Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 968-975.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2457
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of open reduction and internal fixation versus total elbow arthroplasty for distal humeral fracture in the
elderly
Wen Yangning1, Han Xiaoqiang2, Feng Chao1, Sun Haibiao2
- 1First Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2019-04-11Revised:2019-04-19Accepted:2019-06-04Online:2020-02-28Published:2020-01-18 -
Contact:Sun Haibiao, Chief physician, MD, Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Wen Yangning, Master candidate, Physician, First Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Yangning, Han Xiaoqiang, Feng Chao, Sun Haibiao.
Meta-analysis of open reduction and internal fixation versus total elbow arthroplasty for distal humeral fracture in the
elderly
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
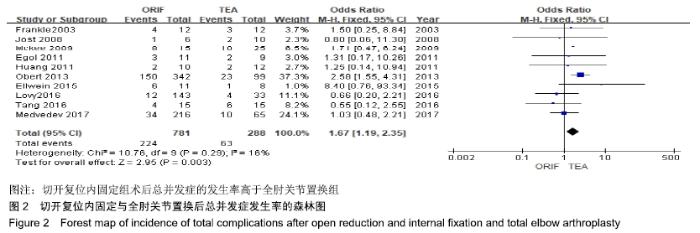
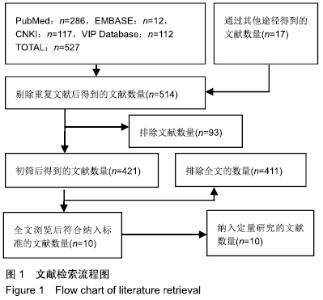
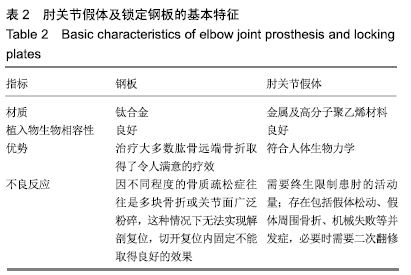
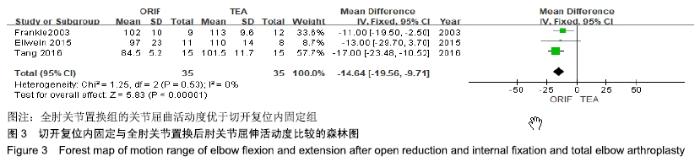
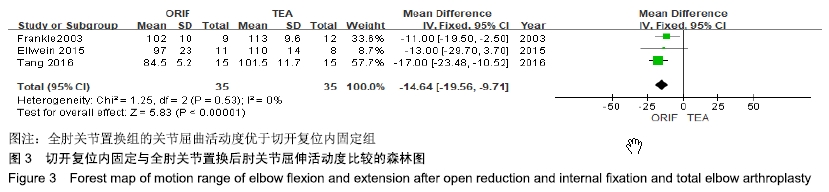
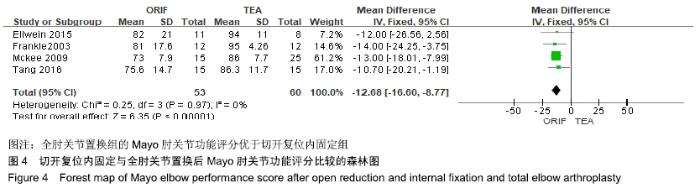
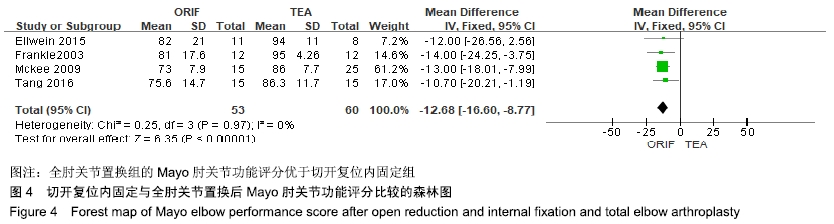
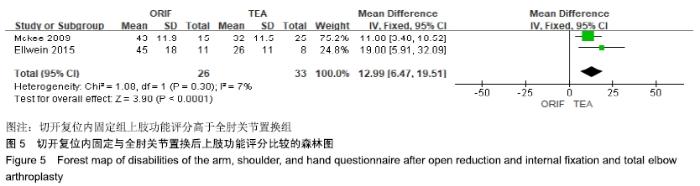
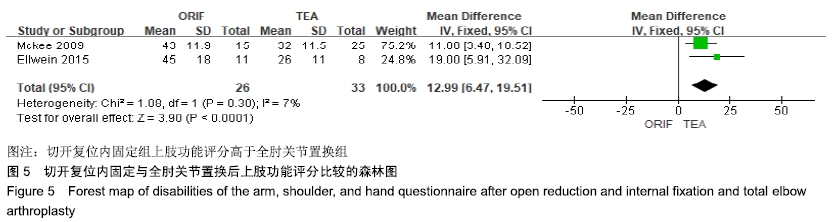
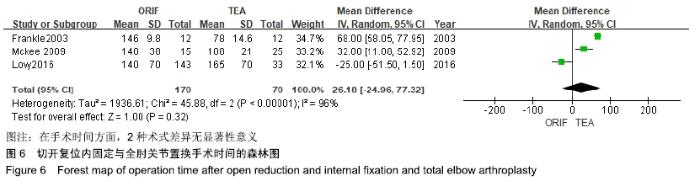
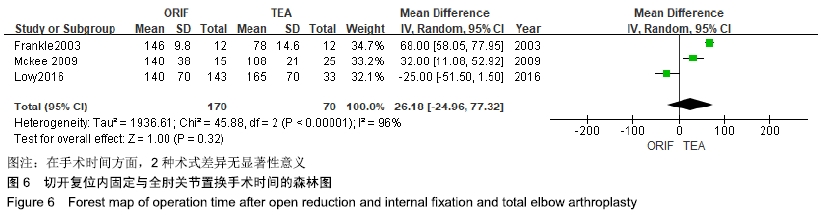
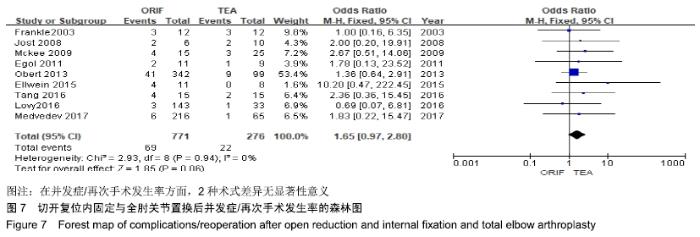
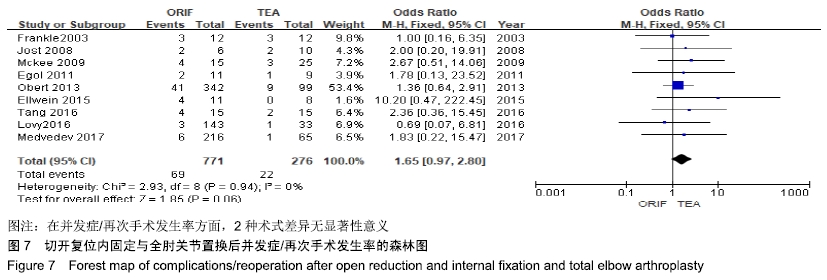
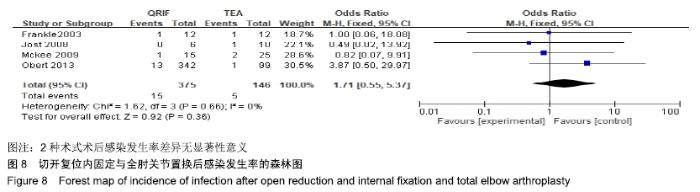
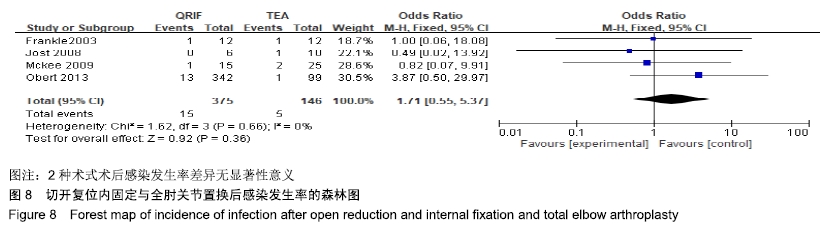
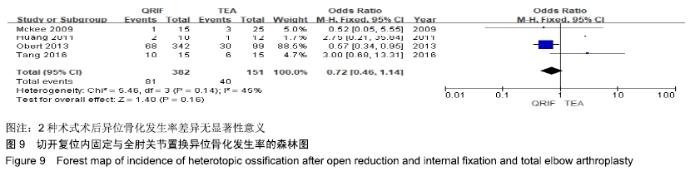
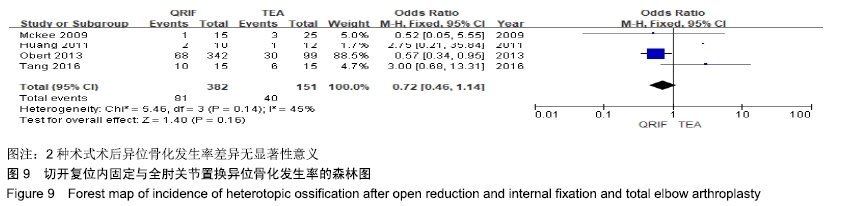
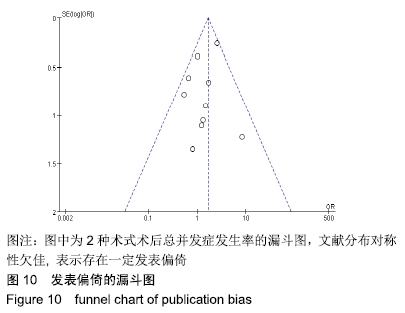
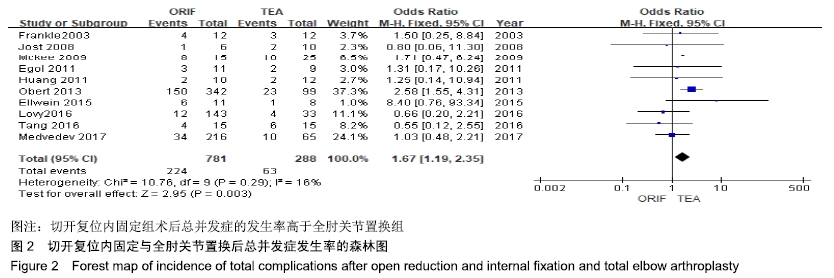
2.2 切开复位内固定与全肘关节置换后总并发症发生率的Meta结果 有10篇文献比较了末次随访总并发症发生数[16-25],共纳入1 069例患者,切开复位内固定组781例、全肘关节置换组288例进行Meta分析。Q检验,I2=16%,P=0.29,显示纳入的10篇文献异质性小,采用固定效应模型计算切开复位内固定组vs.全肘关节置换组的合并OR值为1.67,95%CI(1.19-2.35),P=0.003,结果显示切开复位内固定组术后并发症的发生率高于全肘关节置换组。考虑随访时间长短对术后总并发症率可能产生影响,剔除随访时间较短的2篇文献[24-25],异质性未发生改变,合并效应量未与无效线交叉,P < 0.05,故统计结果稳健,见图2。"
| [1] AMIR S, JANNIS S, DANIEL R. Distal humerus fractures: a review of current therapy concepts. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2016; 9(2):199-206. [2] ROBINSON CM, HILL RM, JACOBS N, et al. Adult distal humeral metaphyseal fractures: epidemiology and results of treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17(1):38-47. [3] SHARMA S, JOHN R, DHILLON MS, et al. Surgical approaches for open reduction and internal fixation of intra-articular distal humerus fractures in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Injury. 