Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (14): 2271-2276.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2443
Previous Articles Next Articles
Important roles of non-coding RNA in peripheral nerve repair
Luo Xuanxiang1, 2, Feng Hu2, Jing Li1, 2, Pan Bin1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2019-07-12Revised:2019-07-24Accepted:2019-08-23Online:2020-05-18Published:2020-03-18 -
Contact:Feng Hu, Master, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Luo Xuanxiang, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81801213
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Xuanxiang, Feng Hu, Jing Li, Pan Bin. Important roles of non-coding RNA in peripheral nerve repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2271-2276.
share this article
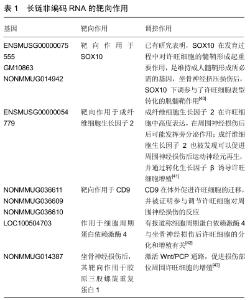
2.1 miRNA miRNA是一种小的非编码单链RNA,平均大小约为22个核苷酸。miRNA的合成始于细胞核。首先,RNA聚合酶II或III生成原始转录本,然后经过Drosha-DGCR8复合物调控,形成含有发卡结构的pre-miRNA。pre-miRNA在出核转运蛋白 Exportin 5的作用下与Ran-GTP和Exportin 5形成异三聚体,转移到达细胞质被释放。在细胞质内,pre-miRNA由Dicer酶剪切成为成熟的miRNA[10]。成熟的miRNA与靶基因配对结合,转录后调节靶基因的表达,并通过对靶基因翻译抑制,调控靶蛋白的表达量。 近年来,许多研究都对神经损伤后特异性miRNA表达与神经修复的关系感兴趣,随着基因测序技术的发展,越来越多的损伤特异性miRNA被发现并经RT-PCR证实。miR-21是此类miRNA的典型代表。编码该miRNA的基因位于染色体17q23.2,广泛表达于哺乳动物的各种组织和器官中。在周围神经系统中,miR-21在损伤后第7天明显上调。它调控Ras/Raf/细胞外调节蛋白激酶(ERK)信号通路,通过对SPRY2的负调控促进轴突生长。miR-21和miR-222还可以通过调节组织抑制物金属蛋白酶3来促进神经元的内在再生能力[11]。组织抑制物金属蛋白酶3具有广泛的抑制作用,可促进多种细胞类型的凋亡。组织抑制物金属蛋白酶家族作为一组基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂得到了越来越多的关注,并且最近被证明具有额外的生物学效应。miR-132是神经系统中最著名的miRNA之一,MENDOZA-VIVEROS等[12]曾报道,miR-132/212可以通过调节甲基CpG结合蛋白2 (MeCP2)和下游脑源性神经营养因子的表达以及雷帕霉素信号转导的哺乳动物靶蛋白的表达,调节小鼠和仓鼠的树突状突起密度和光周期适应。最近有研究表明,在周围神经中,miR-132可能作用于其他mRNA靶点,如Ras p21蛋白激活因子1(Rasa1)mRNA,这是miR-132的下游靶点,在背根神经节神经元发育过程中调控轴突生长[13]。 除了上述典型miRNA的外,许多其他的miRNA也被证明参与了周围神经损伤后的神经再生。坐骨神经损伤后,背根神经节中miR-144、145和214下调,跨膜受体Robo2升高。进一步的研究证实miR-145可能通过slit- Robo-srGAP通路抑制神经生长[14]。PTEN是雷帕霉素和磷酸肌醇3激酶通路的负调控因子,对中枢神经元系统的轴突生长具有重要作用。然而,在周围神经系统中,PTEN的抑制作用似乎增加了轴突的固有再生能力,PTEN在一定程度上对轴突的生长起到调节制动的作用[15]。miR-222、miR-29a和miR-29通过靶向PTEN促进轴突生长。miR-29a和miR-29c直接靶向PTEN mRNA的3’-UTR,从而下调PTEN。 在周围神经系统中,许旺细胞在周围神经的轴突周围形成髓鞘,为轴突提供支持和保护。周围神经损伤后,通常可观察到明显的快速再生反应。在此过程中,无论神经是高度髓鞘化还是无髓鞘化,许旺细胞均分化为功能性祖细胞。通过增殖和迁移,去分化的许旺细胞重建受损组织。支持轴突再生的Bungner条带是由增殖的许旺细胞形成的,这些去分化的许旺细胞还分泌轴突再生所需的各种神经营养因子[16]。miRNA被认为可以调节许旺细胞的凋亡、生长、增殖、分化和迁移。利用微阵列和RT-PCR技术鉴定了48种神经损伤后动态调控的miRNA,其中大部分参与了多基因修饰和增殖,从而增强了驱动许旺细胞重髓鞘化的转录程序。miR-34a和miR-140是这一类miRNA的代表;这些miRNA通过NOTCH1和细胞周期蛋白D1 (CCND1)以及转录因子Egr2影响神经损伤后许旺细胞的活性[17]。miR-221/222在周围神经损伤后上调,直接与LASS2基因的3’-非编码区结合,导致LASS2 mRNA和蛋白表达下调,miR-221/222通过这种方式促进许旺细胞的增殖和迁移[18]。