Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1777-1782.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2432
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osteosarcopenic obesity syndrome: diagnosis, treatment and related influencing factors
Chen Xingcai1, Kong Cunqing1, Xu Lin1, 2, Deng Qiongying1, 2
- 1Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Key Laboratory of Human Development and Disease Research in Guangxi Universities, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-07-13Revised:2019-07-18Accepted:2019-08-23Online:2020-04-18Published:2020-02-29 -
Contact:Deng Qiongying, MD, Professor, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Key Laboratory of Human Development and Disease Research in Guangxi Universities, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chen Xingcai, Master, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Kong Cunqing, MD candidate, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Chen Xingcai and Kong Cunqing contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31160222 and 31360259
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Xingcai, Kong Cunqing, Xu Lin, Deng Qiongying. Osteosarcopenic obesity syndrome: diagnosis, treatment and related influencing factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1777-1782.
share this article
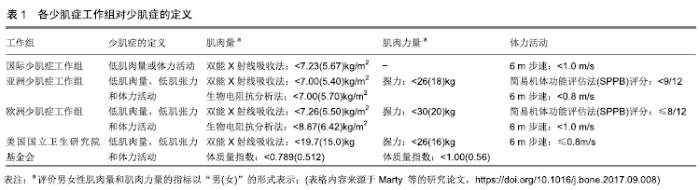
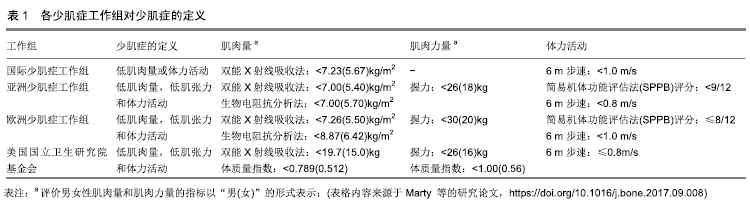
2.1 骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的检出率现况 美国ILICH 等[4]报道,在258名白种绝经女性中,骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的检出率为12.4%(32/258)。一项对434名墨西哥市中老年妇女骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的调查指出,约18.7%(81/434)的个体患有骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖[5],高于美国ILICH等报道的检出率,说明种族差异也是骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖检出率差异的影响因素之一。韩国KIM等[6]在全国健康与营养调查的报告中指出,2 485名男性中大约有13.5%(335/2 485)的个体患有骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖,其中38.9%(967/2 485)和21.4%(532/2 485)的人患有骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖(即骨质疏松症、少肌症和肥胖)中1个或2个组分,而在3 423名女性中,骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的检出率高达25.0%(856/3 423),患骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖中1个或2个组分的检出率分别为46.0%(1 575/3 423)和18.8%(644/3 423)。KIM等的研究结果表明,骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖检出率存在明显的性别差异。本团队前期研究结果显示,广西少数民族<60岁与≥60岁妇女的骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖患病率分别为0.34%(5/1 468)和7.44%(63/847),且在≥60岁妇女中,瑶族、毛南族、仫佬族和苗族骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的检出率分别为0%(0/214)、4.9%(9/182)、12.6%(23/182)和11.5%(31/269),说明骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖发病率存在年龄和民族差异[3]。以上研究说明,骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖检出率存在显著的年龄、性别、民族或种族差异。 2.2 骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的诊断 2.2.1 骨质疏松症的诊断 根据研究人群的年龄分布,在诊断骨质疏松症时需依据不同的骨密度指标。ENSRUD等[7]建议,绝经后女性或≥50岁男性依据T值诊断骨质疏松症(即WHO对骨质疏松症的诊断[8],T≤-2.5),而未绝经女性或50岁以下的男性,则采用Z值进行诊断(即Z≤-2.0)。 2.2.2 少肌症的诊断 近年来,少肌症的定义尚未有统一标准。目前,主要有国际少肌症工作组、亚洲少肌症工作组、欧洲少肌症工作组和美国国立卫生研究院基金会等组织对少肌症的定义进行了详细说明。见表1。 "