2018: S0020138318302894. [4] NIJS S. Distal Humerus Fracture// Fracture Reduction and Fixation Techniques. 2018. [5] JUPITER JB, RING D.Fractures of the distal humerus. Orthop Clin North Am. 2000;31(1):103-113. [6] CORRADI A, TALAMONTI T, CABITZA P, et al. Innovative techniques for the osteosynthesis of distal humeral fractures. Injury. 2010; 41(11):1117-1119. [7] KORNER J, LILL H, MÜLLER LP, et al. Distal humerus fractures in elderly patients: results after open reduction and internal fixation. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(2):73-79. [8] MEHLHOFF TL, BENNETT JB. Distal humeral fractures: fixation versus arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20(2):S97-S106. [9] GAMBIRASIO R, RIAND N, STERN R, et al. Total elbow replacement for complex fractures of the distal humerus an option for the elderly patient. J Bone Joint Surg. 2001;83(7): 974-978. [10] COBB TK, MORREY BF. Total elbow arthroplasty as primary treatment for distal humeral fractures in elderly patients. Injury. 2000; 31(9):687-692. [11] GARCIA JA , MYKULA R , STANLEY D . Complex fractures of the distal humerus in the elderly. J Bone Joint Surg. 2002; 84(6):812-816. [12] PROUST J, OKSMAN A, CHARISSOUX JL, et al. Intra-articular fracture of the distal humerus: outcome after osteosynthesis in patients over 60. Revue De Chirurgie Orthopédique Et Réparatrice De L Appareil Moteur. 2007; 93(8):798-806. [13] WELSINK CL, LAMBERS KTA, VAN DEURZEN DFP, et al. Total elbow arthroplasty: a systematic review. JBJS Rev. 2017;5(7):e4. [14] SHIN SJ, SOHN HS, DO NH. A clinical comparison of two different double plating methods for intraarticular distal humerus fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010;19(1):2-9. [15] GITHENS M, YAO J, SOX AH, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation versus total elbow arthroplasty for the treatment of geriatric distal humerus fractures: a systematic review and metaanalysis.J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(8): 481-488. [16] FRANKLE MA , HERSCOVICI D, DIPASQUALE TG, et al. A comparison of open reduction and internal fixation and primary total elbow arthroplasty in the treatment of intraarticular distal humerus fractures in women older than age 