrocarbon head prosthesis: preliminary results of a multicentric prospective study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2006; 16(1):1-9. [14] 王大鹏.切开复位内固定术治疗成人桡骨头骨折的临床效果研究[J].中国医药指南,2017,15(34):61-62. [15] CHEN X, WANG SC, CAO LH, et al. Comparison between radial head replacement and open reduction and internal fixation in clinical treatment of unstable, multi-fragmented radial head fractures. Int Orthop. 2011;35(7):1071-1076. [16] LIU R, LIU P, SHU H, et al. Comparison of primary radial head replacement and ORIF (open reduction and internal fixation) in Mason type III fractures: a retrospective evaluation in 72 elderly patients. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:90-93. [17] 曾欢高,毕殿海,廖勇,等.外固定支架与切开复位内固定术对老年不稳定性桡骨远端骨折的疗效及对腕关节功能的影响[J].中国当代医药,2017,24(31):92-94+97. [18] 王新武,罗元标,林宗锦,等.不同掌侧入路在桡骨远端骨折切开复位内固定术中应用的比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018, 33(11):1143-1146. [19] RYU SM, PARK SG, KIM JH, et al. Treatment of modified mason type iii or iv radial head fracture: open reduction and internal fixation versus arthroplasty. Indian J Orthop. 2018; 52(6):590-595. [20] 孙永新. 用切开复位锁定加压钢板内固定术治疗桡骨远端骨折的效果探究[J]. 当代医药论丛,2018,16(17):32-33. [21] WATTERS TS, GARRIGUES GE, RING D, et al. Fixation versus replacement of radial head in terrible triad: is there a difference in elbow stability and prognosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(7):2128-2135. [22] 魏志远,邹鸿星,邵银初,等.桡骨小头假体置换治疗桡骨小头粉碎性骨折八例[J].海南医学,2018,29(1):115-117. [23] LEIGH WB, BALL CM. Radial head reconstruction versus replacement in the treatment of terrible triad injuries of the elbow. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2012;21(10):1336-1341. [24] SCHNETZKE M, AYTAC S, DEUSS M, et al Radial head prosthesis in complex elbow dislocations: effect of oversizing and comparison with ORIF. Int Orthop. 2014;38(11):2295-2301. [25] YAN M, NI J, SONG D, et al. Radial head replacement or repair for the terrible triad of the elbow: which procedure is better? ANZ J Surg. 2015;85(9):644-648. [26] RING D. Radial head fracture: open reduction-internal fixation or prosthetic replacement. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2011;20(8): 107-112. [27] LI N, CHEN S. Open reduction and internal-fixation versus radial head replacement in treatment of Mason type III radial head fractures. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(6):851-855. [28] HIGGINS JP, THOMPSON SG, DEEKS JJ, et al. Mea- suring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ Br Med J. 2013; 327(2): 557. [29] 商俊刚,邵新中,王立,等.桡骨小头置换联合锚钉重建侧副韧带术治疗肘关节“恐怖三联征”的临床分析[J].河北医科大学学报, 2017,38(11):1348-1352. [30] RUAN HJ, FAN CY, LIU JJ, et al. A comparative study of internal fixation and prosthesis replacement for radial head fractures of Mason type III. Int Orthop. 2009; 33(7):249-253. [31] AL-BURDENI S, ABUODEH Y, IBRAHIM T, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation versus radial head arthroplasty in the treatment of adult closed comminuted radial head fractures (modified Mason type III and IV). Int Orthop. 2015; 39(8):1659-1664. [32] 顾海伦,杨军,王维,等.人工桡骨小头置换治疗不稳定Mason Ⅲ型桡骨小头骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2017,19(7):538-539. [33] ATHWAL GS, FRANK SG, GREWAL R, et al. Determination of correct implant size in radial head arthroplasty to avoid over lengthening surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010; 92 Suppl 1 Pt 2:250-257. [34] 刘传芳,黄小顺,钟祖欣,等.对50例桡骨小头粉碎性骨折患者实施桡骨小头假体置换术的疗效与肘关节功能恢复情况观察[J].黑龙江医药,2017,30(3):654-656. [35] VAN GLABBEEK F, VAN RIET RP, BAUMFELD JA, et al. Detrimental effects of over- stuffing or understuffing with a radial head replacement in the medial collateral-ligament deficient elbow. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86(4): 2629-2635. [36] VAN RIET RP, SANCHEZ J, MORREY BF. Failure of metal radial head replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2010;92(3): 661-667. [37] 吴昌盛,付义刚. 切开复位掌侧钢板内固定术治疗老年桡骨远端C型骨折的疗效[J].临床骨科杂志,2018,21(4):484-486. [38] HA AS, PETSCAVAGE JM. Radial head arthroplasty: a radi- ologic outcome study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 199: 1078-1082. [39] HARTZLER RU, MORREY BF, STEINMANN SP, et al. Radial head reconstruction in elbow frac- ture-dislocation: Monopolar or bipolar prosthesis? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(3):2144. [40] RING D. Open reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the radial head. Hand Clin. 2004;20(4):415-427. [41] 王斌.两种手术方式治疗桡骨小头粉碎性骨折的临床效果对比[J].中国现代药物应用,2018,12(12):56-57. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||