miR-132在缺血周围神经损伤引起的缺氧中表达升高,并与蛋白激酶amp活化的非催化亚单位gamma 3 (PRKAG3)的3’-UTR结合,从而下调PRKAG3的表达,从而增加许旺细胞的增殖和迁移[19]。 同时许多miRNA也会抑制许旺细胞的增殖和迁移。miR-182直接靶向成纤维细胞生长因子9。miR-182对成纤维细胞生长因子9的抑制作用直接抑制许旺细胞的迁移和增殖[20]。miR-9抑制正常细胞和肿瘤细胞的迁移,其沉默促进周围神经损伤后许旺细胞的迁移。这是因为胶原三股螺旋重复蛋白1是miR-9的直接靶点,胶原三股螺旋重复蛋白1可使Rac1 GTP酶失活[21]。miR-146b是一种类Kruppel因子7靶向miRNA,抑制Kruppel因子7表达,可以减少许旺细胞增殖和迁移,Kruppel因子7是一种周围神经损伤后刺激许旺细胞增殖和轴突再生的转录因子,是一种潜在治疗神经损伤的候选药物[22]。miR-sc4通过靶向周期蛋白依赖性激酶5激活剂1发挥作用,周期蛋白依赖性激酶5激活剂1对许旺细胞活性具有抑制作用[23]。let-7 miRNA可以减少原代许旺细胞的迁移和增殖,let-7 miRNA下调可促进神经生长因子的合成和分泌,因此,神经损伤后let-7的表达下调为轴突再生创造了有利条件[24]。 2.2 circRNA circRNA是近年来发现的一类闭合环状结构非编码RNA,其特征是既不具有5'-3'极性,也没有多聚腺苷酸尾巴,大量存在于真核转录组,是目前神经科学领域的研究热点[25]。 circRNA通常来源于蛋白编码基因和完整的外显子,真核circRNA主要在剪接过程中产生,除了外显子反剪接环化形成circRNA外,根据不同的生物发生机制存在着不同类型的circRNA。circRNA在哺乳动物大脑中富集,在神经元分化过程中保守并动态表达。近年来,有报道称circRNA具有多种生物学功能,包括促进滚圈翻译、控制亲本基因转录、促进形成选择性剪接mRNA、充当miRNA海绵等。在这些功能中,越来越多的研究报道circRNA与miRNA发生海绵样作用,调节基因表达,在人类疾病的发病和诊断中发挥着重要的作用。在成年大鼠心室下区(SVZ),有一个SVZ特异性的circRNA 结合miR-138-5p作为神经干细胞增殖的潜在负调控因子。CircRNA CDR1as (ciRS-7)在脑组织中特异性高表达,在神经元组织中作为一种潜在的环状miR-7海绵。在人类脑组织中,ciRS-7随着miR-7表达的增加而降低,可以下调多种相关基因的表达,如泛素结合酶(UBE2A)蛋白。circRNA在神经系统的高稳定性、组织和时序高特异性等特征,使其在神经再生与修复的研究中越来越受到人们的关注[26]。 近年来,circRNA在神经损伤中的研究日益增多。已有多项研究通过微阵列和RNA-seq技术揭示了创伤性脑损伤和神经性疼痛模型中circRNA的表达模式。在大鼠脊髓中检测到188个表达差异的circRNA (68个表达上调,120个表达下调),表达时间为神经损伤后第14天。其中,circ_0006928可能通过结合miR-184调控神经元凋亡。circRNAs-Filipi11通过ago2依赖的方式结合剪接miRNA-1224负调控,在慢性炎症疼痛中升高,并通过靶向Ubr5调控痛感[27]。有研究表明,circRNA可以在体内和体外诱导神经元自噬,circRNA-2837的下调通过诱导神经元自噬减轻坐骨神经损伤;此外,荧光素酶检测显示circRNA-2837可以与miR-34家族结合,circRNA-2837的沉默直接靶向miR-34a诱导神经元自噬,其通过对miR-34家族发挥海绵作用,扮演着竞争性内源RNA(competing endogenous RNAs, ceRNA)的角色,竞争性抑制miRNA的转录调控,发挥相应的生物学功能[28]。 与线性RNA相比,circRNA不被RNA酶降解,具有更强的稳定性,且分离、鉴定和检测较为容易,但目前circRNA的具体生成机制仍不明确,涉及到的信号剪切及稳定性调控等还有待进一步研究,circRNA在发挥miRNA海绵样作用的吸附及释放过程中的信号调控尚不清楚,关于circRNA的生物信息学数据库尚未完全建立,因此导致circRNA的研究进展比较缓慢。 2.3 lncRNA lncRNA是指长度大于200个核苷酸的非编码RNA,是非编码RNA中最大的一类RNA。转录开始后,lncRNA由RNA聚合酶Ⅱ合成,经组蛋白修饰后产生。与编码蛋白质的mRNA相比,lncRNA具有更强的组织和细胞表达特异性。利用原位杂交技术,MERCER等[29]在小鼠脑组织中鉴定了大量的lncRNA,进一步分析得出这些lncRNA的表达水平与特定的神经解剖学位置、细胞类型和亚细胞位置相关。lncRNAs已被证实在几乎所有转录和翻译水平上调控基因表达,包括基因组印迹、染色质修饰和细胞质mRNA的翻译[30]。越来越多的研究数据表明,lncRNA在许多生物过程中都具有重要的调控功能。在神经生物学中,lncRNA已经被证实与神经发育障碍、神经系统退行性变和脑部肿瘤有关[31]。例如,linc-Brn1b基因的下调已经被证明会导致大脑中中间祖细胞的减少,这表明这种lncRNA可能在大脑皮质发育中发挥重要作用。 近年来研究发现,大量的lncRNA在周围神经损伤后发生差异性表达,在周围神经再生中发挥着重要作用。例如,坐骨神经损伤后,lncRNA uc.217在背根神经节神经元表达下调。敲除lncRNA uc.217能显著促进培养的背根神经节神经元生长[32]。有研究表明lncRNA BC089918的下调促进背根神经节中神经元的突起生长。基因共表达网络显示lncRNA BC089918的潜在靶点包括Fam57b、Kcns1和Cacng2。在这3个靶点中,Kcns1表达于感觉神经元,坐骨神经损伤后其蛋白水平显著下调,影响神经元的兴奋性[33]。 