65. J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17(7):473-480. [17] JOST B, ADAMS RA, MORREY BF. Management of acute distal humeral fractures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. A case series. J Bone Joint Surg. 2008;90(10):2197-2205. [18] MCKEE MD, VEILLETTE CJ, HALL JA, et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial of open reduction--internal fixation versus total elbow arthroplasty for displaced intra-articular distal humeral fractures in elderly patients. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2009;18(1):3-12. [19] EGOL KA, TSAI P, VAZQUES O, et al. Comparison of functional outcomes of total elbow arthroplasty vs plate fixation for distal humerus fractures in osteoporotic elbows. Am J Orthop. 2011;40(2):67-71. [20] 黄聪,蒋协远,王满宜. 双钢板内固定与入工全肘关节置换术治疗老年肱骨髁间C型骨折的早期疗效比较[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2011,31(3):243-248. [21] OBERT L, FERRIER M , JACQUOT A , et al. Distal humerus fractures in patients over 65: complications. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(8):909-913. [22] ELLWEIN A, LILL H, VOIGT C, et al. Arthroplasty compared to internal fixation by locking plate osteosynthesis in comminuted fractures of the distal humerus. Int Orthop. 2015;39(4):747-754. [23] 唐浩琛,向明,徐虹霞,等. 两种手术治疗老年骨质疏松性复杂肱骨远端骨折的早期疗效比较[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2016, 24(8):11-15. [24] LOVY AJ, KESWANI A, KOEHLER SM, et al. Short-term complications of distal humerus fractures in elderly patients: open reduction internal fixation versus total elbow arthroplasty. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2016;7(1):39-44. [25] MEDVEDEV G, WANG C, AMDUR R, et al. Operative Distal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: Predictors for Early Complications Based on a National Database. HSS J. 2017;13(2 Suppl):212-216. [26] 姜保国.肱骨远端骨折的治疗进展[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2008, 1(2):145-148. [27] PATINO JM. Complex distal humerus fractures in elderly patients:open reduction and internal fixation versus arthroplasty. J Hand Surg. 2012; 37(8): 1699-1701. [28] GUPTA R, KHANCHANDANI P. Intercondylar fractures of the distal humerus in adults: a critical analysis of 55 cases. Injury. 2002;33(6): 511-515. [29] PENNOCK AT, SALGUEIRO L, UPASANI VV, et al. Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning versus open reduction and internal fixation for type ii lateral condyle humerus fractures in children displaced >2 mm. J Pediatr Orthop. 