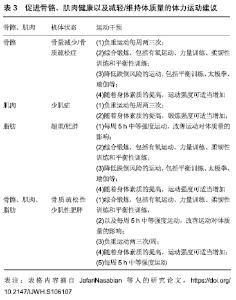
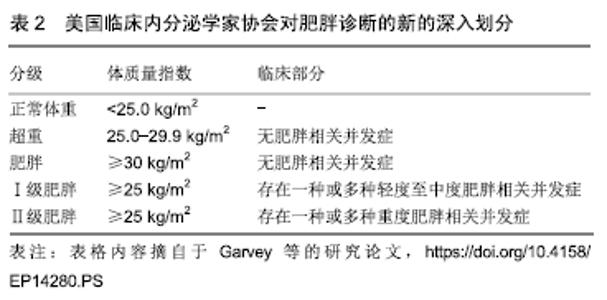
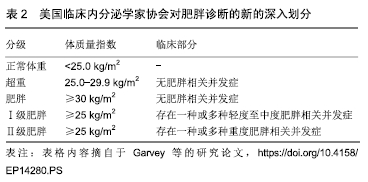
2.3 骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的影响因素 近年来,国内外学者对骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的研究刚刚展开,对其发病机制的研究也处于初步阶段。相关文献指出,骨质疏松症、少肌症和肥胖的影响因素对骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的发病率起着重要作用[1]。 2.3.1 骨质疏松症的影响因素 据报道,低体力活动水平、吸烟、饮酒、摄入过量咖啡因等均是骨质疏松症的危险因素[14-16]。也有研究表明,芳香化酶抑制剂和促炎症细胞因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α),均会加速骨钙的流失,增加个体患骨质疏松症的风险[17-18]。 RIVADENEIRA等[19]指出,相关基因突变可诱发骨质疏松症,如成骨不全症是常见的具有骨脆性的单基因病症,它通常由编码Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的两个基因(COL1A1和COL1A2)突变引起的。其中,对骨质疏松症相关基因研究较多的便是低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5基因[19],而低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5的功能丧失可导致常染色体隐性遗传骨质疏松-假性胶质瘤综合征,其特征是失明和儿童期严重的骨质疏松症[20]。也有文献显示,骨质疏松症可能是其他疾病的一种临床表现,如多发性骨髓瘤、骨软化症、原发性甲状旁腺功能亢进等[21]。 2.3.2 少肌症的影响因素 衰老是肌肉萎缩的主要原因,失用性肌肉萎缩、肌源性肌肉萎缩、神经源性肌肉萎缩是常见的肌肉萎缩类型,而年龄相关的运动神经元终板丢失不仅导致神经元性肌肉萎缩,还致肌肉功能降低,代谢性激素(如睾酮、生长激素和胰岛素生长因子1等)水平下降[22]。其中,胰岛素生长因子1是骨骼和肌肉生长的关键调节因子,其信号传导效率降低和肌肉特异性胰岛素生长因子1表达下降则会引起肌肉萎缩[23-24]。此外,衰老引起的细胞内氧化应激会产生慢性低度炎症,并释放细胞因子,如白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等,增加患少肌症的风险[25-26]。据流行病学调查显示,低体质量指数水平、低体力活动(包括久坐行为)、吸烟等不良生活行为,以及蛋白质、维生素D等营养不足或缺乏常引起肌肉质量或力量的下降[27-30]。此外,研究表明女性在55岁后肌肉力量急剧下降,其主要原因是雌激素(如雌二醇)水平的降低,而雌二醇具有通过改善骨骼肌的内在质量从而使纤维产生力量的作用,因此雌激素水平的下降会增加机体肌肉萎缩的风险[31-32]。 2.3.3 肥胖的影响因素 快餐、不吃早餐和缺乏体力活动是全身性和中心性肥胖的重要危险因素[33-34]。有研究表明,体质量增长量与薯片、土豆、含糖饮料或红肉等食物摄入量呈正比,而与蔬菜、水果、全谷类、坚果和酸奶的摄入量成反比[35]。以上研究表明,生活、饮食习惯是肥胖的重要影响因素。此外,某些病毒在肥胖的发展过程中起着重要作用,如腺病毒36,它可能是儿童和成人患肥胖的原因之一[36-37]。共栖实验表明,Blean菌群可以成功传播到Bobas菌群的小鼠体内,且可抑制部分个体肥胖的发生,说明控制相关肠道菌群可防止肥胖发生[38]。这些研究表明,病毒、肠道菌群对肥胖的发生发展发挥着重要作用。也有文献报道,抗生素水平、机体内分泌蛋白(如瘦蛋白、黑皮质素3受体和黑皮质素4受体)与肥胖的发生存在一定的联系[39-42]。 2.4 骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖与骨折、血脂异常的关系 2.4.1 骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖与骨折间的关系 近年来,仍有不少学者认为肥胖是骨折的保护因素,或许是脂肪组织对跌倒具有缓冲作用。然而,2010年英国骨折协会的一项研究首次报道,脆性骨折的绝经期妇女肥胖率高达27%[43]。此外,PREMAOR等[44]研究表明,与正常人相比,女性肥胖者在踝关节、腿部、肱骨和脊柱等部位发生骨折的风险较高,而在手腕、髋部和骨盆等部位的风险较低,而男性肥胖者在肋骨发生骨折的概率较大。说明肥胖对骨折的作用尚有争议,但现实中肥胖者可能更易发生跌倒或骨折。也有研究者对老年人进行前瞻性队列研究,结果表明骨折老人的体脂率、肌力和髋部骨密度水平均较低于正常人群,且少肌性肥胖者的2年跌倒率和6年内骨折率明显高于正常人群[45-46]。说明少肌性肥胖可明显增加个体骨折的发生率。 此外,WANG等[47]的Meta分析结果显示,低骨密度水平与骨折风险增加有关,且在NEGREIROS等[48]的研究中也证明了这一点,即大约有25%的低骨密度者出现无症状性骨折,说明骨量减少或骨质疏松可促进骨折的发生。陈恒亭等[49]的研究表明,骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖对骨折的发生有一定的促进作用,且骨质疏松症、少肌症、肥胖是骨折的重要危险因素。 2.4.2 骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖与血脂异常间的关系 PLIATSIKA等[50]和HYDER等[51]的研究表明,骨密度与颈动脉粥样硬化斑块的形成、钙化及脂蛋白α水平密切相关。相关文献指出,脂质氧化会促进动脉粥样硬化,并将基质骨髓细胞转化为脂肪,同时增强破骨细胞活性、抑制成骨细胞增殖,从而抑制骨形成,促进骨吸收,导致骨密度水平降低[52-53]。KIM等[54]的研究结果表明,肥胖(特别是内脏脂肪)、少肌症均可增加个体血脂异常的风险,且少肌性肥胖者患血脂异常的风险更大。韩国BAEK等[55]的研究也证明了这一结论,并指出少肌性肥胖者患血脂异常的风险高于单纯性肥胖者或少肌症者,但这种情况仅在于男性中。肥胖者脂肪组织分泌肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6等促炎细胞因子,促进胰岛素抵抗,而高胰岛素血症可促进三酰甘油的产生并升高游离脂肪酸的水平,且肥胖者多食、少运动的习惯可进一步加重血脂异常的风险[56]。此外,肌肉组织也是调节能力代谢的重要器官,肌肉量的降低则会降低胰岛素应答组织,促进胰岛素抵抗,影响血脂代谢[57]。 