许旺细胞的增殖和迁移有助于周围神经损伤后轴突的生长和功能的恢复。研究发现,lncRNA在周围神经损伤后可作用于许旺细胞,在周围神经再生中起着重要作用[34]。周围神经损伤后,lncRNA富含核富集的转录物1(NEAT1)和核基质结合区蛋白1(Satb1)表达增加,miR-34a表达减少。富含核富集的转录物1的过表达促进了许旺细胞的增殖和迁移,富含核富集的转录物1通过与miR-34a发生海绵样作用调控核基质结合区蛋白1表达,是一种竞争性的内源性RNA。富含核富集的转录物1通过调节miR-34a和核基质结合区蛋白1的表达,促进背根神经节神经元轴突的生长[35]。坐骨神经损伤后,lncRNA TNXA-PS1表达下调,其下调可通过作用于miR-24-3p/miR-152-3p促进许旺细胞迁移,影响双特异性磷酸酶1表达[36]。在坐骨神经损伤模型中,lncRNA BC088327表达上调,沉默lncRNA BC088327可抑制许旺细胞的存活,诱导许旺细胞凋亡并抑制细胞增殖。使用微阵列技术检测非编码RNA表达谱与坐骨神经损伤的大鼠模型中神经修复的关系,同时通过在缺氧的许旺细胞模型中对细胞活力、细胞周期和细胞凋亡检测,进一步评估lncRNA Bc088327在周围神经损伤中的具体功能;研究表明,lncRNA的表达谱与heregulin-1β密切相关,在周围神经损伤中,heregulin-1β能够促进皮肤源性前体分化许旺细胞治疗去细胞异体神经再生,而lncRNA Bc088327可能与heregulin-1β通过协同作用修复周围神经损伤[37]。 近年有研究预测lncRNA-mRNA参与周围神经损伤后修复,通过进一步分析,发现lncRNA ENSMUSG00000087366顺式调控Jun,Jun是一种由癌基因编码的蛋白,与c-Fos结合形成AP-1转录因子。先前的一项研究表明Jun是许旺细胞对损伤的中枢调节因子。Jun基因的敲除已被证明会导致轴突的再生和修复功能严重受损[38]。NONMMUG042235和ENSMUSG00000097535靶向作用于细胞间黏附分子1 (Icam1)。最近已经证明细胞间黏附分子1与周围神经损伤后修复的炎性反应和细胞聚集,以及许旺细胞髓鞘形成有关[39]。lncRNA的靶向作用见表1。 "

| [1] GU X, DING F, YANG Y, et al. Construction of tissue engineered nerve grafts and their application in peripheral nerve regeneration. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;93(2):204-230. [2] TIAN L, PRABHAKARAN MP, RAMAKRISHNA S. Strategies for regeneration of components of nervous system: scaffolds, cells and biomolecules. Regen Biomater. 2015;2(1):31-45. [3] GIORGIO T, ANDREW H, MIKAEL W. The nerve injury and the dying neurons: diagnosis and prevention.J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2011;36(9):730-734. [4] ALLODI I, UDINA E, NAVARRO X. Specificity of peripheral nerve regeneration: interactions at the axon level. Prog Neurobiol. 2012; 98(1):16-37. [5] ENGLISH AW, WILHELM JC, SABATIER MJ. Enhancing recovery from peripheral nerve injury using treadmill training. Ann Anat. 2011;193(4):354-361. [6] DEUMENS R, BOZKURT A, MEEK MF, et al. Repairing injured peripheral nerves: Bridging the gap.Prog Neurobiol. 2010;92(3): 245-276. [7] HOUSCHYAR KS, MOMENI A, PYLES MN, et al. The Role of Current Techniques and Concepts in Peripheral Nerve Repair. Plast Surg Int. 2016;2016:4175293. [8] ZHIPENG L, A GREGORY M. Vicinal: a method for the determination of ncRNA ends using chimeric reads from RNA-seq experiments.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(9):e79. [9] BHALALA OG, SRIKANTH M, KESSLER JA. The emerging roles of microRNAs in CNS injuries. Nature Reviews Neurology, 2013; 9(6): 328-339. [10] BARTEL DP, CHEN CZ. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nature Reviews Genetics.2004; 5(5): 396-400. [11] ZHOU S, ZHANG S, WANG Y, et al. MiR-21 and miR-222 inhibit apoptosis of adult dorsal root ganglion neurons by repressing TIMP3 following sciatic nerve injury. Neuroscience Letters.2015;586(14):43-49. [12] MENDOZA-VIVEROS L,CHIANG CK,JLK O,et al.miR-132/212 Modulates Seasonal Adaptation and Dendritic Morphology of the Central Circadian Clock. Cell Reports.2017; 19(3): 505-520. [13] HANCOCK ML, NICOLAS P, JIE Q, et al. MicroRNA-132 is enriched in developing axons, locally regulates Rasa1 mRNA, and promotes axon extension.J Neurosci. 2014;34(1):66-78. [14] ZHANG HY, ZHENG SJ, ZHAO JH, et al. MicroRNAs 144, 145, and 214 are down-regulated in primary neurons responding to sciatic nerve transection.Brain Res. 2011;1383:62-70. [15] CHRISTIE KJ, WEBBER CA, MARTINEZ JA, et al. PTEN inhibition to facilitate intrinsic regenerative outgrowth of adult peripheral axons.J Neurosci. 2010;30(27):9306-9315. [16] BOERBOOM A, DION V, CHARIOT A, et al. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Schwann Cell Plasticity.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:38. [17] ANDREU V, LI-WEI C, TIMOTHY F, et al. MicroRNAs modulate Schwann cell response to nerve injury by reinforcing transcriptional silencing of dedifferentiation-related genes.J Neurosci. 2011;31(48):17358-17369. [18] BIN Y, SONGLIN Z, YONGJUN W, et al. miR-221 and miR-222 promote Schwann cell proliferation and migration by targeting LASS2 after sciatic nerve injury.J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 11): 2675-2683. [19] YAO C, SHI X, ZHANG Z, et al. Hypoxia-Induced Upregulation of miR-132 Promotes Schwann Cell Migration After Sciatic Nerve Injury by Targeting PRKAG3. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(8):5129-39. [20] KOURI FM, HURLEY LA, DANIEL WL, et al. miR-182 integrates apoptosis, growth, and differentiation programs in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2015 ;29(7):732-745. [21] SONGLIN Z, RONG G, WEN H, et al. MiR-9 inhibits Schwann cell migration by targeting Cthrc1 following sciatic nerve injury. J Cell Sci. 2014;127(Pt 5):967-976. [22] LI WY, ZHANG WT, CHENG YX, et al. Inhibition of KLF7-Targeting Micro RNA 146b Promotes Sciatic Nerve Regeneration. Neurosci Bull. 2018;34(3):419-437. [23] QIAN T, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. Novel miR-sc4 regulates the proliferation and migration of Schwann cells by targeting Cdk5r1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;447(1-2):209-215. [24] LI S, WANG X, GU Y, et al. Corrigendum to "let-7 microRNAs regenerate peripheral nerve regeneration by targeting nerve growth factor".Mol Ther. 2015;23(4):790. [25] 程涵蓉,何少茹,吴本清.