2016;36(8):780. [30] MARSH JL, SLONGO TF, AGEL J, et al. Fracture and dislocation classification compendium - 2007: Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, database and outcomes committee. J Orthop Trauma. 2007; 21(10 Suppl):1-133. [31] JOHN H, ROSSO R, NEFF U, et al. Distal humerus fractures in patients over 75 years of age. Long-term results of osteosynthesis. Helv Chir Acta. 1993;60:219-224. [32] KORNER J, LILL H, MÜLLER LP, et al. Distal humerus fractures in elderly patients: results after open reduction and internal fixation. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(2):73-79. [33] MANSAT P, NOUAILLE DEGORCE H, BONNEVIALLE N, et al. Total elbow arthroplasty for acute distal humeral fractures in patients over 65 years old–Results of a multicenter study in 87 patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(7):779-784. [34] CIL A, VEILLETTE CJ, SANCHEZSOTELO J, et al. Linked elbow replacement: a salvage procedure for distal humeral nonunion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(9):1939-1950. [35] PRASAD N, ALI A, STANLEY D. Total elbow arthroplasty for non-rheumatoid patients with a fracture of the distal humerus a minimum ten-year follow-up. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(3): 381-386. [36] BOER YAD, HAZES JM, WINIA PC, et al. Comparative responsiveness of four elbow scoring instruments in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2001; 28(12): 2616-2623. [37] FRANCHIGNONI F, VERCELLI S, GIORDANO A, et al. Minimal clinically important difference of the disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand outcome measure (DASH) and its shortened version (QuickDASH). J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2014;44(1):30-39. [38] MALAY S, SUN SG, CHUNG KC, et al. The minimal clinically important difference after simple decompression for ulnar neuropathy at the elbow. J Hand Surg. 2013; 38(4):652-659. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [13] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [14] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Han Shufeng. Interlocking intramedullary nail for proximal femur versus proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail or proximal femoral anti-rotation intramedullary nail of Asian for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||