据本课题组前期研究报道,骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖组具有较高水平的低密度脂蛋白,且logistic回归分析显示,在≥60岁女性中,与正常人相比,单纯性骨质疏松症、少肌症或肥胖对血脂异常的风险小于少肌性肥胖,而少肌性肥胖对血脂异常的风险远小于骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖对血脂异常的影响[3]。说明骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖对血脂的作用远大于骨质疏松症、少肌症、肥胖或三者中的两两组合。 近年来,不少研究者多次报道,单纯性骨质疏松症、少肌症或肥胖不仅对骨折和血脂异常有较大的发病风险,而且对其他代谢性疾病的发生和发展存在一定的促进作用,如糖尿病、高血压等[58-59]。然而,有关骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖与糖尿病、代谢综合征等代谢性疾病的研究却很少,所以需更多的研究来深入探索骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖与其他代谢性疾病间的关系及其致病机制,从而在体成分水平对相关疾病展开预防措施。 2.5 骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的管理 虽然某些药物、遗传易感性和环境因素是骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖病因学的主要决定因素,但个体的生活方式在骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的管理中也很重要,如饮食模式、体力活动水平等,它们在机体代谢稳态中发挥着重要的作用[60]。相关文献指出,“西方饮食”模式具有高能量、低营养的食物特点[60-61]。受“西方饮食”模式影响,一些维持骨矿物质含量和肌肉量所必需的蛋白质、钙、镁和维生素D等营养素摄入量不足[62]。有学者指出,蛋白质、钙、长链多不饱和脂肪酸、富含抗氧化剂的食物(如水果、蔬菜等)等摄入不足会增加中老年人群患骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的风险[63]。推测原因是膳食蛋白质在肌肉组织中参与合成代谢,蛋白质摄入过量则会增加钙的排泄,而钙质的流失会增加骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的发病率,但也有报告指出,钙摄入过低会加快机体氧化,对肌肉产生不利影响[64]。因此,在增加其他营养素摄入来降低蛋白质摄入过量对骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的风险的同时,需增加抗氧化剂摄入量以降低低钙引起的负面影响。研究表明,高钙饮食可通过抑制脂肪生成和促进脂肪分解来抑制肥胖发生,进而降低骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖的发病率[65]。 体力活动是影响身体组成分、生理和心理健康,以及骨质疏松性少肌性肥胖综合征的重要因素。长期坚持一定的体力活动,即使是低强度或一般性活动,也可维持或改善机体骨密度、肌肉力量和质量,减少肥胖或炎症的发 生[66-68]。老年人的锻炼活动应包括有氧运动、力量训练、灵活性训练和平衡训练等四部分,这些活动有助于降低老年人跌倒的风险,并维持身体组成分,改善老年人的生活质量[69-70]。JAFARINASABIAN等[71]提出了针对促进骨骼、肌肉健康以及减少/维持体质量的活动建议,见表3。 "

| [1] ORMSBEE MJ, PRADO CM, ILICH JZ, et al. Osteosarcopenic obesity: the role of bone, muscle, and fat on health. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle.2014;5(3):183-192. [2] SØGAARD AJ, HOLVIK K, OMSLAND TK, et al. Abdominal obesity increases the risk of hip fracture. A population-based study of 43,000 women and men aged 60-79 years followed for 8 years. Cohort of Norway. J Intern Med.2015;277(3):306-317. [3] MO D, HSIEH P, YU H, et al. Osteosarcopenic obesity and its relationship with dyslipidemia in women from different ethnic groups of China. Arch Osteoporos.2018;13(1):65. [4] ILICH JZ, INGLIS JE, KELLY OJ, et al. Osteosarcopenic obesity is associated with reduced handgrip strength, walking abilities, and balance in postmenopausal women [J].Osteoporos Int,2015,26 (11): 2587-2595. [5] SZLEJF C, PARRA-RODRÍGUEZ L, ROSAS-CARRASCO O. Osteosarcopenic Obesity: Prevalence and Relation With Frailty and Physical Performance in Middle-Aged and Older Women.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2017;18(8):733.e1-733.e5. [6] KIM J, LEE Y, KYE S,et al.Association of serum vitamin D with osteosarcopenic obesity: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2017;8(2):259-266. [7] ENSRUD KE,CRANDALL CJ.Osteoporosis. Ann Intern Med.2017;167 (3):ITC17-ITC32. [8] THE WHO STUDY GROUP. Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosisGeneva: WHO.1994. [9] Oliveros E, Somers VK, Sochor O, et al. The concept of normal weight obesity. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2014;56(4):426-433. [10] HUNG SP, CHEN CY, GUO FR, et al. Combine body mass index and body fat percentage measures to improve the accuracy of obesity screening in young adults.Obes Res Clin Pract.2017;11(1): 11 -18. [11] MCCARTHY HD, ASHWELL M.A study of central fatness using waist- to-height ratios in UK children and adolescents over two decades supports the simple message--'keep your waist circumference to less than half your height'.Int J Obes (Lond).2006;30(6):988-992. [12] BACOPOULOU F, EFTHYMIOU V, LANDIS G, et al.Waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio and waist-to-height ratio reference percentiles for abdominal obesity among Greek adolescents.BMC Pediatr.2015;15(1):50. [13] GARVEY WT, GARBER AJ, MECHANICK JI, et al. American association of clinical endocrinologists and american college of endocrinology position statement on the 2014 advanced framework for a new diagnosis of obesity as a chronic disease. Endocr Pract.2014; 20(9):977-989. [14] BIJELIC R, MILICEVIC S, BALABAN J. Risk Factors for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women. Med Arch. 2017;71(1):25-28. [15] ZHANG X,YU Z,YU M,et al.Alcohol consumption and hip fracture risk.Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(2):531-542. [16] LI S, DAI Z, WU Q. Effect of coffee intake on hip fracture: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.Nutr J.2015;14(1): 38. [17] HOFBAUER LC, GORI F, RIGGS BL, et al.Stimulation of Osteoprotegerin Ligand and Inhibition of Osteoprotegerin Production by Glucocorticoids in Human Osteoblastic Lineage Cells: Potential Paracrine Mechanisms of Glucocorticoid- Induced Osteoporosis. Endocrinology. 1999;140(10):4382-4389. [18] FRANCIOSI LG, PAGE CP, CELLI BR, et al. Markers of disease severity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.2006;19(3):189–199. [19] RIVADENEIRA F, MÄKITIE O. Osteoporosis and Bone Mass Disorders: From Gene Pathways to Treatments. Trends Endocrinol Metab.2016; 27(5):262-281. [20] GONG Y, SLEE RB,FUKAI N, et al. LDL receptor-related protein 5 (LRP5) affects bone accrual and eye development.Cell.2001;107(4):513-523. [21] SZULC P,DELMAS PD.Biochemical markers of bone turnover: potential use in the investigation and management of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int.2008;19(12):1683- 1704. [22] DREY M, KRIEGER B, SIEBER CC, et al. Motoneuron loss is associated with sarcopenia.J Am Med Dir Assoc.2014;15(6): 435-439. [23] PERRINI S,LAVIOLA L,CARREIRA MC,et al.The GH/IGF1 axis and signaling pathways in the muscle and bone: mechanisms underlying age-related skeletal muscle wasting and osteoporosis.J Endocrinol. 