环状RNA研究的新进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21 (36): 5898-5904. [26] VENØ MT, HANSEN TB, VENØ ST, et al. Spatio-temporal regulation of circular RNA expression during porcine embryonic brain development.Genome Biol. 2015;16:245. [27] YAO C, YU B.Role of Long Noncoding RNAs and Circular RNAs in Nerve Regeneration.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:165. [28] ZHOU ZB, NIU YL, HUANG GX, et al. Silencing of circRNA.2837 Plays a Protective Role in Sciatic Nerve Injury by Sponging the miR-34 Family via Regulating Neuronal Autophagy. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;12:718-729. [29] MERCER TR, DINGER ME, SUNKIN SM, et al. Specific expssion of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(2):716-721. [30] MARCHESE FP, MAITE H. Long non-coding RNAs and chromatin modifiers: their place in the epigenetic code. Epigenetics.2014; 9(1): 21-26. [31] ROBERTS TC, MORRIS KV, WOOD MJA. The role of long non-coding RNAs in neurodevelopment, brain function and neurological disease.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014; 369(1652). pii: 20130507. [32] YAO C, WANG J, ZHANG H, et al. Long non-coding RNA uc.217 regulates neurite outgrowth in dorsal root ganglion neurons following peripheral nerve injury.Eur J Neurosci. 2015;42(1): 1718-1725. [33] MICHAEL C, INNA B, GRIFFIN RS, et al. Multiple chronic pain states are associated with a common amino acid-changing allele in KCNS1. Brain. 2010;133(9):2519-2527. [34] BIN Y, SONGLIN Z, SHENG Y, et al. The regulatory roles of non-coding RNAs in nerve injury and regeneration.Prog Neurobiol. 2015;134:122-139. [35] LIU X, YU X, HE Y, et al. Long noncoding RNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 promotes the proliferation and migration of Schwann cells by regulating the miR-34a/Satb1 axis. J Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb 12. [36] YAO C, WANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. lncRNA TNXA-PS1 Modulates Schwann Cells by Functioning As a Competing Endogenous RNA Following Nerve Injury. J Neurosci. 2018;38(29):6574-6585. [37] WANG H, WU J, ZHANG X, et al. Microarray analysis of the expression profile of lncRNAs reveals the key role of lncRNA BC088327 as an agonist to heregulin‑1β‑induced cell proliferation in peripheral nerve injury. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(6): 3477-3484. [38] FONTANA X, HRISTOVA M, COSTA CD, et al. c-Jun in Schwann cells promotes axonal regeneration and motoneuron survival via paracrine signaling. J Cell Biol. 2012;198(1):127-141. [39] CHRISTINE W, DOUGLAS Z. The nerve regenerative microenvironment: early behavior and partnership of axons and Schwann cells. Experimental Neurology.2010; 223(1): 51-59. [40] GLENN TD, TALBOT WS. Signals regulating myelination in peripheral nerves and the Schwann cell response to injury. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2013;23(6):1041-1048. [41] ALLODI I, MECOLLARI V, GONZÁLEZ‐PÉREZ F, et al. Schwann cells transduced with a lentiviral vector encoding Fgf-2 promote motor neuron regeneration following sciatic nerve injury. Glia.2015; 62(10): 1736-1746. [42] ATANASOSKI S, BOENTERT M, VENTURA LD, et al. Postnatal Schwann cell proliferation but not myelination is strictly and uniquely dependent on cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (cdk4).Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;37(3):519-527. [43] PAN B, SHI ZJ, YAN JY, et al. Long non-coding RNA NONMMUG014387 promotes Schwann cell proliferation after peripheral nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12): 2084-2091. |
| [1] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [2] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [3] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [6] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [7] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [8] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [9] | Liu Liu, Zhou Qingzhu, Gong Zhuo, Liu Boyan, Yang Bin, Zhao Xian. Characteristics and manufacturing techniques of collagen/inorganic materials for constructing tissue-engineered bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 607-613. |
| [10] | Ye Haimin, Ding Linghua, Kong Weihao, Huang Zutai, Xiong Long. Role and mechanism of hierarchical microchanneled bone scaffolds in promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [11] | Song Kaikai, Zhang Kai, Jia Long. Microenvironment and repair methods of peripheral nervous system injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 651-656. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [14] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [15] | Gan Lili, Xiong Na, Liu Yanfei. Hydrogel as drug scaffold in skin wound repair: challenges of clinical application possibilities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3578-3583. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||