2010;205(3):201-210. [24] LI M, LI C,PARKHOUSE WS.Age-related differences in the des IGF-I-mediated activation of Akt-1 and p70 S6K in mouse skeletal muscle.Mech Ageing Dev.2003;124(7):771-778. [25] MENG SJ,YU LJ.Oxidative stress, molecular inflammation and sarcopenia.Int J Mol Sci.2010;11(4):1509-1526. [26] KARASIK D. How pleiotropic genetics of the musculoskeletal system can inform genomics and phenomics of aging. Age (Dordr).2011;33(1): 49-62. [27] TRAMONTANO A, VERONESE N, SERGI G, et al.Prevalence of sarcopenia and associated factors in the healthy older adults of the Peruvian Andes. Arch Gerontol Geriatr.2017;68:49-54. [28] CLARK DJ, PATTEN C, REID KF, et al.Impaired voluntary neuromuscular activation limits muscle power in mobility-limited older adults.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.2010;65(5):495- 502. [29] BIJLSMA AY, MESKERS CG, LING CH, et al.Defining sarcopenia: the impact of different diagnostic criteria on the prevalence of sarcopenia in a large middle aged cohort.Age (Dordr).2013; 35(3):871-881. [30] LLOYD BD, WILLIAMSON DA, SINGH NA, et al.Recurrent and injurious falls in the year following hip fracture: a prospective study of incidence and risk factors from the Sarcopenia and Hip Fracture study.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.2009;64(5): 599-609. [31] SAMSON MM, MEEUWSEN IB, CROWE A, et al. Relationships between physical performance measures, age, height and body weight in healthy adults.Age Ageing.2000;29(3):235-242. [32] LOWE DA, BALTGALVIS KA,GREISING SM.Mechanisms behind estrogen's beneficial effect on muscle strength in females. Exerc Sport Sci Rev.2010;38(2):61-67. [33] EL-KASSAS G, ZIADE F.Exploration of the Risk Factors of Generalized and Central Obesity among Adolescents in North Lebanon.J Environ Public Health.2017;2017:1-13. [34] FRASER LK, CLARKE GP, CADE JE, et al.Fast food and obesity: a spatial analysis in a large United Kingdom population of children aged 13-15.Am J Prev Med.2012;42(5):e77-85. [35] MOZAFFARIAN D, HAO T, RIMM EB, et al.Changes in diet and lifestyle and long-term weight gain in women and men.N Engl J Med. 2011;364(25):2392–2404. [36] PARRA-ROJAS I, DEL MORAL-HERNA´NDEZ O, SALGADO- BERNABE´ AB, et al. Adenovirus-36 seropositivity and its relation with obesity and metabolic profile in children.Int J Endocrinol.2013; 2013(10): 463194. [37] ALMGREN M, ATKINSON R, HE J, et al. Adenovirus-36 is associated with obesity in children and adults in Sweden as determined by rapid ELISA.PloS One.2012;7(7):e41652. [38] SANMIGUEL C, GUPTA A, MAYER EA. Gut Microbiome and Obesity: A Plausible Explanation for Obesity.Curr Obes Rep.2015;4(2): 250-261. [39] SINGH RK, KUMAR P, MAHALINGAM K. Molecular genetics of human obesity: A comprehensive review.C R Biol.2017;340(2): 87-108. [40] MCNULTY JC, JACKSON PJ,THOMPSON DA,et al.Structures of the agouti signaling protein.J Mol Biol.2005;346(4):1059-1070. [41] PETSCHOW B, DORE J, HIBBERD P, et al. Probiotics, prebiotics, and the host microbiome: the science of translation.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2013; 1306(1):1-17. [42] GASKINS HR, COLLIER CT, Anderson DB. Antibiotics as growth promotants: mode of action [J].Anim Biotechnol,2002,13(1): 29-42. [43] PREMAOR MO, PILBROW L, TONKIN C, et al.Obesity and fractures in post- menopausal women.J Bone Miner Res.2010;25(2):292-297. [44] PREMAOR MO, COMIM FV, COMPSTON JE.Obesity and fractures. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.2014;58(5):470-477. [45] LANG T, CAULEY JA, TYLAVSKY F, et al.Computed tomographic measurements of thigh muscle cross-sectional area and attenuation coefficient predict hip fracture: the health, aging, and body composition study.J Bone Miner Res.2010;25(3): 513-519. [46] SCOTT D, SEIBEL M, CUMMING R, et al. Sarcopenic Obesity and Its Temporal Associations With Changes in Bone Mineral Density, Incident Falls, and Fractures in Older Men: The Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project.J Bone Miner Res.2017;32(3):575- 583. [47] WANG X, YAN S, LIU C, et al. Fracture risk and bone mineral density levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus:a systematic review and meta-analysis.Osteoporos Int.2016;27(4):1413-1423. [48] NEGREIROS CC,BERIGO MG,DOMINONI RL,et al.Asymptomatic vertebral fractures in patients with low bone mineral density.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992).2016;62(2):145-150. [49] 陈恒亭,马剑雄,卢斌,等.骨量-肌量减少性肥胖综合征与骨折关系的研究进展[J].中华老年医学杂志, 2018,37(3):347-350. [50] PLIATSIKA P, ANTONIOU A, ALEXANDROU A, et al. Serum lipid levels and bone mineral density in Greek postmenopausal women. Gynecol Endocrinol.2012;28(8):655-660. [51] HYDER JA, ALLISON MA, BARRETT-CONNOR E, et al.Bone mineral density and atherosclerosis: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis, Abdominal Aortic Calcium Study. Atherosclerosis.2010;209(1):283-289. [52] KOTANI K, YAMADA S, UURTUYA S, et al.The association between blood glucose and oxidized lipoprotein(a) in healthy young women. Lipids Health Dis.2010;9(1):103. [53] ALMEIDA M, AMBROGINI E, HAN L, et al. Increased lipid oxidation causes oxidative stress, increased peroxisome proliferator activated receptor- gamma expression, and diminished pro-osteogenic Wnt signaling in the skeleton.J Biol Chem.2009;284(40):27438- 27448. [54] KIM TN, CHOI KM.The implications of sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity on cardiometa- bolic disease.J Cell Biochem.2015;116(7): 1171-1178. [55] BAEK SJ, NAM GE, HAN KD, et al.Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity and their association with dyslipidemia in Korean elderly men: the 2008-2010 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.J Endocrinol Invest.2014;37(3):247-260. [56] 王丽娟,汪明芳,李晓琳,等.中青年人群少肌症肥胖与血脂异常的相关性研究[J].中华健康管理学杂志,2015,8(3):186-190. [57] JORNAYVAZ FR, SAMUEL VT, SHULMAN GI.The Role of Muscle Insulin Resistance in the Pathogenesis of Atherogenic Dyslipidemia and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome.Annu Rev Nutr. 2010;30:273-290. [58] RUSSELL-JONES D, KHAN R.Insulin-associated weight gain in diabetes- causes, effects and coping strategies.Diabetes Obes Metab . 2007;9(6): 799-812. [59] DeMarco VG, Aroor AR, Sowers JR.The pathophysiology of hypertension in patients with obesity.Nat Rev Endocrinol.2014;10(6):364-376. [60] KELLY OJ, GILMAN JC, KIM Y, et al. Macronutrient Intake in the Etiology, Prevention and Treatment of Osteosarcopenic Obesity.Curr Aging Sci.2016;9(4):260-278. [61] INGLIS JE, JAFARINASABIAN P, GILMAN JC, et al. Possible nutritional etiology of osteosarcopenic obesity syndrome.FASEB J.2016;30(1):1156.8. [62] PRICE CT, LANGFORD JR, LIPORACE FA.Essential Nutrients for Bone Health and a Review of their Availability in the Average North American Diet.Open Orthop J.2012;6(1):143-149. [63] KIM J, LEE Y, KYE S, et al.Diet quality and osteosarcopenic obesity in community-dwelling adults 50 years and older.Maturitas.2017;104:73-79. [64] ANDERSSON DC, BETZENHAUSER MJ, REIKEN S, et al. Ryanodine receptor oxidation causes intracellular calcium leak and muscle weakness in aging.Cell Metab.2011;14(2):196-207. [65] ZEMEL MB, SHI H, GREER B, et al.Regulation of adiposity by dietary calcium.FASEB J.2000;14(9):1132-1138. [66] BOOTH FW, GORDON SE, CARLSON CJ, et al.Waging war on modern chronic diseases: primary prevention through exercise biology. J Appl Physiol.2000;88(2):774-787. [67] HUGHES VA, FRONTERA WR, WOOD M, et al.Longitudinal muscle strength changes in older adults: influence of muscle mass, physical activity, and health.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.2001;56(5):B209-B217. [68] KELLY OJ, GILMAN JC.Can Unconventional Exercise be Helpful in the Treatment, Management and Prevention of Osteosarcopenic Obesity?. Curr Aging Sci.2017;10(2): 106-121. [69] GARBER CE, BLISSMER B, DESCHENES MR, et al.American College of Sports Medicine. Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoske- letal, and neuromotor ftness in apparently healthy adults: guidance for prescribing exercise.Med Sci Sports Exerc.2011;43(7):1334-1359. [70] FRANCO MR, PEREIRA LS, FERREIRA PH. Exercise interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community.Br J Sports Med.2014;48(10):867-868. [71] TARANTINO U, BALDI J, SCIMECA M, et al.The role of sarcopenia with and without fracture.Injury. 2016;47(Suppl 4):S3-S10. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [3] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [4] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [5] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [8] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [9] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [10] | Li Zhongfeng, Chen Minghai, Fan Yinuo, Wei Qiushi, He Wei, Chen Zhenqiu. Mechanism of Yougui Yin for steroid-induced femoral head necrosis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1256-1263. |
| [11] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [12] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [13] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [14] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| [15] | Zhang Jing, Wang Bin, Lü Xin. Application of anatomic intramedullary nail in tubular bone fractures of limbs: stronger holding force and anti-rotation ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 917-922. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||